Abstract
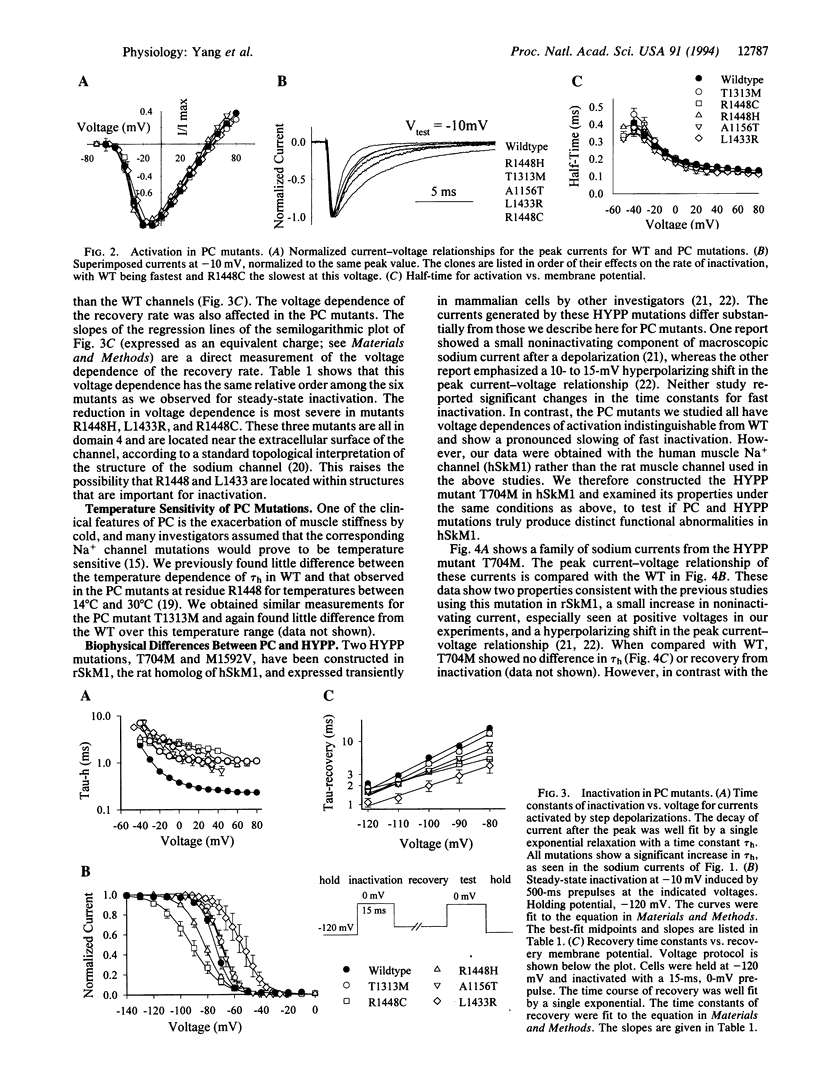
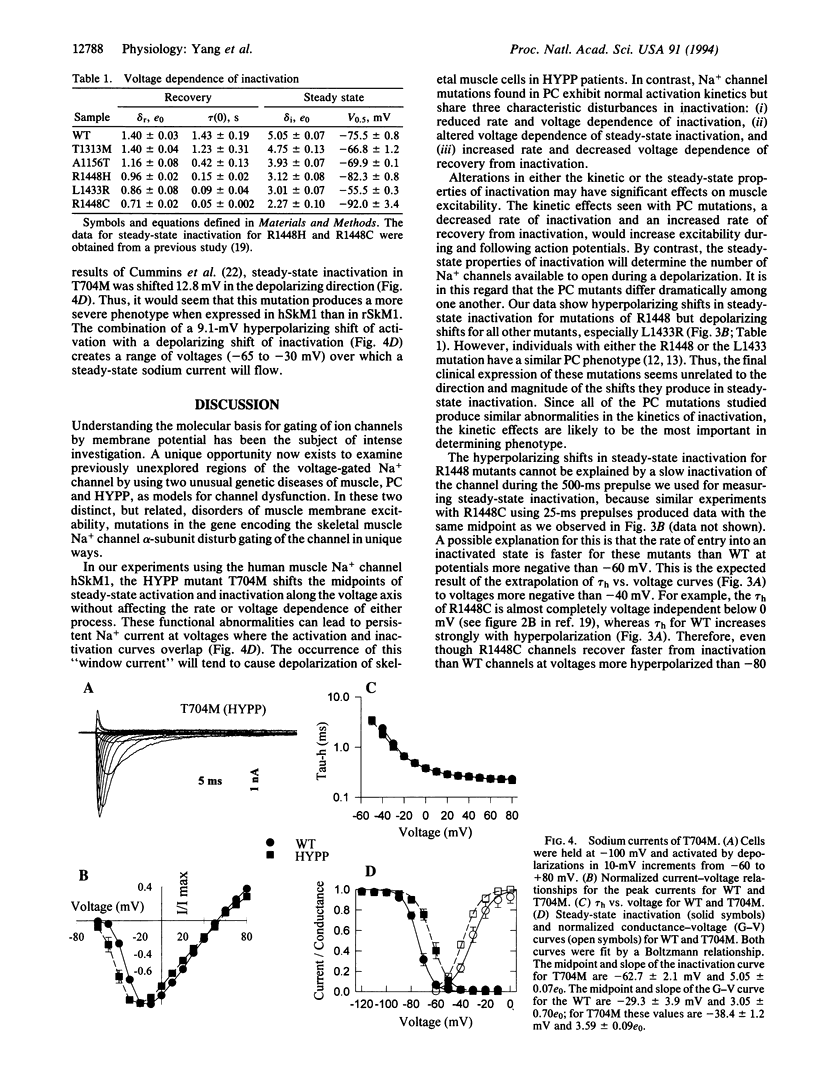
Mutations in the skeletal muscle voltage-gated Na+ channel alpha-subunit have been found in patients with two distinct hereditary disorders of sarcolemmal excitation: hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HYPP) and paramyotonia congenita (PC). Six of these mutations have been functionally expressed in a heterologous cell line (tsA201 cells) using the recombinant human skeletal muscle Na+ channel alpha-subunit cDNA hSkM1. PC mutants from diverse locations in this subunit (T1313M, L1433R, R1448H, R1448C, A1156T) all exhibit a similar disturbance in channel inactivation characterized by reduced macroscopic rate, accelerated recovery, and altered voltage dependence. PC mutants had no significant abnormality in activation. In contrast, one HYPP mutation studied (T704M) has a normal inactivation rate but exhibits shifts in the midpoints of steady-state activation and inactivation along the voltage axis. These findings help to explain the phenotypic differences between HYPP and PC at the molecular and biophysical level and contribute to our understanding of Na+ channel structure and function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cannon S. C., Brown R. H., Jr, Corey D. P. A sodium channel defect in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis: potassium-induced failure of inactivation. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. C., Strittmatter S. M. Functional expression of sodium channel mutations identified in families with periodic paralysis. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90321-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahine M., George A. L., Jr, Zhou M., Ji S., Sun W., Barchi R. L., Horn R. Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita uncouple inactivation from activation. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins T. R., Zhou J., Sigworth F. J., Ukomadu C., Stephan M., Ptácek L. J., Agnew W. S. Functional consequences of a Na+ channel mutation causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Neuron. 1993 Apr;10(4):667–678. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90168-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., George A. L., Barchi R. L., Ting-Passador S. S., Kallen R. G., Lathrop G. M., Beckmann J. S., Hahn A. F., Brown W. F., Campbell R. D. Paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis are linked to the adult muscle sodium channel gene. Ann Neurol. 1991 Dec;30(6):810–816. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine B., Khurana T. S., Hoffman E. P., Bruns G. A., Haines J. L., Trofatter J. A., Hanson M. P., Rich J., McFarlane H., Yasek D. M. Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and the adult muscle sodium channel alpha-subunit gene. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):1000–1002. doi: 10.1126/science.2173143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. L., Jr, Komisarof J., Kallen R. G., Barchi R. L. Primary structure of the adult human skeletal muscle voltage-dependent sodium channel. Ann Neurol. 1992 Feb;31(2):131–137. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs R. C. The myotonic disorders and the periodic paralyses. Adv Neurol. 1977;17:143–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacoff E. Y., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Putative receptor for the cytoplasmic inactivation gate in the Shaker K+ channel. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):86–90. doi: 10.1038/353086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji S., Sun W., George A. L., Jr, Horn R., Barchi R. L. Voltage-dependent regulation of modal gating in the rat SkM1 sodium channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Oct;104(4):625–643. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R., Ricker K., Lorković H., Dengler R., Hopf H. C. Two cases of adynamia episodica hereditaria: in vitro investigation of muscle cell membrane and contraction parameters. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Feb;6(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R., Ricker K. Membrane defects in paramyotonia congenita (Eulenburg). Muscle Nerve. 1987 Sep;10(7):633–641. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makita N., Bennett P. B., Jr, George A. L., Jr Voltage-gated Na+ channel beta 1 subunit mRNA expressed in adult human skeletal muscle, heart, and brain is encoded by a single gene. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7571–7578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchey A. I., McKenna-Yasek D., Cros D., Worthen H. G., Kuncl R. W., DeSilva S. M., Cornblath D. R., Gusella J. F., Brown R. H., Jr Novel mutations in families with unusual and variable disorders of the skeletal muscle sodium channel. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):148–152. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClatchey A. I., Van den Bergh P., Pericak-Vance M. A., Raskind W., Verellen C., McKenna-Yasek D., Rao K., Haines J. L., Bird T., Brown R. H., Jr Temperature-sensitive mutations in the III-IV cytoplasmic loop region of the skeletal muscle sodium channel gene in paramyotonia congenita. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):769–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):121–127. doi: 10.1038/312121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptacek L. J., Gouw L., Kwieciński H., McManis P., Mendell J. R., Barohn R. J., George A. L., Jr, Barchi R. L., Robertson M., Leppert M. F. Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Ann Neurol. 1993 Mar;33(3):300–307. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptacek L. J., Trimmer J. S., Agnew W. S., Roberts J. W., Petajan J. H., Leppert M. Paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis map to the same sodium-channel gene locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):851–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptácek L. J., George A. L., Jr, Barchi R. L., Griggs R. C., Riggs J. E., Robertson M., Leppert M. F. Mutations in an S4 segment of the adult skeletal muscle sodium channel cause paramyotonia congenita. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):891–897. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90203-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptácek L. J., George A. L., Jr, Griggs R. C., Tawil R., Kallen R. G., Barchi R. L., Robertson M., Leppert M. F. Identification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):1021–1027. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas C. V., Wang J. Z., Schwartz L. S., Hoffman E. P., Powell B. R., Brown R. H., Jr A Met-to-Val mutation in the skeletal muscle Na+ channel alpha-subunit in hyperkalaemic periodic paralysis. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):387–389. doi: 10.1038/354387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Lehmann-Horn F. Membrane changes in cells from myotonia patients. Physiol Rev. 1985 Apr;65(2):310–356. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Inhibition of inactivation of single sodium channels by a site-directed antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8147–8151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Patton D. E., Scheuer T., Wang Y., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10910–10914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



