Abstract
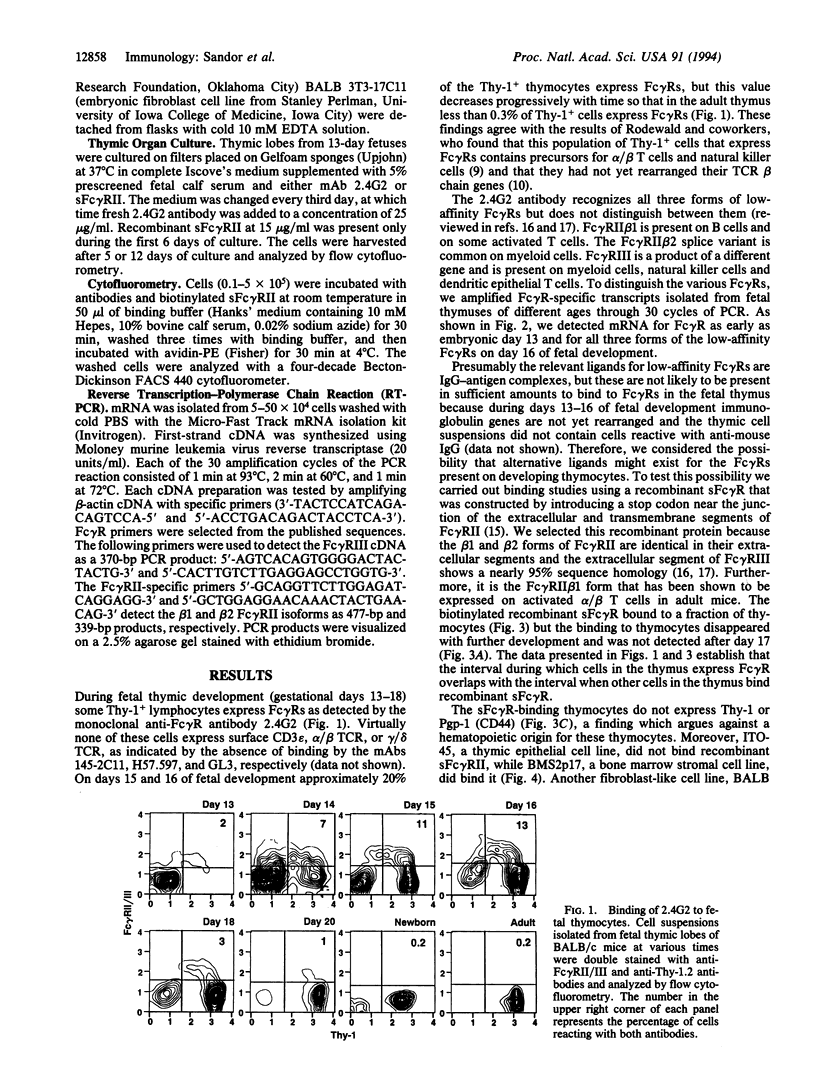
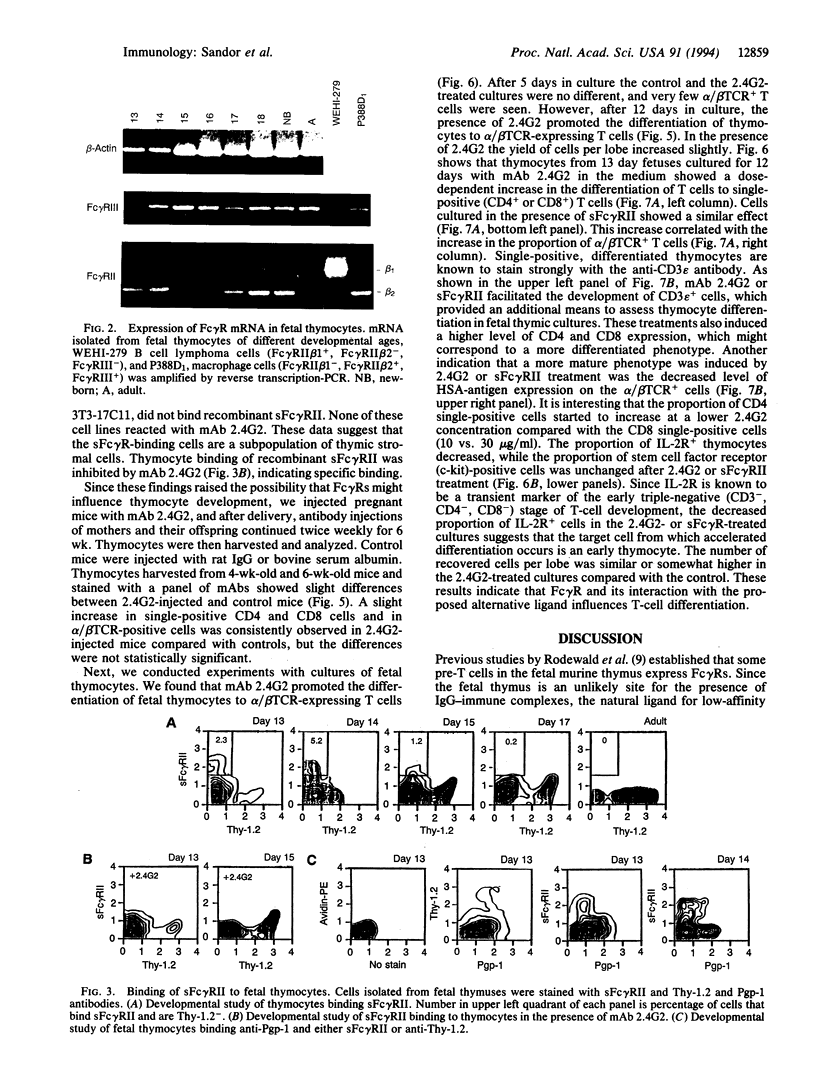
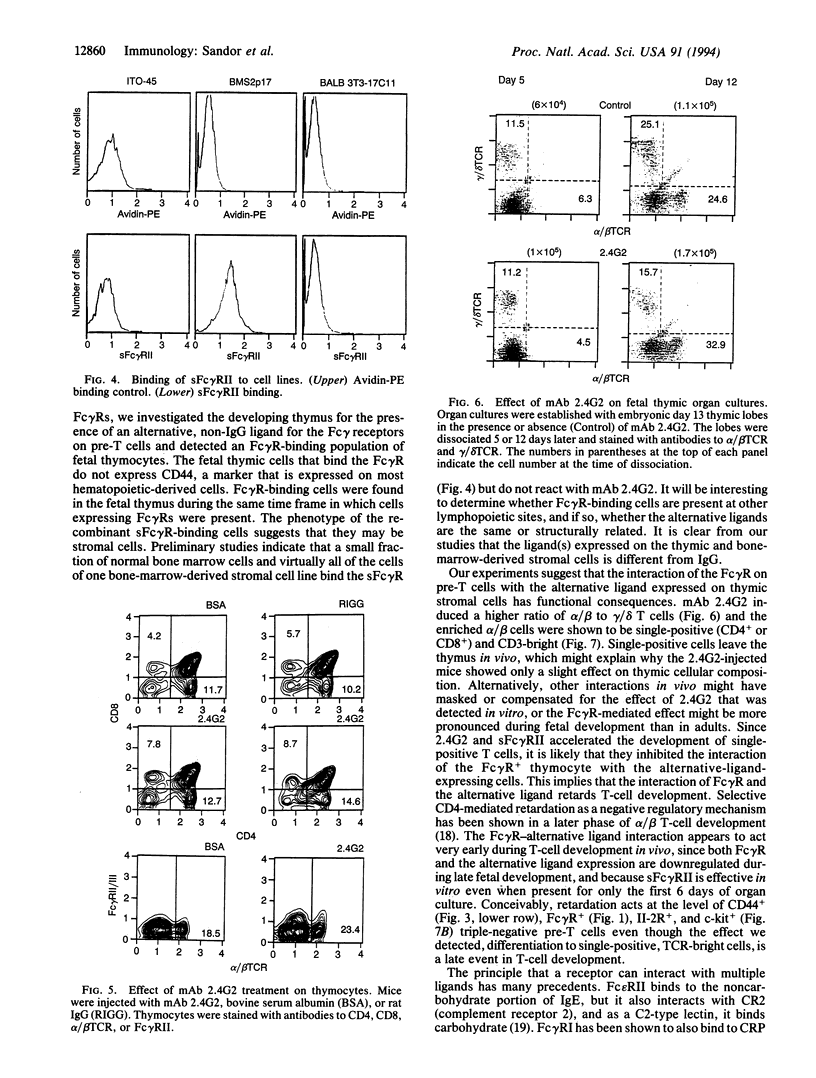
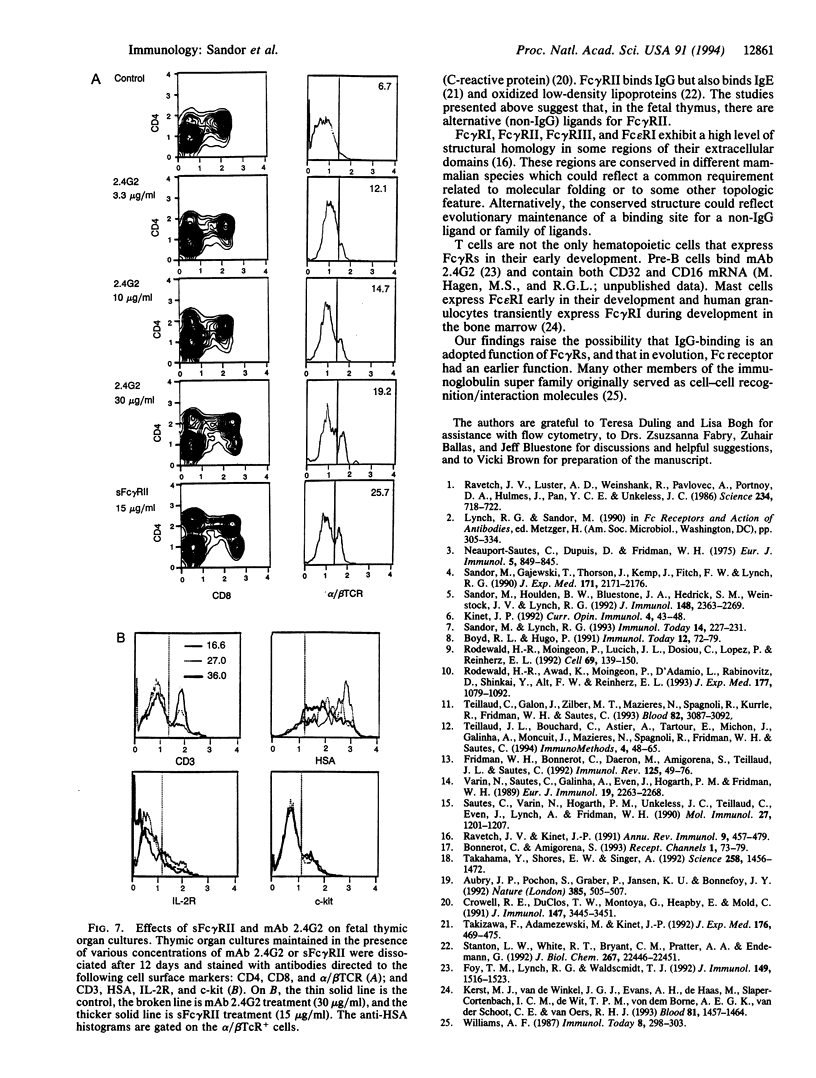
Fetal pre-T cells express low-affinity receptors for IgG (Fc gamma R) at a developmental stage prior to the rearrangement and expression of immunoglobulin genes. The present studies investigated the possible functional significance of Fc gamma R on fetal pre-T cells. Between 13 and 17 days of fetal development a subpopulation of T-cell receptor-, Thy-1+ thymocytes express for gamma R. The same cells contain mRNA for several forms of Fc gamma R (Fc gamma RII beta 1, beta 2, and Fc gamma RIII). Concurrently, a Pgp-1-, Thy-1-, surface-immunoglobulin- fetal thymic cell binds recombinant soluble Fc gamma R. In principle this cell can interact with the pre-T cells through this counter-receptor. To test this possibility anti-Fc gamma RII/III antibody (2.4G2) was injected into pregnant mice and then into their offspring for 6 wk postpartum. The injected antibody induced a slight increase in the proportion of CD4 or CD8 single-positive, alpha/beta T cells in the thymus. However, in fetal thymic cultures in the presence of 2.4G2 or the recombinant soluble Fc gamma R there was an accelerated differentiation of thymocytes to single-positive, CD3-bright, heat-stable antigen-dull, alpha/beta T cells. These experiments show that Fc gamma Rs are present on pre-T cells during early fetal thymic development, and that a non-IgG ligand of the Fc gamma R is expressed concurrently on Thy- fetal thymocytes. Furthermore, the presumed interaction of Fc gamma R and the alternative ligand(s) influences T-cell development. IgG binding could be an adapted function of Fc gamma Rs, and, as shown for many members of the Ig super family, these receptors may have originally served as cell-cell recognition/interaction molecules required for hematopoietic development.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubry J. P., Pochon S., Graber P., Jansen K. U., Bonnefoy J. Y. CD21 is a ligand for CD23 and regulates IgE production. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):505–507. doi: 10.1038/358505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Amigorena S. Murine low-affinity receptors for the Fc portion of IgG. Roles in cell activation and ligand internalization. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(1):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. L., Hugo P. Towards an integrated view of thymopoiesis. Immunol Today. 1991 Feb;12(2):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90161-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell R. E., Du Clos T. W., Montoya G., Heaphy E., Mold C. C-reactive protein receptors on the human monocytic cell line U-937. Evidence for additional binding to Fc gamma RI. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3445–3451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy T. M., Lynch R. G., Waldschmidt T. J. Ontogeny and distribution of the murine B cell Fc gamma RII. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1516–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridman W. H., Bonnerot C., Daeron M., Amigorena S., Teillaud J. L., Sautes C. Structural bases of Fc gamma receptor functions. Immunol Rev. 1992 Feb;125:49–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb00625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerst J. M., van de Winkel J. G., Evans A. H., de Haas M., Slaper-Cortenbach I. C., de Wit T. P., von dem Borne A. E., van der Schoot C. E., van Oers R. H. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor induces hFc gamma RI (CD64 antigen)-positive neutrophils via an effect on myeloid precursor cells. Blood. 1993 Mar 15;81(6):1457–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinet J. P. The gamma-zeta dimers of Fc receptors as connectors to signal transduction. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Luster A. D., Weinshank R., Kochan J., Pavlovec A., Portnoy D. A., Hulmes J., Pan Y. C., Unkeless J. C. Structural heterogeneity and functional domains of murine immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2946078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald H. R., Awad K., Moingeon P., D'Adamio L., Rabinowitz D., Shinkai Y., Alt F. W., Reinherz E. L. Fc gamma RII/III and CD2 expression mark distinct subpopulations of immature CD4-CD8- murine thymocytes: in vivo developmental kinetics and T cell receptor beta chain rearrangement status. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1079–1092. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald H. R., Moingeon P., Lucich J. L., Dosiou C., Lopez P., Reinherz E. L. A population of early fetal thymocytes expressing Fc gamma RII/III contains precursors of T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90125-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandor M., Gajewski T., Thorson J., Kemp J. D., Fitch F. W., Lynch R. G. CD4+ murine T cell clones that express high levels of immunoglobulin binding belong to the interleukin 4-producing T helper cell type 2 subset. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):2171–2176. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandor M., Houlden B., Bluestone J., Hedrick S. M., Weinstock J., Lynch R. G. In vitro and in vivo activation of murine gamma/delta T cells induces the expression of IgA, IgM, and IgG Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2363–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandor M., Lynch R. G. Lymphocyte Fc receptors: the special case of T cells. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90168-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sautès C., Varin N., Hogarth P. M., Unkeless J. C., Teillaud C., Even J., Lynch A., Fridman W. H. Molecular and functional studies of recombinant soluble Fc gamma receptors. Mol Immunol. 1990 Dec;27(12):1201–1207. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90023-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., White R. T., Bryant C. M., Protter A. A., Endemann G. A macrophage Fc receptor for IgG is also a receptor for oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22446–22451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahama Y., Singer A. Post-transcriptional regulation of early T cell development by T cell receptor signals. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1456–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.1439838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa F., Adamczewski M., Kinet J. P. Identification of the low affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E on mouse mast cells and macrophages as Fc gamma RII and Fc gamma RIII. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):469–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varin N., Sautès C., Galinha A., Even J., Hogarth P. M., Fridman W. H. Recombinant soluble receptors for the Fc gamma portion inhibit antibody production in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2263–2268. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




