Abstract
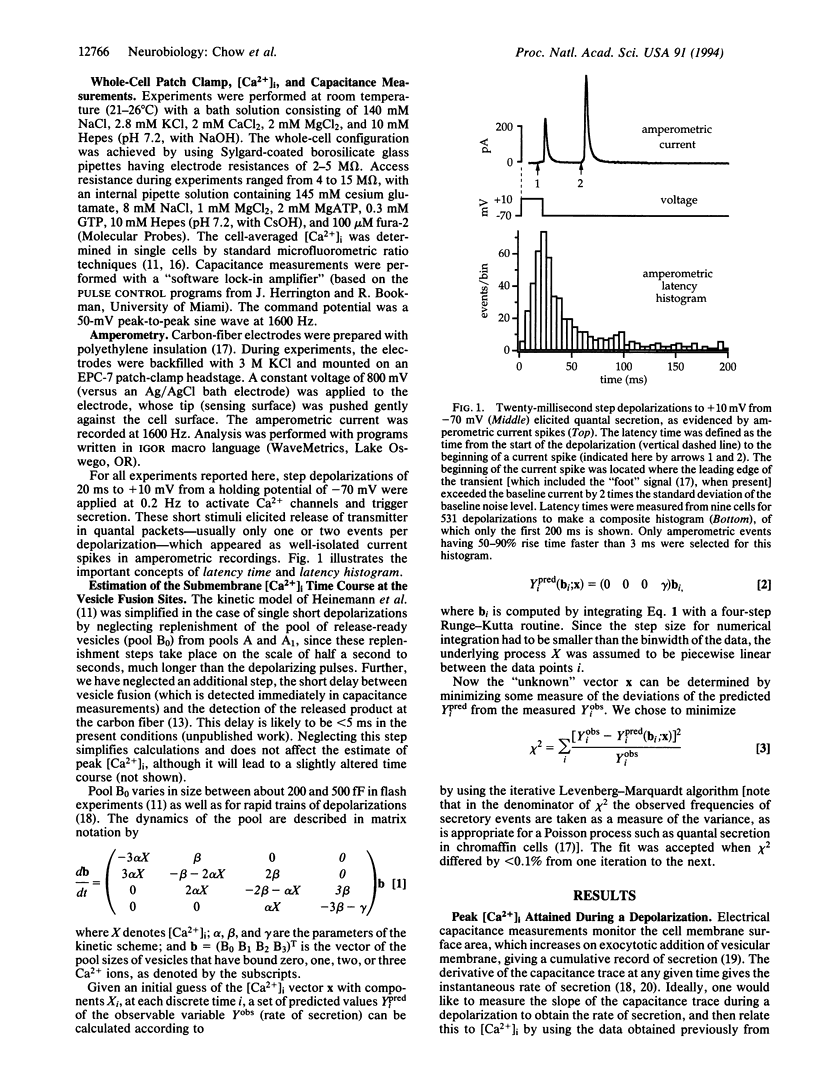
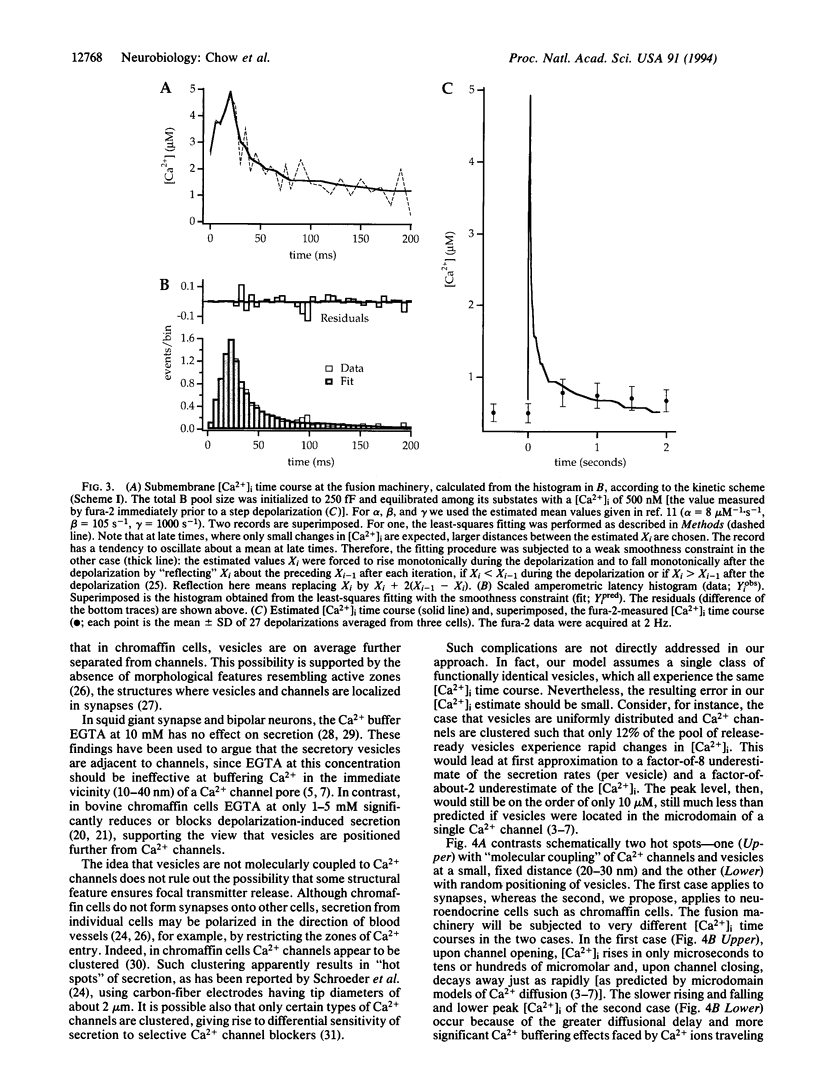
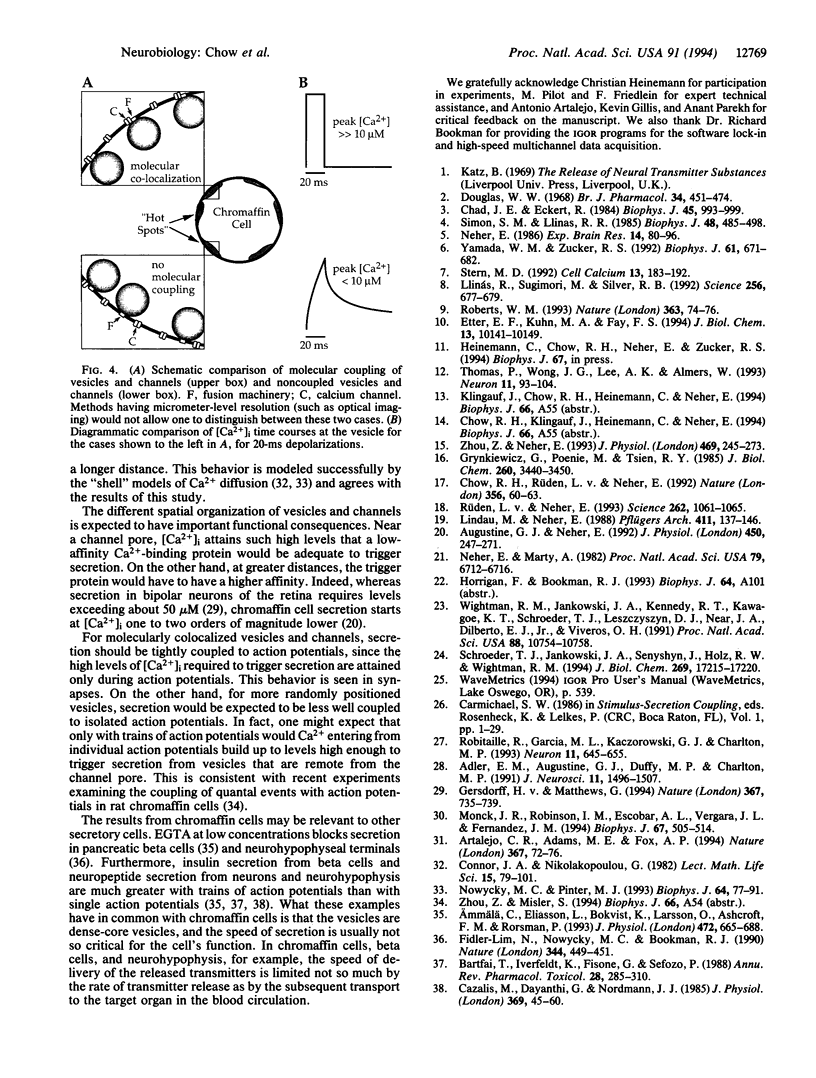
We have used the secretory response of chromaffin cells to estimate the submembrane intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) "seen" by secretory granules during short depolarizations. The rate of secretion during a depolarization was assessed by combining the electrochemical method of amperometry and electrical capacitance measurements. The rate was then related to [Ca2+]i based on a previous characterization of how Ca2+ affects the dynamics of vesicle priming and fusion in chromaffin cells [Heinemann, C., Chow, R. H., Neher, E. & Zucker, R. S. (1994) Biophys. J. 67, in press]. Calculated [Ca2+]i rose during the depolarization to a peak of < 10 microM, then decayed over tens of milliseconds. In synapses, vesicles are presumed to be located within nanometers of Ca2+ channels where [Ca2+]i is believed to rise in only microseconds to near steady-state levels of hundreds of micromolar. Channel closure should lead to a decrease in [Ca2+]i also in microseconds. Our findings of the slower time course and the lower peak [Ca2+]i suggest that in chromaffin cells, unlike synapses, Ca2+ channels and vesicles are not strictly colocalized. This idea is consistent with previously published data on dense-core vesicle secretion from diverse cell types.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler E. M., Augustine G. J., Duffy S. N., Charlton M. P. Alien intracellular calcium chelators attenuate neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1496–1507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01496.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammälä C., Eliasson L., Bokvist K., Larsson O., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Exocytosis elicited by action potentials and voltage-clamp calcium currents in individual mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:665–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Adams M. E., Fox A. P. Three types of Ca2+ channel trigger secretion with different efficacies in chromaffin cells. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):72–76. doi: 10.1038/367072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Calcium requirements for secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:247–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Iverfeldt K., Fisone G., Serfözö P. Regulation of the release of coexisting neurotransmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988;28:285–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.28.040188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazalis M., Dayanithi G., Nordmann J. J. The role of patterned burst and interburst interval on the excitation-coupling mechanism in the isolated rat neural lobe. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:45–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chad J. E., Eckert R. Calcium domains associated with individual channels can account for anomalous voltage relations of CA-dependent responses. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):993–999. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84244-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. H., von Rüden L., Neher E. Delay in vesicle fusion revealed by electrochemical monitoring of single secretory events in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):60–63. doi: 10.1038/356060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etter E. F., Kuhn M. A., Fay F. S. Detection of changes in near-membrane Ca2+ concentration using a novel membrane-associated Ca2+ indicator. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10141–10149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
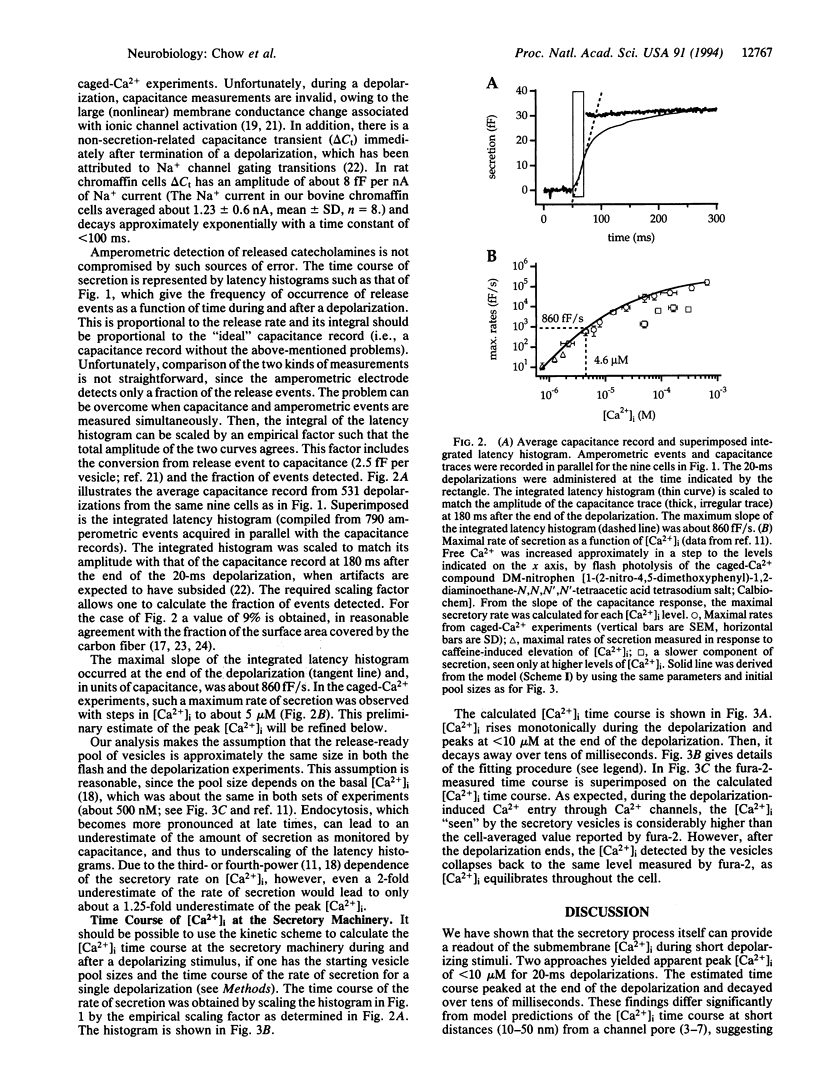
- Lim N. F., Nowycky M. C., Bookman R. J. Direct measurement of exocytosis and calcium currents in single vertebrate nerve terminals. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):449–451. doi: 10.1038/344449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindau M., Neher E. Patch-clamp techniques for time-resolved capacitance measurements in single cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):137–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00582306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Robinson I. M., Escobar A. L., Vergara J. L., Fernandez J. M. Pulsed laser imaging of rapid Ca2+ gradients in excitable cells. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):505–514. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80554-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Marty A. Discrete changes of cell membrane capacitance observed under conditions of enhanced secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6712–6716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Pinter M. J. Time courses of calcium and calcium-bound buffers following calcium influx in a model cell. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81342-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M. Spatial calcium buffering in saccular hair cells. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):74–76. doi: 10.1038/363074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robitaille R., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J., Charlton M. P. Functional colocalization of calcium and calcium-gated potassium channels in control of transmitter release. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):645–655. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. J., Jankowski J. A., Senyshyn J., Holz R. W., Wightman R. M. Zones of exocytotic release on bovine adrenal medullary cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17215–17220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Llinás R. R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83804-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Buffering of calcium in the vicinity of a channel pore. Cell Calcium. 1992 Mar;13(3):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90046-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Wong J. G., Lee A. K., Almers W. A low affinity Ca2+ receptor controls the final steps in peptide secretion from pituitary melanotrophs. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90274-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman R. M., Jankowski J. A., Kennedy R. T., Kawagoe K. T., Schroeder T. J., Leszczyszyn D. J., Near J. A., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Viveros O. H. Temporally resolved catecholamine spikes correspond to single vesicle release from individual chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10754–10758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada W. M., Zucker R. S. Time course of transmitter release calculated from simulations of a calcium diffusion model. Biophys J. 1992 Mar;61(3):671–682. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81872-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Neher E. Mobile and immobile calcium buffers in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:245–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gersdorff H., Matthews G. Dynamics of synaptic vesicle fusion and membrane retrieval in synaptic terminals. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):735–739. doi: 10.1038/367735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Rüden L., Neher E. A Ca-dependent early step in the release of catecholamines from adrenal chromaffin cells. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1061–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.8235626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]