Abstract
Purpose
Central corneal thickness (CCT) is a quantitative trait associated with keratoconus and primary open-angle glaucoma. Although CCT is highly heritable, known genetic variations explain only a fraction of the phenotypic variability. The purpose of this study was to identify additional CCT-influencing loci using inbred strains of mice.
Methods
Cohorts of 82 backcrossed (N2) and 99 intercrossed (F2) mice were generated from crosses between recombinant inbred BXD24/TyJ and wild-derived CAST/EiJ mice. Using anterior chamber optical coherence tomography, mice were phenotyped at 10 to 12 weeks of age, genotyped based on 96 genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), and subjected to quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis.
Results
In an analysis of total CCT among all mice, two loci passed the significance threshold of P = 0.05. These were on Chr 3 and Chr 11 (Cctq4 and Cctq5, respectively). A third locus of interest was identified in a two-dimensional pairwise analysis; this locus on Chr 14 (Cctq6) exhibited a significant additive effect with Cctq5. Independent analyses of the dataset for epithelial and stromal thickness revealed that Cctq4 is specific to the epithelial layer and that Cctq5 and Cctq6 are specific to the stromal layer.
Conclusions
Our findings demonstrate a quantitative multigenic pattern of CCT inheritance in mice and identify three previously unrecognized CCT-influencing loci: Cctq4, Cctq5, and Cctq6. This is the first demonstration that distinct layers of the cornea are under differential genetic control and highlights the need to refine the design of future genome-wide association studies of CCT.
Keywords: quantitative traits, central corneal thickness, cornea, QTL analysis
We have identified three new quantitative trait loci (QTL) that regulate central corneal thickness in mice. Two of these QTL specifically influence the stroma while the third influences the epithelium. This suggests there is differential genetic regulation of corneal epithelial and stromal thickness.
Central corneal thickness (CCT) is a continuously distributed quantitative trait.1–4 As a sum of the thickness of the three corneal tissue layers (the epithelium, stroma, and endothelium), CCT remains relatively stable over time within individuals, but varies widely between individuals and ethnicities.5–10 Extreme variations in CCT are often associated with rare connective tissue disorders such as brittle cornea syndrome and osteogenesis imperfecta,11–15 whereas modest differences are associated with relatively common diseases such as keratoconus16 and risk of primary open-angle glaucoma.17–19 Central corneal thickness is one of the most heritable human traits, with estimates of up to 0.95 reported.2,3,14,20–22 Despite this high heritability and the fact that CCT has been implicated in several human diseases, currently known genetic variations explain only a small fraction of this phenotypic variability.
Of the genes known to influence the normal range of CCT variation, most were identified in human genome-wide association studies (GWAS).13,16,23–25 Several of the currently known CCT-influencing factors include genes that have an impact on collagen,16,24,25 a major structural component of the stromal layer. Other CCT-influencing genes have unknown function, including ZNF469, a zinc-finger encoding gene, mutations in which can cause brittle cornea syndrome.13,16,25 Although important progress has been made toward understanding how the genes identified by GWAS to date contribute to CCT variability, these account for <10% of the total heritability; the vast majority of CCT inheritance remains to be explained. Current knowledge of CCT-influencing variations points to a potentially large number of genes that might be considered as candidates based on pathway or homology predictions.
One means of identifying genes that quantitatively influence CCT is phenotype-driven mouse genetics. The mouse and human cornea are very similar in structure and function,26 and are therefore likely to be influenced by similar genetic pathways. Based on the demonstration that corneal thickness is continuously distributed among inbred strains of mice,1 we have initiated approaches to map quantitative trait loci (QTL) that influence CCT. Here we report results from crosses between two inbred strains of mice. These identify several previously unknown CCT-influencing QTL, and also demonstrate that distinct genetic pathways regulate the thicknesses of the corneal epithelium and stroma.
Methods
Experimental Animals
BXD24/TyJ-Cep290rd16/J (abbreviated as BXD24b throughout) and CAST/EiJ (abbreviated as CAST throughout) mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA) and subsequently housed and bred at the University of Iowa Research Animal Facility. BXD24b is a recombinant inbred strain of mice derived from C57BL/6J and DBA/2J progenitors27 and contains a spontaneous mutation within the Cep290 gene.28 CAST is an inbred strain originally derived from wild mice trapped in a grain warehouse in Thailand.29 BXD24b × CAST F1 mice were either backcrossed with BXD24b mice to produce a population of BXD24b × CAST N2 mice, or intercrossed to produce F2 mice. The study on corneal thickness reported here was an accompaniment to a broader ongoing study that seeks to identify genetic modifiers of the recessive Cep290rd16 mutation; therefore, all N2 and F2 mice available for the study were preselected, by PCR-based genotyping at weaning, for homozygosity of Cep290rd16. All animals were treated in accordance with the ARVO Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research. All experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Iowa.
Mouse Genotyping
Genomic DNA was isolated from ear tissue of each mouse. Genome-wide genotyping of genomic DNA was performed at the University of Iowa using Fluidigm technology, following the manufacturer's instructions, and a panel of 96 (Fluidigm Corporation, South San Francisco, CA, USA) assays for single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that differentiate BXD24b from CAST alleles.30 The average spacing between markers was 16 cM (Fig. 1). For SNP assays, DNA was simultaneously PCR amplified from each sample using a multiplex PCR kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA), with specific target amplification (STA) primers and locus-specific primers (LSP). Preamplified DNA samples were diluted 1:10 and then combined with allele-specific primers (ASP), LSP, and the required Fluidigm buffers and reagents and loaded into the integrated fluidic circuits for SNP genotyping. Genotyping calls were made using the SNP Genotyping Analysis Software v.3.0.2 (Fluidigm Corporation) and Fluidigm Data Collection Software v.3.0.2. All primer sequences are available upon request.
Figure 1.
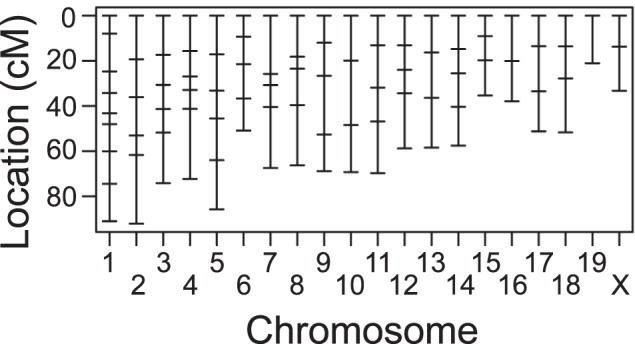
Distribution of polymorphic markers across the mouse genome. The horizontal dashes along each chromosome represent one marker. The mean distance between markers is 16 cM.
CCT Phenotyping
All measurements were recorded from 10- to 12-week-old mice, a time at which the adult cornea has fully developed and reached a stable thickness.1,31 The animals were injected with a standard mixture of ketamine/xylazine (intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg ketamine + 10 mg xylazine/kg body weight; Ketaset, Fort Dodge Animal Health, Fort Dodge, IA, USA; AnaSed, Lloyd Laboratories, Shenandoah, IA, USA). During induction of anesthesia, the mice were provided supplemental indirect warmth by a heating pad. Immediately following anesthesia, eyes were hydrated with balanced salt solution (BSS; Alcon Laboratories, Fort Worth, TX, USA), and corneal images were obtained with Bioptigen spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT; Bioptigen, Inc., Durham, NC, USA). A 12-mm telecentric bore with a reference arm position of 1048 was used to image the anterior segment of each eye. The bore was positioned such that the pupil of the eye was centered in the volume intensity projection. Scan parameters were as follows: radial volume scans 2.0 mm in diameter, 1000 A-scans/B-scan, 100 B-scans/volume, 1 frame/B-scan, and 1 volume. Using the Bioptigen InVivoVue computer software, CCT was measured for each eye with vertical angle-locked B-scan calipers. Mice were included in the analysis if the variation between the right and left eyes was less than 5 μm and if both of the eyes were free from opacity.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical comparisons of CCT between parental strains of mice (BXD24b and CAST) were calculated using an unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. Quantitative trait locus analysis was performed with R/qtl, using the N2 and F2 datasets separately and in combination.32–34 The genome-wide scan (scanone) and two-dimensional genome-wide scan (scantwo) were conducted as previously described.35 The significance thresholds for the genome-wide scan were determined by performing traditional permutation testing, using 1000 permutations. Loci with logarithm of the odds ratio (LOD) scores above the P = 0.05 threshold were considered significant QTL; loci with LOD scores above the P = 0.63 threshold were considered suggestive QTL36; and loci with LOD scores above the P = 0.1 threshold were considered highly suggestive. For the two-dimensional genome-wide scan, significance thresholds were determined empirically by permutation testing, using 1000 permutations.
The validity of a multiple QTL model was tested by performing multiple regression analysis. Phenotypic variance was estimated and the full model was statistically compared to reduced models in which one QTL was dropped. The analysis follows the formula: LOD(QTL1) = log10 [Pr(data|QTL1, QTL2, …, QTLk) / Pr(data|QTL2, …, QTLk)].33 If the probability of the data with all “k” QTL is close to the last “k-1” QTL, then the LOD score is low, and support for QTL1 within the model is decreased. If the data are more probable when QTL1 is included in the model, then the LOD score is large and support for QTL1 within the model is increased. To determine the level of support for the LOD scores resulting from the multiple regression analysis, they were compared to the significance thresholds from the one-dimensional genome-wide scan.
To compare differences of allelic effects at a single SNP marker, an unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test was used. Differences in CCT were considered significant if the P values were less than 0.05 and the level of confidence was >95% after correction for multiple comparisons. Unless otherwise stated, all CCT values are reported based on the number of mice and are expressed as an average ± SD.
Bioinformatics Analysis
The 95% Bayes credible intervals for Cctq4-6 were calculated using R/qtl. The protein-coding genes and noncoding RNA genes within the Bayes credible intervals for Cctq4-6 were identified using the Mouse Genome Informatics (MGI) Genes & Markers Query (http://www.informatics.jax.org/marker [in the public domain]). The interrogated cM positions for the genes of interest spanned the following intervals: for Cctq4, Chr 3 from 28 to 48 cM; for Cctq5, Chr 11 from 43.6 to 58.6 cM; for Cctq6, Chr 14 from 5 to 37.5 cM. The genome base-position coordinates provided in the Supplementary Tables are from assembly GRCm38/mm10. The resulting gene lists were then filtered such that genes were included as candidates underlying the QTL only if they (1) contained one or more DNA base pair changes that affect the encoded protein and (2) were expressed in mouse corneal tissue (see Supplementary Tables S1–S3).
To identify genes with potentially important DNA base pair changes within the Bayes credible intervals, the chromosomal regions used for the MGI query (converted to Mb using GRCm38/mm10 assembly coordinates) were examined using the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute's Mouse Genomes Project SNP and Indel Query tool (http://www.sanger.ac.uk/sanger/Mouse_SnpViewer/rel-1410 [in the public domain]).37,38 The SNP/Indel types selected for analysis were as follows: coding sequence variants, frame-shift variants, in-frame deletions, in-frame insertions, initiator codon variants, missense variants, regulatory region ablations, regulatory region amplifications, splice acceptor variants, splice donor variants, stop-gain variants, stop-loss variants, transcription factor binding site (TFBS) ablation, and TFBS amplification. The strains selected for analysis were CAST/EiJ and DBA/2J (C57BL6/J is the reference strain). The results were exported as a spreadsheet and sorted by the Snp/Indel consequence (Csq).
To further prioritize genes of interest within each of the Bayes credible intervals of Cctq4-6, we determined which are expressed in corneal tissue using our previously published microarray data.1 In that study, RNA had been isolated from central corneal tissue derived from C57BL/6J, C57BLKS/J, and SJL/J mice. Genes were considered to be expressed in the cornea if their log2 expression values were greater than 5.0 in at least one of the strains analyzed. The overlap of genes with at least one protein-altering DNA base pair change and with corneal expression was compiled into a single spreadsheet each for Cctq4, Cctq5, and Cctq6 (Supplementary Tables S1, S2, and S3, respectively).
Results
Phenotypes of Parental Strains, N2 Mice, and F2 Mice
The CAST and BXD24b parental mouse strains are genetically distinct from one another39 and have overtly healthy corneas that differ significantly in thickness. We found that CAST mice have a CCT of 91.8 ± 6.2 μm, whereas BXD24b have a CCT of 99.9 ± 3.2 μm (six mice each group; P = 0.02). Although the phenotypes of these inbred strains are next to one another on the relative spectrum of CCT in mice,35 they are significantly different from each other. The phenotypic distributions of both the backcross (N2) and intercross (F2) mice followed a broad bell-shaped curve, suggesting the presence of many genes causing the difference in phenotype (Supplementary Fig. S1). A Shapiro-Wilk goodness-of-fit test indicated that the data did not differ statistically from a normal distribution and therefore did not need to be transformed (P = 0.89 and P = 0.51, N2 and F2, respectively). Central cornea thickness of the N2 progeny ranged from 83.5 to 121.5 μm (a difference of 38 μm; n = 82 mice; Supplementary Fig. S1A), and the mean was 102.4 ± 7.1 μm; this is thicker than the CCT of the parental strains. In the F2 progeny, the phenotypic distribution was similar to that in the N2 progeny (range, 82–121.5 μm; n = 99 mice), and the mean CCT was also greater than that in either of the parental strains (102.4 ± 8.5 μm; Supplementary Fig. S1B).
Combining information from multiple mouse crosses has proven to be an effective means of increasing the ability to detect and resolve QTL.34,40,41 We employed this methodology using our datasets. The combined N2 and F2 dataset of total corneal thickness followed a normal distribution (goodness-of-fit, P = 0.55; Fig. 2A), similar to the N2 and F2 crosses alone (Supplementary Fig. S1).
Figure 2.
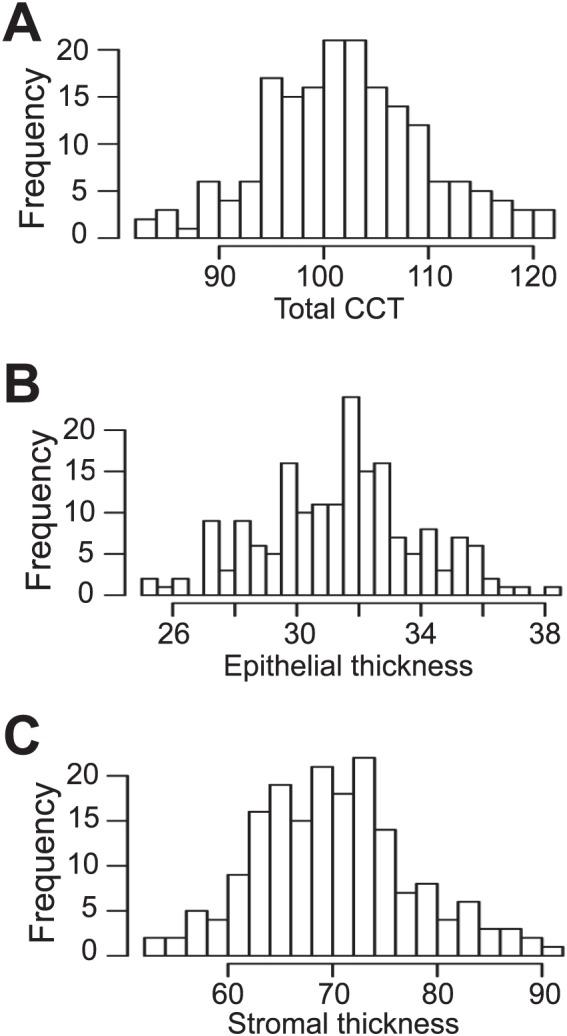
Phenotypic distributions of combined (BXD24b × CAST) N2 + F2 mice. (A) Total CCT. (B) Epithelial thickness. (C) Stromal thickness. Frequency, number of mice; thickness measured in micrometers.
Our CCT measurement data were generated using OCT. A benefit of this approach is that it produces an image of the corneal cross section in which the epithelial and stromal layers are visually distinct. Thus it is possible not only to measure total corneal thickness, but also to independently measure the epithelial and stromal thicknesses. The phenotypic distribution of both of these variables in the combined N2 + F2 dataset resembled that of total CCT in that it followed a normal distribution (goodness-of-fit, P = 0.30 and 0.16 for epithelium and stroma, respectively; Figs. 2B, 2C). The CAST and BXD24b parental strains mice had similar epithelial thicknesses (29.3 ± 2.9 vs. 29.7 ± 2.0 μm, respectively; P = 0.8), but significantly different stromal thicknesses (62.3 ± 7.9 vs. 70.1 ± 3.1 μm, respectively; P < 0.05). Although epithelial thickness is the same for the two parental strains, there is a continuous distribution of phenotypes in their crossed progeny (Fig. 2B). This suggests that the similarity in CCT phenotype is due to different genetic causes. Collectively, the data on CCT, epithelial thickness, and stromal thickness suggested that multiple loci influence CCT and were well suited for identifying QTL.
QTL Analysis
To identify loci that affect the CCT phenotype, N2 and F2 mice were genotyped based on 96 polymorphic markers (see Fig. 1) and genotype: Phenotype associations were assessed using R/qtl. A one-dimensional genome-wide scan of total CCT across the combined dataset (82 N2 mice and 99 F2 mice) identified two loci that passed the P = 0.05 significance threshold: one on Chr 3 and one on Chr 11 (Fig. 3A; dotted-dashed horizontal line). The SNP with the maximum LOD score on Chr 3 was at 44 cM (rs3720779; LOD = 3.5), and that on Chr 11 was at 53 cM (rs3688569; LOD = 4.2). These QTL were named Cctq4 and Cctq5 (central corneal thickness QTL 4 and 5, respectively). Several other loci of interest were detected on Chr 12, 13, 14, 17, and 19; they all exceeded the suggestive threshold of P = 0.63 (Fig. 3A; dashed horizontal line). No additional statistically significant loci were identified when the N2 or the F2 datasets were analyzed independently (Supplementary Figs. S2, S3).
Figure 3.
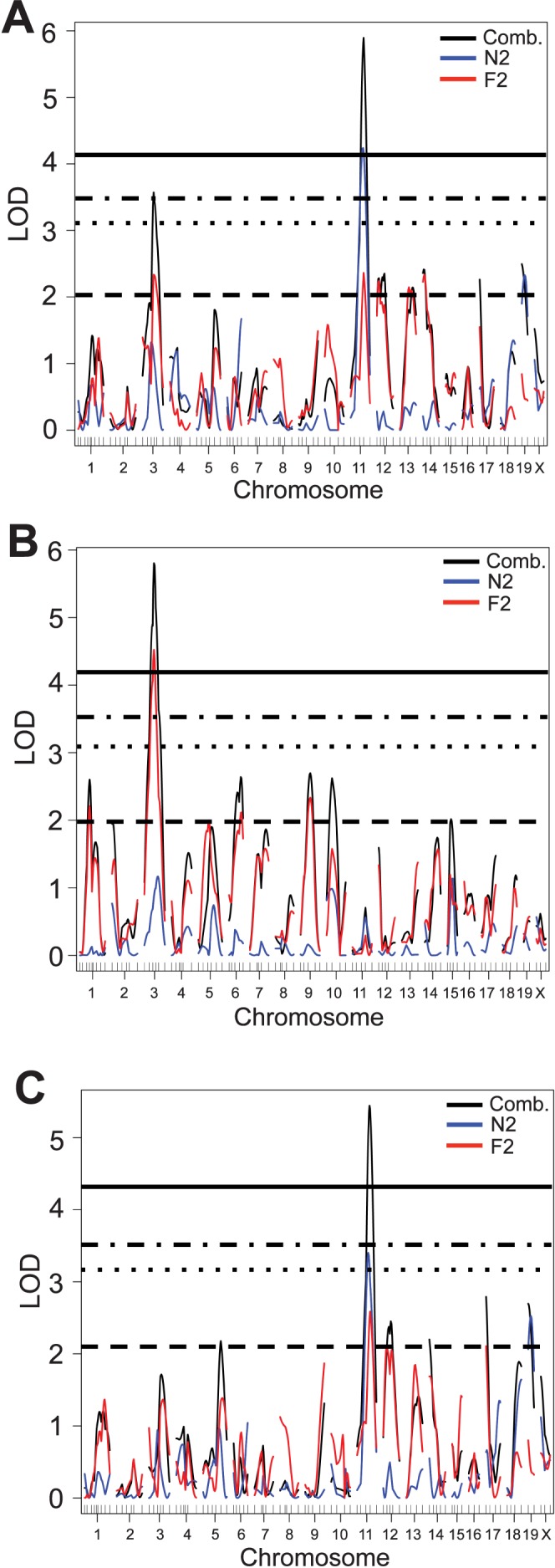
Genome-wide scans of combined (BXD24b × CAST) N2 + F2 mice. (A) Total CCT. Significant loci were observed on Chr 3 and 11; suggestive loci were observed on Chr 12, 13, 14, 17 and 19. (B) Epithelial thickness. A significant locus was observed on Chr 3; suggestive loci were observed on Chr 1, 6, 9, 10, and 15. (C) Stromal thickness. A significant locus was observed on Chr 11; suggestive loci were observed on Chr 5, 12, 14, 17, and 19. Significance thresholds are as follows: solid line, P = 0.01; dashed-dotted, P = 0.05 (significant); dotted, P = 0.1; dashed, P = 0.63 (suggestive). LOD, logarithm of odds.
A striking result was uncovered when epithelial thickness was analyzed independent of stromal thickness: A genome-wide one-dimensional scan using epithelial thickness as the quantitative trait resulted in the preservation of Cctq4 on Chr 3, but resulted in the loss of Cctq5 on Chr 11 (Fig. 3B). An analysis of stromal thickness resulted in the disappearance of Cctq4 and the presence of Cctq5 (Fig. 3C). These findings suggest that the thicknesses of the corneal epithelial and stromal layers are controlled by different sets of genes. Several other loci of potential interest exceeded the suggestive significance threshold of P = 0.63. For epithelial thickness, these loci were on Chr 1, 6, 9, and 10; for stromal thickness, they were on Chr 5, 12, 14, 17, and 19.
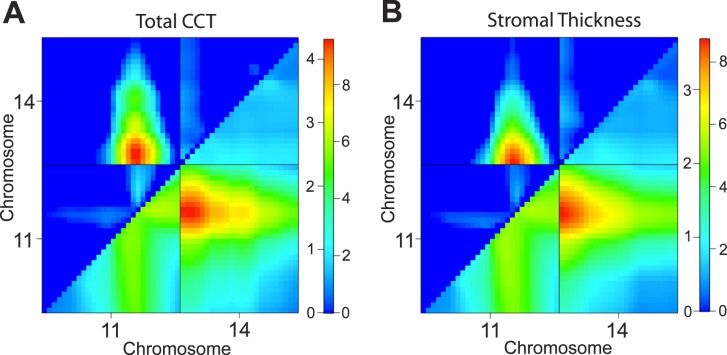
A two-dimensional pairwise scan, which examines two loci simultaneously to consider epistatic interactions and/or additive effects, identified a third CCT-regulating QTL. Specifically, this analysis identified an additive effect between loci on Chr 11 (at 53.6 cM; significant in the one-dimensional scan) and Chr 14 (at 7.5 cM; suggestive in the one-dimensional scan; Fig. 4A). In the case of an additive effect, an interaction is considered interesting if the pair of loci exceed two P = 0.05 significance thresholds: Ta (additive threshold) and Tav1 (additive versus one threshold). Permutation testing on the total CCT dataset revealed that the maximum LOD scores for this additive interaction exceeded both of these thresholds (Ma = 9.6 > Ta = 5.9 and Mav1 = 4.4 > Tav1 = 3.1).
Figure 4.
Plots of the two-dimensional pairwise scans showing an additive interaction between loci on Chr 11 and Chr 14. (A) Results using total CCT as the quantitative phenotype. (B) Results using stromal thickness as the quantitative phenotype. For both (A) and (B), the lower right triangle displays the additive LOD score (LODa; right side of the heat map), and the upper left triangle displays the LOD score in which the additive model is compared to the single QTL model (LODav1; left side of the heat map).
A two-dimensional pairwise scan using stromal thickness as the quantitative trait identified the same additive interaction between Chr 11 and Chr 14 (Ma = 8.8 > Ta = 6.0, Mav1 = 3.8 > Tav1 = 3.2; Fig. 4B). No significant interactive loci were detected using the epithelial thickness data. Because the locus on Chr 14 was significant in the two-dimensional analyses of total CCT and stromal thickness, we consider this a true CCT-regulating QTL and therefore name it Cctq6. Cctq6 likely exerts its effect through the stroma.
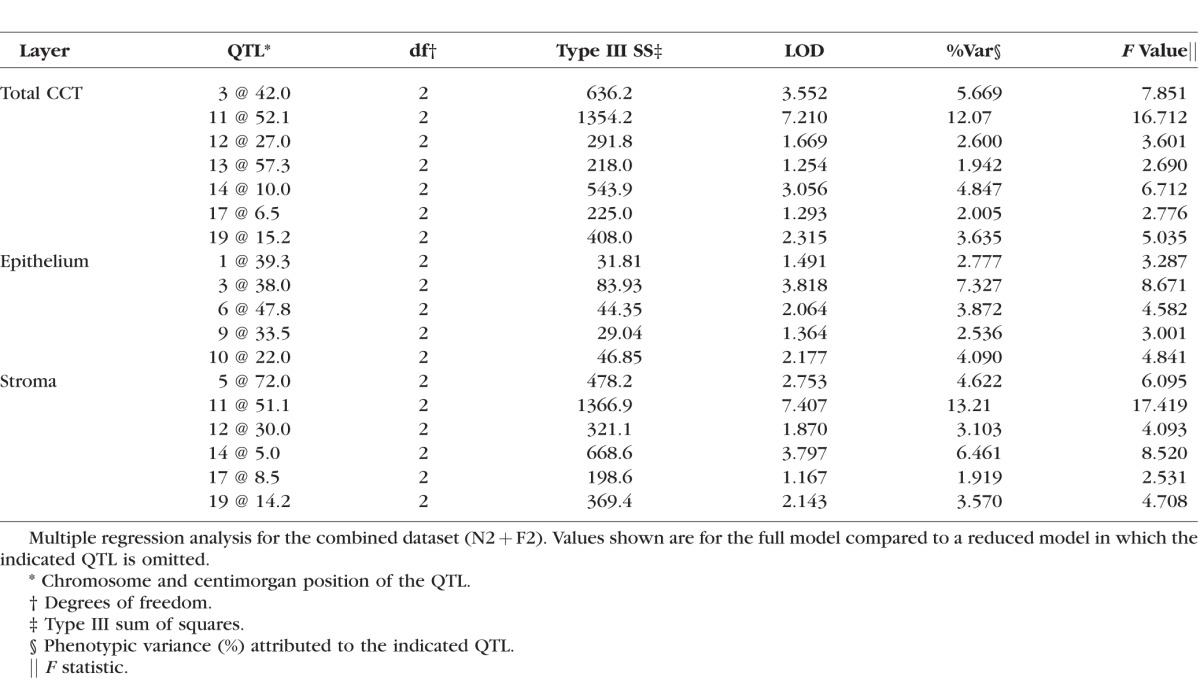
To further test the importance of the loci identified through the one- and two-dimensional scans, multiple regression analysis was performed, with the full model compared to reduced models in which one locus is dropped. For all analyses, the combined (N2 + F2) datasets were used. Also, all loci exceeding the P = 0.63 suggestive significance threshold were included (Table). That is, for total CCT, a seven-QTL model was used; for epithelial thickness, a five-QTL model; and for stromal thickness, a six-QTL model. Support for a QTL was determined by comparing the LOD scores in the Table to the genome-wide significance thresholds. Multiple regression analysis of total CCT resulted in evidence for QTL on Chr 3, 11, 14, and 19, but not on Chr 12, 13, or 17. Analysis of epithelial thickness supported QTL on Chr 3, 6, and 10, but not on Chr 1 and 9. Analysis of stromal thickness supported a model with QTL on Chr 5, 11, 14, and 19. In sum, multiple regression analysis provided evidence that up to seven QTL regulate CCT in these mouse crosses, through independent actions on either epithelial or stromal thickness. Based on the significance thresholds from the one- and two-dimensional scans and the multiple regression analyses, the strongest evidence is for QTL on Chr 3 (Cctq4), Chr 11 (Cctq5), and Chr 14 (Cctq6).
Table.
Multiple Regression Analysis
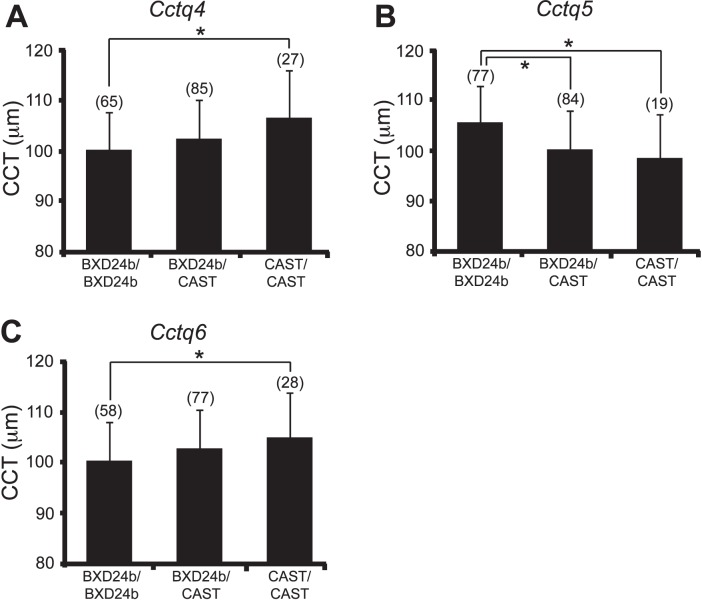
The markers nearest to the loci with the maximum LOD score for each significant QTL were examined for their effects on the CCT phenotype in these mouse crosses. The allelic effects at the peak Cctq4 SNP (rs3720779) and peak Cctq6 SNP (rs3707741) revealed that the CAST sequence at these loci promotes an increase in corneal thickness (Figs. 5A, 5C). The allelic effect at the peak Cctq5 SNP (rs3688569) showed that the CAST sequence at that locus is associated with a decrease in corneal thickness (Fig. 5B).
Figure 5.
Effect plots for combined (BXD24b × CAST) N2 + F2 mice. Allelic effects of (A) Cctq4 (Chr 3, rs3720779), (B) Cctq5 (Chr 11, rs3688569), and (C) Cctq6 (Chr 14, rs3707741). The numbers in parentheses are the numbers of mice with the indicated genotype. The numbers do not add up to the same value for (A–C) because of missing genotypes at that SNP for a variable number of mice. Asterisks denote P < 0.05 significance. Error bars: standard deviation.
Bioinformatics Analysis Within the Cctq4-6 Loci
Genes within each QTL were prioritized based on two levels of filtering: first, by comparing known protein-coding and regulatory region differences between C57BL/6J or DBA/2J (the two strains from which BXD24b is derived) and CAST/EiJ, using the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute's Mouse SNP query tool; second, by considering corneal gene expression in our previously published microarray study.1 The 95% Bayes credible interval for Cctq4 spanned 28 to 48 cM (57.6–109.2 Mb; GRCm38 build). Within this interval, there are 575 protein-coding genes and 41 noncoding RNA genes. Of the regulatory elements that were queried (regulatory region amplifications and ablations, transcription factor binding site amplifications and ablations), there were no known variants. Of the protein-coding genes expressed in the cornea, 178 contained one or more missense changes and/or in-frame insertions or deletions, 3 contained frame-shift mutations (Ttf2, Atp5f1, and Gstm7), 15 contained splice-site acceptor or donor mutations (Rsrc1, Lmna, Adam15, Ubap2l, Adamtsl4, Bola1, Bcl2l15, Pogz, Arnt, Phgdh, Wars2, Trim45, Wdr77, Slc6a17, and Clcc1), and 5 contained stop-gain mutations (BC027582, Glrb, Pmvk, Dclre1b, and Stxbp3a; Supplementary Table S1).
The 95% Bayes credible interval for Cctq5 spanned 43.6 to 58.6 cM (71.6–93.2 Mb; GRCm38 build). Within this interval, there are 316 protein-coding genes and 54 noncoding RNA genes. Of the protein-coding genes expressed in the cornea, 133 contained one or more missense changes and/or in-frame insertions or deletions, 10 contained frame-shift mutations (4933427D14Rik, Xaf1, Hic1, Rpa1, Suz12, Rnf135, Slfn8, Tubd1, Msi2, and Stxbp4), 9 contained splice-site acceptor or donor mutations (Gemin4, Nek8, Rph3al, Glod4, Ccl9, Vezf1, 4930556N13Rik, Smyd4, and Vtn), and 5 contained stop-gain or -loss mutations (Xaf1, Slfn9, Slfn8, Spns3, and Crk; Supplementary Table S2). There were no known variants in regulatory elements.
The 95% Bayes interval for Cctq6 spanned a large portion of the chromosome (∼60%), 5 to 37.5 cM (8.8–72.2 Mb; GRCm38 build). There are 659 protein-coding genes and 51 noncoding RNA genes within this interval. Of the protein-coding cornea-expressed genes, 170 have one or more missense changes and/or in-frame insertions or deletions, 7 have frame-shift changes (1700112E06Rik, 2010107H07Rik, A630023A22Rik, Glud1, Hacl1, Hmbox1, and Kctd9), 7 have splice site acceptor or donor mutations (Nkiras1, Ndst2, Txndc16, Lgals3, Osgep, Mettl3, and Rcbtb1), 6 have stop-gain or -loss mutations (Fhit, Nisch, Dlgap5, Mtmr9, Ints9, and Gfra2), and 1 has an initiator-codon variant (Ptprg; Supplementary Table S3). There were no known variants in regulatory elements.
Discussion
Quantitative trait analysis can be a powerful approach for studying medically important phenotypes.42,43 Though simply measured, CCT is a complex and intriguing quantitative trait. It is highly heritable and follows a continuous distribution among the general population, with distinct variations across ethnicities. Within the range of CCT among normal human eyes (473–595 μm; mean = 534 μm),4 the phenotypic variation has little direct impact on the quality of vision. However, individuals at the lower end of the CCT spectrum are at greater risk for developing keratoconus or progressing from ocular hypertension to glaucoma. Although CCT is highly heritable, the genes known to influence the phenotype account for only a very low proportion of the heritability. In this study, we sought to identify genetic determinants of CCT by using mouse genetics to identify QTL. In crosses of BXD24b and CAST mice, significant CCT-modifying loci were identified on Chr 3 (Cctq4) and Chr 11 (Cctq5). Several loci were also found to pass the suggestive significance threshold in this analysis; of particular interest is a locus on Chr 14. Pairwise scans showed that this locus has a significant additive effect with Cctq5. Further support for this was provided by multiple regression analysis. For this reason, we considered this to be a true QTL and named it Cctq6. Finally, independent analyses of epithelial and stromal thickness uncovered that Cctq4 specifically affects thickness of the epithelium, whereas Cctq5 and Cctq6 specifically affect thickness of the stroma. This is the first indication that the epithelium and stroma are under differential genetic control.
To date, GWAS in humans have identified 27 CCT-associated loci,13,16,23–25 and QTL analysis in mice has identified 6 CCT-associated loci. Some of the genes identified in GWAS were independently identified as CCT regulators because of their association with rare connective tissue disorders (i.e., brittle cornea syndrome and osteogenesis imperfecta).11,12,15 The genes identified by GWAS show an enrichment of pathways involving collagen and extracellular matrix (ECM), which might be expected since the cornea is composed largely of an ECM-rich stroma. Other CCT-influencing genes (e.g., Twist2, Bnc1, Bcl-2, and Bax) have been identified through studies that used candidate-driven approaches.44–46 A comparison of the syntenic regions of Cctq4 indicated that this locus overlaps partially with Tiparp, a locus previously reported to be associated with CCT in humans based on a meta-analysis by Lu et al.16 However, Tiparp is unlikely to be the gene underlying the association between Cctq4 and CCT because it (1) does not harbor any protein-affecting DNA base pair changes between the inbred strains we used, and (2) is approximately 37 Mb distant from the SNP with the maximum LOD score. Cctq5 appears not to overlap with previously identified loci. In the case of Cctq6, the 95% Bayes credible interval was quite large, spanning ∼60% of the chromosome. Although two previously identified CCT-associated genes (Fgf9 and Sgcg) lie within the syntenic interval of Cctq6, neither of these is likely to be responsible for the association between Cctq6 and CCT because (1) they are a large distance away from the location with the max LOD score, (2) Sgcg is not expressed in the mouse cornea, and (3) Fgf9 in the strains of mice used does not contain any protein-altering DNA base pair changes.
In our previous study using F2 mice from a cross of C57BLKS/J and SJL/J strains, we identified three other CCT-associated QTL: Cctq1 (at 49 cM on Chr 7), Cctq2 (at 14 cM on Chr 11), and Cctq3 (at 60 cM on Chr 17).35 None of them overlap with the loci found in the present study. This is not surprising as it is common for quantitative traits, such as CCT, to be complex (controlled by many genes) and their associated QTL to be context specific. Because this was an independent cross using different inbred strains of mice, we anticipated discovering different QTL. The wild-derived CAST mouse used here provided substantial genetic heterogeneity from the C57BL/6J-derived BXD24b strain, as well as an increased power to identify loci. The human and mouse data combined suggest that Cctq4-6 are likely novel discoveries.
Among the potential caveats of this study, two merit particular mention. First, the genome-wide scan we conducted was low resolution; consequently, the QTL intervals were large. Because of this, we included only major regulatory element changes and DNA base pair changes that affected an encoded protein in the bioinformatics analyses; we did not include noncoding RNAs or less obvious regulatory element variants. Since the three QTL intervals identified were large and each contained hundreds of genes with many missense polymorphisms, we did not find it reasonable to consider less obvious variants yet. The physical sizes of the QTL need to be narrowed through recombination mapping before any gene (or noncoding element) could be confidently suggested as the causative variant underlying the QTL. The combined mouse and human data point to the possibility that numerous genes contribute to the CCT phenotype. Because these genes contribute to continuous variation in CCT, it is plausible that each of the contributing alleles individually has only small effects on the phenotype and is associated with only subtle changes to protein structure–function. As such, it is possible that genes with subtle amino acid changes should be prioritized before genes with changes such as frame-shift or premature stop mutations that have more drastic consequences for protein function. Regulatory regions and noncoding RNAs are also worthy of closer inspection.
A second caveat of the study is that the analysis of CCT was an accompaniment to an ongoing study using the same strains of mice to examine retinal phenotypes associated with the Cep290 gene. Independently studying a second phenotype in these cohorts was an efficient and ethical means of reducing the overall numbers of mice used, but came with the caveat that all mice studied were homozygous for the Cep290rd16 mutation. Thus, sequence variations linked to Cep290 on chromosome 10 did not segregate in these crosses, and our design did not address Cep290 dependency.
The three loci identified in this study exert their influence specifically on a single corneal layer. This is thought-provoking not only in the context of the basic biology of the cornea, but also with respect to the association of CCT with glaucoma. It is unknown if the risk correlated with a thinner cornea is mediated via the epithelium, the stroma, or a combination of the two. In humans, the stroma composes ∼90% of the total corneal thickness and is more variable in thickness than the epithelium.47,48 Thus far, most of the CCT genes identified by GWAS encode structural proteins (e.g., collagens) and are presumably associated with the stroma; however, none of these genes has been linked to glaucoma susceptibility. If the glaucoma risk is actually associated with a thinner epithelium, the implications would be quite different and would likely support different hypotheses about how CCT and glaucoma are related. Future GWAS studies of CCT might also benefit from separately considering epithelial versus stromal thickness; as their variability can be genetically independent, studying the thickness of each layer might result in an increase in the number of gene associations made.
In sum, this study has identified a multigenic pattern of CCT inheritance between two inbred strains of mice, and identifies three previously unrecognized loci, Cctq4, Cctq5, and Cctq6, of particular significance. These results are relevant not only to studies of CCT, but also to a broad array of ophthalmic studies using mice with the DBA/2J, C57BL/6J, or CAST/EiJ backgrounds, including the collaborative cross and Diversity Outbred mice,49–52 which would be under the influence of these same QTL. In our ongoing work, we intend to pursue fine-mapping experiments to narrow the intervals and ultimately identify the underlying genes.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Karl Broman for technical advice, particularly with the interpretation of the scantwo and multiple regression analyses, and Christine M. Blaumueller for professional editing of the manuscript.
Supported by National Eye Institute Grants EY017673, EY018825, and EY021436.
Disclosure: D.R. Koehn, None; K.J. Meyer, None; M.G. Anderson, None
References
- 1. Lively GD,, Jiang B,, Hedberg-Buenz A,, et al. Genetic dependence of central corneal thickness among inbred strains of mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51: 160–171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Toh T,, Liew SH,, MacKinnon JR,, et al. Central corneal thickness is highly heritable: the twin eye studies. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46: 3718–3722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Zheng Y,, Ge J,, Huang G,, et al. Heritability of central corneal thickness in Chinese: the Guangzhou Twin Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008; 49: 4303–4307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Doughty MJ,, Zaman ML. Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta-analysis approach. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000; 44: 367–408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Aghaian E,, Choe JE,, Lin S,, Stamper RL. Central corneal thickness of Caucasians, Chinese, Hispanics, Filipinos, African Americans, and Japanese in a glaucoma clinic. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111: 2211–2219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Hahn S,, Azen S,, Ying-Lai M,, Varma R, Los Angeles Latino Eye Study Group. Central corneal thickness in Latinos. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44: 1508–1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. La Rosa FA,, Gross RL,, Orengo-Nania S. Central corneal thickness of Caucasians and African Americans in glaucomatous and nonglaucomatous populations. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119: 23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lam AK,, Douthwaite WA. The corneal-thickness profile in Hong Kong Chinese. Cornea. 1998; 17: 384–388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Wolfs RC,, Klaver CC,, Vingerling JR,, Grobbee DE,, Hofman A,, de Jong PT. Distribution of central corneal thickness and its association with intraocular pressure: the Rotterdam Study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 123: 767–772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Yo C,, Ariyasu RG. Racial differences in central corneal thickness and refraction among refractive surgery candidates. J Refract Surg. 2005; 21: 194–197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Abu A,, Frydman M,, Marek D,, et al. Deleterious mutations in the Zinc-Finger 469 gene cause brittle cornea syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2008; 82: 1217–1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. EM, BurkittWright,, HL Spencer,, Daly SB, et al. Mutations in PRDM5 in brittle cornea syndrome identify a pathway regulating extracellular matrix development and maintenance. Am J Hum Genet. 2011; 88: 767–777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lu Y,, Dimasi DP,, Hysi PG,, et al. Common genetic variants near the Brittle Cornea Syndrome locus ZNF469 influence the blinding disease risk factor central corneal thickness. PLoS Genet. 2010; 6: e1000947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Dimasi DP,, Burdon KP,, Craig JE. The genetics of central corneal thickness. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010; 94: 971–976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Pederson U,, Bramsen T. Central corneal thickness in osteogenesis imperfecta and otosclerosis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 1984; 46: 38–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Lu Y,, Vitart V,, Burdon KP,, et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify multiple loci associated with central corneal thickness and keratoconus. Nat Genet. 2013; 45: 155–163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Gordon MO,, Beiser JA,, Brandt JD,, et al. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: baseline factors that predict the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002; 120: 714–720, discussion 829–830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. European Glaucoma Prevention Study Group , Miglior S, Pfeiffer N, et al. Predictive factors for open-angle glaucoma among patients with ocular hypertension in the European Glaucoma Prevention Study. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114: 3–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Leske MC,, Heijl A,, Hyman L,, et al. Predictors of long-term progression in the early manifest glaucoma trial. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114: 1965–1972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Alsbirk PH. Corneal thickness. II. Environmental and genetic factors. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1978; 56: 105–113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Landers JA,, Hewitt AW,, Dimasi DP,, et al. Heritability of central corneal thickness in nuclear families. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50: 4087–4090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Vitart V,, Bencic G,, Hayward C,, et al. Heritabilities of ocular biometrical traits in two Croatian isolates with extended pedigrees. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51: 737–743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Cornes BK,, Khor CC,, Nongpiur ME,, et al. Identification of four novel variants that influence central corneal thickness in multi-ethnic Asian populations. Hum Mol Genet. 2012; 21: 437–445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Vitart V,, Bencic G,, Hayward C,, et al. New loci associated with central cornea thickness include COL5A1, AKAP13 and AVGR8. Hum Mol Genet. 2010; 19: 4304–4311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Vithana EN,, Aung T,, Khor CC,, et al. Collagen-related genes influence the glaucoma risk factor, central corneal thickness. Hum Mol Genet. 2011; 20: 649–658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Treuting PM,, Wong R,, Tu DC,, Phan I. Special senses: eye. : Treuting PM,, Dintzis SM, Comparative Anatomy and Histology: A Mouse and Human Atlas. San Diego, CA: Elsevier; 2012: 400–401. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Taylor BA. Genetic Variants and Strains of the Laboratory Mouse. 2nd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 28. Chang B,, Khanna H,, Hawes N,, et al. In-frame deletion in a novel centrosomal/ciliary protein CEP290/NPHP6 perturbs its interaction with RPGR and results in early-onset retinal degeneration in the rd16 mouse. Hum Mol Genet. 2006; 15: 1847–1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Chapman VM,, Ruddle FH. Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (got) genetics in the mouse: polymorphism of got-1. Genetics. 1972; 70: 299–305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Petkov PM,, Cassell MA,, Sargent EE,, et al. Development of a SNP genotyping panel for genetic monitoring of the laboratory mouse. Genomics. 2004; 83: 902–911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Gao F,, Toriyama K,, Ma H,, Nagata T. Light microscopic radioautographic study on DNA synthesis in aging mice corneas. Cell Mol Biol. 1993; 39: 435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Broman KW,, Wu H,, Sen S,, Churchill GA. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics. 2003; 19: 889–890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Broman KW,, Sen S. A Guide to QTL Mapping with R/qtl. New York: Springer Science+Business Media; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 34. Li R,, Lyons MA,, Wittenburg H,, Paigen B,, Churchill GA. Combining data from multiple inbred line crosses improves the power and resolution of quantitative trait loci mapping. Genetics. 2005; 169: 1699–1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lively GD,, Koehn D,, Hedberg-Buenz A,, Wang K,, Anderson MG. Quantitative trait loci associated with murine central corneal thickness. Physiol Genomics. 2010; 42: 281–286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Lander E,, Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet. 1995; 11: 241–247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Keane TM,, Goodstadt L,, Danecek P,, et al. Mouse genomic variation and its effect on phenotypes and gene regulation. Nature. 2011; 477: 289–294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Yalcin B,, Wong K,, Agam A,, et al. Sequence-based characterization of structural variation in the mouse genome. Nature. 2011; 477: 326–329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Petkov PM,, Ding Y,, Cassell MA,, et al. An efficient SNP system for mouse genome scanning and elucidating strain relationships. Genome Res. 2004; 14: 1806–1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Cheverud JM,, Lawson HA,, Funk R,, Zhou J,, Blankenhorn EP,, Heber-Katz E. Healing quantitative trait loci in a combined cross analysis using related mouse strain crosses. Heredity. 2012; 108: 441–446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Parker CC,, Carbonetto P,, Sokoloff G,, Park YJ,, Abney M,, Palmer AA. High-resolution genetic mapping of complex traits from a combined analysis of F2 and advanced intercross mice. Genetics. 2014; 198: 103–116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Flint J,, Valdar W,, Shifman S,, Mott R. Strategies for mapping and cloning quantitative trait genes in rodents. Nat Rev Genet. 2005; 6: 271–286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Lynch M,, Walsh B. Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Traits. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, Inc.; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 44. Robertson DM,, Ladage PM,, Yamamoto N,, Jester JV,, Petroll WM,, Cavanagh HD. Bcl-2 and Bax regulation of corneal homeostasis in genetically altered mice. Eye Contact Lens. 2006; 32: 3–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Weaving L,, Mihelec M,, Storen R,, et al. Twist2: role in corneal stromal keratocyte proliferation and corneal thickness. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51: 5561–5570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Zhang X,, Tseng H. Basonuclin-null mutation impairs homeostasis and wound repair in mouse corneal epithelium. PLoS One. 2007; 2: e1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Reinstein DZ,, Archer TJ,, Gobbe M,, Silverman RH,, Coleman DJ. Epithelial thickness in the normal cornea: three-dimensional display with Artemis very high-frequency digital ultrasound. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24: 571–581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Reinstein DZ,, Archer TJ,, Gobbe M,, Silverman RH,, Coleman DJ. Stromal thickness in the normal cornea: three-dimensional display with artemis very high-frequency digital ultrasound. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25: 776–786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Mott R,, Flint J. Dissecting quantitative traits in mice. Ann Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2013; 14: 421–439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Churchill GA,, Airey DC,, Allayee H,, et al. The Collaborative Cross, a community resource for the genetic analysis of complex traits. Nat Genet. 2004; 36: 1133–1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Churchill GA,, Gatti DM,, Munger SC,, Svenson KL. The Diversity Outbred mouse population. Mammal Genome. 2012; 23: 713–718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Svenson KL,, Gatti DM,, Valdar W,, et al. High-resolution genetic mapping using the Mouse Diversity outbred population. Genetics. 2012; 190: 437–447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.