Abstract
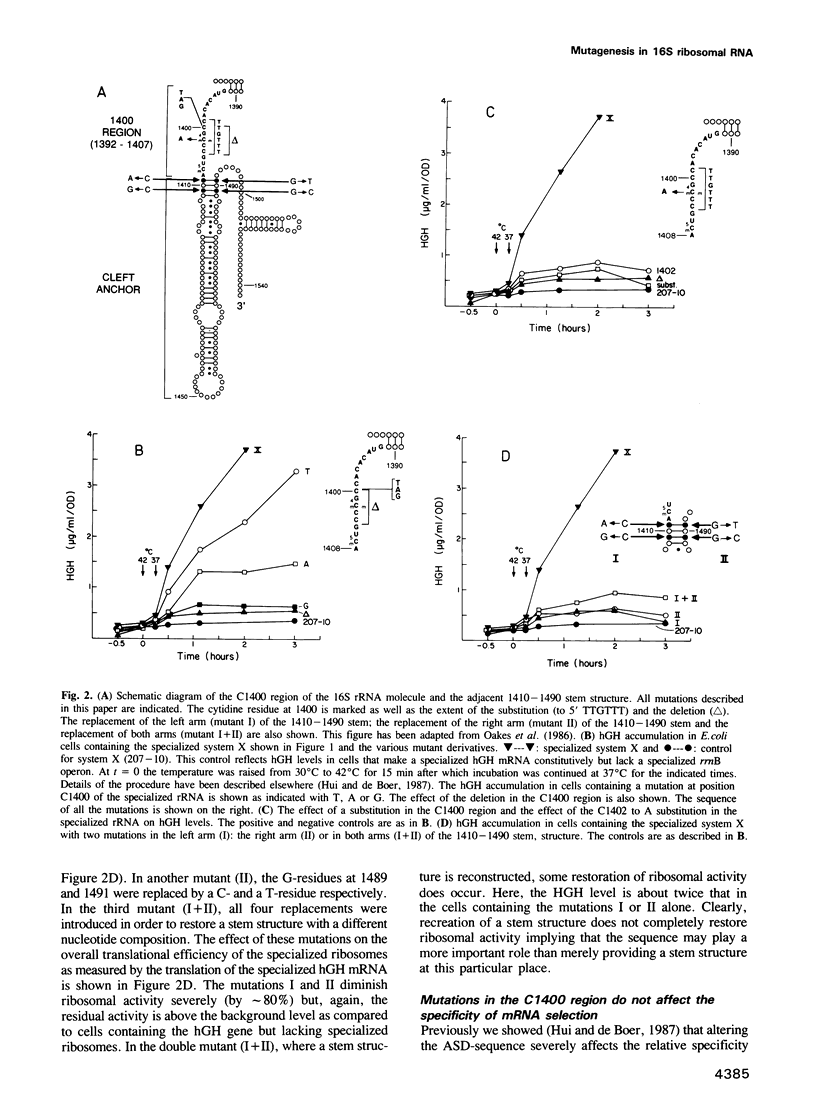
In the specialized ribosome system, a distinct pool of mutated ribosomes is dedicated to the translation of one particular mRNA species. This was accomplished by altering the Shine-Dalgarno sequence on the mRNA and its complementary anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence on the plasmid-borne 16S rRNA gene. Here, using the specialized ribosome system, we were able to introduce mutations in key regions of the 16S rRNA and could study their effect on translation in vivo. The C1400 region has been implicated to play a role in the actual mRNA decoding process. Several ribosomal mutations were introduced in this region. We showed that substitution of the evolutionary highly conserved C1400 residue by a G- or an A-residue inhibits ribosomal activity by 80% and 50% respectively, whereas, a C to a U change at this conserved position does not affect overall ribosomal activity. The adjacent stem structure (1410-1490) was also examined. Disruption of the stem by replacing either one of the arms of this stem, with a different sequence, inhibits ribosomal activity by approximately 80%. A small but significant restoration of translation could be achieved by recreating a complementary stem with a different sequence. We found that full reversion of activity could be obtained when such mutated ribosomes were made spectinomycin resistant by introducing a C to A substitution at position 1192 which is located far away in the secondary structure map of the 16S rRNA molecule. Based on these results we conclude that some, but not all, of the nucleotides in the conserved C1400 region play a key role in translation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B., Millon R., Ebel J. P., Nurse K., Ofengand J. Cross-linking of the anticodon of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis acetylvalyl-tRNA to the ribosomal P site. Characterization of a unique site in both E. coli 16S and yeast 18S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):429–437. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettayebi M., Prasad S. M., Morgan E. A. Chloramphenicol-erythromycin resistance mutations in a 23S rRNA gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):551–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.551-557.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L., Hozumi T., Arentzen R., Itakura K., Yansura D. G., Ross M. J., Miozzari G., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. Direct expression in Escherichia coli of a DNA sequence coding for human growth hormone. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):544–548. doi: 10.1038/281544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gornicki P., Nurse K., Hellmann W., Boublik M., Ofengand J. High resolution localization of the tRNA anticodon interaction site on the Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10493–10498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Stark M. J., Dahlberg A. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of ribosomal RNA. Construction and characterization of deletion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):397–416. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., Takebe Y., Sharrock R. A., Nomura M. Feedback regulation of rRNA and tRNA synthesis and accumulation of free ribosomes after conditional expression of rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1069–1073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., Jhurani P., de Boer H. A. Directing ribosomes to a single mRNA species: a method to study ribosomal RNA mutations and their effects on translation of a single messenger in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:432–452. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemiolo D. K., Zwieb C., Dahlberg A. E. Point mutations in the 3' minor domain of 16S rRNA of E.coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8631–8643. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren-Zur M., Boublik M., Ofengand J. Localization of the decoding region on the 30S Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit by affinity immunoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1054–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzosiak W., Denman R., Nurse K., Hellmann W., Boublik M., Gehrke C. W., Agris P. F., Ofengand J. In vitro synthesis of 16S ribosomal RNA containing single base changes and assembly into a functional 30S ribosome. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2353–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. Evolving ribosome structure: domains in archaebacteria, eubacteria, eocytes and eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:507–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Transfer RNA shields specific nucleotides in 16S ribosomal RNA from attack by chemical probes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):985–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90813-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgola E. J., Hijazi K. A., Göringer H. U., Dahlberg A. E. Mutant 16S ribosomal RNA: a codon-specific translational suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4162–4165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes M. I., Clark M. W., Henderson E., Lake J. A. DNA hybridization electron microscopy: ribosomal RNA nucleotides 1392-1407 are exposed in the cleft of the small subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):275–279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofengand J., Liou R., Kohut J., 3rd, Schwartz I., Zimmermann R. A. Covalent cross-linking of transfer ribonucleic acid to the ribosomal P site. Mechanism and site of reaction in transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4322–4332. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince J. B., Taylor B. H., Thurlow D. L., Ofengand J., Zimmermann R. A. Covalent crosslinking of tRNA1Val to 16S RNA at the ribosomal P site: identification of crosslinked residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5450–5454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4653–4663. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Dahlberg A. E. Point mutations in the middle of 16S ribosomal RNA of E. coli produced by deletion loop mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4361–4375. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]