Abstract
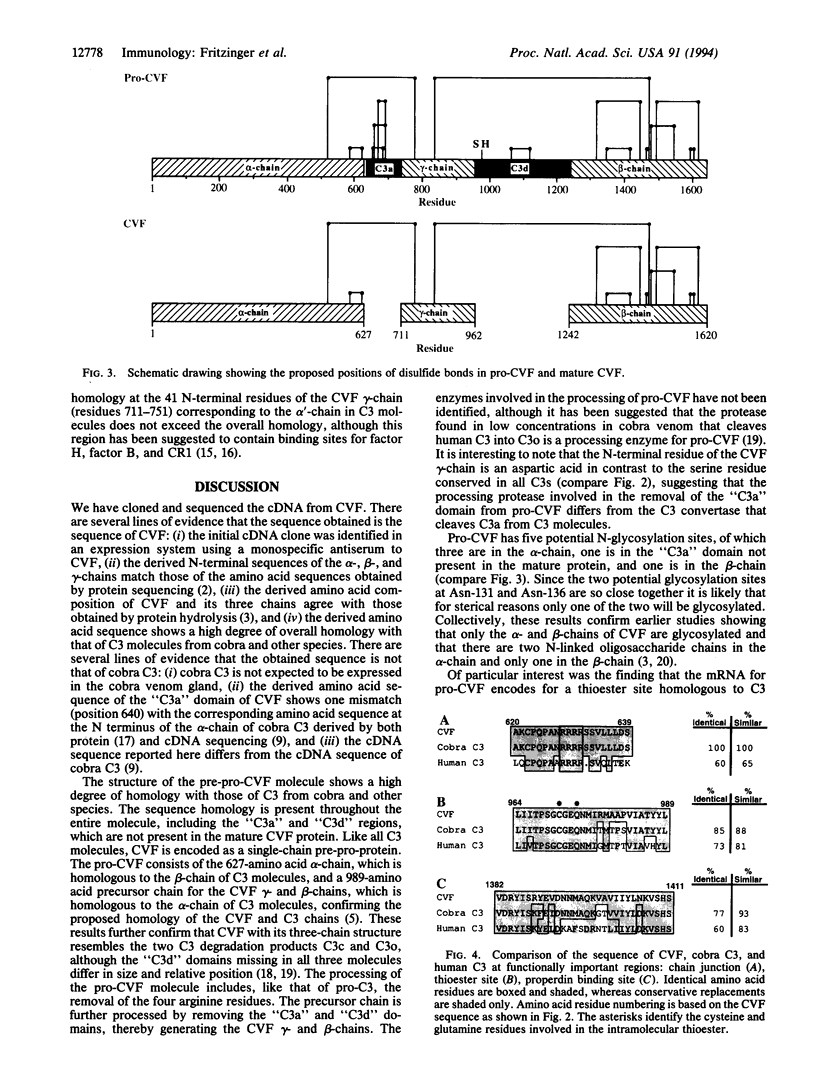
Cobra venom factor (CVF) is the complement-activating protein in cobra venom. Like C3b, CVF forms with factor B and factor D in human and mammalian serum the bimolecular C3/C5 convertase. This functional similarity of CVF and C3 correlates with many structural similarities, which led to the suggestion that CVF is evolutionally related to C3. We report here the molecular cloning and derived primary structure of CVF. CVF mRNA is > 5924 nucleotides in length. It contains a single open reading frame of 4926 nucleotides, coding for a pre-pro-protein of 1642 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence reveals approximately 70% protein similarity to mammalian and human C3 and exceeds 91% in the case of cobra C3. The single-chain pre-pro-CVF consists of a 22-amino acid signal sequence, a 627-amino acid alpha-chain, and a 989-amino acid precursor chain for the CVF gamma- and beta-chains. The processing of pro-CVF involves the removal of 4 arginine residues between the alpha- and precursor chains as well as of the C3a-like and C3d-like domains from the precursor chain, thereby confirming the predicted chain homologies to C3. Pro-CVF contains five potential N-glycosylation sites, of which only three can be expected to be glycosylated in mature CVF. Like C3, pro-CVF contains 27 cysteine residues and a homologous thioester site in the C3d-like region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Balavitch D. Cobra venom factor: evidence for its being altered cobra C3 (the third component of complement). Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1275–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.56780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becherer J. D., Lambris J. D. Identification of the C3b receptor-binding domain in third component of complement. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14586–14591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daoudaki M. E., Becherer J. D., Lambris J. D. A 34-amino acid peptide of the third component of complement mediates properdin binding. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1577–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolmer K., Sottrup-Jensen L. Disulfide bridges in human complement component C3b. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 2;315(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81139-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggertsen G., Lind P., Sjöquist J. Molecular characterization of the complement activating protein in the venom of the Indian cobra (Naja N. siamensis). Mol Immunol. 1981 Feb;18(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzinger D. C., Petrella E. C., Connelly M. B., Bredehorst R., Vogel C. W. Primary structure of cobra complement component C3. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3554–3562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda D. C., Petrella E. C., Raj T. T., Bredehorst R., Vogel C. W. Immunoreactivity and function of oligosaccharides in cobra venom factor. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):2977–2986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Scholze H., Pâques E. P., Deisenhofer J. Crystal structure analysis and molecular model of human C3a anaphylatoxin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Sep;361(9):1389–1399. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.2.1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Avila D., Becherer J. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A discontinuous factor H binding site in the third component of complement as delineated by synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12147–12150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Takahashi M. Complete complementary DNA sequence of the third component of complement of lamprey. Implication for the evolution of thioester containing proteins. J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3290–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe M. C., Caporale L. H., Vogel C. W. A novel cleavage product of human complement component C3 with structural and functional properties of cobra venom factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12690–12697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K. Spontaneous reformation of the intramolecular thioester in complement protein C3 and low temperature capture of a conformational intermediate capable of reformation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8584–8590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel C. W., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Cobra venom factor: improved method for purification and biochemical characterization. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Oct 12;73(1):203–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel C. W., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Induction of immune cytolysis: tumor-cell killing by complement is initiated by covalent complex of monoclonal antibody and stable C3/C5 convertase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7707–7711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel C. W., Smith C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Cobra venom factor: structural homology with the third component of human complement. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3235–3241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. H., Fey G. H. Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived primary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):708–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





