Abstract
Background
Mannheimia haemolytica is a commensal bacterium that resides in the upper respiratory tract of cattle that can play a role in bovine respiratory disease. Prophages are common in the M. haemolytica genome and contribute significantly to host diversity. The objective of this research was to undertake comparative genomic analysis of phages induced from strains of M. haemolytica serotype A1 (535A and 2256A), A2 (587A and 1127A) and A6 (1152A and 3927A).
Results
Overall, four P2-like (535AP1, 587AP1, 1127AP1 and 2256AP1; genomes: 34.9–35.7 kb; G+C content: 41.5–42.1 %; genes: 51–53 coding sequences, CDSs), four λ-like (535AP2, 587AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP1; genomes: 48.6–52.1 kb; 41.1–41.4 % mol G+C; genes: 77–83 CDSs and 2 tRNAs) and one Mu-like (3927AP2; genome: 33.8 kb; 43.1 % mol G+C; encoding 50 CDSs) phages were identified. All P2-like phages are collinear with the temperate phage φMhaA1-PHL101 with 535AP1, 2256AP1 and 1152AP1 being most closely related, followed by 587AP1 and 1127AP1. Lambdoid phages are not collinear with any other known λ-type phages, with 587AP2 being distinct from 535AP2, 3927AP1 and 1152AP2. All λ-like phages contain genes encoding a toxin-antitoxin (TA) system and cell-associated haemolysin XhlA. The Mu-like phage induced from 3927A is closely related to the phage remnant φMhaMu2 from M. haemolytica PHL21, with similar Mu-like phages existing in the genomes of M. haemolytica 535A and 587A.
Conclusions
This is among the first reports of both λ- and Mu-type phages being induced from M. haemolytica. Compared to phages induced from commensal strains of M. haemolytica serotype A2, those induced from the more virulent A1 and A6 serotypes are more closely related. Moreover, when P2-, λ- and Mu-like phages co-existed in the M. haemolytica genome, only P2- and λ-like phages were detected upon induction, suggesting that Mu-type phages may be more resistant to induction. Toxin-antitoxin gene cassettes in λ-like phages may contribute to their genomic persistence or the establishment of persister subpopulations of M. haemolytica. Further work is required to determine if the cell-associated haemolysin XhlA encoded by λ-like phages contributes to the pathogenicity and ecological fitness of M. haemolytica.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12866-015-0494-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Background
Mannheimia haemolytica is a primary etiological agent of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) [1] and a member of the Pasteurellaceae family which includes other zoonotic pathogens of the genera Pasteurella, Haemophilus and Actinobacillus [2]. M. haemolytica resides as a commensal bacterium in the upper respiratory tract of healthy cattle, but under some circumstances pathogenic populations can predominate [3]. Of the 12 capsular serotypes, A2 is most frequently isolated from healthy cattle, while A1 and A6 are more common in cattle with BRD [1]. The shift from a commensal to pathogenic population is a multi-factorial response to altered host conditions [3], and is likely influenced by the ecology of the microbial community, including the prevalence and nature of bacteriophages.
Bacteriophages (phages) are viruses that infect bacteria in various ecosystems including soil, water and within the intestinal tracts of animals. Based on their life cycle, phage can be classified as lytic or temperate. Upon infection, lytic phages lyse their host and release progeny viral particles that can continue the cycle of infection. In contrast, temperate phages may enter a lysogenic cycle, whereby their genomes are repressed and integrated into the bacterial chromosome. Lysogeny is common in bacteria [4] with integrated viral DNA, termed prophages (cryptic prophages or prophages remnant) being identified in almost all sequenced bacterial genomes. These genetic elements are thought to be important contributors to bacterial diversity and evolution [5, 6]. Prophages can contain genes encoding for virulence factors (e.g. toxins) that play an important role in bacterial pathogenesis. Prophages have also been shown to contribute to host survival [5] by conferring fitness against antimicrobials and other environmental selective pressures [7].
The genome of M. haemolytica genome is approximately 2.5–2.7 Mb [8–11]. In-silicon PHAST analysis [12] of eight sequenced strains revealed that they carry between 4 and 10 prophages about half of which are deemed to be intact. Genomic analysis of M. haemolytica serotype A1 PHL213 (GenBank accession #: AASA00000000) and M. haemolytica serotype A2 str. OVINE (GenBank accession #: ACZX00000000) revealed that phage associated genes accounted for up to 30 % of the unique genes within their genomes [10]. Previously, we found that prophages are widespread within the genome of M. haemolytica and contribute significantly to host diversity [13]. The objective of the current study was to conduct a comparative genomic analysis of temperate phages induced from M. haemolytica strains representing serotypes A1, A2 and A6.
Results and discussion
Induction growth curve
Growth curves of induced M. haemolytica strains all showed an obvious depreciation of growth compared to equivalent cultures not treated with mitomycin C (Fig. 1). No spontaneous release of prophages was observed from any of the M. haemolytica strains.
Fig. 1.
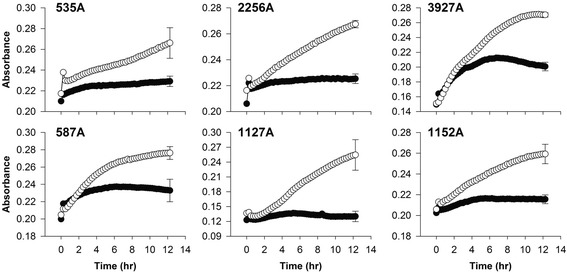
Absorbance of dual wavelength (450–600 nm) measures of log-phase Mannheimia haemolytica strains. Strains were induced at 0 h with mitomycin C (●) or untreated (○). Values are means with average SD error bar on the final point, n = 7
Genomic features
P2- and λ-like phages were induced from all M. haemolytica strains with the exception of strain 3927A, which released λ-and Mu-like phages. Genomes were sequenced, assembled and annotated resulting in four P2-, four λ- and one Mu-like phages (Table 1). Annotation of the genomes is shown in Tables 2 and 3 and additional files (Tables S1−S9).
Table 1.
Genomic nature of the temperate phages induced from Mannheimia haemolytica
| Strains | Serotypes | # phages induced | Designation | Taxonomy | Genome size (bp) | Total CDSs | G+C content (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 535A | 1 | 2 | 535AP1 | P2, Myoviridae | 34,565 | 51 | 41.6 | This study |
| 535AP2 | λ, Siphoviridae | 50,078 | 79 | 41.3 | This study | |||
| 2256A | 1 | 2 | 2256AP1 | P2, Myoviridae | 34,926 | 52 | 41.5 | This study |
| 587A | 2 | 2 | 587AP1 | P2, Myoviridae | 35,764 | 51 | 42.1 | This study |
| 587AP2 | λ, Siphoviridae | 48,594 | 77 | 41.3 | This study | |||
| 1127A | 2 | 2 | 1127AP1 | P2, Myoviridae | 36,745 | 52 | 42.0 | This study |
| 1152A | 6 | 2 | 1152AP1 | P2, Myoviridae | 34,719 | 53 | 41.6 | [13] |
| 1152AP2 | λ, Siphoviridae | 52,139 | 79 | 41.1 | This study | |||
| 3927A | 6 | 2 | 3927AP1 | λ, Siphoviridae | 52,049 | 83 | 41.4 | This study |
| 3927AP2 | Mu, Myoviridae | 33,755 | 50 | 43.1 | This study |
Table 2.
Major gene products shared among lambda-like phages induced from Mannheimia haemolytica
| No. (Gene name) | Size (aa)/MW (kDa)/pI | Function | Motifsa | Best homologs | % identity (aa) to Aaphi23b | Absent in phages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 terS | 174/19.1/5.4−5.6 | Terminase, small subunit | Terminase_2 (pfam03592) | Bacteriophage terminase small subunit (M. haemolytica) | 52−54 | |
| 2 terL | 406−410/46.3−47.3/5.9−6.1 | Terminase, large subunit | Terminase_3 superfamily (cl12054) | Phage terminase, large subunit, PBSX (M. haemolytica) | 19−21 | |
| 3 porT | 458−467/50.6−52.2/4.9−5.1 | Portal protein | phage_prot_Gp6 (pfam05133) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 20−25 | |
| 4 MHP | 312−553/35.4−63.3/9.3−9.5 | Head morphogenesis protein | Phage_Mu_F superfamily (cl10072) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 12−23 | |
| 5 MTP | 160/17.3/5.1 | Major tail protein | Phage_tail_2 (pfam06199) | Phage major tail protein (M. haemolytica) | 1152AP2 | |
| 6 | 137/15.1/10.2 | Hypothetical protein | DUF4128 (pfam13554) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 587AP2 | |
| 7 hicB | 138/15.5/4.6 | HicB | UPF0150 (pfam03681) | Toxin-antitoxin , antitoxin component, HicB (M. haemolytica) | 1152AP2 | |
| 8 hicA | 58/6.6/10.1 | HicA | YcfA (pfam07927) | Toxin-antitoxin, toxin component, HicA (M. haemolytica) | 1152AP2 | |
| 9 TMP | 816−1008/88.1−108.8/5.2−6.2 | Tail length tape measure protein | Tape_meas_nterm superfamily (cl15680); TMD(1) | Tail length tape measure-related protein (M. haemolytica) | 17−19 | |
| 10 M | 107−109/12.3−12.5/8.8−9 | Minor tail protein M | Phage_min_tail (pfam05939) | Gifsy-1 prophage VmtM (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 11 L | 156/17.6/5 | Minor tail protein L | Phage_tail_L superfamily (cl01908) | Phage-related minor tail protein L (M. haemolytica) | 1152AP2 | |
| 12 L | 238/26.5/6−6.3 | Minor tail protein L | Phage_tail_L superfamily (cl01908) | Phage minor tail protein L (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 13 K | 243/28.5/5.3 | Minor tail protein K | MPN_NLPC_P60 (cd08073) | Bacteriophage tail protein (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 14 I | 196−209/20.9−22.1/9.6−9.9 | Tail assembly protein I | Lambda_tail_I superfamily (cl01945); TM(2) | Bacteriophage tail protein and tail assembly protein I (M. haemolytica) | 15−19 | |
| 15 J | 1954−2352/213.3−255/6.3−8 | Host specificity protein J | Phage-tail_3 (pfam13550); TM(2) | Host specificity protein J (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 16 int | 329−351/37.9−40.8/9.7−9.9 | Integrase | Phage_integrase (pfam00589); Phage_integ_N superfamily (cl07565); DNA_BRE_C superfamily (cl00213) | Integrase/recombinase (M. haemolytica) | 17−24 | |
| 17 MTase | 163/19.2/8.3 | Methyltransferease | Methyltransf_25 (pfam13649) | Putative bacteriophage methyltransferase (M. haemolytica) | 3927AP1, 1152AP2, 587AP2 | |
| 18 | 127/14.6/5.6 | Hypothetical protein | flap endonuclease-1-like (cl14815) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 535AP2, 587AP2 | |
| 19 ant | 218−233/26−26.9/7.1−7.7 | Antirepressor protein Ant | P22_AR_N (pfam10547); P22_AR_C superfamily (cl11179); AntA superfamily (cl01430) | Antirepressor protein Ant (M. haemolytica, Avibacterium paragallinarum for 587AP2) | 19−21 | 535AP2 |
| 20 | 71/8/9.9 | Hypothetical protein | PRK11675 superfamily (cl08198) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 535AP2, 587AP2 | |
| 21 | 76/8.8/4.5 | Hypothetical protein | KilA-N (pfam04383) | KilA-N domain-containing protein (M. haemolytica) | 535AP2, 587AP2 | |
| 22 HNH | 168/19.4/9.6 | HNH homing endonuclease | HNH_3 (pfam13392) | Putative HNH endonuclease (Lactococcus) | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 1152AP2 | |
| 23 MTase | 198/21.3/8.3 | Cytosine-specific DNA methyltransferease | Cyt_C5_DNA_methylase superfamily (cl18939) | Cytosine-specific methyltransferase (Haemophilus parasuis) | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 1152AP2 | |
| 24 PK | 150/17.1−17.3/4.8−5 | Pyruvate kinase | Hypothetical protein and pyruvate kinase (M. haemolytica) | |||
| 25 exo | 211−225/23.5−25.9/ 4.8−5.9 | Exonuclease | YqaJ (pfam09588) | Bacteriophage exonuclease (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 26 bet | 264−307/29.2−35.3/5.2−5.3 | Recombinase | RecT (pfam03837); bet_lambda (TIGR01913) | Bet protein (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 27 | 154/17.9/6.5 | Hypothetical protein | NTP-PPase_u3 (cl16941) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 28 higB | 91/10.8/6.9 | HigB | HigB (COG3549) | Plasmid maintenance system killer (M. haemolytica) | 587AP2 | |
| 29 higA | 101/11.4/8.1 | HigA | Antidote_HigA (TIGR02607) | Plasmid maintenance system antidote protein (M. haemolytica) | 587AP2 | |
| 30 TRase | 346/39.6/8.8 | Transposase | HTH_28 (pfam13518) | Transposase (M. haemolytica) | 587AP2 | |
| 31 xhlA | 161/18.5/5.5−5.8 | Hypothetical protein | XhlA (pfam10779); TM (1) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 32 cI | 219−228/24.8−26.3/4.9−5.5 | CI repressor | S24_LexA-like (cd06529) | LexA family repressor/S24 family protease (M. haemolytica); bacteriophage transcriptional regulator (Haemophilus parasuis, for 587AP2) | 20−24 | |
| 33 cro | 68−90/7.5−10.1/6.1−9.1 | Cro repressor | HTH_XRE (cd00093) | XRE family transcriptional regulator (M. haemolytica) | 14−28 | |
| 34 cII | 86/9.8/8 | CII protein | Bacteriophage CII protein (M. haemolytica) | 23 | 587AP2 | |
| 35 | 80/9/9.6 | Hypothetical protein | HTH_39 (pfam14090) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 1152AP2 | |
| 36 O | 276−289/31.8−33.3/8.9−9.1 | Replication protein O | Phage_rep_O (pfam04492) | Bacteriophage replication protein (M. haemolytica) | 18−21 | 587AP2 |
| 37 P | 215/24.9/9.2 | Replication protein P | Phage_lambda_P superfamily (cl06169) | Putative bacteriophage replication protein (M. haemolytica) | 13 | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 1152AP2 |
| 38 hel | 453/50.9/5.7 | Helicase | DnaB (TIGR00665) | Replicative DNA helicase (M. haemolytica) | 587AP2 | |
| 39 MTase | 178/20.7/8.8 | Methyltransferase | MT-A70 (pfam05063) | Hypothetical protein and modification methylase MunIM (M. haemolytica) | 587AP2 | |
| 40 MTase | 190/21.6/5 | DNA N-6-adenine-methyltransferas | Dam superfamily (cl05442) | DNA N-6-adenine methyltransferase (M. haemolytica) | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 1152AP2 | |
| 41 | 150−168/17.7−19.9/6.1−8.6 | Hypothetical protein | DUF1367 superfamily (cl06231) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | ||
| 42 ninG | 189/22.3/9.7 | NinG protein | NinG (pfam05766) | Protein NinG (M. haemolytica) | 43 | 587AP2 |
| 43 | 94/10.6/9 | Hypothetical protein | DUF1364 (pfam07102) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 1152AP2 | |
| 44 RusA | 122/13.9/9.4 | Endodeoxyribonuclease RusA | RusA (pfam05866) | Endodeoxyribonuclease RusA (Haemophilus influenzae) | 535AP2, 3927AP1, 1152AP2 | |
| 45 Q | 121−157/14.3−18.6/9.2−9.5 | Antitermination protein Q | Phage_antitermQ (pfam06530) | Phage anti termination protein Q (M. haemolytica) | 18−22 | |
| 46 S | 81−117/9.5−12.8/9−9.3 | Holin | Phage_holin_3 superfamily;TM (1–3) | Hemophilus-specific protein (M. haemolytica) | 11−17 | |
| 47 R | 189−197/21.2−22.3/9.1−9.5 | Endolysin | endolysin_autolysin (cd00737); lysozyme_like superfamily (cl00222); TM (1) | Lysozyme (M. haemolytica) | 21−55 | |
| 48 Rz | 116/13.2/7.8−8.6 | Lytic protein Rz | DUF2570 (pfam10828); TM (1) | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 34−36 | |
| 49 Rz1 | 57−74/6.6−8.4/5−8 | Lytic protein Rz1 | Hypothetical protein (M. haemolytica) | 30−44 |
aTM: transmembrane α-helice; only 1152AP2 contains domain of Tape_meas_nterm superfamily (cl15680) and 587AP2 contains Phage_holin_3 superfamily; only protein J from 1152AP2 contains 2 TM
bIdentity of amino acids sequence was calculated by ALIGN [66]
Table 3.
Major gene products of Mannheimia haemolytica phage 3927AP2
| CDS | Gene name | Size (aa)/MW(kDa)/pI | Motifsa | Function | % Identity (aa) to related Mu-like phagesb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Su-Mu | phiMhaMu2 | |||||
| 1 | c | 242/26.8/5.2 | S24_LexA-like (cd06529) | Transcriptional regulatory protein | 46.1 | 100 |
| 2 | ner | 75/8.4/9.8 | HTH_Tnp_Mu_1 superfamily (cl15894) | DNA-binding protein | 41.6 | 100 |
| 3 | A | 645/73.1/9.3 | Mu-transpos_C (pfam09299) | Transposase | 63.7 | 99.1 |
| 4 | B | 293/32.2/8.6 | HTH_LacI (cd01392) | Mu-like prophage FluMu DNA transposition protein B | 54.6 | 100 |
| 14 | gemA | 141/16.1/9.9 | DUF1018 (pfam06252) | Mu-like prophage protein gp16 | 66 | 100 |
| 18 | mor | 141/16.0/7.5 | Mor superfamily (cl02360) | Mor transcription activator family protein | 70.9 | 100 |
| 19 | lys | 177/19.8/7.7 | Glyco_hydro_108 (pfam05838) and PG_binding_3 (pfam09374) | Hypothetical protein | 20 | 94.4 |
| 25 | DNA-binding | 166/18.4/6.1 | TM (1) | DNA-binding protein | 48.5 | 100 |
| 27 | terL | 541/62.3/6.2 | Terminase_6 (pfam03237) | Terminase, large subunit | 71.3 | 100 |
| 28 | porT | 541/59.9/5.2 | COG4383 (COG4383) | Portal protein | 84 | 100 |
| 29 | F | 434/50.1/9.3 | Phage_Mu_F (pfam04233) | Phage head morphogenesis protein | 73.6 | 100 |
| 30 | G | 138/15.3/5.8 | COG5005 (COG5005) | Mu-like prophage FluMu G protein 2 | 73.9 | 100 |
| 31 | I | 356/38.9/5.2 | Mu-like_Pro (pfam10123) | Bacteriophage Mu I protein Gp32 | 76.9 | 99.7 |
| 32 | T | 305/33.9/5.4 | Mu-like_gpT (pfam10124) | Major head subunit T | 75.6 | 100 |
| 34 | J/K | 141/15.9/4.7 | DUF1320 (pfam07030) | Mu-like prophage protein gp36 | 71.5 | 100 |
| 35 | J/K | 213/23.6/5.9 | DUF1834 (pfam08873) | Mu-like prophage protein gp37 | 69.5 | 100 |
| 37 | L | 469/50.7/5.7 | Phage_sheath_1 (pfam04984) | Mu-like prophage FluMu tail sheath protein | 74.1 | 85.1 |
| 38 | M/Y | 124/13.7/4.8 | Tail_tube (pfam10618) | Phage tail tube protein | 75.8 | NA |
| 41 | tmp | 759/81.5/9.2 | PhageMin_Tail (pfam10145) | Tail length tape measure protein | 64.2 | 100 |
| 42 | N | 430/48.6/5.4 | DNA_circ_N (pfam07157) | Mu-like DNA circularization protein | 45.8 | 100 |
| 43 | P | 375/41.8/7.6 | Phage_GPD superfamily (cl15796) | Mu-like tail protein P | 75 | 99.7 |
| 44 | Q | 219/22.8/6.9 | Phage_Mu_Gp45 (pfam06890) | Mu-like baseplate assembly protein | 70.8 | 99.5 |
| 45 | V | 116/13.1/6.8 | GP46 (pfam07409) | Mu-like protein gp46 | 81.9 | 100 |
| 46 | W | 353/38.7/4.7 | Baseplate_J superfamily (cl01294) | Mu-like baseplate J protein | 54.1 | 100 |
| 47 | R | 196/21.9/5.2 | DUF2313 (pfam10076) | Tail protein | 35.8 | 99.5 |
| 48 | S | 686/75.7/5.9 | Pectate_lyase_3 (pfam12708) | Mu-like prophage FluMu defective tail fiber protein | 20.6 | NA |
aTM: transmembrane α-helice
bIdentity of amino acids sequence was calculated by ALIGN [66]
P2-like phages
Phages 535AP1, 587AP1, 1127AP1 and 2256AP1 possess linear dsDNA of 34.9 to 35.7 kb in length with a G+C content of 41.5–42.1 %, encoding 51–53 CDSs (Additional file 1: Table S1, Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3, Additional file 4: Table S4). Comparative genomics revealed that 535AP1 and 2256AP1 are collinear with 98.5–98.7 % nucleotide similarity to P2-like phage φMhaA1-PHL101, previously identified within the genome of M. haemolytica [14], whereas 587AP1 and 1127AP1 exhibited 85.7 and 88.4 % similarity, respectively, to this phage (Fig. 2). Among the P2-like phages studied, including 152AP1 which we previously reported [13], genome 535AP1, 2256AP1 and 1152AP1 are more closely related (97.2–97.9 % pairwise identity), followed by 587AP1 and 1127AP1 with a similarity of 95.7 %. Computational analysis using CoreGenes [15–17] showed that 535AP1, 2256AP1, 587AP1 and 1127AP1 share 47 (95.9 %), 47 (95.9 %), 43 (87.8 %) and 42 (85.7 %) homologs with phage PHL101, respectively. Moreover, the tail fibre proteins of P2-like phages from serotype A1 (535AP1 and 2256AP1) and A6 (1152AP1) share an amino acid identity of >99 %, as did the tail fibre proteins from A2-induced phages (587AP1 and 1127AP1). But, the amino acid sequence of tail fibre proteins from A2-induced phages differe considerably (35 % ID) from those of either A1 or A6. Phage infection is generally initiated by specific adsorption to the bacterial cell surface. Bacterial receptors for phages belong to various biochemical families and are mainly represented by surface proteins, polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides [18]. Well conserved tail fibres may reflect identical receptors shared within common or pathogenic M. haemolytica strains.
Fig. 2.

Whole genome comparisons of φMhaA1-PHL101 and all-P2 like Mannheimia haemolytica phages as well as using a progressive MAUVE alignment. The degree of sequence similarity is indicated by the intensity of the red region. The contiguous black boxes under the red region represent the position of genes. a, PHL101; b, 1152AP1; c, 535AP1; d, 2256AP1; e, 587AP1; f, 1127AP1
Similarly, a phylogenetic tree of structural genes (capsid and tail genes) of the known P2-like phages from different bacterial species reflected their respective host specificity [19]. To date, P2-like phages have been detected in a number of serotypes of M. haemolytica [9, 13, 14, 20], but differ from other members of the P2 genus [14], illustrating the specificity of temperate phages for their respective host [19].
λ-like phages
The genomes of 535AP2, 587AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP1 range from 48.6 to 52.1 kb (41.1–41.4 % mol G+C) encoded for 77–83 CDSs and 2 tRNAs, and possessed a similar gene arrangement. Of the annotated gene products, 32–34 CDSs linked to essential functions which include components of the head and tail morphogenesis, infection specificity, site-specific recombination as well as replication initiation and cell lysis (Table 2 and Additional file 5: Table S5, Additional file 6: Table S6, Additional file 7: Table S7, Additional file 8: Table S8 and Fig. 3). Specifically, λ-like genes coding for minor tail proteins M, L and K, tail assembly protein I, host specificity protein J, integrase, replication proteins O and P, and antitermination protein Q were identified. However, these phage genome are not collinear with any other known λ-like phages, an outcome that was not unexpected as many prophages of the Lambdalikevirus from γ-proteobacteria maintain only the overall lambda-like synteny without demonstrating high sequence similarity [21]. To date, temperate phage Aaphi23 of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans [22] is only λ-like phage with a complete genome sequence identified from the Pasteurellaceae family. Considering A.actinomycetemcomitans and M. haemolyica are both member of the Pasteurellaceae and their respective infecting λ-like phages show relatively high similarities at amino acid sequence level, we aligned the amino acid sequence of major gene products with known function of Aaphi23, respectively, with 535AP2, 587AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP. Irrespective of their function, amino acid sequences of the gene products from each λ-like phage studied exhibited low similarly (12–53 %) to those from Aaphi23 (Table 2), illustrating the highly mosaic nature of lambdoid phage genomes [21].
Fig. 3.
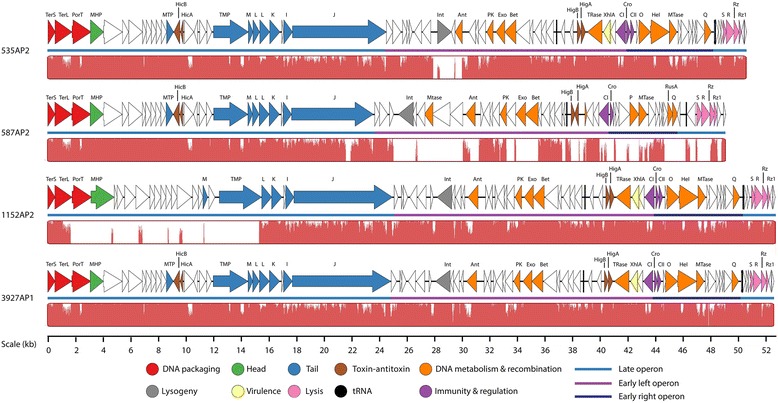
Genomic structure and nucleotide sequence comparison of λ-like Mannheimia haemolytica phages. Genetic map was constructed using Easyfig [67]. The four genomes were aligned using a progressive MAUVE alignment and the degree of sequence similarity is indicated by the intensity of the red region
Among the four λ-like phages, 535AP2 and 3927AP1 are the most genomically genetically similar (91.8 %), whereas phages 535AP2 and 3927AP1 are 77 and 84.9 % identical to 1152AP2, respectively (Fig. 4). The genome of 587AP2 diverges from the others exhibiting a pairwise sequence similarity of 72–73 % to 535AP2 and 3927AP1 and a low sequence identity of only 59.1 % to 1152AP2. Compared to the reference genome of 3927AP1 the majority of dissimilar regions were observed in 27.6-29.7 Kb of 535AP2, 24.8-48.2 Kb of 587AP2 and 1.7-15.2 Kb regions of 1152AP2 (Fig. 3). Likewise, comparative using GeneOrder4.0 [23] showed that 3927AP1 and 1152AP2 shared 72 (91.1 %) and 52 (65.8 %) of homologs with 535AP2. Phage 1152AP2 shares 62 (74.7 %) homologs in common with 3927AP1. Again, 587AP2 is very distant from the other three phages with 44–45 proteins in common with 535AP2 and 3927AP2 and only 26 homologs in common with 1152AP2. In addition, BLASTN showed that 97 % of a draft consensus of 2256AP2 is 99–100 % identical to 3927AP1 and 91 % of a draft consensus of 1127AP2 is 99 % identical to 587AP2 (data not shown), indicating that 2256AP2 and 1127AP2 are both likely lambdoid phages.
Fig. 4.
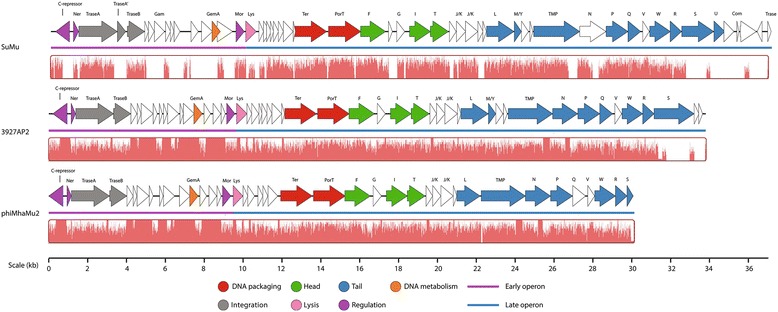
Genomic structure of Mannheimia haemolytica phage 3927AP2 and comparison with related Mu-like phages. Genetic map was constructed using Easyfig [67]. The four genomes were aligned using a progressive MAUVE alignment and the degree of sequence similarity is indicated by the intensity of the red region
Integration and lysogenic control
A λ-like int gene was identified in the mid-region of the genome of all four phage (Table 2 and Fig. 3), which encodes integrase for the insertion of phage DNA into the bacterial chromosome [21]. Interestingly, int gene from 535AP2 is located in a cluster of genes transcribed is in the opposite orientation to the majority of the genes (Fig. 3), with a similar observation being made for the int gene of phage Aaphi23 [22]. Unlike typical lambdoid phages, these phages lack a xis gene coding for an excisionase upstream of int a situation also observed in lambiod phages Aaphi23 [22] and D3 from Pseudomonas aeruginose [24]. Others have observed that some staphylococcal prophages possess the xis gene for excision, while other prophage exclusively utilize integrase to excise from the host chromosome [25]. Further experiments are required to elucidate the excision mechanism among the four prophages associated with M. haemolytica. Between the int (CDS31) and the CDSs 42–44 promoting homologous recombination of 1152AP2, CDS33 contains a flap endonuclease-1-like domain (cl1485), CDS35 contains amino- and carboxy-domain of the phage P22 anti-repressor (cl11178 and cl11179), CDS36 contains a domain of LexA regulated protein (cl08198) and CDS37 contains a conserved DNA binding domain (pfam04383) (Table 2 and Additional file 7: Table S7). This suggests that this cluster of genes may be involved in regulating phage DNA integration and excision. A similar cassette of genes was also identified in 3927AP1, whereas 535AP2 and 587AP2 lack this gene cluster.
Immunity and regulation
A typical λ-like gene cassette of cI−cro was identified in all λ-like phages (Table 2 and Fig. 3). Phages 535AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP1 share an identical repressor protein CI (100 % aa ID). Moreover, of 91 amino acid sequences of repressor Cro protein from 535AP2, 69 are perfectly aligned with that at N-terminus from 1152AP2 and 3927AP2. In contrast, CI (CDS56) and Cro (CDS57) proteins of 587AP differ remarkably (less than 21 % aa ID) from their counterparts in the other three phages. The CI and Cro regulators maintain the lysogenic and lytic states, respectively, as a bistable genetic switch [26]. The CI is able to repress Cro and vice versa. After infection of a target bacterium, the decision between lytic or lysogenic development of phage lambda is based upon environmental signals and the number of infecting phages per cell. Additionally, the prophage may enter lytic development in response to DNA-damaging agents. Noticeably, unlike 535AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP1; 587AP2 lacks cII for stimulating CI transcription, although the CDS59 of 587AP2 was predicted to contain an HTH motif, suggestive of the presence of a CII homolog. The immunity and regulation of the phages induced from M. haemolytica serotype A1 and A6 differ from those induced from M. haemolytica serotype A2, indicating that λ-like phages may employ different mechanisms in regulating their life circle between common and pathogenic serotypes of M. haemolytica.
Host recognition
All four λ-like phage encod a host specificity tail protein J (also called tail fiber) ranging from 1955 to 2353 amino acids in length, which functions to bind to the host receptor. Protein J id only well conserved between 1152AP2 and 3927AP1 (98.7 % aa ID), especially at the C-terminus, although all four phages exhibited an amino acid sequence identity of >86.5 % for this protein. Phages 1152AP2 and 3927AP1 were both induced from M. haemolytica A6 and shares an identical host recognition protein, confirming their origin from a common host.
Host cell lysis
Genes coding for holin, endolysin, lysis proteins Rz and Rz1 were identified from the right end of the genome of all four λ-like phages (CDSs 72–81, Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5, Additional file 6: Table S6, Additional file 7: Table S7, Additional file 8: Table S8, Fig. 3) which are organized similarly to the archetypical lambda lysis cassette SRRzRz1 [21]. Holins are small transmembrane proteins that form non-specific pores in the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane for exporting endolysins to the bacterial cell wall [27]. Based on a new classification scheme of holins as proposed by Reddy and Saier Jr. [27], all known holins can be divided into 7 superfamilies (I–VII). All members of Superfamily II contain 78 ± 14 amino acids and are predicted to have 1 to 2 transmembrane α-helices (TMs). The CDS74 of phages 535AP2 and 1152AP2 as well as CDS78 of 3927AP1 (81aa) located immediately upstream of the endolysin gene, did not align with any homologs with holin function. However, they were predicted to have 1 TMD, a dual-translation start regulatory motif (MKLM) [28] and a highly charged, hydrophilic, C-terminal domain. Collectively these features indicate that these CDS are likely members of Superfamily II holin.
Virulence encoding genes
A gene product of 162 amino acids was predicted to have 1 TM and a XhlA (pfam10779) domain in the early left operon of each phage (Table 2). XhlA is a cell-surface associated haemolysin that lyses granulocytes and plasmatocytes immune cells of insects [29]. Cowles et al. [29] demonstrated that XhlA is required for full virulence of the γ-proteobacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila, towards Manduca sexta larvae. In addition, XhlA shows haemolytic activity against mammalian erythrocytes in vitro [29]. To date, there is no report of haemolysin XhlA playing a role in M. haemolytica infection and further experimentation is required to verify whether this phage-encoded protein plays a role in M. haemolytica pathogenesis.
Toxin-antitoxin gene cassettes
All λ-like phages contain genes encoding for a toxin-antitoxin (TA) system (Table 2). Prophages 535AP2 and 3927AP1 encod 2 TA, located in early (higBA) and late operon (hicAB), respectively, whereas 1152AP2 encod 1 TA (higBA) in the early operon and 587AP encod 1 TA (hicAB) in the late operon. The first TA cassettes were characterized as plasmid-borne ‘killer’ genes that ensure plasmid maintenance after cell replication by eliminating plasmid-free cells [30]. However, TA systems are not only restricted to plasmids, but have also been identified in the chromosome of bacteria and archaea, where they function to regulate bacterial programmed cell death, biofilm formation, cope with nutritional stress, establish persister subpopulations and offer protection from phage attack [31]. As well, the TA systems have been identified in E. coli temperate phage P1, N15 and streptococcal temperate phage [32–34]. In the temperature sensitive plasmid Rts1 from E. coli K12, the higBA locus encodes HigB toxin and HigA antitoxin, which stabilize plasmid Rts1 by inhibiting the growth of plasmid-free cells [30]. The hicAB locus of E. coli K12 encodes HicA and HicB, which help the cell cope with nutritional stress [35]. Presumably, the higBA and/or hicAB pairs may act on the toxin-antitoxin principle to stabilize inheritance of the four prophages within their host chromosome, as previously observed of the phd/doc cassettes in phage P1 [34].
Transposase
Excluding 587AP2, transposase-encoding genes were discovered immediately downstream of the XhlA domain in phages 535AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP1 (Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5, Additional file 7: Table S7 and Additional file 8: Table S8, Fig. 3). Transposases were also identified from P2-like phages of 587AP1 (CDS31), 1127AP1 (CDSs 31 and 50) and 2256AP1 (CDS17) (Additional file 1: Table S1, Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Table S3, Additional file 4: Table S4). Transposases are responsible for catalysing relocation, transposition and horizontal transfer of mobile genetic elements such as transposon within and/or between genomes [36]. A well characterized transposase MuA, is required for insertion of phage Mu genome into the host chromosome as well as replication of the phage DNA during the lytic cycle [37]. Transposase genes have also been detected within the genomes of Staphylococcus lytic phages [38, 39] and P2-like phages of Burkholderia cepacia [40]. Existence of the transposase-encoding genes in the λ-like phages and P2-like phages studied, suggests that they play a role in the acquisition of foreign genes from other bacteria or other phages.
Methyltransferease
A methyltransferease coding gene was identified upstream of int in 535AP2 (CDS37, pfam13649) and 587AP2 (CDS34, cytosine-specific DNA methyltransferase, cl18939) (Table 2, Additional file 5: Table S5 and Additional file 6: Table S6, Fig. 3). Another methyltransferase was identified immediately downstream of helicase coding genes of all the λ-like phages (Table 2 and Additional file 5: Table S5, Additional file 6: Table S6, Additional file 7: Table S7, Additional file 8: Table S8, Fig. 3). Specifically for 587AP2, a DNA N-6-adenine-methyltransferase (Dam, cl05442) was identified. Methyltransferase functions as a powerful epigenetic gene regulator switching genes on and off by adding a methyl group to a particular base within a defined short DNA sequence. The enzyme is frequently found in various prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells [41, 42] and plays a pivotal role in regulating virulence genes as well as repairing mismatches during DNA replication in bacteria [42]. Although methyltransferase is commonly found in phages, its function remains unclear. Methyltransferase may play a role in regulating the life cycle of phages, confer protection against host restriction systems and modify the expression of virulence genes in the host [42, 43].
Mu-like phages
Mu-like phage 3927AP2 consists of 33.8 kb of double strand genome (43.1 % mol G+C) in length, encoding 50 CDSs (Tables 1, 3 and Additional file 9: Table S9; Fig. 4). Comparative genomic analysis showed that this phage is 88.8 % identical to prophage Mu remnant phiMhaMu2 present in PHL213 strain of M. haemolytica [9], but only 47−59 % similar to Heamophilus parasius-infecting phage SuMu (59 % similarity) [44] as well as other known Mu-like phages [45]. Of 50 CDSs, 26 resemble functions within Mu-like phages including DNA metabolism and packaging, immunity and regulation, head and tail structures as well as lysis function (Table 3 and Fig. 4). Moreover, the amino acid sequence of these Mu-like gene products in 3927AP2 better align with those from phiMhaMu2 (85–100 % ID) than from SuMu (20.6–84 % ID) (Table 3). Specially, extreme low identity (20–21 %) of amino acid sequence between 3927AP2 and SuMu occur in genes of lys and S, which encode endolysin and tail fibres, respectively. M. haemolytica and H. parasius both belong to the Pasteurellaceae family, but their respective infecting Mu-like phages differ considerably in genes for host recognition and lysis, confiming the intragene mosaicism of Mu-like phages [45]. High DNA nucleotide and amino acid sequence similarity shared between 3927AP2 and phiMhaMu2 suggest that Mu type phages of M. haemolytica may possibly be more related.
Typically, the Mu-like phage module is divided into early, middle and late regions on the basis of the level of transcription at different times during the lytic phase of Mu’s life cycle [45]. Comparing with phage Mu [45], diverse genes were more identified from the early region (12/18, 67 %) than from the late region (13/32, 41 %) in 3927AP2. This suggests that early and middle regions are less conserved than the late regions in Mu type phages [45]. In phage Mu [46], the semi-essential early (SEE) region located between the B and C genes (4.3–10 kb) contains kil, gam, sot, arm, cim and gemA/B (the gemB also known as mor), which are involved in DNA replication, immunity and regulation as well as host killing function. In contrast, only gam and/or gemA/B were annotated in SEE region of phages 3927AP2, phiMhaMu2 and SuMu. Presumably, other hypothetical proteins located in this region are responsible for the functions described above and/or some of these SEE genes may be lost depending upon selective pressures and a lack of their necessity for phage development [45]. Another striking feature shared among phages 3927AP2, phiMhaMu2 and SuMu is that the late gene of lys is located immediately downstream of the early genes of mor, indicating that these phages lack middle genes such as C, a transcription activator for late genes transcription [46]. Also, no typical com-mom module was identified at the right extremity of the 3927AP2 genome. A pair of com-mom genes is utilized for phage Mu to regulate late gene transcription and expression [46]. As a consequence, experimental investigation is required for identification of genes encoding similar function to C, Com and Mom.
Inducible prophages
Together with the P2- and λ-like phages induced, PHAST [12] analysis detected more intact prophages including Mu-like phages in the genomes of 535A and 587A (Data not shown). In contrast, the genome of 3927A only carried λ- and Mu-like phages. Interestingly, Mu-like phages were only induced from 3927A and not from 535A or 587A. It is unclear as to why Mu-like phages were not induced in 535A or 587A even though they were clearly present in the genome of these strains. It may be related to the method of induction, or possibly competitive interactions among multiple prophages occurring within the host during induction using mitomycin C. When P2-, λ- and Mu-type prophages co-exist in M. haemolytica chromosome, the former two may be more sensitive to switching to the lytic state or have the capability of out-competing the latter for the resources required for DNA replication within the host cell. The implications of within-host competition between co-infecting phages are largely undefined. However, Refardt [47] studied within-host competition between lambdoid phages induced using mitomycin C with E. coli. Singularly, both phages were equally inducible, but when combined replication of one of the phage was highly restricted. Likewise, James et al. [48] reported that an inducible siphovirus LESφ2 outcompeted two co-infecting siphorviruses when norfloxacin was used to induce phages from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain LESB58. We also cannot exclude the possibility that some of the intact phages within the genome of M. haemolytica may no longer be active or inducible. In Lactobacillus plantarum strain WCFS1, prophages Lp1 and Lp2 with genome size of 40 kb as members of Sfi11-like, Siphoviridae, are not inducible using mitomycin C [49]. Prophages seem to be only transient passengers of the bacterial chromosomes, with some decaying and eventually being lost from the genome. However, even with this evolutionary process occurring, up to 20 % of bacterial genome can be accounted for by phage and their associated genes [6]. Inducible prophages may be of greater significance than uninducible prophages as they can play a role in horizontal gene transfer and disseminate virulence determinants and other genetic traits among bacteria [48, 50]. One may argue that carriage of phages that are prone to induction may represent a significant burden to host cells, selecting against their persistence in natural populations. However, P2- and λ-type prophages have been widely reported with the M. haemolytica genome [8, 9, 13, 51].
Endolysin
According to CLUSTAL multiple sequence alignment results, four types of endolysins including P2-like, λ-like, 587AP2-like and Mu-like were discovered in this study. Additional file 10: Figure S1 illustrates the tertiary structure of the lysins with 87 to 92 % residues modelled with 100 % confidence. The P2-like endolysins contain 188 amino acids and are virtually identical (pairwise sequence identities, 99 to 100 %) at both the nucleotide and amino acid level. Likewise, endolysins from λ-like phages 535AP2, 1152AP2 and 3927AP1 are composed of 189 amino acids with identical nucleotide sequences. Interestingly, the genome of 587AP2 did not align with λ-like endolysins, exhibiting low nucleotide (46.8 %) and amino acids identities (19.2 %). Endolysins are hydrolases produced by phages to degrade the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell wall, enabling release of phage progeny. Their antibacterial activity is highly specific and in situ application of endolysins has been shown to reduce bacterial colonization in the respiratory and vaginal tract of mice and humans [52]. Previously, application of endolysins against gram negative bacteria was limited as their outer membrane blocks their access to the peptidoglycan layer. Recent developments have overcome this limitation by combining endolysins with peptides that disrupt the outer membrane [53]. Thus, with this approach endolysin-based products may be developed that have activity against M. haemolytica and aide in the prevention of BRD.
Conclusions
P2-, λ- and Mu-like phages were simultaneously induced from individual M. haemolytica isolates. Moreover, when these three types of phages co-existed within the M. haemolytica genome, P2- and λ-like phages were only recovered after induction, suggesting that within-host competition might exist among P2-, λ- and Mu-like phages with Mu-like phages being less competitive for lytic resources. Toxin-antitoxin gene cassettes in λ-like phages suggest that these genetic elements may contribute to the development of persister subpopulations of M. haemolytica. Cell-associated haemolysin XhlA encoded within λ-like phage genomes suggests that this element may contribute to the pathogenicity of M. haemolytica. Further investigations are required to verify how phages contribute to the pathogenesis and ecological fitness of M. haemolytica.
Methods
Temperate phages induction
Six field M. haemolytica isolates representing serotypes A1 (n = 2; 535A, 2256A), A2 (n = 2; 587A, 1127A) and A6 (n = 2; 1152A, 3927A) were selected for induction of temperate phage, as described previously [13]. Bacterial isolates were collected from healthy cattle housed in two commercial feedlots in Alberta, Canada. Phage filtrates were stored at 4 °C prior to DNA extraction.
Induction growth curve
To plot the growth of M. haemolytica, with and without mitomycin, overnight cultures of each strain (n = 6) were diluted (1:10) in brain-heard infusion broth (BHI) and replicates (n = 14) were incubated in 96-well microplates at 37 °C. Optical density at 600 nm was recorded every 15 min to measure growth. When the absorbance of each strain reached log-phase (OD600 = 0.25–0.3), mitomycin C (Sigma Aldrich Canada Ltd., Oakville, ON; 10 ng/ml) was added to a final concentration of 0.2 μg/ml in half of the wells (n = 7), while the other wells received a similar volume of sterile water (n = 7). After induction with mitomycin C, absorbance at 450 and 600 nm was recorded at 15 min intervals for 12 h. Absorbance measures at 600 nm were subtracted from the 450 nm values, to give a final corrected optical density.
Genome sequencing and annotation
Phage genomic DNA was isolated from each single induced preparation. Bacterial nucleotides were removed from the six filtered phage lysates using DNase 1 (Sigma-Aldrich) and RNase A (Sigma-Aldrich), and the phage lysates were concentrated using polyethylene glycol (PEG) 8000 [54]. Genomic phage DNA was extracted from concentrated phage suspensions using proteinase K (Qiagen, Toronto, ON) and a Phage DNA Isolation Kit (Norgen Biotek Corp., Thorold, ON) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted DNA was quantified fluorometrically using the Quant-iT PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit (Invitrogen, Burlington, ON) on a NanoDrop 3300 fluorospectrometer (Fisher Scientific Limited, Nepean, ON). Subsequent DNA quality control assurance and amplification of the six phage samples was conducted by Eurofins MWG Operon (Huntsville, AL) prior to sequencing by GS FLX Titanium series chemistry (Roche 454). Whole genome sequencing yielded 100 to 300× coverage. Sequencing data were assembled by Celera Assembler (Version 5.3) and Staden gap4 and critical gaps were identified and closed by conventional Sanger sequencing. Whole genome sequence data of M. haemolytic isolates 535A, 587A and 3927A were also used for confirmation of the assembly of phage genomes and to identify phage genomes that were within the bacterial genomes, but not recovered by induction (Data not shown). Initial genome annotation was completed using myRAST [55]. SeqBuilder application (DNASTAR, Inc., Madison, WI) was used to visually scan the sequence for potential genes. All translated proteins were scanned for homologs using BLASTP and PSI-BLAST [56]. Rho-independent terminators were identified using WebGeSTer at http://pallab.serc.iisc.ernet.in/gester/rungester.html [57] and TransTermHP [58]. Promoters were identified by neural network promoter prediction [59] along with manual annotation. Transmembrane domains were described using TMHMM 2.0 at http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/ [60], Phobius at http://phobius.sbc.su.se/ [61] and SPLIT 4.0 at http://split.pmfst.hr/split/4/ [62]. Pairwise nucleotide sequence identity was calculated by EMBOSS Stretcher analysis [63, 64]. CLUSTAL omega [65] was used to align amino acid sequences of tail fibres proteins and endolysin proteins. ALIGN [66] at http://xylian.igh.cnrs.fr/bin/align-guess.cgi was used to generate amino acid identities of gene products. The GenBank accession number for 535AP1, 535AP2, 587AP1, 587AP2, 1127AP1, 1152AP2, 2256AP1, 3927AP1 and 3927AP2 sequences are KP137432, KP137433, KP137434, KP137435, KP137436, KP137437, KP137438, KP137439 and KP137440, respectively.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Agriculture Funding Consortium, Canada Matching Investment Initiative, Alberta Innovates Biosolutions and Genome Alberta.
Abbreviations
- BLASTN
Basic local alignment search tool-nucleotide
- BRD
Bovine respiratory disease
- CDS
Coding sequence
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- G+C
Guanine plus cytosine
- int gene
Intergrase gene
- PHAST
Phage search tool
- TA
Toxin-antitoxin
- TM
Transmembrane α-helices
- tRNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid
- XhlA
Cell associated haemolysin
- xis
Gene coding for an excisionase
Additional files
Feature of phage 535AP1 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 13 kb)
Feature of phage 587AP1 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 13 kb)
Feature of phage 1127AP1 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 13 kb)
Feature of phage 2256AP1 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 13 kb)
Feature of phage 535AP2 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 21 kb)
Feature of phage 587AP2 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 15 kb)
Feature of phage 1152AP2 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 17 kb)
Feature of phage 3927AP1 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 16 kb)
Feature of phage 3927AP2 gene products and their functional assignments. (XLSX 14 kb)
Teritiary structure of four types of lysins (a, P2-like; b, λ-like; c, 587AP2; d, Mu-like) with 87 to 92 % residues modelled with 100 % confidence generated by Phyre V2.0 [68] (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index). Image coloured by rainbow N → C terminus, model dimensions (Å):X:53.821; Y:51.063; Z:34.680. (TIFF 948 kb)
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: YDN, SRC, YHH, TAM. Performed the experiments: SRC, YHH, CLK. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: TAM. Analyzed data: YDN, SRC, JW, CLK, AMK, DT. Wrote the manuscript: YDN, SRC, JW, CLK, YHH, AMK, DK, TAM. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Yan D. Niu, Phone: +1-403-381-5351, Email: dongyan.niu@gov.ab.ca
Shaun R. Cook, Email: shaun.cook@agr.gc.ca
Jiaying Wang, Email: jiaying.wang@agr.gc.ca.
Cassidy L. Klima, Email: cassidy.klima@agr.gc.ca
Yu-hung Hsu, Email: hsuyuhung@yahoo.com.
Andrew M. Kropinski, Email: kropinsk@queensu.ca
Dann Turner, Email: Dann2.Turner@uwe.ac.uk.
Tim A. McAllister, Phone: +1-403-317-2240, Email: tim.mcallister@agr.gc.ca
References
- 1.Griffin D, Chengappa MM, Kuszak J, McVey DS. Bacterial pathogens of the bovine respiratory disease complex. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2010;26:381–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2010.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Highlander SK. Molecular genetic analysis of virulence in Mannheimia (pasteurella) haemolytica. Front Biosci. 2001;6:D1128–50. doi: 10.2741/Highland. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rice JA, Carrasco-Medina L, Hodgins DC, Shewen PE. Mannheimia haemolytica and bovine respiratory disease. Anim Health Res Rev. 2007;8:117–28. doi: 10.1017/S1466252307001375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Weinbauer MG. Ecology of prokaryotic viruses. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004;28:127–81. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2003.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brüssow H, Canchaya C, Hardt WD. Phages and the evolution of bacterial pathogens: from genomic rearrangements to lysogenic conversion. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004;68:560–602. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.3.560-602.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Casjens S. Prophages and bacterial genomics: what have we learned so far? Mol Microbiol. 2003;49:277–300. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fortier L-C, Sekulovic O. Importance of prophages to evolution and virulence of bacterial pathogens. Virulence. 2013;4:354–65. doi: 10.4161/viru.24498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Harhay GP, Koren S, Phillippy AM, McVey DS, Kuszak J, Clawson ML, et al. Complete closed genome sequences of Mannheimia haemolytica serotypes A1 and A6, isolated from cattle. Genome Announc. 2013;1:art.no. e00188–00113. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00188-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gioia J, Qin X, Jiang H, Clinkenbeard K, Lo R, Liu Y, et al. The genome sequence of Mannheimia haemolytica A1: insights into virulence, natural competence, and Pasteurellaceae phylogeny. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:7257–66. doi: 10.1128/JB.00675-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lawrence PK, Kittichotirat W, McDermott JE, Bumgarner RE. A three-way comparative genomic analysis of Mannheimia haemolytica isolates. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:535. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Eidam C, Poehlein A, Brenner Michael G, Kadlec K, Liesegang H, Brzuszkiewicz E, et al. Complete genome sequence of Mannheimia haemolytica strain 42548 from a case of bovine respiratory disease. Genome Announc. 2013;1:art.no. e00318–00313. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00318-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhou Y, Liang Y, Lynch KH, Dennis JJ, Wishart DS. PHAST: a fast phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:W347–52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hsu YH, Cook SR, Alexander TW, Klima CL, Niu YD, Selinger LB, et al. Investigation of Mannheimia haemolytica bacteriophages relative to host diversity. J Appl Microbiol. 2013;114:1592–603. doi: 10.1111/jam.12185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Highlander SK, Weissenberger S, Alvarez LE, Weinstock GM, Berget PB. Complete nucleotide sequence of a P2 family lysogenic bacteriophage, φMhaA1-PHL101, from Mannheimia haemolytica serotype A1. Virology. 2006;350:79–89. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mahadevan P, King JF, Seto D. Data mining pathogen genomes using GeneOrder and CoreGenes and CGUG: gene order, synteny and in silico proteomes. Int J Comput Biol Drug Des. 2009;2:100–14. doi: 10.1504/IJCBDD.2009.027586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mahadevan P, King JF, Seto D. CGUG: in silico proteome and genome parsing tool for the determination of “core” and unique genes in the analysis of genomes up to ca. 1.9 Mb. BMC Res Notes. 2009;2:168. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-2-168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mahadevan P, Seto D. Taxonomic parsing of bacteriophages using core genes and in silico proteome-based cgug and applications to small bacterial genomes. In: Arabnia HR, editor. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. Vol. 680. 2010. pp. 379–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Samson JE, Magadán AH, Sabri M, Moineau S. Revenge of the phages: defeating bacterial defences. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:675–87. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nilsson AS, Haggård-Ljungquist E. Evolution of P2-like phages and their impact on bacterial evolution. Res Microbiol. 2007;158:311–7. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2007.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Davies RL, Lee I. Diversity of temperate bacteriophages induced in bovine and ovine Mannheimia haemolytica isolates and identification of a new P2-like phage. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;260:162–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hendrix RW, Casjens S. Bacteriophage λ and its genetic neighborhood. In: Calendar R, editor. The bacteriophages. 2. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2006. pp. 409–47. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Resch G, Kulik EM, Dietrich FS, Meyer J: Complete genomic nucleotide sequence of the temperate bacteriophage AaPhi23 of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Bacteriol 2004, 186:5523−5528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Mahadevan P, Seto D: Rapid pair-wise synteny analysis of large bacterial genomes using web-based GeneOrder4.0. BMC Res Notes 2010, 3:41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Kropinski AM: Sequence of the genome of the temperate, serotype-converting, Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage D3. J Bacteriol 2000, 182:6066−6074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Carroll D, Kehoe MA, Cavanagh D, Coleman DC: Novel organization of the site-specific integration and excision recombination functions of the Staphylococcus aureus serotype F virulence-converting phages phi 13 and phi 42. Mol Microbiol 1995, 16:877−893. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Oppenheim AB, Kobiler O, Stavans J, Court DL, Adhya S: Switches in bacteriophage lambda development. Annu Rev Genet 2005, 39:409−429. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Reddy BL, Saier Jr MH: Topological and phylogenetic analyses of bacterial holin families and superfamilies. Biochimica et biophysica acta 2013, 1828:2654−2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Loessner MJ, Gaeng S, Scherer S: Evidence for a holin-like protein gene fully embedded out of frame in the endolysin gene of Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage 187. J Bacteriol 1999, 181:4452−4460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Cowles KN, Goodrich-Blair H: Expression and activity of a Xenorhabdus nematophila haemolysin required for full virulence towards Manduca sexta insects. Cell Microbiol 2005, 7:209−219. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 30.Gerdes K, Christensen SK, Lobner-Olesen A: Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat Rev Microbiol 2005, 3:371−382. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 31.Ghafourian S, Raftari M, Sadeghifard N, Sekawi Z: Toxin-antitoxin systems: classification, biological function and application in biotechnology. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2014, 16:9−14. [PubMed]
- 32.Romero P, Croucher NJ, Hiller NL, Hu FZ, Ehrlich GD, Bentley SD, Garcia E, Mitchell TJ: Comparative genomic analysis of ten Streptococcus pneumoniae temperate bacteriophages. J Bacteriol 2009, 191:4854−4862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Dziewit L, Jazurek M, Drewniak L, Baj J, Bartosik D: The SXT conjugative element and linear prophage N15 encode toxin-antitoxin-stabilizing systems homologous to the tad-ata module of the Paracoccus aminophilus plasmid pAMI2. J Bacteriol 2007, 189:1983−1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Lehnherr H, Maguin E, Jafri S, Yarmolinsky MB: Plasmid addiction genes of bacteriophage P1: doc, which causes cell death on curing of prophage, and phd, which prevents host death when prophage is retained. J Mol Biol 1993, 233:414−428. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 35.Jørgensen MG, Pandey DP, Jaskolska M, Gerdes K: HicA of Escherichia coli defines a novel family of translation-independent mRNA interferases in bacteria and archaea. J Bacteriol 2009, 191:1191−1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 36.Roberts AP, Chandler M, Courvalin P, Guédon G, Mullany P, Pembroke T, Rood JI, Smith CJ, Summers AO, Tsuda M et al: Revised nomenclature for transposable genetic elements. Plasmid 2008, 60:167−173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Montaño SP, Pigli YZ, Rice PA: The Mu transpososome structure sheds light on DDE recombinase evolution. Nature 2012, 491:413−417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Vandersteegen K, Kropinski AM, Nash JH, Noben JP, Hermans K, Lavigne R: Romulus and Remus, two phage isolates representing a distinct clade within the Twortlikevirus genus, display suitable properties for phage therapy applications. J Virol 2013, 87:3237−3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Takemura-Uchiyama I, Uchiyama J, Kato Si, Ujihara T, Daibata M, Matsuzaki S: Genomic and phylogenetic traits of Staphylococcus phages S25-3 and S25-4 (family Myoviridae, genus Twort-like viruses). Ann Microbiol 2013:1−4.
- 40.Lynch KH, Stothard P, Dennis JJ: Genomic analysis and relatedness of P2-like phages of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. BMC Genomics 2010, 11:599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Jones PA, Takai D: The role of DNA methylation in mammalian epigenetics. Science 2001, 293:1068−1070. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Bochow S, Elliman J, Owens L: Bacteriophage adenine methyltransferase: a life cycle regulator? Modelled using Vibrio harveyi myovirus like. J Appl Microbiol 2012, 113:1001−1013. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Smith MJ, Jeddeloh JA: DNA methylation in lysogens of pathogenic Burkholderia spp. requires prophage induction and is restricted to excised phage DNA. J Bacteriol 2005, 187:1196−1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 44.Zehr ES, Tabatabai LB, Bayles DO: Genomic and proteomic characterization of SuMu, a Mu-like bacteriophage infecting Haemophilus parasuis. BMC Genomics 2012, 13:331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45.Morgan GJ, Hatfull GF, Casjens S, Hendrix RW: Bacteriophage Mu genome sequence: analysis and comparison with Mu-like prophages in Haemophilus, Neisseria and Deinococcus. J Mol Biol 2002, 317:337−359. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Paolozzi L, Ghelardini P: The Bacteriophage Mu. In: The bacteriophages. Edited by Calendar R, 2nd edn. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2006: 469–496.
- 47.Refardt D: Within-host competition determines reproductive success of temperate bacteriophages. ISME J 2011, 5:1451–1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 48.James CE, Fothergill JL, Kalwij H, Hall AJ, Cottell J, Brockhurst MA, Winstanley C: Differential infection properties of three inducible prophages from an epidemic strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Ventura M, Canchaya C, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM, Siezen RJ, Brüssow H. The prophage sequences of Lactobacillus plantarum strain WCFS1. Virology. 2003;316:245–55. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2003.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Asadulghani M, Ogura Y, Ooka T, Itoh T, Sawaguchi A, Iguchi A, et al. The defective prophage pool of Escherichia coli O157: prophage-prophage interactions potentiate horizontal transfer of virulence determinants. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:art.no.e1000408. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Klima CL, Cook SR, Hahn KR, Amoako KK, Alexander TW, Hendrick S, et al. Draft genome sequence of a Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 6 isolate collected from the nasopharynx of a beef calf with bovine respiratory disease. Genome Announc. 2013;1:art.no.e0005113. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00051-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.O’Flaherty S, Ross RP, Coffey A. Bacteriophage and their lysins for elimination of infectious bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009;33:801–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Schmelcher M, Donovan DM, Loessner MJ. Bacteriophage endolysins as novel antimicrobials. Future Microbiol. 2012;7:1147–71. doi: 10.2217/fmb.12.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sambrook J, Russell DW, editors. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 3. New York, NY: Cold Spring Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, et al. The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mitra A, Kesarwani AK, Pal D, Nagaraja V. WebGeSTer DB―a transcription terminator database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:D129–35. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kingsford CL, Ayanbule K, Salzberg SL. Rapid, accurate, computational discovery of Rho-independent transcription terminators illuminates their relationship to DNA uptake. Genome Biol. 2007;8:R22. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-2-r22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Reese MG. Application of a time-delay neural network to promoter annotation in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Comput Chem. 2001;26:51–6. doi: 10.1016/S0097-8485(01)00099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sonnhammer EL, von Heijne G, Krogh A. A hidden Markov model for predicting transmembrane helices in protein sequences. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol. 1998;6:175–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kall L, Krogh A, Sonnhammer EL. A combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction method. J Mol Biol. 2004;338:1027–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Juretic D, Zoranic L, Zucic D. Basic charge clusters and predictions of membrane protein topology. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 2002;42:620–32. doi: 10.1021/ci010263s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Olson SA. EMBOSS opens up sequence analysis. European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Brief Bioinform. 2002;3:87–91. doi: 10.1093/bib/3.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A. EMBOSS: the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000;16:276–7. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 65.Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7:539. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pearson WR, Wood T, Zhang Z, Miller W: Comparison of DNA sequences with protein sequences. Genomics 1997, 46:24−36. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 67.Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA: Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27:1009−1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 68.Kelley LA, Sternberg MJ. Protein structure prediction on the Web: a case study using the Phyre server. Nat Protoc. 2009;4:363–71. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


