Abstract
Thermostable alkaline pectate lyases have potential applications in the textile industry as an alternative to chemical-based ramie degumming processes. In particular, the alkaline pectate lyase from Bacillus sp. strain N16-5 (BspPelA) has potential for enzymatic ramie degumming because of its high specific activity under extremely alkaline conditions without the requirement for additional Ca2+. However, BspPelA displays poor thermostability and is inactive after incubation at 50°C for only 30 min. Here, directed evolution was used to improve the thermostability of BspPelA for efficient and stable degumming. After two rounds of error-prone PCR and screening of >12,000 mutants, 10 mutants with improved thermostability were obtained. Sequence analysis and site-directed mutagenesis revealed that single E124I, T178A, and S271G substitutions were responsible for improving thermostability. Structural and molecular dynamic simulation analysis indicated that the formation of a hydrophobic cluster and new H-bond networks was the key factor contributing to the improvement in thermostability with these three substitutions. The most thermostable combined mutant, EAET, exhibited a 140-fold increase in the t50 (time at which the enzyme loses 50% of its initial activity) value at 50°C, accompanied by an 84.3% decrease in activity compared with that of wild-type BspPelA, while the most advantageous combined mutant, EA, exhibited a 24-fold increase in the t50 value at 50°C, with a 23.3% increase in activity. Ramie degumming with the EA mutant was more efficient than that with wild-type BspPelA. Collectively, our results suggest that the EA mutant, exhibiting remarkable improvements in thermostability and activity, has the potential for applications in ramie degumming in the textile industry.
INTRODUCTION
Pectin, a naturally ubiquitous constituent of the middle lamella of the primary cell wall in plants, is a heteropolysaccharide composed of α-1,4-linked galacturonate chains with a high percentage of methyl esterification and functions to form a network with other noncellulosic materials, such as proteins and waxes (1–3). Pectin degradation requires the combined action of several enzymes that can be classified into two main groups: methylesterases, which remove methoxyl groups from pectin, and depolymerases (hydrolases and lyases), which cleave the bonds between galacturonate units (4–6).
Pectate lyases (Pels) (EC 4.2.2.2) cleave α-1,4-linked galacturonate units of pectate by β-elimination, giving rise to an unsaturated C-4–C-5 bond at the nonreducing end of the newly formed oligogalacturonate (7). Pels are widely distributed among microbial plant pathogens and have been the focus of several studies aiming to elucidate the roles of these enzymes as virulence factors (8, 9). Pels have also been found in some other microorganisms, including bacteria of the genus Bacillus (10) and some thermophilic bacteria (11). In general, Pels work efficiently at alkaline pH (between pH 8 and 10), and additional Ca2+ ions are required for efficient enzymatic activity (12–14).
Pels that play an important role in the degradation of natural bioresources have important industrial applications in food production and textile industries. Alkaline Pels in particular are being introduced in textile industrial processing and degumming to facilitate the release of fibers from flax, ramie, sunn hemp, buel, and jute (15–19) as an alternative to conventional retting. Compared with conventional chemical degumming processes, enzymatic degumming has several advantages, including flexible and mild processing conditions, limited damage to fibers, environmentally friendly operation, and easy quality control (20–23). However, enzymatic degumming has not been widely used in the textile industry because of the high cost and unsatisfactory degumming efficiency of currently available enzymes. Thus, in the textile industry, microbial or enzymatic degumming processes are commonly combined with chemical degumming processes for maximal efficiency (24, 25).
In enzymatic degumming, an alkaline environment at a moderate temperature is critical for effective degumming and improvement of fiber quality because the gumlike materials are soluble under these conditions (26); thus, operation of industrial degumming processes is generally carried out at moderate temperatures (40°C to 70°C) and alkaline pH (pH 8 to 11) (27). Therefore, enzymes that are thermostable and active under alkaline conditions are desirable for industrial degumming applications. Because of the increasing interest in and potential market for enzymatic degumming, various alkaline Pels have recently been cloned and isolated from microbes (17, 25, 26, 28–34) or from metagenomic DNA obtained from soils from alkaline environments (35). However, few Pels have been found to be economically efficient for industrial applications owing to their low activity, poor stability, or specific degumming efficiency under the required processing conditions. Therefore, alkaline Pels with good thermostability and high specific degumming activity under industrial processing conditions are still in great demand.
In a previous study, we overexpressed and characterized an alkaline Pel from Bacillus sp. strain N16-5 (BspPelA) (36). This enzyme has high activity toward polygalacturonic acid (PGA), displays maximal enzyme activity at 50°C and pH 11.5, and has good alkaline tolerance. Interestingly, BspPelA can maintain full pectolytic activity without requiring additional Ca2+ to be added to the reaction mixture, a feature that distinguishes BspPelA from other reported Pels and would be expected to reduce the cost of industrial application of BspPelA (37). Ramie degumming by this enzyme has also been tested, with significant fiber weight loss being observed after a 4-h processing step. These characteristics make BspPelA a great candidate for industrial use in ramie degumming. However, BspPelA is not stable at high temperatures, and its activity is completely lost after incubation at 50°C for only 30 min; this would substantially decrease the efficiency and applicability of this enzyme in industrial degumming.
Therefore, in this study, we engineered BspPelA using evolutionary strategies in order to improve thermostability, specific activity, and ramie degumming capability.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and materials.
The expression vector pET28a-pelA (carrying the pelA gene, which encodes BspPelA [GenBank accession no. GU088530]) was constructed as previously described (36). Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) was used as a host strain for expression of recombinant enzymes and random library screening. PGA and galacturonic acid (GalpA) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). All the enzymes for DNA manipulations were purchased from TaKaRa Biotechnology Co. Ltd. (Dalian, Liaoning, China). Isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), kanamycin, and imidazole were obtained from Amresco Inc. (Solon, OH, USA). All other chemicals were of reagent grade.
Construction of random mutagenesis libraries.
Random mutagenesis libraries were generated by error-prone PCR (ep-PCR) using the primers listed in Table 1. PCR amplification was carried out with rTaq DNA polymerase, an additional 0.35 mM MnCl2 was added to the reaction buffer, and plasmid pET28a-pelA was used as the template. The following PCR profile was used: 1 cycle of 94°C for 4 min and 30 cycles of 94°C for 45 s, 55°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 7 min, followed by a final extension step at 72°C for 10 min. The PCR product was used as a megaprimer to perform megaprimer PCR of whole plasmids (MEGAWHOP) (38), using the pET28a-pelA plasmid as a template. Following MEGAWHOP, the amplification products were digested with DpnI at 37°C overnight, transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3) by electroporation transformation, and plated in LB medium containing kanamycin (50 μg ml−1) for further screening. For the second round of ep-PCR, the mutant plasmid harboring the most beneficial mutations from the first round of screening was used as a template. Single colonies from the mutant library were picked with sterilized toothpicks, plated in 160 μl LB medium containing kanamycin (50 μg ml−1) in sterilized 96-well microplates, and incubated overnight at 37°C with shaking at 900 rpm. Fifty microliters of sterilized 60% glycerol was then added to each well, and plates were stored at −70°C to create the variant library.
TABLE 1.
Primers used for PCRs
| Purpose or substitution | Primer direction | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ep-PCR | Forward | ATGAATGGAGGCACAACCG |
| Reverse | GTTGATAACACCTACTCCAG | |
| N289H | Forward | TTTGTCAATACACCGCATAGTCATTTAAACTCT |
| Reverse | AGAGTTTAAATGACTATGCGGTGTATTGACAAA | |
| N227S | Forward | TATTTTAAAGACATTAGTGATACAGCGATTAAC |
| Reverse | GTTAATCGCTGTATCACTAATGTCTTTAAAATA | |
| K313R | Forward | TCAGCTACTCAAGCAAGATCATCTGTTGAACAA |
| Reverse | TTGTTCAACAGATGATCTTGCTTGAGTAGCTGA | |
| T178A | Forward | GAATCATTGGAAAGCGATGCTCGTCGG |
| Reverse | CCGACGAGCATCGCTTTCCAATGATTC | |
| S308L | Forward | AGTTACCAAGTCCAATTAGCTACTCAAGCAAAA |
| Reverse | TTTTGCTTGAGTAGCTAATTGGACTTGGTAACT | |
| R72S | Forward | GTTAAAAATCACAGTGGAAAAGCTC |
| Reverse | GAGCTTTTCCACTGTGATTTTTAAC | |
| N186D | Forward | CGGTCATACTGATGATGCATCATTAGC |
| Reverse | GCTAATGATGCATCATCAGTATGAC | |
| I211V | Forward | GTGTCCCGCTTGTTCGATACGCT |
| Reverse | TCAGCGTATCGAACAAGCGGGACAC | |
| A254T | Forward | AGGATCAGGACAAACTGACCCAACGAC |
| Reverse | GTCGTTGGGTCAGTTTGTCCTGATCCT |
Screening for variants with improved thermostability.
Each mutant in the microplate was replicated in LB medium containing kanamycin (50 μg ml−1), and IPTG (0.1 mM) was prepared in a microplate by using a sterile 96-pin replicator. After cultivation for 15 h at 37°C, cultures containing the induced variant enzyme were diluted 10-fold with deionized water, heat treated at 65°C for 10 min, and then quickly placed on ice. Residual enzyme activities were assayed immediately. For the second round of screening, cultures containing induced variant enzymes were diluted 20-fold and heat treated at 70°C for 10 min. Mutants were subjected to primary screening on a 96-well plate. Variants maintaining significant increases in residual enzyme activities compared to the control were regarded as candidate mutants with improved thermostability. The t50 (time at which the enzyme loses 50% of its initial activity) values were further determined to evaluate the thermostability of the wild-type and mutated enzymes. Purified enzymes were adjusted to a concentration of ∼1 μg ml−1 and were then incubated in 50 mM glycine-NaOH buffer (pH 10.0) at 50°C. Sample enzymes were collected at various times and assayed for enzyme activity.
Site-directed mutagenesis.
Site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) and site-directed saturation mutagenesis (SSM) were performed according to a protocol for SDM reported previously (39). Primers containing the appropriate base substitutions are listed in Table 1. PCR was carried out with 50 ng template plasmid (pET28a-pelA), 1 μmol primer pairs, 0.2 mM deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs), and 1 U Pyrobest DNA polymerase in a final volume of 50 μl. The following PCR profile was used: 1 cycle of 94°C for 4 min and 20 cycles of 94°C for 45 s, 55°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 7 min, followed by a final extension step at 72°C for 20 min. The PCR products were then digested by DpnI overnight. The products were transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3) competent cells by electroporation transformation. DNA sequencing was performed by SinoGenoMax Co. Ltd. (Beijing, China).
Expression and purification of wild-type and mutant enzymes.
A single colony of E. coli BL21(DE3) harboring a plasmid carrying the gene encoding wild-type or mutant BspPelA was cultured in LB medium containing kanamycin (50 μg ml−1) at 37°C and induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG when the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reached ∼0.8. After cultivation for another 5 h, cells were harvested by centrifugation at 8,000 × g for 10 min and disrupted by sonication in lysis buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 0.5 M NaCl, 5 mM imidazole [pH 8.0]). Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 16,000 × g at 4°C for 20 min. The supernatants were loaded onto a preequilibrated nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) column (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA), and the column was washed with washing buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 0.5 M NaCl, 60 mM imidazole [pH 8.0]). The bound protein was then eluted with elution buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 0.5 M NaCl, 500 mM imidazole [pH 8.0]). The obtained protein solution was desalted by using a desalting column (GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB, Uppsala, Sweden) with 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.5). The purity of the proteins was assessed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The protein concentration was defined according to the Bradford method (40), using bovine serum albumin as the standard.
Enzyme assay and determination of kinetic parameters.
The enzyme activity was determined by measuring the GalpA released from the substrate PGA by the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) method (32, 41), with GalpA as the standard. The reaction mixture consisted of 190 μl of 50 mM glycine-NaOH buffer (pH 10.5) containing 0.2% (wt/vol) PGA and 10 μl of appropriately diluted enzyme. The reaction mixture was incubated at 50°C for 10 min, and the reaction was stopped by the addition of 200 μl DNS reagent, followed by heating in a boiling-water bath for 5 min. The absorbance at 540 nm was measured with a Spectra Max 190 microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). One unit of enzyme activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that released reducing sugar equivalent to 1 μmol GalpA per min. All activity measurements were repeated three times. The statistical analysis of changes in specific activity was done by using SPSS 16.0 software with the t test.
The kinetic parameters of wild-type and mutant BspPelAs were determined as previously described (42), using the DNS method at 50°C and pH 10.0. The substrate concentrations of PGA were 0.2 to 6.0 mg ml−1 for both wild-type BspPelA and mutant enzymes. All data were averages of data from triplicate measurements. The kinetic parameters were calculated by using GraphPad Prism software based on a nonlinear regression analysis.
Enzymatic degumming.
Degumming of ramie fibers by wild-type BspPelA and the EA mutant was evaluated by measuring the weight loss of ramie fibers after degumming, as follows. First, 1.0 g of ramie fibers was bathed in 30 ml of 50 mM glycine-NaOH buffer (pH 10.0) with a final concentration of 100 U ml−1 enzymes and incubated at 50°C for 4 h. After enzymatic treatment, fibers were washed twice with water after beating to remove residual gum from the surface of the ramie fibers and then dried to a constant weight at 105°C. Ramie fibers treated in 50 mM glycine-NaOH buffer (pH 10.0) without enzyme were used as a control. All data were averages of data from sextuplicate measurements.
The combined enzyme-chemical method for ramie degumming using mutant EA was also performed according to methods described previously by Kapoor et al. (17), with some modifications. After enzymatic treatment, ramie fibers were directly bathed in 30 ml of 0.5% (wt/vol) NaOH and then treated at 120°C for 30 min. The ramie fibers were then washed twice with water after beating and dried to a constant weight at 105°C. Ramie fibers treated in 0.5% (wt/vol) NaOH only were used as a control. All data were averages of data from sextuplicate measurements. The statistical analysis of increases in weight loss was done by using SPSS 16.0 software with the t test.
Scanning electron microscopy of enzyme-treated and untreated ramie fibers.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe the microstructure and surface morphology of untreated and enzyme-treated ramie fibers after large- or small-scale production. The samples were coated with a 200-Å gold layer by using a vacuum sputterer, and samples were then observed by SEM using an FEI-Quanta200 scanning electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA).
Structure, molecular dynamic simulation, and FoldX analysis.
The structure of wild-type BspPelA was described previously by Zheng et al. (37). The three-dimensional (3D) structure was displayed by using PyMOL 1.3.X (Delano Scientific, San Carlos, CA, USA). The intramolecular interactions of the protein were analyzed by using the Protein Interactions Calculator (PIC) server (http://pic.mbu.iisc.ernet.in/) (43).
The crystal structure of BspPelA (PDB accession no. 3VMW) was neutralized and solvated in a periodic box containing TIP3P (“transferable intermolecular potential 3 points”) water and 0.29% NaCl. All simulations were performed by using force fields AMBER03 and GAFF (general AMBER force field); partial charges were derived by using the AM1/BCC (bond charge correction) procedure implemented in YASARA. Electrostatic interactions were calculated by using a cutoff of 7.86 Å; long-range interactions were calculated by using the particle mesh Ewald integration. After initial minimization by steepest descent and simulated annealing until convergence (<0.05 kJ mol−1 atom−1 for 200 steps), a molecular dynamic simulation was performed for 10 ns at two different temperatures (328 and 353 K). Snapshots were taken every 25 ps, and the recorded trajectories were statistically analyzed by using YASARA and Chimera 1.9.
The changes in the Gibbs free energy (ΔG) induced by mutations at positions 124, 178, and 271 at three different temperatures (298, 328, and 353 K) were calculated by FoldX (version 3.0). The crystal structure of BspPelA (PDB accession no. 3VMW) was rotamerized and energy was minimized by using the “RepairObject” command to correct residues that had nonstandard torsion angles. Additionally, to consider possible conformational changes introduced by the mutations, structures taken from the last snapshot of each mutant molecular dynamic (MD) simulation were mutated back to the wild-type residues, and the ΔΔG value was computed.
RESULTS
Construction and screening of random mutagenesis libraries.
The ratio of the activity of heat-treated bacteria to the activity of untreated bacteria was designated residual activity and was used to select mutants with improved thermostability; the selection criterion included an increase of at least 10% in the residual activity of the mutant compared to that of the wild-type enzyme after heat treatment. For the first round of ep-PCR, a library with a total of ∼6,000 clones was constructed. Approximately 65% of randomly picked clones in this library displayed Pel activity. In general, 1 to 5 nucleotide mutations were observed per gene. For first-round screening, wild-type BspPelA served as a control and was completely inactivated after heat treatment for 10 min at 65°C. A total of 20 mutants showing higher residual enzyme activities than those of the wild-type enzyme after heat treatment were obtained. By measuring the t50 values of the purified enzymes, a total of seven mutants with significantly improved thermostability were identified (Table 2). At 50°C, the t50 values of these mutants increased 3- to 5-fold compared with that of the wild-type enzyme. Interestingly, the specific activities of the 2B9, 1G4, and 3F7 mutants were also improved. Among these, the 1G4 mutant was considered the best variant because it had the highest t50 value (50 min) at 50°C, and its catalytic activity was increased by ∼50% compared with that of the wild-type enzyme.
TABLE 2.
Mutation sites, t50 values, and specific activities for mutants with improved thermostability
| Enzymea | Sourceb | Substitution(s) in mutant | t50 (min)c | Activity (U mg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 10 | 1,870 | ||
| 2B9 | 1st | S271G | 35 | 3,001 |
| 1G4 | 1st | S271G, N289H | 50 | 3,079 |
| 1D2 | 1st | N227S, S271G, K313R | 50 | 1,758 |
| 3F6 | 1st | T178A, S233C | 45 | 1,121 |
| 115 | 1st | E124I | 30 | 1,304 |
| 3F7 | 1st | S271G, S308L | 40 | 1,997 |
| 3B9 | 1st | R72S, S271G | 40 | 1,316 |
| T178A | SDM | T178A | 40 | 836 |
| B7 | 2nd | S271G, N289H, A254T | 120 | 2,385 |
| D11 | 2nd | S271G, N289H, N186D | 100 | 2,003 |
| E2 | 2nd | S271G, N289H, N186D, I211V | 150 | 2,195 |
| EA | CM | N186D/I211V/A254T/S271G/N289H | 240 | 2,305 |
| EAT | CM | T178A/N186D/I211V/A254T/S271G/N289H | 840 | 901 |
| EAE | CM | E124I/N186D/I211V/A254T/S271G/N289H | 900 | 1,130 |
| EAET | CM | E124I/T178A/N186D/I211V/A254T/S271G/N289H | 1,400 | 293 |
WT, wild type.
1st and 2nd indicate the first and the second rounds of ep-PCR, respectively. SDM, site-directed mutagenesis; CM, combined mutagenesis.
The t50 values were determined at 50°C.
The plasmid of mutant strain 1G4 was chosen as the template for the second round of ep-PCR. A library with >6,000 clones was constructed, and ∼67% of randomly picked clones from this library were active. The incubation temperature of preheating for screening of the second library was raised to 70°C, as the 1G4 mutant was almost inactive after heat treatment for 10 min at 70°C. After screening and measurement of the t50 values at 50°C for the purified enzymes, three variants (B7, D11, and E2) with significantly improved thermostability compared with that of 1G4 were identified (Table 2). The most thermostable mutant (E2) had the highest t50 value at 50°C, 150 min, which is a 15-fold increase compared with that of the wild-type enzyme and a 3-fold increase compared with that of the 1G4 variant. However, the specific activities of these mutants were all lower than that of 1G4 although still higher than that of the wild-type enzyme.
Mutation site analysis and SDM.
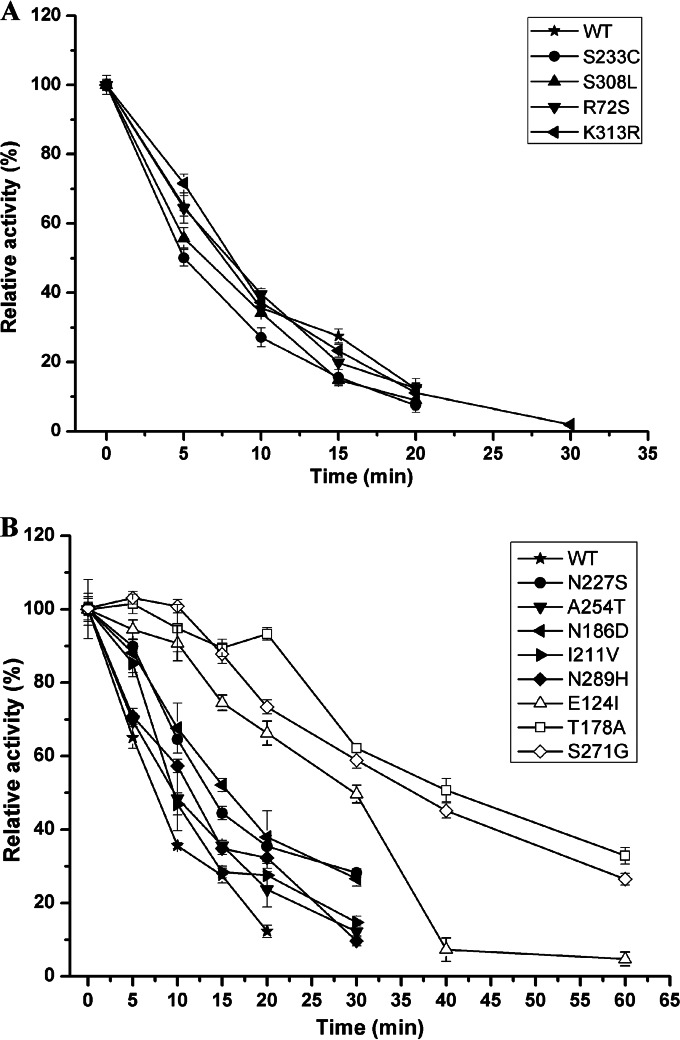
The 10 improved mutants obtained from second-round libraries were sequenced; there were 1 to 4 amino acid substitutions in each mutant, and a total of 12 different amino acids substitutions occurred (Table 2). The effects of these mutations were tested for individual mutants by SDM. As shown in Fig. 1A, the single mutations K313R, S233C, S308L, and R72S did not result in improved thermostability. Changes in the t50 values at 50°C for these mutants were <10%. The mutations N227S, N289H, N186D, I211V, and A254T resulted in only slight increases in thermostability, while the mutations E124I, S271G, and T178A resulted in significant increases in thermostability compared with the thermostability of the other mutations (Fig. 1B). The t50 values for these three mutants at 50°C were 3-, 3.5-, and 4-fold higher, respectively, than that for wild-type BspPelA (Table 2), indicating that these three sites may be responsible for the improvement in the thermal tolerance of the BspPelA variants.
FIG 1.
Thermostability of single-substitution mutants. The purified wild-type and mutant enzymes were incubated at 50°C for different times, and the residual activity was then determined. The activity without incubation was taken as 100%. The measurements were performed in three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations.
Among the mutants that were improved during the first round of ep-PCR, five mutants contained the S271G substitution, indicating that S271 was important for the thermostability of BspPelA. Thus, an SSM library of S271 was constructed. After screening of ∼500 mutants in the SSM library of S271, no mutants with better thermal tolerance than that of the 2B9 mutant (S271G) were found, indicating that S271G was the best substitution at this position.
To further elucidate the effects of these three site substitutions on enzyme activity, the steady-state kinetic parameters and specific activities of wild-type BspPelA and the S271G, E124I, and T178A mutants were determined at 50°C. As shown in Table 2, the specific activity of the S271G mutant increased significantly, by ∼60.5% (P < 0.05), compared with that of wild-type BspPelA. Conversely, the activities of the E124I and T178A mutants decreased significantly, by ∼28.3% and 55.3% (P < 0.05), respectively. The S271G mutation not only improved thermostability but also increased the specific activity. The Km values for enzymes with single substitutions (S271G, E124I, and T178A) were not substantially different from each other or from that for the wild-type enzyme (Table 3), indicating that these mutations did not influence substrate binding. The kcat value and kcat/Km value of the S271G substitution also did not differ significantly from those of wild-type BspPelA. However, the kcat values for the E124I and T178A mutants significantly decreased, by 24.9% and 53.8%, respectively (Table 3), leading to decreases in the kcat/Km values of ∼24.3% and 59.2%, respectively; this suggested that these two mutations affected not only the thermostability but also the catalytic efficiency of BspPelA. The results of the kinetic analysis revealed that the S271G substitution was an ideal mutation for improving the thermostability of BspPelA while maintaining its catalytic activity and enzymatic efficiency.
TABLE 3.
Kinetic parameters for wild-type BspPelA and single- and combined-substitution mutants
| Enzyme/mutation | Mean Km (g liter−1) ± SD | Mean kcat (s−1) ± SD | Mean kcat/Km (s−1 liter g−1) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 1.13 ± 0.14 | 3,319 ± 153 | 2,932 ± 394 |
| S271G | 1.20 ± 0.12 | 3,637 ± 140 | 3,044 ± 337 |
| E124I | 1.12 ± 0.12 | 2,492 ± 96 | 2,219 ± 251 |
| T178A | 1.28 ± 0.19 | 1,532 ± 87 | 1,196 ± 192 |
| 1G4 | 1.10 ± 0.23 | 3,450 ± 266 | 3,128 ± 711 |
| E2 | 1.58 ± 0.28 | 3,353 ± 180 | 2,126 ± 282 |
| EA | 1.74 ± 0.20 | 3,932 ± 136 | 2,255 ± 141 |
| EAT | 2.13 ± 0.26 | 1,625 ± 85 | 763 ± 101 |
| EAE | 2.80 ± 0.24 | 2,006 ± 79 | 716 ± 67 |
| EAET | 3.96 ± 0.66 | 526 ± 47 | 133 ± 25 |
Combination of beneficial mutations.
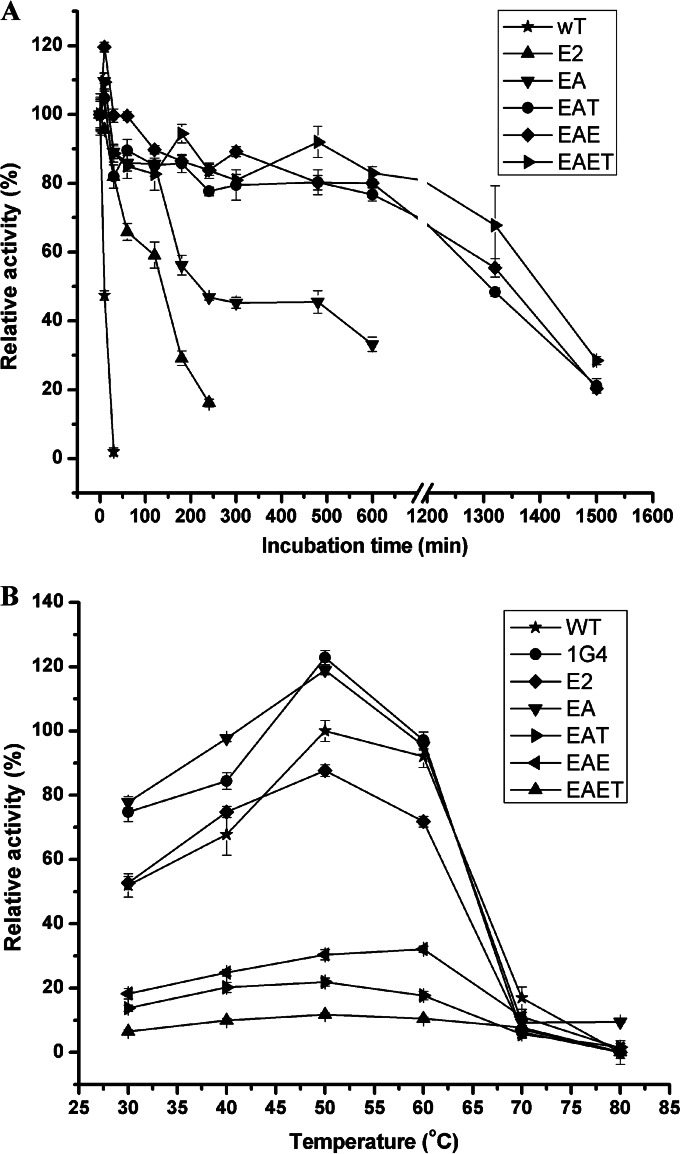
To achieve greater thermostability, the beneficial amino acid substitutions were combined. Since mutant E2 was the most thermostable mutant screened here and exhibited increased specific activity, each beneficial amino acid substitution was introduced into mutant E2 by using SDM to determine whether the effect of each mutation was cumulative. Although the single A254T mutation did not significantly improve thermostability, a notable increase in the t50 value at 50°C was observed when the A254T mutation was combined with the 1G4 variant (mutant B7). Thus, the A254T substitution was combined with mutant E2 to create mutant EA. The T178A and E124I substitutions were then introduced into EA to create mutants EAT and EAE. The T178A substitution was combined with EAE to create EAET (Table 2). As shown in Fig. 2A, all four of these combined mutants were more thermostable than mutant E2. At 50°C, the t50 values of mutants EA, EAT, EAE, and EAET were 24-, 84-, 90-, and 140-fold higher, respectively, than that of wild-type BspPelA, while the t50 of mutant E2 was only 15-fold higher than that of the wild-type enzyme (Table 2). However, except for mutant EA, which had a significant specific activity increase of 23.3% (P < 0.05) compared to that of the wild-type enzyme, the combined mutants EAT, EAE, and EAET exhibited only 48.2%, 60.4%, and 15.7% of the specific activity of the wild-type enzyme, respectively (Table 2).
FIG 2.
Thermostability and optimal reaction temperature of the combined mutants. (A) Thermostability curves for combined mutants. The purified wild-type and mutant enzymes were incubated at 50°C for different times. The activity without incubation was taken as 100%. (B) Optimal temperature for combined mutants. The activity was determined with 50 mM glycine-NaOH buffer (pH 10.5) containing 0.2% (wt/vol) PGA. The measurements were performed in three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations.
The optimal reaction temperatures for each of the combined mutants and the most beneficial mutants, 1G4 and E2, were also determined. As shown in Fig. 2B, mutants 1G4, E2, EA, EAT, and EAET exhibited the same optimal reaction temperature of 50°C. In contrast, mutant EAE displayed optimal activity at 60°C, which was 5°C higher than the optimal temperature for the wild-type enzyme. Thus, the steady-state kinetic parameters for the combined mutants were determined at 50°C (Table 3). The Km of mutant 1G4 decreased slightly, while the kcat increased slightly, resulting in a 7.0% increase in the kcat/Km value. The Km values of mutants E2, EA, EAT, EAE, and EAET increased by 45.4%, 54.5%, 90.9%, 154.5%, and 254.5%, respectively, compared to that of wild-type BspPelA, indicating that these enzymes exhibited reduced affinities for the substrate. Mutants EAT, EAE, and EAET also displayed decreases in kcat values of 51.0%, 39.6%, and 84.2%, respectively, leading to lower kcat/Km values than that for the wild-type enzyme. The kcat value for mutant E2 did not change significantly, while that for mutant EA increased by ∼18.5%, resulting in 27.5% and 23.1% decreases in the kcat/Km values, respectively. The results of enzymatic characterization indicated that while the thermal tolerance of BspPelA was further improved with these mutants, mutants E2, EA, EAE, EAT, and EAET displayed weakened affinities for the substrate and lower catalytic efficiencies.
Degumming of ramie fibers.
Among all the mutants, EA showed both a 24-fold increase in the t50 value (240 min) at 50°C and a 23.3% increase in specific activity (2,305 U mg−1) compared to the values for wild-type BspPelA, making mutant EA the most optimal mutant in terms of catalytic efficiency and thermostability. Thus, a comparative study was performed to evaluate the ramie degumming efficiencies of purified wild-type and EA mutant enzymes. Each enzyme was used to degum ramie fibers at 50°C by using both enzymatic and combined enzyme-chemical methods.
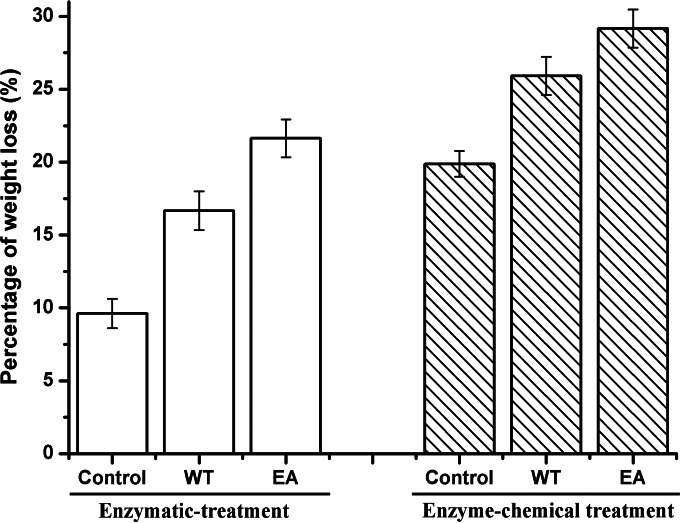
The weight losses of ramie fibers treated with wild-type BspPelA and mutant EA were 16.7% and 21.6%, respectively (Fig. 3). Only 9.7% weight loss was observed for the negative control, in which the ramie fibers were treated only with alkaline buffer. As shown in Fig. 3, the weight losses of ramie fibers treated with the enzyme-chemical method were 25.9% for the wild-type enzyme and 29.1% for mutant EA; both of these values were significantly higher than that for the control, at 19.9% (P < 0.05). Mutant EA displayed significant increases in weight loss of ramie fibers of 29.3% (enzymatic method) and 12.3% (combined enzyme-chemical method) compared to the wild-type enzyme (P < 0.05). Moreover, the weight loss of ramie fibers treated with mutant EA (21.6%) was also significantly higher (P < 0.05) than that of ramie fibers treated with only 0.5% (wt/vol) NaOH (19.9%) (Fig. 3). Morphologically, the EA-degummed ramie fibers were whiter, softer, and more dispersed than the fibers degummed by the wild-type enzyme or chemicals (Fig. 4A to D). Electron microscopy images of single fibers also showed that the surfaces of EA-degummed ramie fibers were smoother than those of ramie fibers degummed by the wild-type enzyme or chemicals (Fig. 4E to H). These results indicated that the degumming efficiency of mutant EA was significantly higher than that of wild-type BspPelA.
FIG 3.
Percent weight loss after degumming of ramie fibers by enzymatic or enzyme-chemical methods. The measurements were performed in six independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations.
FIG 4.
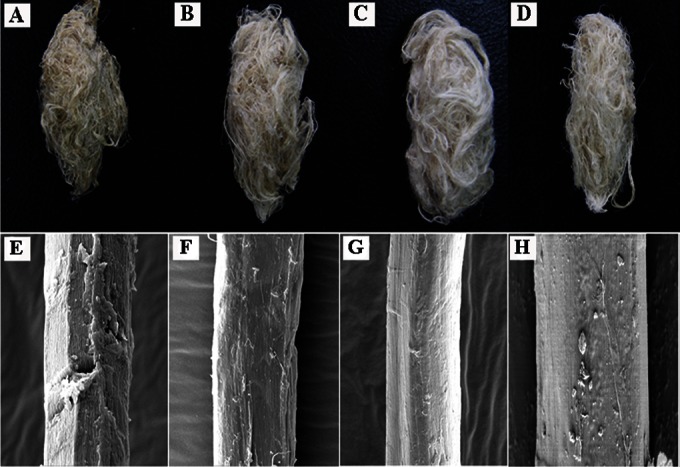
Scanning electron microscopy imaging of degumming ramie fibers. (A and E) Ramie fibers treated with buffer only (control). (B and F) Ramie fibers treated with wild-type BspPelA. (C and G) Ramie fibers treated with the mutant EA. (D and H) Ramie fibers treated with chemicals only. Panels A to D show exterior images of ramie fibers; panels E to H show surface images of single fibers obtained by scanning electron microscopy (magnification, ×5,000).
Analysis of molecular interactions and 3D structure of mutated BspPelA.
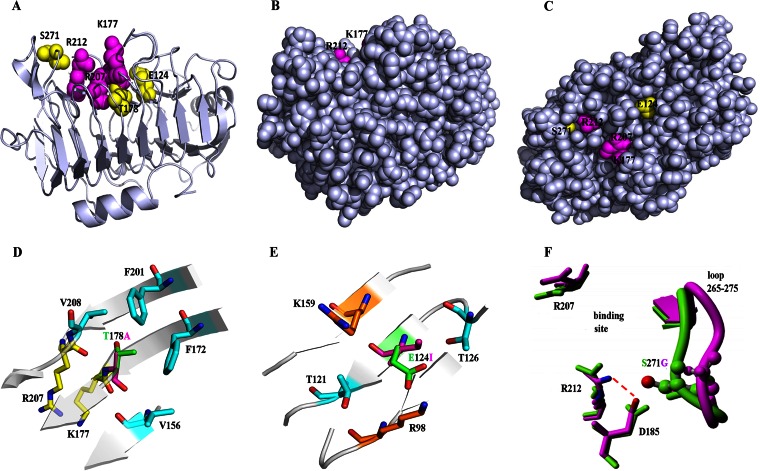
SDM showed that the single mutations E124I, T178A, and S271G were responsible for improvements of the thermal tolerance of BspPelA; these three sites were the first sites identified as contributing to the thermostability of Pels. Among these three mutants, E124I and T178A improved thermostability but decreased enzyme activity, while the S271G substitution increased thermostability and enzyme activity simultaneously. Thus, we analyzed the intramolecular interactions of the three key single-substitution mutants and wild-type BspPelA using the PIC server. In the 3D structure, all three mutations were located close to the active site (Fig. 5A), and the residues were buried, with <5% side chain solvent accessibility, calculated by Discovery Studio (Fig. 5B and C). Moreover, these three mutations resulted in a change from polar to hydrophobic residues.
FIG 5.
Locations and structural analysis of three key mutation sites. (A) Mutations location in the crystal structure of BspPelA (PDB accession no. 3VMW). The side chains of the catalytic triad (K177, R207, and R212) and mutations (E124, T178, and S271) are represented as spheres. (B and C) Views of BspPelA with all residues in a real space with van der Waals representation, where the image in panel B is in an orientation identical to that of the image shown in panel A and panel C shows a 90°C turn of the image in panel B along the x axis. Only the respective side chains are shown in color, and the backbone is shown in gray. (D) Location and mutation of T178A. T178 and A178 are represented in green and purple, respectively. (E) Location and mutation of E124I. E124 and I124 are represented in green and purple, respectively. (F) Location and mutation of S271G. The H-bond network around Arg212 in the crystal structure of BspPelA is shown in green; S271G (last snapshot from a 10-ns MD simulation) is shown in purple.
The catalytic triad of BspPelA was K177, R207, and R212. Residue T178 coordinates the position of the catalytic site residue K177, and the T178A substitution may affect the efficiency of catalytic activity (Fig. 5A). Moreover, this mutation provides only a slight stabilizing effect compared with the wild-type BspPelA structure (Table 4). Interestingly, after a 10-ns MD relaxation of the T178A mutant, we observed a stabilizing rearrangement. Subsequent FoldX stability analysis of the relaxed structure showed a stabilizing effect of ∼1 kcal mol−1 (see FoldX calculations in Table 4) by forming a hydrophobic cluster with V156, F172, F201, and V208 (Fig. 5D), which would stabilize the secondary structures and enhance rigidity.
TABLE 4.
ΔΔG values calculated by FoldX for mutations at different temperatures
| Substitution | ΔΔG valuea (kcal mol−1) at temp |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 K | 328 K | 353 K | |
| Glu124Ile (WT to M1)b | −3.83 | −3.77 | −3.52 |
| Thr178Ala (WT to M2)b | −0.16 | −0.12 | −0.09 |
| Ser271Gly (WT to M3)b | 1.07 | 1.05 | 1.01 |
| Glu124Ile (MD M1)c | −4.11 | −4.07 | −4.12 |
| Thr178Ala (MD M2)c | −1.01 | −1.01 | −1.02 |
| Ser271Gly (MD M3)c | −4.82 | −4.97 | −5.10 |
The predicted ΔΔG value is a measure of the changes in the Gibbs free energy (ΔG) induced by the mutations. The stabilizing mutations have a negative value (ΔΔG).
The crystal structure of BspPelA (PDB accession no. 3VMW) was used for FoldX calculations. M1 represents the Glu124Ile mutant, M2 represents the Thr178Ala mutant, and M3 represents the Ser271Gly mutant.
The last snapshot of the MD simulation of the mutant in water at 353 K (10 ns) was used for FoldX calculations (mutant mutated back to the wild type).
However, the E124I substitution, which eliminated the ion pairs among E124, K159, and R98 (Fig. 5E), and the S271G substitution, which eliminated the hydrogen bonds between S271 and D185 (Fig. 5F), enhanced the thermal tolerance of the enzyme. Interestingly, the G124I mutation was buried below the binding pocket loop next to the catalytic residue K177 (Fig. 5A), and the introduction of Ile stabilized BspPelA by ∼4 kcal mol−1 (see FoldX calculations in Table 4) by forming a hydrophobic cluster with the methyl groups of T121 and T126 in the wild-type enzyme and after a 10-ns MD relaxation (Fig. 5E). The S271G mutation, located in the loop next to the catalytic residue R212 (Fig. 5F), was shown to be destabilizing in the wild-type structure because of the elimination of a direct H-bond interaction. After MD relaxation, the loop containing G271 moved away from catalytic residue R212, and a new salt bridge from D185 to R212 with a distance of 2.8 Å was formed (Fig. 5F). Based on the relaxed structure, FoldX predicted a stabilization energy of the S271G mutation of −5 kcal mol−1 (Table 4) due to the newly formed H-bond network around R212.
DISCUSSION
Thermostability is considered critical for enzymes in the degumming process. Although successful approaches for improving the thermostability of pectin hydrolysis enzymes have been reported (27, 42, 44), improvement of thermostability by protein engineering is still challenging. Directed evolution is a widely used technique for protein engineering in which proteins are improved through iterative cycles of diversity generation and screening; this method has been successfully carried out for various enzymes to improve their thermostability or catalytic activity (27, 45–47). In this study, BspPelA was successfully engineered by directed-evolution strategies, including random mutagenesis and SSM, in order to improve its thermostability and catalytic efficiency for degumming of ramie fibers. Our data showed that mutant EA exhibited a 24-fold increase in the t50 value at 50°C and a substantial increase in specific activity, suggesting that this mutant may have potential industrial applications in ramie degumming. Thus, directed evolution is applicable for improvement of the thermostability of engineered proteins.
Decreased conformational flexibility in thermophilic enzymes is thought to result in low enzyme activity, while increased flexibility in less stable enzymes is associated with enhanced enzyme activity. Thus, in several cases, thermostability and enzyme activity could not be improved simultaneously (27, 46). This phenomenon was also found in this study, and the specific activities of 4 of 10 thermostable mutants obtained from two rounds of random mutagenesis decreased. However, the other six mutants exhibiting improved thermostability also had improved specific activity compared to that of the wild-type enzyme (Table 2). Similar results have also been reported for improvement of thermostability in other Pels from Bacillus pumilus (27) and Xanthomonas campestris (42), indicating that the relationship between thermostability and enzyme activity does not have to be opposing.
The general mechanisms for improving thermostability of enzymes are complex and involve disulfide bridges, hydrophobic or aromatic interactions, contact order, hydrogen bonding, ion pairing, and dimer-dimer interactions (48–51). Three key single-substitution sites, E124I, T178A, and S271G, which were responsible for the improvement of the thermal tolerance of BspPelA, were the first sites identified as contributing to the thermostability of Pels. Interestingly, analysis of the intramolecular interactions showed that while some mutants exhibited increased molecular interactions with stabilizing effects, the thermal tolerance of the enzyme was enhanced with the E124I and S271G substitutions, which eliminated several ion pairs or hydrogen bonds; this observation cannot be explained based on our current understanding of the enzyme and enzyme structure (48, 50, 51). The stabilizing effects of point mutations can be cumulative (27, 42, 45, 47). Indeed, in our study, some further-improved combined mutants were also obtained. In particular, the combined mutant EA displayed both improved thermostability and higher specific activity. In contrast, the other three combined mutants (EAT, EAE, and EAET) displayed decreased specific activity compared to that of the wild-type enzyme, possibly because of the introduction of the E124I and/or T178A substitution, which proved to disrupt BspPelA activity in this study.
The amount of the EA mutant enzyme used in the ramie degumming experiment in this study was smaller than that of the wild-type enzyme because of the increased specific activity of the EA mutant. Indeed, when the same amount of mutant EA was used, weight loss of ramie fibers reached 23.5%, indicating that BspPelA was successfully engineered for more efficient ramie degumming by directed evolution. The enzymatic degumming of some alkaline and thermostable Pels was also reported in the past years. The polygalacturonase from Bacillus sp. strain MG-cp-2 (17) and the pectate lyases from Amycolata sp. (15) and Bacillus pumilus DKS1 (24) showed ∼20%, 16.7%, and 17% weight losses of ramie fibers after 12 h, 15 h, and 24 h of degumming, respectively, while ∼13.5% and 23.1% weight losses were found with pectate lyases from Bacillus subtilis 7-3-3 (52) and Bacillus pumilus ATCC 7061 (27), respectively, after 4 h of degumming. Therefore, compared with these results, the degumming efficiency of the mutant EA enzyme was among the highest of the alkaline and thermostable Pels reported.
Combined with 0.5% NaOH treatment for 30 min, the enzyme-chemical degumming method with the mutant EA enzyme increased the weight loss of ramie fibers to 29.1%; this method decreased the amount of caustic soda used by ∼60% compared with the classical chemical degumming process and maintained high degumming efficiency. Overall, our findings indicated that the mutant EA enzyme could be used for efficient ramie degumming via the combined enzyme-chemical process, confirming its potential application in the textile industries. However, the total gum content of ramie fibers used in this experiment was ∼34%, and only fibers with <2.5% residual gum, which means those with at least >30% weight loss, can be directly used in further textile processes (53). The enzyme-chemical degumming efficiency of mutant EA was close to the efficiency (at least >30% weight loss) of the traditional chemical degumming method which had been widely used in the ramie textile industry, and moreover, the ramie degumming efficiency could be further improved by using mutant EA in conjunction with other enzymes, such as xylanase or other Pels (23), and subsequent processes, such as bleaching, in the future.
In conclusion, in this study, the alkaline and low-Ca2+-dependent Pel BspPelA from the alkaliphilic bacterium Bacillus sp. N16-5 was successfully engineered by the directed-evolution method in order to improve thermostability. The most beneficial mutant (EA) exhibited a 24-fold increase in the t50 value at 50°C compared with that of the wild-type enzyme and had a 23.3% increase in catalytic activity. The most thermostable mutant (EAET) exhibited a 140-fold increase in the t50 value at 50°C but accompanied by an 84.3% decrease in activity compared with those of the wild-type enzyme. For industrial use, mutant EA was also more efficient than wild-type BspPelA in ramie degumming. Three key site mutations, E124I, T178A, and S271G, were responsible for the thermostability of BspPelA. The structural information available for BspPelA reasonably explained the effects of the mutations on thermostability and provided clues for the structure-based engineering of Pels and for future mutation/selection or other strategies similar to that employed in this study. One limitation of this work was that our best mutant (EA) exhibited only a 23.3% increase in catalytic activity. Thus, further directed evolution for improvement of enzyme activity using mutant EA as the template enzyme is needed to develop an alkaline low-Ca2+-dependent BspPelA that is more efficient for ramie degumming.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences grant KSZD-EW-Z-015-2, National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 31300667, and Chinese National Programs for High Technology Research and Development grant 2012AA022204.
We thank Marco Bocola for help with the structural analysis of the mutant enzymes.
REFERENCES
- 1.Carpita NC, Gibeaut DM. 1993. Structural models of primary cell walls in flowering plants: consistency of molecular structure with the physical properties of the walls during growth. Plant J 3:1–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.1993.tb00007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schols HA, Voragen A. 2003. Pectic polysaccharides, p 829–843. In Whitaker JR, Voragen A, Wong DWS (ed), Handbook of food enzymology. Dekker, New York, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Whitaker JR. 1994. Principles of enzymology for the food sciences, p 425–437. Dekker, New York, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alkorta I, Garbisu C, Llama MJ, Serra JL. 1998. Industrial applications of pectic enzymes: a review. Process Biochem 33:21–28. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(97)00046-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Benen JA, Voragen A, Visser J. 2003. Pectic enzymes, p 845–848. In Whitaker JR, Voragen A, Wong DWS (ed), Handbook of food enzymology. Dekker, New York, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schwan RF, Rose AH, Board RG. 1995. Microbial fermentation of cocoa beans with emphasis on enzymatic degradation of the pulp. J Appl Bacteriol Symp Suppl 79:S96–S107. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Benen JA, Visser J. 2003. Pectate and pectin lyases, p 1029–1041. In Whitaker JR, Voragen A, Wong DWS (ed), Handbook of food enzymology. Dekker, New York, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barras F, Van Gijsegem F, Chatterjee AK. 1994. Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu Rev Phytopathol 32:201–234. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.32.090194.001221. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N, Condemine G, Nasser W, Reverchon S. 1996. Regulation of pectinolysis in Erwinia chrysanthemi. Annu Rev Microbiol 50:213–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nasser W, Chalet F, Robert-Baudouy J. 1990. Purification and characterization of extracellular pectate lyase from Bacillus subtilis. Biochimie 72:689–695. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90053-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kozianowski G, Canganella F, Rainey FA, Hippe H, Antranikian G. 1997. Purification and characterization of thermostable pectate-lyases from a newly isolated thermophilic bacterium, Thermoanaerobacter italicus sp. nov. Extremophiles 1:171–182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sakai T, Sakamoto T, Hallaert J, Vandamme EJ. 1993. Pectin, pectinase, and protopectinase: production, properties, and applications. Adv Appl Microbiol 39:213–294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Scavetta RD, Herron SR, Hotchkiss AT, Kita N, Keen NT, Benen JA, Kester HC, Visser J, Jurnak F. 1999. Structure of a plant cell wall fragment complexed to pectate lyase C. Plant Cell 11:1081–1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yoder MD, Jurnak F. 1995. The parallel β-helix and other coiled folds. FASEB J 9:335–342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bruhlmann F, Leupin M, Erismann KH, Fiechter A. 2000. Enzymatic degumming of ramie bast fibers. J Biotechnol 76:43–50. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(99)00175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Henriksson G, Akin DE, Slomczynski D, Eriksson K-EL. 1999. Production of highly efficient enzymes for flax retting by Rhizomucor pusillus. J Biotechnol 68:115–123. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(98)00192-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kapoor M, Beg QK, Bhushan B, Singh K, Dadhich KS, Hoondal GS. 2001. Application of an alkaline and thermostable polygalacturonase from Bacillus sp. MG-cp-2 in degumming of ramie (Boehmeria nivea) and sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) bast fibers. Process Biochem 36:803–807. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kashyap DR, Vohra P, Soni SK, Tewari R. 2001. Degumming of buel (Grewia optiva) bast fibers by pectinolytic enzyme from Bacillus sp. DT7. Biotechnol Lett 23:1297–1301. doi: 10.1023/A:1010565205698. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sreenath HK, Shah AB, Yang VW, Gharia MM, Jefferies TW. 1996. Enzymatic polishing of jute/cotton blended fabrics. J Ferment Bioeng 81:18–20. doi: 10.1016/0922-338X(96)83113-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hoondal G, Tiwari R, Tewari R, Dahiya N, Beg Q. 2002. Microbial alkaline pectinases and their industrial applications: a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:409–418. doi: 10.1007/s00253-002-1061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lenting HBM, Warmoeskerken MMCG. 2004. A fast, continuous enzyme-based pretreatment process concept for cotton containing textiles. Biocatal Biotransformation 22:361–368. doi: 10.1080/10242420400024557. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tzanov T, Calafell M, Guebitz GM, Cavaco-Paulo A. 2001. Bio-preparation of cotton fabrics. Enzyme Microb Technol 29:357–362. doi: 10.1016/S0141-0229(01)00388-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zou M, Li X, Zhao J, Qu Y. 2013. Characteristics of polygalacturonate lyase C from Bacillus subtilis 7-3-3 and its synergistic action with PelA in enzymatic degumming. PLoS One 8:e79357. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Basu S, Saha M, Chattopadhyay D, Chakrabarti K. 2009. Large-scale degumming of ramie fibre using a newly isolated Bacillus pumilus DKS1 with high pectate lyase activity. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:239–245. doi: 10.1007/s10295-008-0490-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li X, Wang H, Zhou C, Ma Y, Li J, Song J. 2014. Cloning, expression and characterization of a pectate lyase from Paenibacillus sp. 0602 in recombinant Escherichia coli. BMC Biotechnol 14:18–27. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-14-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang C, Yao J, Zhou C, Mao L, Zhang G, Ma Y. 2013. The alkaline pectate lyase PEL168 of Bacillus subtilis heterologously expressed in Pichia pastoris is more stable and efficient for degumming ramie fiber. BMC Biotechnol 13:26. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liang C, Gui X, Zhou C, Xue Y, Ma Y, Tang SY. 2015. Improving the thermoactivity and thermostability of pectate lyase from Bacillus pumilus for ramie degumming. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:2673–2682. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6091-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Berensmeier S, Singh SA, Meens J, Buchholz K. 2004. Cloning of the pelA gene from Bacillus licheniformis 14A and biochemical characterization of recombinant, thermostable, high-alkaline pectate lyase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:560–567. doi: 10.1007/s00253-003-1446-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Boland WE, Henriksen ED, Doran-Peterson J. 2010. Characterization of two Paenibacillus amylolyticus strain 27C64 pectate lyases with activity on highly methylated pectin. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6006–6009. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00043-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chiliveri SR, Linga VR. 2014. A novel thermostable, alkaline pectate lyase from Bacillus tequilensis SV11 with potential in textile industry. Carbohydr Polym 111:264–272. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hatada Y, Kobayashi T, Ito S. 2001. Enzymatic properties of the highly thermophilic and alkaline pectate lyase Pel-4B from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain P-4-N and the entire nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Extremophiles 5:127–133. doi: 10.1007/s007920100182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Klug-Santner BG, Schnitzhofer W, Vrsanská M, Weber J, Agrawal PB, Nierstrasz VA, Guebitz GM. 2006. Purification and characterization of a new bioscouring pectate lyase from Bacillus pumilus BK2. J Biotechnol 121:390–401. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Soriano M, Diaz P, Pastor FI. 2006. Pectate lyase C from Bacillus subtilis: a novel endo-cleaving enzyme with activity on highly methylated pectin. Microbiology 152(Part 3):617–625. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28562-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tardy F, Nasser W, Robert-Baudouy J, Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N. 1997. Comparative analysis of the five major Erwinia chrysanthemi pectate lyases: enzyme characteristics and potential inhibitors. J Bacteriol 179:2503–2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang H, Li X, Ma Y, Song J. 2014. Characterization and high-level expression of a metagenome-derived alkaline pectate lyase in recombinant Escherichia coli. Process Biochem 49:69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2013.10.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li G, Rao L, Xue Y, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Ma Y. 2010. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a highly active alkaline pectate lyase from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. N16-5. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:670–677. doi: 10.4014/jmb.0911.11019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zheng Y, Huang CH, Liu W, Ko TP, Xue Y, Zhou C, Guo RT, Ma Y. 2012. Crystal structure and substrate-binding mode of a novel pectate lyase from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. N16-5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 420:269–274. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Miyazaki K. 2011. MEGAWHOP cloning: a method of creating random mutagenesis libraries via megaprimer PCR of whole plasmids. Methods Enzymol 498:399–406. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385120-8.00017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zheng L, Baumann U, Reymond JL. 2004. An efficient one-step site-directed and site-saturation mutagenesis protocol. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bradford MM. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Miller GL. 1959. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. doi: 10.1021/ac60147a030. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Xiao Z, Bergeron H, Grosse S, Beauchemin M, Garron ML, Shaya D, Sulea T, Cygler M, Lau PC. 2008. Improvement of the thermostability and activity of a pectate lyase by single amino acid substitutions, using a strategy based on melting-temperature-guided sequence alignment. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1183–1189. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02220-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tina KG, Bhadra R, Srinivasan N. 2007. PIC: protein interactions calculator. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W473–W476. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Silva I, Larsen D, Jers C, Derkx P, Meyer A, Mikkelsen J. 2013. Enhancing RGI lyase thermostability by targeted single point mutations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9727–9735. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-5184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hirokawa K, Ichiyanagi A, Kajiyama N. 2008. Enhancement of thermostability of fungal deglycating enzymes by directed evolution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:775–781. doi: 10.1007/s00253-008-1363-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liang C, Fioroni M, Rodríguez-Ropero F, Xue Y, Schwaneberg U, Ma Y. 2011. Directed evolution of a thermophilic endoglucanase (Cel5A) into highly active Cel5A variants with an expanded temperature profile. J Biotechnol 154:46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Minagawa H, Yoshida Y, Kenmochi N, Furuichi M, Shimada J, Kaneko H. 2007. Improving the thermal stability of lactate oxidase by directed evolution. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:77–81. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6409-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kumar S, Tsai C-J, Nussinov R. 2000. Factors enhancing protein thermostability. Protein Eng 13:179–191. doi: 10.1093/protein/13.3.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Robinson-Rechavi M, Godzik A. 2005. Structural genomics of Thermotoga maritima proteins shows that contact order is a major determinant of protein thermostability. Structure 13:857–860. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2005.03.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sterner R, Liebl W. 2001. Thermophilic adaptation of proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 36:39–106. doi: 10.1080/20014091074174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vieille C, Zeikus GJ. 2001. Hyperthermophilic enzymes: sources, uses, and molecular mechanisms for thermostability. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:1–43. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.65.1.1-43.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zou M, Li X, Shi W, Guo F, Zhao J, Qu Y. 2013. Improved production of alkaline polygalacturonate lyase by homologous overexpression PelA in Bacillus subtilis. Process Biochem 48:1143–1150. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2013.05.023. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zheng L, Du Y, Zhang J. 2001. Degumming of ramie fibers by alkalophilic bacteria and their polysaccharide-degrading enzymes. Bioresour Technol 78:89–94. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]