Abstract
Dexmedetomidine is a sedative and analgesic agent that exerts its effects by selectively agonizing α2 adrenoceptor. Histamine is a pathophysiological amine that activates G protein-coupled receptors, to induce Ca2+ release and subsequent mediate or progress inflammation. Dexmedetomidine has been reported to exert inhibitory effect on inflammation both in vitro and in vivo studies. However, it is unclear that dexmedetomidine modulates histamine-induced signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. This study was carried out to assess how dexmedetomidine modulates histamine-induced Ca2+ signaling and regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes encoding interleukin (IL)-6 and -8. To elucidate the regulatory role of dexmedetomidine on histamine signaling, HeLa cells and human salivary gland cells which are endogenously expressed histamine 1 receptor were used. Dexmedetomidine itself did not trigger Ca2+ peak or increase in the presence or absence of external Ca2+. When cells were stimulated with histamine after pretreatment with various concentrations of dexmedetomidine, we observed inhibited histamine-induced [Ca2+]i signal in both cell types. Histamine stimulated IL-6 mRNA expression not IL-8 mRNA within 2 hrs, however this effect was attenuated by dexmedetomidine. Collectively, these findings suggest that dexmedetomidine modulates histamine-induced Ca2+ signaling and IL-6 expression and will be useful for understanding the antagonistic properties of dexmedetomidine on histamine-induced signaling beyond its sedative effect.
Keywords: Ca2+ signaling, Dexmedetomidine, Histamine, Interleukin, Pro-inflammatory cytokines
INTRODUCTION
Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride (chemical name (+)4(S) [1(2,3-dimethylphenyl)ethyl]1Himidazole monohydrochloride) is a highly selective and specific α2 adrenoceptor agonist, with particularly high affinity for α2A-adrenergic receptor subtype [1]. It is a powerful sedative and analgesic agent with high efficacy and safety compared with other sedatives, such as, opioids, benzodiazepines, and propofol [2]. Dexmedetomidine hydrochloride has been reported to have protective effects on cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury, renal injury, and incomplete forebrain ischemia in various species [3,4,5,6] and it is considered a suitable sedative for use in adult intensive care patients [7].
Furthermore, several lines of evidences indicate that dexmedetomidine regulates inflammation. In microglial cells, dexmedetomidine inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide (NO) and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) accumulation by preventing extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation [8]. In C6 glioma cells, dexmedetomidine inhibits interleukin (IL)-1β-induced IL-6 synthesis independently of the adenylyl cyclase-cAMP pathway [9]. Dexmedetomidine also inhibits neuronal apoptosis caused by the inhalational anesthetic agent isoflurane by activating c-JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK) and P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathways [10]. In glial cells, dexmedetomidine markedly reduced LPS-induced increases in pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as, tumor necrosis factor-α, NO, prostaglandin E2, IL-1β, and IL-6 [11,12]. Interestingly, dexmedetomidine induces Ca2+ response in astrocytes but not in neural cells, suggesting that its effect on central nervous system provides through astrocytes [13].
Ca2+ is one of the most universal and versatile intracellular second messengers and is responsible for initiating numerous cellular processes [14]. Receptor-evoked Ca2+ signaling involves the activation of phospholipase C to generate inositol-1, 4, 5 trisphosphate (IP3), which binds to IP3 receptors (IP3Rs) and initiates an initial increase in intracellular Ca2+ from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stores. This triggers Ca2+ signals in the form of oscillations and sparks that control a plethora of physiological function mediated by gene expression changes and various metabolic responses [15].
Histamine is a pathophysiological biogenic amine and an important inflammatory mediator. It contributes to the inductions of IL-6 and IL-8, ultimately inducing inflammation [16,17]. Histamine exerts its effects by activating G protein-coupled receptors, H1 to H4 receptor (H1R-H4R) that induce Ca2+ release and ultimately initiate inflammatory processes including nociceptive effects [18]. Despite growing knowledge of dexmedetomidine in inflammation, the effect of dexmedetomidine on intracellular Ca2+ signaling mediated by histamine remains unknown. Here, we investigated dexmedetomidine-modulated Ca2+ signaling in HeLa and human salivary glands (HSG) cells, expressing endogenous H1R [19]. The primary aim of the present study was to determine the effects of dexmedetomidine on the regulation of histamine-induced Ca2+ signaling and the expressions of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA.
METHODS
Reagents and molecular cloning
Dexmedetomidine chloride (Prededex®, 100 mcg/mL) was kindly gifted by Dr. Teo Jeon Shin at Seoul National University Dental Hospital. Fura-2/AM and Pluronic F-127 (20% in dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]) were purchased from Teflabs (Austin, TX) and Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA), respectively. Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM), penicillin-streptomycin, trypsin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were from Invitrogen and cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) was from Alomone Labs (Jerusalem, Israel). Histamine and other chemicals not specifically mentioned here were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO).
Cell culture
HeLa and HSG cells were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD) and maintained in DMEM containing 10% FBS with antibiotics including 100 µg/mL streptomycin and 100 U/mL penicillin at 37℃ in a cell culture incubator with a 5% CO2/95% air atmosphere. When cells were 80% confluent, they were washed with PBS and dispersed with a 2 min trypsin/EDTA treatment before they were transferred to new culture dishes or glass coverslips-in dishes for later use.
Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from HeLa and HSG cells using the TRIzol extraction system (Invitrogen), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Extracted total RNA pellets were washed with ice-cold 75% ethanol, and resolved in 20 µL of diethylpyrocarbonate-treated water. RNA was amplified using AccuPower® RT PreMix from Bioneer (Seoul, South Korea), according to the manufacturer's instructions, and the cDNA obtained was amplified by PCR using HiPi™ Thermo-stable DNA polymerase from Elpis (Seoul, South Korea) and primers (Table 1). PCR was started with a denaturation step at 95℃ for 5 min, followed by 36 cycles of 95℃ for 1 min, an annealing step for 1 min, and an extension step of 72℃ for 1 min, and a final extension of 72℃ for 7 min. PCR products were electrophoresed on 0.8% agarose gels. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) levels were measured as a loading control.
Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR.
Measurement of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations ([Ca2+]i)
HeLa or HSG cells were cultured on cover slips in 35 mm2 dishes. Cells were incubated with 5 µM Fura-2/AM in the presence of the same volume of 20% (w/v, in DMSO) pluronic acid F-127 for 15 min in physiological salt solution (PSS) at room temperature in the dark and then washed for 5 min with PSS containing the following [in mM]: 140 NaCl, 5 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 1 CaCl2, 10 HEPES, and 10 D-glucose and titrated to pH 7.4. For Ca2+ free solution (0 Ca2+), CaCl2 was removed, and 10 mM EGTA was added. Coverslips with cells were mounted onto the chamber. Changes in [Ca2+]i were determined by measuring fluorescence intensities at excitation wavelengths of 340 and 380 nm and an emission wavelength of 510 nm. The results were presented as fluorescence ratios calculated by dividing the fluorescence intensity at 340 by that at 380 nm (R340/380). Evoked [Ca2+]i (ΔCa2+) were calculated as the differences between the 340/380 basal and peak values. Emitted fluorescence was monitored using a high performance CCD camera (Photometrics, AZ) attached to an inverted microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and analyzed with MetaFluor system (Molecular Devices, PA). Fluorescence images were obtained at 1 sec intervals, and background fluorescence was subtracted from raw signals at each excitation wavelength.
Statistical analyses
Data from more than three or more independent experiments are expressed as means±standard error of means (SEMs). Statistically significant differences (p<0.01) between experimental groups were determined using paired Student's t-tests.
RESULTS
Dexmedetomidine did not elicit [Ca2+]i signals in HeLa cells
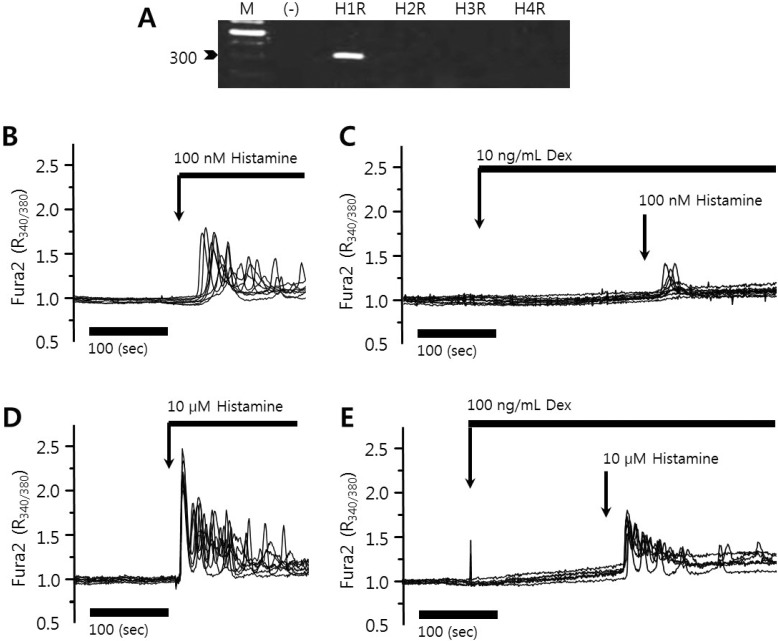
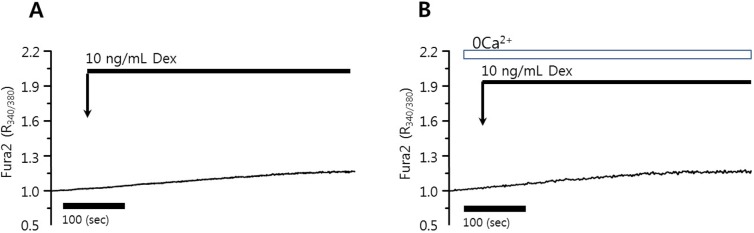
Dexmedetomidine is a highly selective α2 adrenoceptor agonist and induced aortic contraction via an influx of extracellular Ca2+ [20]. To evaluate the role of dexmedetomidine in Ca2+ signaling, HeLa cells were treated with 10 or 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine. The application of 10 ng/mL dexmedetomidine did not alter the basal [Ca2+]i level or induce a [Ca2+]i peak in the presence or absence of Ca2+ in the PSS media in HeLa cells (Figs. 1A and 1B, 89 and 102 cells from three independent experiments, respectively) and in HSG cells (data not shown). Even 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine failed to elicit an intrinsic [Ca2+]i response in HeLa cells (data not shown).
Fig. 1. Dexmedetomidine did not elicit [Ca2+]i signals in HeLa cells. Changes in [Ca2+]i induced by 10 ng/mL dexmedetomidine in (A) 1 mM Ca2+ medium and (B) Ca2+ free medium (0 Ca2+). The upper bars indicate the extracellular solutions applied to the cells.
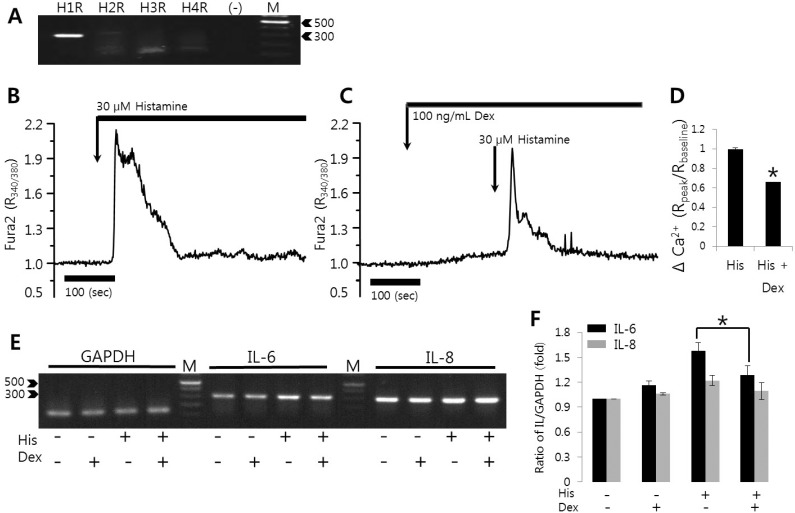
Histamine-induced [Ca2+]i signals were inhibited by dexmedetomidine
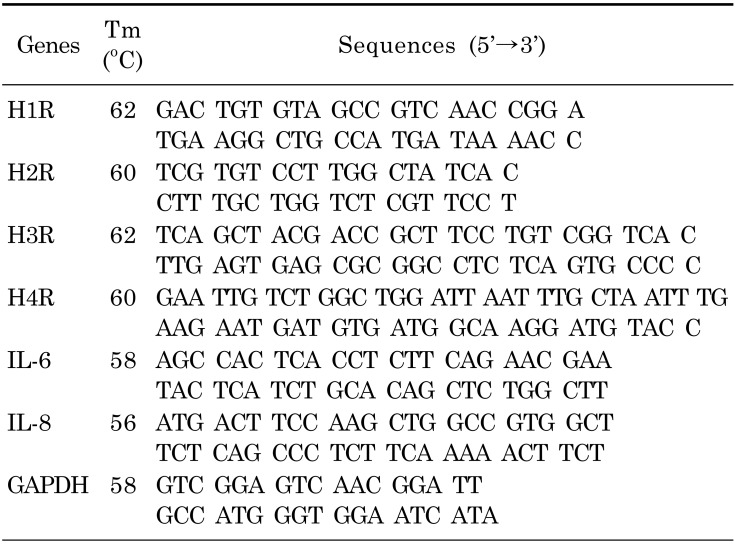
HeLa cells were examined to detect the expression of histamine receptors subtypes H1R through H4R. The specificity of the primers was confirmed by sequencing the gene products. HeLa cells predominantly expressed H1R (Fig. 2A). To examine the modulatory role of dexmedetomidine on histamine, cells were compared with respect to histamine-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations and dexmedetomidine-pretreated histamine-induced [Ca2+]i signals. As shown in Fig. 2B and 2C (54 cells and 49 cells from three independent experiments, respectively), 10 ng/mL dexmedetomidine pretreatment inhibited histamine-induced [Ca2+]i oscillation. Even at histamine concentrations of 10 µM, [Ca2+]i increases were inhibited by the pretreatment with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine (Fig. 2D and 2E show 64 and 70 cells from three independent experiments, respectively). These results revealed that dexmedetomidine inhibited the maximal Ca2+ peak and Ca2+ oscillatory patterns.
Fig. 2. Histamine-induced [Ca2+]i signals were inhibited by dexmedetomidine. (A) Expression levels of histamine receptors mRNA (H1R to H4R) in HeLa cells. (B) Changes in [Ca2+]i induced by 100 nM histamine. (C) Changes in [Ca2+]i after pretreatment with 10 ng/mL dexmedetomidine (Dex) and subsequent treatment with 100 nM histamine. (D) Changes in [Ca2+]i after pretreatment with 10 µM histamine (E) Changes in [Ca2+]i after pretreatment with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine and subsequent treatment with 10 µM histamine. The upper bars indicate the extracellular solutions applied to the cells and traces were selected randomly. Three separate experiments were performed and each point represents a mean±SEM. (-): no RNA, M: DNA ladder (bp).
The effect of dexmedetomidine on CPA-induced [Ca2+]i release and Ca2+ entry
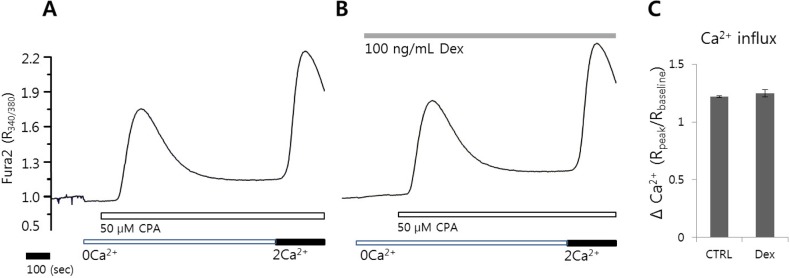
The transient increase in [Ca2+]i evoked by CPA in Ca2+ free solution depletes internal Ca2+ stores and subsequent induces Ca2+ influx signal by adding back Ca2+. To determine the effect of dexmedetomidine on Ca2+ release and influx, the HeLa cells were pretreated with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine for 3 min. No differences in CPA-induced Ca2+ release and Ca2+ entry were observed in the presence or absence of dexmedetomidine (121 and 108 cells from three independent experiments, respectively, Fig. 3). These data addressed that modulation of dexmedetomidine was independent on store-operated Ca2+ influx.
Fig. 3. The effect of dexmedetomidine on CPA-induced [Ca2+]i release and Ca2+ entry. The CPA-induced [Ca2+]i increase in the presence of 2 mM extracellular Ca2+ in the absence (A) or presence (B) of 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine. (C) Analysis of CPA-induced Ca2+ release and influx as determined using R340/380 fluorescence ratios. The upper bars indicate the extracellular solutions applied to the cells. Three separate experiments were performed and each point represents a mean±SEM.
Effects of dexmedetomidine on the histamine-induced IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA expression
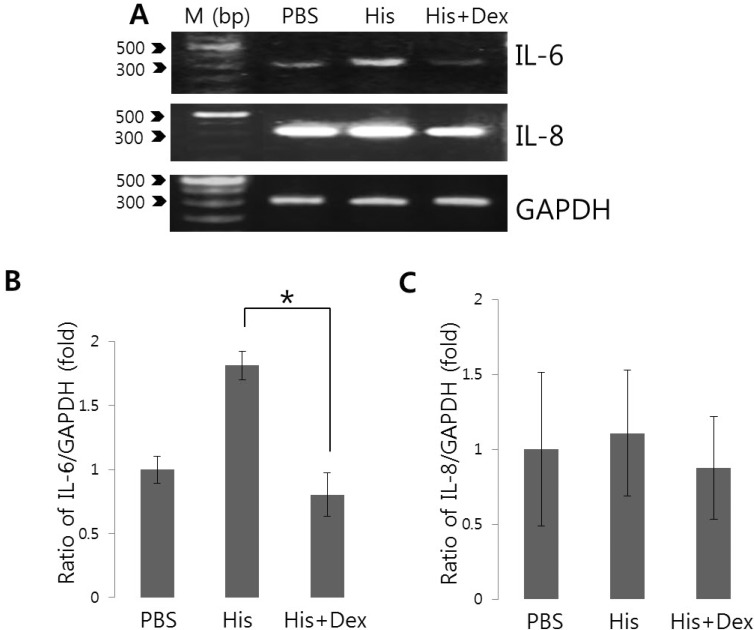
Changes in [Ca2+]i are intimately involved in various stress responses and the inflammatory responses elicit by pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [21,22,23]. Even though Ca2+ signaling itself do not dictate cytokine induction, it is quite clear that Ca2+ is an important control element for the induction of cytokines and facilitates this process [24]. To assess the effect of dexmedetomidine on histamine-mediated IL-6 and IL-8 production, cells were pretreated with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine for 30 min and then treated with 100 nM histamine for 90 min. Histamine increased IL-6 mRNA level (Fig. 4), whereas pretreatement with dexmedetomidine suppressed histamine-mediated IL-6 mRNA expression to 55.8% compared to histamine-treated cells (Fig. 4B and 4C). Histamine stimulation did not alter IL-8 mRNA expression within 2 hrs. These findings suggested that dexmedetomidine potently inhibited histamine signaling by suppressing histamine-induced expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6.
Fig. 4. Effects of dexmedetomidine on histamine-induced IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA expression. (A) After pre-treatment with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine (Dex) for 30 min, HeLa cells were stimulated with PBS and 100 nM histamine (His) for 90 min and then total RNA was extracted and amplified with primers specific for IL-6, IL-8, and GAPDH. Data are from one of experimental replicates. IL-6 (B) and IL-8 mRNA (C) expressions were quantified after normalizing to GAPDH levels as a loading control (n=6 and n=3, respectively). Results are the means±SEMs of independent experiments. M: DNA ladder (bp), PBS: phosphate buffered saline. *p<0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Histamine-induced [Ca2+]i signals were inhibited by dexmedetomidine in HSG cells
To evaluate whether the modulatory effect of dexmedetomidine was mediated through the histamine receptor activation, experiments were performed in HSG cells which expressed H1R [25]. HSG cells were tested and confirmed histamine receptor subtype expression (Fig. 5A). HSG cells did not exhibit an altered Ca2+ response at less than 10 µM histamine despite predominant H1R expression. Cells were stimulated with 30 µM histamine, and histamine-triggered [Ca2+]i responses were inhibited in the presence of 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine (Fig. 5B and 5C; 81 and 78 cells from three independent experiments, respectively). In HSG cells, dexmedetomidine reduced Ca2+ signals to 67% compared to histamine-treated cells. To assess the effect of dexmedetomidine on histamine-mediated IL-6 and IL-8 production, HSG cells were pretreated with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine for 30 min and then treated with 30 µM histamine for 90 min. Histamine increased IL-6 mRNA level (Fig. 5E), whereas dexmedetomidine pretreatment suppressed histamine-mediated IL-6 mRNA expression to 81.6% compared to histamine-treated cells (Fig. 5E and 5F). Histamine stimulation also did not alter IL-8 mRNA expression within 2 hrs in HSG cells. Dexmedetomidine itself did not affect pro-inflammatory cytokines expression. These findings confirmed that dexmedetomidine potently inhibited histamine signaling by suppressing histamine-induced expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6. These results suggested that the ability of dexmedetomidine suppressed histamine-induced Ca2+ signals is not cell type specific.
Fig. 5. Histamine-induced [Ca2+]i signals were inhibited by dexmedetomidine in HSG cells. (A) Expression levels of histamine receptor mRNA (H1R to H4R) in HSG cells. (B) Changes in [Ca2+]i induced by 30 µM histamine. (C) Changes in [Ca2+]i after pretreatment with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine (Dex) and subsequent treatment with 30 µM histamine (His). (D) Evoked [Ca2+]i (Δ Ca2+) calculated by the peak value of 30 µM histamine stimulation in the presence or absence of 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine. The upper bars indicate the extracellular solutions applied to the cells and traces were represented with average value. (E, F) After pre-treatment with 100 ng/mL dexmedetomidine for 30 min, HSG cells were stimulated with PBS or with 30 µM histamine for 90 min and then total RNAs were extracted and amplified with primers specific for IL-6, IL-8, and GAPDH. Data are from one of three experimental replicates. IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA expressions were quantified after normalizing to GAPDH levels as a loading control. Results are the mean±SEMs of three independent experiments. (-): no RNA, M: DNA ladder (bp), *p<0.01 was considered statistically significant.
DISCUSSION
The aim of this study was to perform the first investigation of the direct regulatory effects of dexmedetomidine on histamine-induced Ca2+ signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. We demonstrated that dexmedetomidine acts as a modulator of histamine signaling to inhibit histamine-induced Ca2+ signaling and IL-6 mRNA expression. Notably, dexmedetomidine-induced inhibitory effect on Ca2+ signaling was obvious in the low range of histamine stimulation, suggesting that dexmedetomidine exerts a regulatory role of histamine-induced signaling.
Histamine signaling is a novel target for inflammatory processes and secretory dysfunction such as xerostomia. Histamine released by mast cells acts as an inflammatory mediator in several allergies and during inflammation-related responses via its effects on smooth muscle, endothelial cells, and nerve endings [26,27]. Histamine stimulates four types of seven transmembrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptors, H1R-H4R [28,29], and this stimulates phospholipase C, which hydrolyzes inositol phosphates to generate IP3 and diacylglycerol. IP3 released to cytosol then binds IP3R and stimulates Ca2+ release from stores (e.g., the ER) into the cytosol [15]. The Ca2+ ion has versatile, important roles as a second messenger during gene expression, growth, apoptosis, differentiation, muscle contraction, memory, and learning [15,22,30]. During signaling processes, temporal or spatial [Ca2+]i changes transmit specific signals to cells, and these signals elicit diverse responses. Moreover, histamine-mediated vascular inflammation is linked to the activation of Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channels. Histamine-induced Ca2+ increases initiate a signaling cascade, involving CRAC channels STIM1 and Orai1, which is critically involved in gene regulation and the transcription of inflammatory factors [26]. Dexmedetomidine itself did not alter the store-operated Ca2+ influx (Fig. 3). Little is known about the mechanism linking dexmedetomidine-mediated receptor signaling to CRAC channels. Although this point was not addressed in the present study, the modulation of dexmedetomidine on CRAC or other ion channels deserves future investigation.
Previous studies have shown that histamine activation induces H1 receptor up-regulation associated with the protein kinase C δ/extracellular signal-regulated Kinase/poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 signaling pathway in allergic diseases, such as, rhinitis [31,32]. In addition, histamine preferentially stimulates mechano-insensitive nociceptors of primary afferent fibers [33] and has been considered an itch-triggering element [34,35].
Pro-inflammatory cytokine, most notably IL-6 is an important mediator of acute phase reaction and has been found in damaged areas of the salivary glands and have been implicated in the pathophysiology [36,37]. These results show that dexmedetomidine inhibited both histamine-evoked Ca2+ mobilization (Fig. 2 and Fig. 5) and the mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokine IL-6 (Fig. 4 and Fig. 5), which suggest that dexmedetomidine might be useful for treating histamine/IL-6-associated inflammatory disorders or itching events. A high concentration of dexmedetomidine would be clinically practicable; relevant range for dexmedetomidine plasma concentration is up to 20 nM [11,38]. A dexmedetomidine dose to suppress histamine effects in the micromolar range would elicit other effects besides anti-inflammation and would lead to unacceptable side effects [39]. In HSG cells, high concentration of histamine more than 30 µM was required to elicit Ca2+ signal to evaluate the inhibitory role of dexmedetomidine (Fig. 5). Dexmedetomidine also attenuated histamine-induced IL-6 expression at 30 µ M histamine. Histamine treatment at 100 µM masked the inhibitory effect on dexmedetomidine in Ca2+ signaling in HSG cells (data not shown). However the modulation of IL-6 expression by dexmedetomidine in salivary gland cell addresses will be a beneficial research of salivary pathology such as Sjögren's syndrome (SS). Salivary gland cells stimulate T cell differentiation through the production of IL-6 which is currently being explored as a therapeutic target in SS [40]. Thus, our results provide evidence that an appropriate concentration of dexmedetomidine can be potential therapeutic strategy to modulate histamine/IL-6 signaling.
In addition, dexmedetomidine can cross the blood brain barrier and has been shown to improve neurological outcomes in stroke and brain injury models [4,41]. It can also modulate inflammatory responses and exert anti-apoptotic effects by directly activating α2-adrenergic receptors in vitro and in vivo [42,43]. Dexmedetomidine may have biphasic effects, those are, an anti-inflammatory effect at low doses or analgesic and sedative effects at high concentrations. Recently, Unal et al. [44] examined ineffective doses of dexmedetomidine potentiate the anti-nociceptive effects of opioids such as morphine and proposed the synergistic potentiation of dexmedetomidine on anti-nociception induced by opioids.
This study provides novel insight into inflammatory process resulting from Ca2+ signaling based on an investigation of the expressional levels of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 inhibited by dexmedetomidine. These results suggest that histamine-induced Ca2+ signaling is modulated by dexmedetomidine and its inhibitory effect on histamine-induced cytokine expression should be considered a potential therapeutic treatment for itching caused by histamine-mediated activation of sensory neurons. However, further studies are required to clarify how dexmedetomidine modulates inflammatory processes and which channels are involved. It should be clarified whether a down-regulation of stimulus-triggered Ca2+ increase by dexmedetomidine is protective because it prevents a Ca2+ increase or if other signaling cascades or channels are involved. In conclusion, the identification of the Ca2+ mobilizing characteristics of dexmedetomidine will be an important step to modulate histamine signaling beyond its sedative effect.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2014R1A1A3049477) and by the Gachon University research fund in 2014 (GCU 2014-5096).
ABBREVIATIONS
- Dex
dexmedetomidine
- IL
interluekin
- HSG
human salivary glands
- STIM1
stromal interaction molecule 1
- CRAC
Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Kamibayashi T, Maze M. Clinical uses of alpha2-adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:1345–1349. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200011000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jackson KC, 3rd, Wohlt P, Fine PG. Dexmedetomidine: a novel analgesic with palliative medicine potential. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2006;20:23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kocoglu H, Karaaslan K, Gonca E, Bozdogan O, Gulcu N. Preconditionin effects of dexmedetomidine on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2008;69:150–158. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2008.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hoffman WE, Kochs E, Werner C, Thomas C, Albrecht RF. Dexmedetomidine improves neurologic outcome from incomplete ischemia in the rat. Reversal by the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist atipamezole. Anesthesiology. 1991;75:328–332. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199108000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Okada H, Kurita T, Mochizuki T, Morita K, Sato S. The cardioprotective effect of dexmedetomidine on global ischaemia in isolated rat hearts. Resuscitation. 2007;74:538–545. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2007.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Si YN, Bao HG, Xu L, Wang XL, Shen Y, Wang JS, Yang XB. Dexmedetomidine protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat kidney. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:1843–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Plambech MZ, Afshari A. Dexmedetomidine in the pediatric population: a review. Minerva Anestesiol. 2015;81:320–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhang X, Wang J, Qian W, Zhao J, Sun L, Qian Y, Xiao H. Dexmedetomidine inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia by suppression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Neurol Res. 2015;37:238–245. doi: 10.1179/1743132814Y.0000000426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tanabe K, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kozawa O, Iida H. Dexmedetomidine suppresses interleukin-1β-induced interleukin-6 synthesis in rat glial cells. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34:1032–1038. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liao Z, Cao D, Han X, Liu C, Peng J, Zuo Z, Wang F, Li Y. Both JNK and P38 MAPK pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. Brain Res Bull. 2014;107:69–78. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2014.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang X, Wang J, Qian W, Zhao J, Sun L, Qian Y, Xiao H. Dexmedetomidine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 6 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated astrocytes by suppression of c-Jun N-terminal kinases. Inflammation. 2014;37:942–949. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9814-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Peng M, Wang YL, Wang CY, Chen C. Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory response in primary microglia. J Surg Res. 2013;179:e219–e225. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.05.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhao Z, Code WE, Hertz L. Dexmedetomidine, a potent and highly specific alpha 2 agonist, evokes cytosolic calcium surge in astrocytes but not in neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1992;31:1077–1079. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(92)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. doi: 10.1038/35036035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–529. doi: 10.1038/nrm1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lim SA, Hwang KY, Chung SH. Niflumic acid reduces histamine-induced interleukin-6 and -8 expression in human conjunctival epithelial cells. Ophthalmic Res. 2013;50:192–196. doi: 10.1159/000354177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dunford PJ, O'Donnell N, Riley JP, Williams KN, Karlsson L, Thurmond RL. The histamine H4 receptor mediates allergic airway inflammation by regulating the activation of CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 2006;176:7062–7070. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.7062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Coruzzi G, Adami M, Guaita E, de Esch IJ, Leurs R. Antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of the selective histamine H4-receptor antagonists JNJ7777120 and VUF6002 in a rat model of carrageenan-induced acute inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;563:240–244. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mizuguchi H, Ono S, Hattori M, Sasaki Y, Fukui H. Usefulness of HeLa cells to evaluate inverse agonistic activity of antihistamines. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;15:539–543. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ok SH, Bae SI, Shim HS, Sohn JT. Dexmedetomidine-induced contraction of isolated rat aorta is dependent on extracellular calcium concentration. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012;63:253–259. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2012.63.3.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dewitt S, Laffafian I, Morris MR, Hallett MB. Cytosolic Ca2+ measurement and imaging in inflammatory cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2003;225:47–59. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-374-7:47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hong JH, Lee SI, Kim KE, Yong TS, Seo JT, Sohn MH, Shin DM. German cockroach extract activates protease-activated receptor 2 in human airway epithelial cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:315–319. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2003.11.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Newton K, Dixit VM. Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4:pii: a006049. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hoffmann A, Kann O, Ohlemeyer C, Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H. Elevation of basal intracellular calcium as a central element in the activation of brain macrophages (microglia): suppression of receptor-evoked calcium signaling and control of release function. J Neurosci. 2003;23:4410–4419. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-11-04410.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim JH, Park SH, Moon YW, Hwang S, Kim D, Jo SH, Oh SB, Kim JS, Jahng JW, Lee JH, Lee SJ, Choi SY, Park K. Histamine H1 receptor induces cytosolic calcium increase and aquaporin translocation in human salivary gland cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;330:403–412. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.153023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhou MH, Zheng H, Si H, Jin Y, Peng JM, He L, Zhou Y, Muñoz-Garay C, Zawieja DC, Kuo L, Peng X, Zhang SL. Stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and Orai1 mediate histamine-evoked calcium entry and nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:29446–29456. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.578492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Repka-Ramirez MS, Baraniuk JN. Histamine in health and disease. Clin Allergy Immunol. 2002;17:1–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hill SJ, Ganellin CR, Timmerman H, Schwartz JC, Shankley NP, Young JM, Schunack W, Levi R, Haas HL. International Union of Pharmacology. XIII. Classification of histamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1997;49:253–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Oda T, Morikawa N, Saito Y, Masuho Y, Matsumoto S. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel type of histamine receptor preferentially expressed in leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36781–36786. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006480200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Firth AL, Won JY, Park WS. Regulation of Ca2+ signaling in pulmonary hypertension. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17:1–8. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Das AK, Yoshimura S, Mishima R, Fujimoto K, Mizuguchi H, Dev S, Wakayama Y, Kitamura Y, Horio S, Takeda N, Fukui H. Stimulation of histamine H1 receptor up-regulates histamine H1 receptor itself through activation of receptor gene transcription. J Pharmacol Sci. 2007;103:374–382. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fp0061411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mizuguchi H, Terao T, Kitai M, Ikeda M, Yoshimura Y, Das AK, Kitamura Y, Takeda N, Fukui H. Involvement of protein kinase Cdelta/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) signaling pathway in histamine-induced up-regulation of histamine H1 receptor gene expression in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:30542–30551. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.253104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schmelz M, Schmidt R, Weidner C, Hilliges M, Torebjork HE, Handwerker HO. Chemical response pattern of different classes of C-nociceptors to pruritogens and algogens. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89:2441–2448. doi: 10.1152/jn.01139.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shim WS, Tak MH, Lee MH, Kim M, Kim M, Koo JY, Lee CH, Kim M, Oh U. TRPV1 mediates histamine-induced itching via the activation of phospholipase A2 and 12-lipoxygenase. J Neurosci. 2007;27:2331–2337. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4643-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Laidlaw A, Flecknell P, Rees JL. Production of acute and chronic itch with histamine and contact sensitizers in the mouse and guinea pig. Exp Dermatol. 2002;11:285–291. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0625.2002.110401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sisto M, Lisi S, Lofrumento DD, Cucci L, Mitolo V, D'Amore M. Blockade of TNF-α signaling suppresses the AREG-mediated IL-6 and IL-8 cytokines secretion induced by anti-Ro/SSA autoantibodies. Lab Invest. 2010 doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.168. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Son GY, Shin DM, Hong JH. Bacterial PAMPs and Allergens Trigger Increase in [Ca2+]i-induced Cytokine Expression in Human PDL Fibroblasts. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;19:291–297. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.3.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ebert TJ, Hall JE, Barney JA, Uhrich TD, Colinco MD. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:382–394. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200008000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sullivan GW, Linden J, Buster BL, Scheld WM. Neutrophil A2A adenosine receptor inhibits inflammation in a rat model of meningitis: synergy with the type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitor, rolipram. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:1550–1560. doi: 10.1086/315084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Maier-Moore JS, Horton CG, Mathews SA, Confer AW, Lawrence C, Pan Z, Coggeshall KM, Farris AD. Interleukin-6 deficiency corrects nephritis, lymphocyte abnormalities, and secondary Sjögren's syndrome features in lupus-prone Sle1.Yaa mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:2521–2531. doi: 10.1002/art.38716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Benggon M, Chen H, Applegate R, Martin R, Zhang JH. Effect of dexmedetomidine on brain edema and neurological outcomes in surgical brain injury in rats. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:154–159. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31824e2b86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Engelhard K, Werner C, Kaspar S, Möllenberg O, Blobner M, Bachl M, Kochs E. Effect of the alpha2-agonist dexmedetomidine on cerebral neurotransmitter concentrations during cerebral ischemia in rats. Anesthesiology. 2002;96:450–457. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200202000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Taniguchi T, Kidani Y, Kanakura H, Takemoto Y, Yamamoto K. Effects of dexmedetomidine on mortality rate and inflammatory responses to endotoxin-induced shock in rats. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:1322–1326. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000128579.84228.2a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Unal M, Gursoy S, Altun A, Duger C, Kol IO, Kaygusuz K, Bagcivan I, Mimaroglu C. Ineffective doses of dexmedetomidine potentiates the antinociception induced by morphine and fentanyl in acute pain model. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17:417–422. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.5.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]