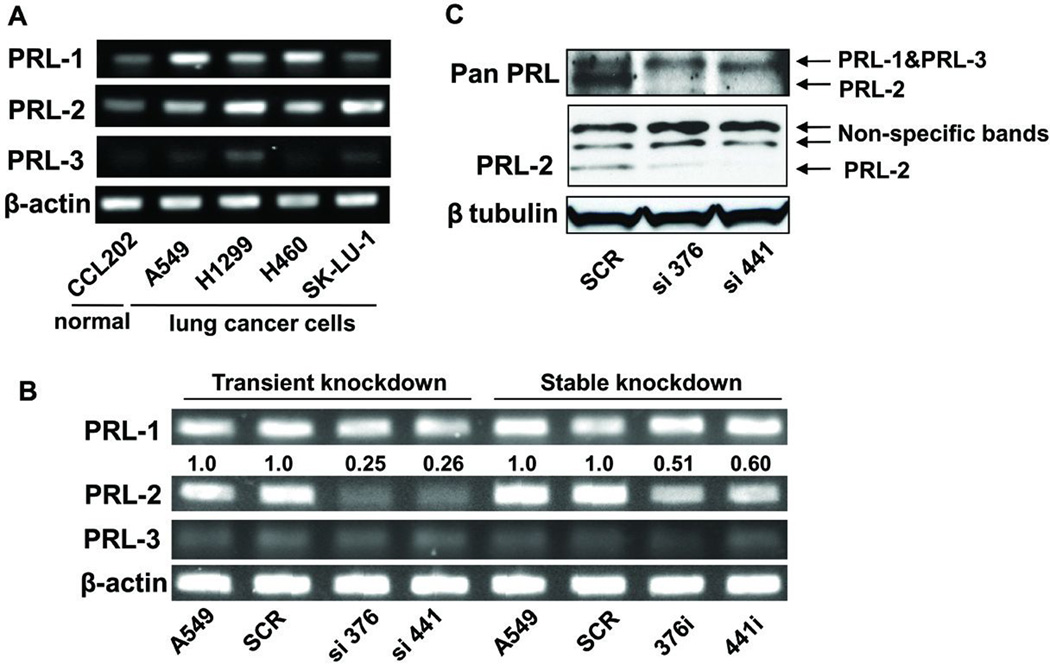
Figure 1. PRL-2 mRNA and protein levels were significantly suppressed in the PRL-2 knockdown cells.
The cell clone numbers 376 and 441 indicate the starting nucleotide number of siRNA- or shRNA-targeting sequences of PRL-2 mRNA. RT-PCR and Western blotting images were processed and quantified with Fuji Multi Gauge software (Fujifilm). A) RT-PCR demonstrated that PRL-2 was over-expressed in several lung cancer cells including A549 cells. β-actin was used as internal control. B) PRL-2 was selectively down-regulated at the mRNA level in cells with transient and stable PRL-2 knockdown. The siRNA transiently transfected cells displayed ~80% decrease in PRL-2 mRNA level, while there was a ~50% decrease in the shRNA transfected stable knockdown cells. β-actin was used as the internal control to determine expression levels. The average fold changes, as shown above the blot, were calculated from three independent experiments and normalized to relative PRL-2 levels in the parental A549 cells. C) PRL-2 protein level was selectively down-regulated. The upper blot was obtained with an antibody from R & D Systems (MAB32191) that recognizes all three PRL proteins and the middle blot was produced with a PRL-2 specific polyclonal antibody from Bethyl (BL1205). β tubulin was used as an internal control.