Abstract
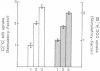
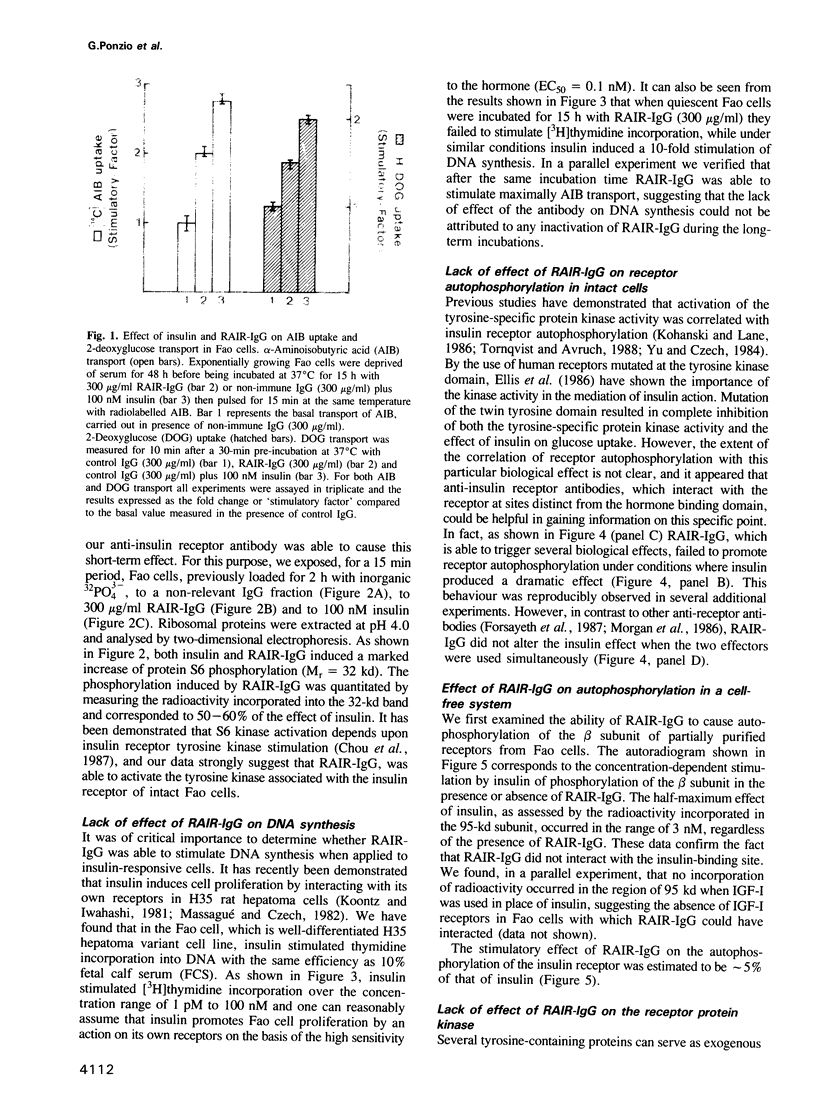
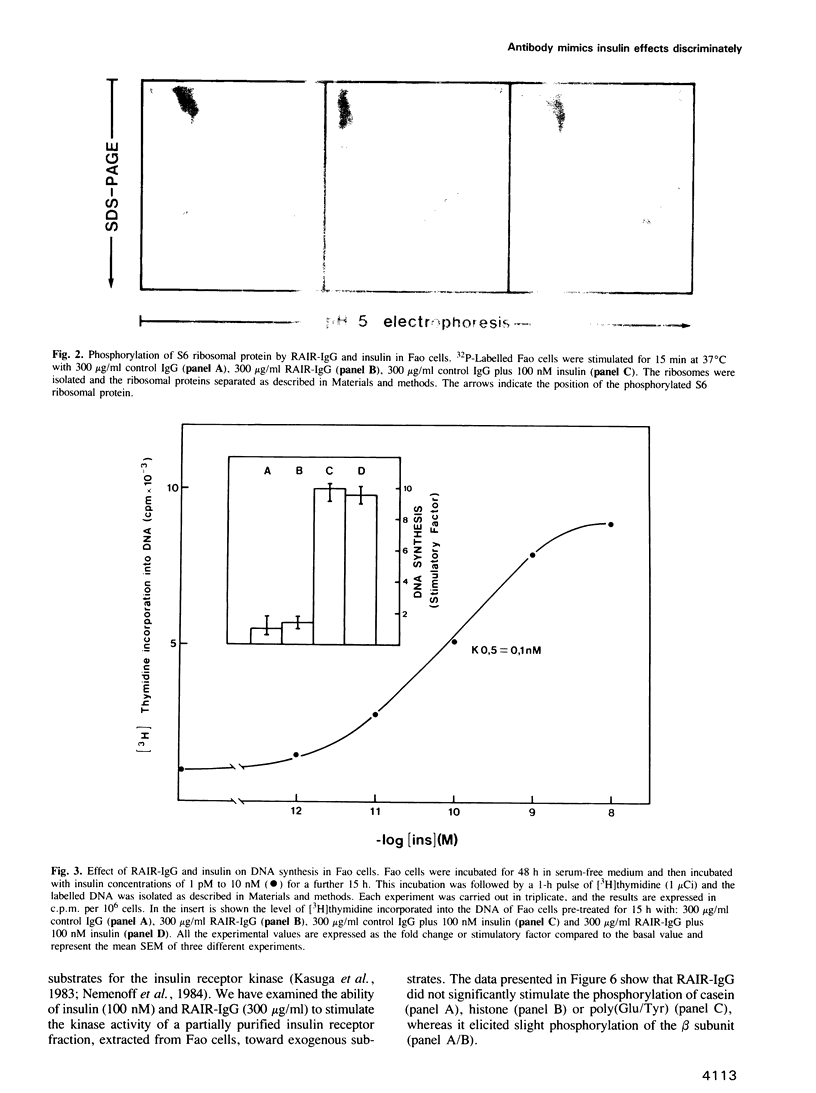
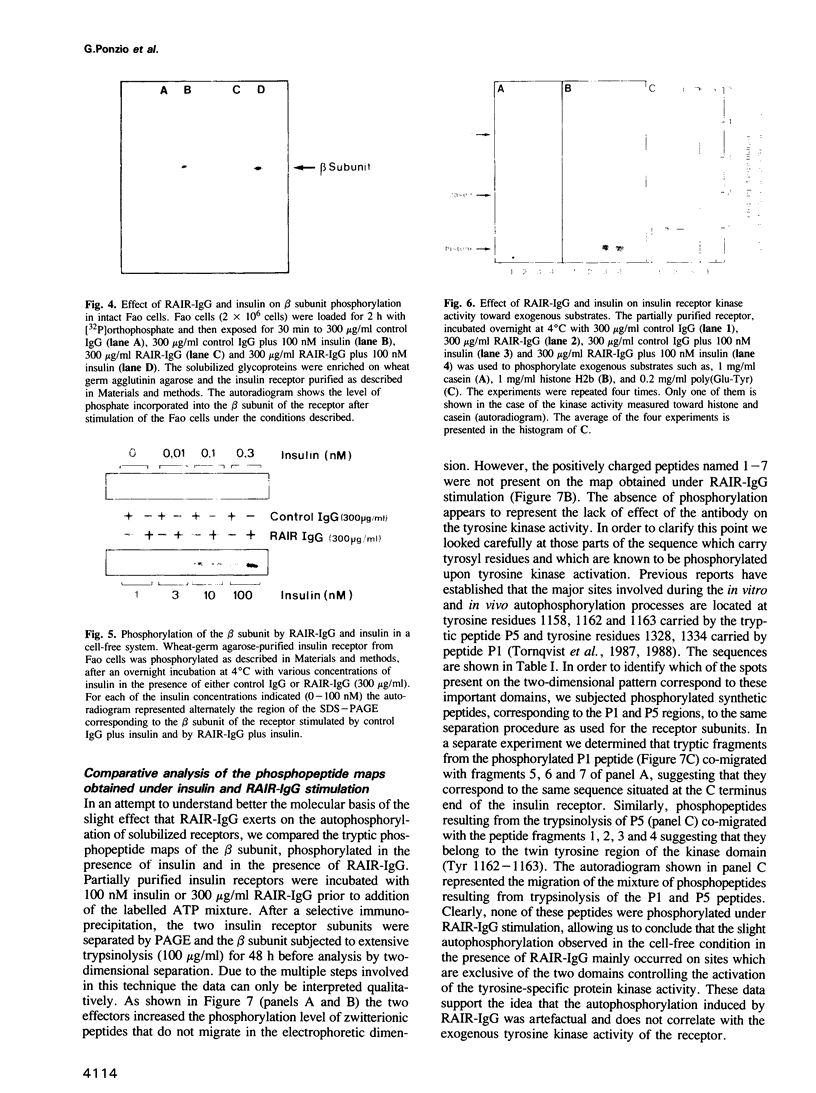
In a previous report we described the properties of a rabbit anti-insulin receptor antibody (RAIR-IgG) and its effects on the autophosphorylation and kinase activity of human insulin receptors. The present study was carried out on the hepatoma cell line Fao. We tested the mimetic effects of RAIR-IgG on different biological parameters known to be stimulated by insulin, receptor autophosphorylation and kinase activity. RAIR-IgG stimulated the metabolic effects (glucose and amino acid transport) but, unlike insulin, was unable to promote cell proliferation. These data clearly demonstrated the existence of two distinctly controlled pathways in the mediation of the hormonal response. When we investigated the effects of this antibody at the molecular level we found that in a cell-free system RAIR-IgG weakly stimulated receptor autophosphorylation on non-regulatory sites and failed to stimulate tyrosine kinase activity toward exogenous substrates. Accordingly, RAIR-IgG did not stimulate receptor autophosphorylation in 32P-labelled intact cells. Interestingly, under similar conditions RAIR-IgG elicited ribosomal S6 protein phosphorylation, as did insulin. The possibility that RAIR-IgG activated a cryptic tyrosine kinase activity is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun S., Raymond W. E., Racker E. Synthetic tyrosine polymers as substrates and inhibitors of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2051–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J. R., Caro J. F., Sinha M. K., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor that activate glucose transport but not insulin receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3448–3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Warner J. R. Coordinate regulation of the synthesis of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1547–1551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Rosen O. M. Autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vitro. Designation of phosphorylation sites and correlation with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11980–11985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Blithe D. L., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Characterization of the insulin receptor kinase purified from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10973–10980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohanski R. A., Lane M. D. Kinetic evidence for activating and non-activating components of autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1312–1318. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koontz J. W., Iwahashi M. Insulin as a potent, specific growth factor in a rat hepatoma cell line. Science. 1981 Feb 27;211(4485):947–949. doi: 10.1126/science.7008195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Grémeaux T., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):676–679. doi: 10.1038/315676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Blinderman L. A., Czech M. P. The high affinity insulin receptor mediates growth stimulation in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13958–13963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Ho L., Korn L. J., Roth R. A. Insulin action is blocked by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Acute insulin action requires insulin receptor kinase activity: introduction of an inhibitory monoclonal antibody into mammalian cells blocks the rapid effects of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison B. D., Pessin J. E. Insulin stimulation of the insulin receptor kinase can occur in the complete absence of beta subunit autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2861–2868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Kwok Y. C., Shulman G. I., Blackshear P. J., Osathanondh R., Avruch J. Insulin-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase. Characterization and relation to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5058–5065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen-Hamilton M., Allen W. R., Hamilton R. T. Rapid and efficient method for analyzing phosphorylation of the S6 ribosomal protein in 32Pi-labeled, tissue culture cells. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):438–449. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen-Hamilton M., Hamilton R. T., Allen W. R., Potter-Perigo S. Synergistic stimulation of S6 ribosomal protein phosphorylation and DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor and insulin in quiescent 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Soos M. A., Siddle K. Monoclonal antibodies to the insulin receptor stimulate the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity by cross-linking receptor molecules. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4003–4010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierre M., Toru-Delbauffe D., Gavaret J. M., Pomerance M., Jacquemin C. Activation of S6 kinase activity in astrocytes by insulin, somatomedin C and TPA. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):162–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzio G., Dolais-Kitabgi J., Louvard D., Gautier N., Rossi B. Insulin and rabbit anti-insulin receptor antibodies stimulate additively the intrinsic receptor kinase activity. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):333–340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Shimizu N. Rat hepatoma cell variants resistant to insulin-diphtheria toxin A fragment conjugates. Genetic evidence for the separate pathways for insulin receptor-mediated mitogenic and hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7342–7346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Hedo J. A. Insulin receptor phosphorylation may not be a prerequisite for acute insulin action. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1301–1304. doi: 10.1126/science.6367041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmauer L. A., Rosen O. M. Phosphorylation of exogenous substrates by the insulin receptor-associated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6682–6685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Avruch J. Relationship of site-specific beta subunit tyrosine autophosphorylation to insulin activation of the insulin receptor (tyrosine) protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4593–4601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Gunsalus J. R., Nemenoff R. A., Frackelton A. R., Pierce M. W., Avruch J. Identification of the insulin receptor tyrosine residues undergoing insulin-stimulated phosphorylation in intact rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):350–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Pierce M. W., Frackelton A. R., Nemenoff R. A., Avruch J. Identification of insulin receptor tyrosine residues autophosphorylated in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10212–10219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Ksauga M., Le Cam A., Hedo J. A., Itin A., Harrison L. C. Biosynthetic labeling of insulin receptor: studies of subunits in cultured human IM-9 lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor beta subunit activates the receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5277–5286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Rees-Jones R. W., Taylor S. I., Gorden P., Roth J. The role of antireceptor antibodies in stimulating phosphorylation of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4396–4400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]