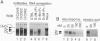Abstract
Cell cycle-controlled human histone genes are coordinately expressed during S phase, and transcriptional regulation involves a series of trans-acting factors (HiNFs). The proliferation-specific factor HiNF-D interacts with multiple recognition motifs in histone H4, H3, and H1 promoters. Using gel shift immunoassays, we show that CDC2, cyclin A, and an RB-related protein are ubiquitous subunits of HiNF-D binding activity isolated from several cell types. HiNF-D levels in vivo are sensitive to okadaic acid and staurosporine, indicating that HiNF-D activity and/or assembly is influenced by phosphorylation status. Thus, HiNF-D appears to be a multicomponent phosphoprotein that participates in coordinate control of multiple histone H4, H3, and H1 genes during the cell cycle. The presence of cell cycle mediators in the HiNF-D complex suggests linkage between transcriptional control of histones, enzymes involved in DNA synthesis, and the onset of DNA replication during the G1/S phase transition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Urso G., Marraccino R. L., Marshak D. R., Roberts J. M. Cell cycle control of DNA replication by a homologue from human cells of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):786–791. doi: 10.1126/science.2173140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. RNA polymerase II transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2 require metal to bind specific DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4582–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Markell P. J., Pardee A. B. Thymidine kinase transcription is regulated at G1/S phase by a complex that contains retinoblastoma-like protein and a cdc2 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Richman R., Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Lodgson N., Harper J. W. CDK2 encodes a 33-kDa cyclin A-associated protein kinase and is expressed before CDC2 in the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2907–2911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Xing Y. G., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the cDNA for p107, a retinoblastoma gene product-related protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1155–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90038-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadbois D. M., Hamaguchi J. R., Swank R. A., Bradbury E. M. Staurosporine is a potent inhibitor of p34cdc2 and p34cdc2-like kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):80–85. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91160-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., McCall C., Whyte P., Franza B. R., Jr Human cyclin A and the retinoblastoma protein interact with similar but distinguishable sequences in the adenovirus E1A gene product. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling R., Partridge J. F., Bandara L. R., Burden N., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., La Thangue N. B. A new component of the transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):83–87. doi: 10.1038/362083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña X., Claudio P. P., De Luca A., Sang N., Giordano A. PISSLRE, a human novel CDC2-related protein kinase. Oncogene. 1994 Jul;9(7):2097–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña X., De Luca A., Sang N., Fu Y., Claudio P. P., Rosenblatt J., Morgan D. O., Giordano A. PITALRE, a nuclear CDC2-related protein kinase that phosphorylates the retinoblastoma protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3834–3838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Demetrick D., Beach D. Isolation of the Rb-related p130 through its interaction with CDK2 and cyclins. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2378–2391. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. The regulation of histone gene expression during the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer R., Denhardt D. T. Cell cycle-regulated and proliferation stimulus-responsive genes. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(4):247–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis J., Owen T. A., van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Ramsey-Ewing A., Kennedy M. B., Carter R., Cosenza S. C., Soprano K. J., Lian J. B. Tumor cells exhibit deregulation of the cell cycle histone gene promoter factor HiNF-D. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q. J., Bautista C., Edwards G. M., Defeo-Jones D., Jones R. E., Harlow E. Antibodies specific for the human retinoblastoma protein identify a family of related polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5792–5799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Cross F., Fisher A., Schumacher J., Leguellec K., Philippe M., Roberts J. M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L. J., Naeve G. S., Lee A. S. Temporal regulation of cyclin A-p107 and p33cdk2 complexes binding to a human thymidine kinase promoter element important for G1-S phase transcriptional regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3554–3558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Graham C., Lacy S., Duncan A. M., Whyte P. The adenovirus E1A-associated 130-kD protein is encoded by a member of the retinoblastoma gene family and physically interacts with cyclins A and E. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2366–2377. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayol X., Graña X., Baldi A., Sang N., Hu Q., Giordano A. Cloning of a new member of the retinoblastoma gene family (pRb2) which binds to the E1A transforming domain. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2561–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A. The regulation of histone synthesis in the cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:827–861. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.004143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
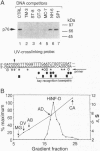
- Pauli U., Chrysogelos S., Stein G., Stein J., Nick H. Protein-DNA interactions in vivo upstream of a cell cycle-regulated human H4 histone gene. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1308–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.3035717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey-Ewing A., Van Wijnen A. J., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Delineation of a human histone H4 cell cycle element in vivo: the master switch for H4 gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4475–4479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Stein J. L., van Wijnen A. J., Lian J. B. Histone gene transcription: a model for responsiveness to an integrated series of regulatory signals mediating cell cycle control and proliferation/differentiation interrelationships. J Cell Biochem. 1994 Apr;54(4):393–404. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240540406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K. L., Dell'Orco R. T., van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Multiple mechanisms regulate the proliferation-specific histone gene transcription factor HiNF-D in normal human diploid fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 17;31(10):2812–2818. doi: 10.1021/bi00125a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Choi T. K., Owen T. A., Wright K. L., Lian J. B., Jaenisch R., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Involvement of the cell cycle-regulated nuclear factor HiNF-D in cell growth control of a human H4 histone gene during hepatic development in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2573–2577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Protein/DNA interactions involving ATF/AP1-, CCAAT-, and HiNF-D-related factors in the human H3-ST519 histone promoter: cross-competition with transcription regulatory sites in cell cycle controlled H4 and H1 histone genes. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Dec;47(4):337–351. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Ramsey-Ewing A. L., Bortell R., Owen T. A., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Transcriptional element H4-site II of cell cycle regulated human H4 histone genes is a multipartite protein/DNA interaction site for factors HiNF-D, HiNF-M, and HiNF-P: involvement of phosphorylation. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Jun;46(2):174–189. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240460211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Human H4 histone gene transcription requires the proliferation-specific nuclear factor HiNF-D. Auxiliary roles for HiNF-C (Sp1-like) and HiNF-A (high mobility group-like). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15034–15042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., van den Ent F. M., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Overlapping and CpG methylation-sensitive protein-DNA interactions at the histone H4 transcriptional cell cycle domain: distinctions between two human H4 gene promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3273–3287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ent F. M., van Wijnen A. J., Last T. J., Bortell R., Stein J. L., Lian J. B., Stein G. S. Concerted control of multiple histone promoter factors during cell density inhibition of proliferation in osteosarcoma cells: reciprocal regulation of cell cycle-controlled and bone-related genes. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2399–2409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ent F. M., van Wijnen A. J., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Cell cycle controlled histone H1, H3, and H4 genes share unusual arrangements of recognition motifs for HiNF-D supporting a coordinate promoter binding mechanism. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Jun;159(3):515–530. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041590316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]