Abstract
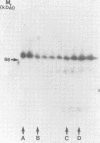
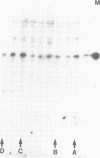
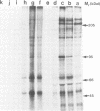
The Drosophila engrailed protein which contains a homeobox domain and specific DNA binding activity is believed to function in the regulation of gene expression during embryogenesis. Here we show that the engrailed protein interacts stably with specific complexes of soluble nuclear proteins when expressed artificially in a cell line and in the developing embryo. The engrailed complexes have molecular masses between 10(7) and 10(8) which suggests they contain a polymeric protein component. The complex is able to bind reversibly to DNA and a definitive purification shows it to be constituted of 12 distinct protein species, two of which are predominant. Purified, bacterially produced engrailed protein can be reconstituted with both culture cell and embryo nuclear protein fractions to form complexes of the same and related composition respectively. On the basis of these results we propose that protein--protein interactions as well as DNA binding are important for correct engrailed protein function in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Scott M. P. Localization of the fushi tarazu protein during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The Drosophila developmental gene, engrailed, encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):630–635. doi: 10.1038/318630a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Kuner J. M., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. Development of embryonic pattern in D. melanogaster as revealed by accumulation of the nuclear engrailed protein. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90012-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjose A., McGinnis W. J., Gehring W. J. Isolation of a homoeo box-containing gene from the engrailed region of Drosophila and the spatial distribution of its transcripts. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):284–289. doi: 10.1038/313284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bellido A., Santamaria P. Developmental analysis of the wing disc in the mutant engrailed of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1972 Sep;72(1):87–104. doi: 10.1093/genetics/72.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr T. L., Alberts B. M. Organization of the cytoskeleton in early Drosophila embryos. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1494–1509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karr T. L., Ali Z., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of D. melanogaster provides an essential zygotic function in precellular embryos. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T. Engrailed: a gene controlling compartment and segment formation in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg T., Sidén I., O'Farrell P., Simon M. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: in situ localization of transcripts reveals compartment-specific expression. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Struhl G. A molecular gradient in early Drosophila embryos and its role in specifying the body pattern. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):537–545. doi: 10.1038/324537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kauvar L. M., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: structural analysis of an embryonic transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. Transformation of cultured Drosophila melanogaster cells with a dominant selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1833–1838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]