Abstract
Eras encodes a Ras-like GTPase protein that was originally identified as an embryonic stem cell-specific Ras. ERAS has been known to be required for the growth of embryonic stem cells and stimulates somatic cell reprogramming, suggesting its roles on mouse early embryonic development. We now report a dynamic expression pattern of Eras during mouse peri-implantation development: its expression increases at the blastocyst stage, and specifically decreases in E7.5 mesoderm. In accordance with its expression pattern, the increased expression of Eras promotes cell proliferation through controlling AKT activation and the commitment from ground to primed state through ERK activation in mouse embryonic stem cells; and the reduced expression of Eras facilitates primitive streak and mesoderm formation through AKT inhibition during gastrulation. The expression of Eras is finely regulated to match its roles in mouse early embryonic development during which Eras expression is negatively regulated by the β-catenin pathway. Thus, beyond its well-known role on cell proliferation, ERAS may also play important roles in cell lineage specification during mouse early embryonic development.
Keywords: Eras, primitive streak, mesoderm, embryonic stem cells, cell lineage
1. Introduction
Totipotent mammalian zygote undergoes several cleavage divisions to form the blastocyst composed of the trophoblast and inner cell mass which continuously segregates into the hypoblast and the epiblast [1]. Because the epiblast can give rise to all cell lineages of the fetus and individual epiblast cells can commit into three germ layers when they are injected into blastocyst, pre-implantation epiblast is thought to be the developmental ground state [2]. After implantation, the embryo dramatically increases its cell number dependent on a rapid burst of pluripotent cell proliferation with average generation times of approximately 4.5–8.0 h [3]; at the same time, the embryo enters the primed state and initiates cell lineage specification through gastrulation, during which three primary germ layers are established [2]. Numerous cell-cycle regulators and pluripotent transcription factors have been shown to be involved in the rapid proliferation in mouse early embryos [4]. However, little is known about cell lineage specification during this process.
Mouse early embryos include a population of pluripotent cells which were cultured with fibroblast feeder cells in vitro to form embryonic stem cells (ESCs) [5,6]. Although the precise origin and identity of ESCs in vivo has long been debated [7], recent research showed that mouse ground state ESCs closely resemble the cells in pre-implantation epiblast of E4.5 embryos [8]. The gene expression pattern of ESCs is heterogeneous when they are cultured in serum and leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) without feeders [9]; however, their gene expression pattern becomes homogeneous when they are maintained with the inhibitors MEK and GSK3 (2i) [10]. Considering their stability, homogeneity and equipotency, ESCs in the 2i condition are thought to be an early epiblast-like ground state for embryonic development [11]. Thus, the pluripotency is proposed as two phases: naive and primed state [2]. Mouse ESCs can propagate without ERK signalling; however, the independence of ESCs on ERK signalling is lost in post-implantation egg cylinder cells [8]. The inhibition of ERK signalling is critical for maintaining ESCs in the ground state [12–14], and the activation of ERK1/2 by FGF4 is important for naive ESCs to exit from self-renewal [15]. Other factors, FGFR, SHP2 and GRB2, have also been shown to regulate ERK activity at different molecular levels in ESCs [15–17]. However, the detailed regulation of ESC pluripotency from naive into primed state still needs to be defined.
Gastrulation is a critical process of embryogenesis, through which three primary germ layers are established. Nodal heterozygous mouse embryos undergo gastrulation, but then display abnormalities in positioning of the antero-posterior axis, midline patterning and left–right asymmetric development. Furthermore, Nodal null mutations show blocked gastrulation and mesoderm formation [18]. In Wnt3 knockout embryos, egg cylinder develops normally, but the embryos do not form primitive streak (PS), mesoderm or node [19]. Bmp4 homozygous mutant embryos die between E6.5 and E9.5, and show little or no mesoderm differentiation [20]. Thus Nodal, Wnt and Bmp4 signalling pathways play critical roles in cell specification of three primary germ layers during mouse gastrulation [18–21]. In addition, E-cadherin is decreased during gastrulation and has been shown to function through epithelial–mesenchymal transitions [22–25], implying the important roles of downregulated genes during this process. Currently, the roles of downregulated genes during gastrulation are largely unclear.
Eras, encoding a Ras-like GTPase protein, was originally identified as Ecat5 (ES cell-associated transcripts) by analysing the mouse EST databases and is involved in tumourigenicity of mouse ESCs [26]. It has been shown that ERAS binds to phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K; p110δ), instead of Raf1, to phosphorylate AKT to promote the growth of ESCs [26] and that increased ERAS–AKT–FOXO1 signalling stimulates the efficiency of somatic cell reprogramming [27], suggesting its role in cell proliferation of mouse early embryonic development [28]. Human ERAS was initially characterized as a homologue of mouse Eras [26]; later research revealed the ERAS gene is absent in human ESCs and concluded that ERAS exists as a pseudogene in humans. Several groups reported that human ERAS is involved in human tumourigenesis. The full-length transcript and protein were recently reported to be expressed in several gastric cancer cell lines and in some human gastric cancer tissues [29–32]. Currently, the exact role of Eras in mouse and human early embryonic development is still largely unknown.
In this study, we find Eras expression increases at the blastocyst stage, and decreases specifically in E7.5 mesoderm. The enhanced expression of Eras stimulates cell proliferation through AKT activation and accelerates ESC commitment from ground to primed state through ERK activation. The reduction of Eras facilitates PS and mesoderm differentiation through AKT inhibition during germ layer specification. Furthermore, we demonstrate the expression of Eras is negatively regulated by β-catenin signal in ESCs, epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) and mouse early embryos.
2. Results
2.1. The dynamic pattern of Eras expression during mouse germ layer specification
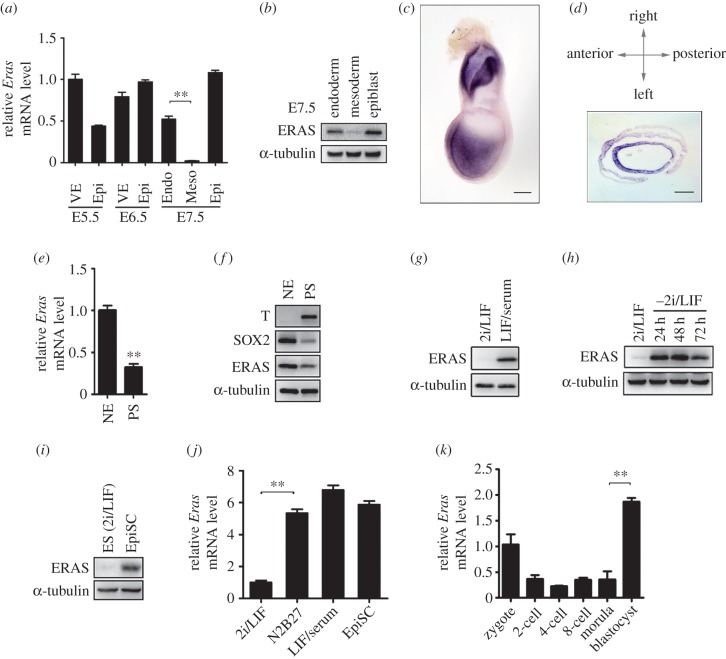
In order to screen the functional genes involved in germ layer specification, we performed microarray analysis on E7.5 endoderm, mesoderm and epiblast. Interestingly, we found Eras mRNA was highly enriched in endoderm and epiblast compared with its expression in mesoderm of E7.5 embryos (data not shown). To investigate the detailed expression of Eras in mouse germ layer specification, we separated the germ layers from E5.5 to E7.5 embryonic regions. Real-time RT-PCR showed that Eras mRNA was highly expressed in E5.5–7.5 endoderm and epiblast compared with its expression in E7.5 mesoderm (figure 1a). ERAS protein was observed to be dramatically downregulated in mesoderm (figure 1b). The location of Eras mRNA in E7.5 embryo was further detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization. It was enriched in the anterior and extraembryonic regions of E7.5 embryo (figure 1c). In the section of the E7.5 embryonic region, Eras mRNA concentrated in anterior visceral endoderm and epiblast, in which its expression was higher in neuroectoderm than that in PS (figure 1d). When E7.5 epiblast was separated into anterior neuroectoderm and posterior PS by micromanipulation, Eras mRNA and protein were observed to be abundantly expressed in the anterior neuroectoderm compared with the PS (figure 1e,f).
Figure 1.
The expression of Eras in mouse early embryos and embryonic stem cells. (a) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of Eras mRNA in E5.5–7.5 germ layers (one-way ANOVA; **p < 0.01). VE, visceral endoderm; Epi, epiblast; Endo, endoderm; Meso, mesoderm. (b) Western blot analysis of ERAS protein in E7.5 germ layers. (c) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of Eras mRNA in E7.5 mouse embryos. (d) Cross-section of E7.5 embryonic region after whole-mount in situ hybridization. Scale bars in (c) and (d), 100 µm. (e,f) Expression of Eras in E7.5 neuroectoderm (NE) and primitive streak (PS) detected by real-time RT-PCR (Student's t-test; **p < 0.01) (e) and western blot (f). (g) Western blot analysis of ERAS in ESCs cultured in 2i/LIF and LIF/serum medium. (h) ERAS protein expression in ESCs cultured in 2i/LIF and 2i/LIF withdrawal for indicated time points. (i) Comparison of ERAS protein expression between ESCs cultured in 2i/LIF medium and EpiSCs. (j) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of Eras mRNA in ESCs cultured in 2i/LIF, N2B27, LIF/serum and EpiSCs (one-way ANOVA; **p < 0.01). (k) Eras mRNA expression from zygote to blastocyst stage was detected by real-time RT-PCR (one-way ANOVA; **p < 0.01).
ESCs are usually cultured in a LIF/serum condition [33], and can also be maintained at ground state in 2i/LIF (CHIR99021, PD0325901 and LIF) medium, which had been used for derivation of ESCs from previously recalcitrant mouse strains and rat [12–14]. Surprisingly, ERAS protein was dramatically decreased in ESCs cultured in 2i/LIF medium compared with the LIF/serum condition (figure 1g). In addition, ERAS was increased in the ESCs after 2i/LIF withdrawal from N2B27 medium (figure 1h). We also examined the expression of ERAS in epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs). Compared with the expression in ground state ESCs (cultured in 2i/LIF medium), both Eras protein and mRNA levels were much higher in EpiSCs (figure 1i,j). During mouse pre-implantation development, the expression of Eras mRNA was decreased in two-cell embryos, and then significantly increased in blastocysts (figure 1k). Because ESCs and EpiSCs are isolated from early stage embryos, they may represent epiblast cells in mouse peri-implantation embryos. Thus, we conclude Eras is highly expressed in specific types of cells in mouse peri-implantation embryos.
2.2. Establishing ESC lines for Eras knockdown and over-expression
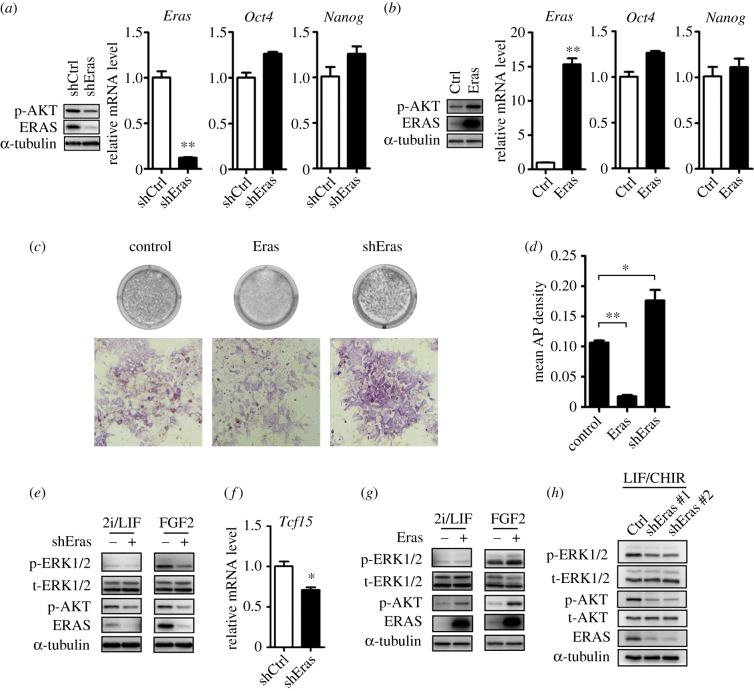
To investigate the function of ERAS, we established mouse ESC lines for the stable knockdown and over-expression of Eras by lenti-virus vectors. Compared with the control, the mRNA of Eras reduced 88% in the knockdown ESCs and increased approximately 15-fold in the over-expression ESCs (figure 2a,b). The efficiencies of knockdown and over-expression of Eras were further confirmed by western blot (figure 2a,b). Eras knockdown and over-expression ESC lines could be routinely passaged in ESC culture medium containing LIF and serum on MEF feeder (data not shown). Consistent with previous findings [26], the Eras over-expression cell line grew fast and the knockdown cell line grew slowly (data not shown); knockdown of Eras was observed to also inhibit AKT phosphorylation and over-expressed Eras accelerated AKT phosphorylation in ESCs (figure 2a,b). Real-time RT-PCR results showed that knockdown and over-expression of Eras did not significantly affect pluripotent markers expression (figure 2a,b). Thus, ESC lines for stable Eras knockdown and over-expression were established.
Figure 2.
Eras was important for ESCs to exit from ground state through regulating ERK activity. (a,b) Efficiency of Eras knockdown (a) and over-expression (b) in ESCs cultured in LIF/serum condition. Pluripotency markers showed normal expression (Student's t-test; **p < 0.01). (c,d) AP staining analysis of ESCs was performed after 3 days of differentiation in N2B27 medium. Weaker AP staining was observed in Eras over-expressed ESCs, while Eras shRNA ESCs showed increased AP staining, indicating Eras expression accelerated the exiting of ESCs from ground state. Mean density was calculated by (IOD SUM)/area (one-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). (e) Eras knockdown inhibited ERK phosphorylation during ESC commitment. ESCs were cultured in 2i/LIF, or differentiated in N2B27 containing 12 ng ml−1 FGF2 for 24 h. (f) Tcf15 expression was decreased during ESC commitment after Eras was knocked down. (Student's t-test; *p = 0.013). (g) Eras over-expression increased ERK phosphorylation during ESC commitment. Western blot analysis was performed after ESCs were cultured in 2i/LIF or differentiated in N2B27 containing FGF2 for 24 h. (h) Undifferentiated ESCs cultured in LIF/CHIR showed decreased phosphorylation of AKT and ERK in Eras shRNA ESCs.
2.3. Eras is required for efficient ESC commitment through ERK signalling
Beyond its known role in cell growth, the dramatic increase of ERAS in ESCs during the transition from ground into primed state prompted us to investigate its novel function during this transition. To this end, the ground state ESCs were cultured in N2B27 medium on matrigel-coated plates without 2i/LIF to induce differentiation for 3 days. Alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining was performed to assay the undifferentiated ESCs. Compared with the control, significant weaker AP staining was observed in Eras over-expression ESCs, suggesting that Eras participated in the progression from ground state into primed state (figure 2c,d). When Eras was knockeddown, more AP positive cells were detected in the differentiating ESCs (figure 2c,d). Furthermore, we replated single cells after 3 days of differentiation in 2i/LIF and quantified the percentage of undifferentiated ES cell colonies, which were visualized by AP staining. Compared with control, Eras over-expression significantly decreased the clonogenicity of ESCs after a 3-day differentiation, and Eras shRNA knockdown cells showed increased colony-forming ability (electronic supplementary material, figure S1). Thus, these data suggest ERAS may also play an important role in the transition of mouse ESCs from ground into primed state.
Ras family proteins function mainly through Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways [34,35]. The ERK pathway is one of MAPK pathways, and its inhibition is essential for maintaining the ground state of mouse ESCs [12,15]. To examine if ERAS was involved in the ERK pathway during ESC transition from ground into primed state, we cultured Eras knockdown and over-expressed ESCs in N2B27 medium for 24 h by adding FGF2, which had been shown to promote ESC commitment through ERK activation [36], and then analysed phospho-ERK by western blot. Eras knockdown inhibited ERK phosphorylation during ESC commitment (figure 2e). In addition, Tcf15, a critical transcription factor regulated by ERK signalling in the primed state [37], was significantly decreased by Eras knockdown during the commitment of the ESCs for 24 h (figure 2f). Furthermore, Eras over-expression slightly enhanced phospho-ERK level during the commitment of ESCs (figure 2g). To detect the role of Eras on ERK phosphorylation in undifferentiated ESCs, we cultured Eras knockdown ESCs in LIF/CHIR condition. Compared with the control, phospho-ERK was also decreased in Eras knockdown ESCs (figure 2h). Thus, these results show that Eras regulates ERK phosphorylation in both undifferentiated ESCs and differentiating ESCs from ground state.
ERAS has been shown to directly interact with PI3K (p110δ), but not bind to Raf, to activate the AKT pathway [26]. To examine if ERAS regulated ERK activity through the AKT pathway, Ly294002, a highly specific inhibitor of PI3K, was added to the culture medium. Ly294002 could efficiently inhibit AKT phosphorylation, but did not affect ERK activity (electronic supplementary material, figure S2). Thus, ERK is not a direct target of AKT during ESC commitment from ground state into primed state.
2.4. Downregulated Eras is important for primitive streak and mesoderm formation
Considering the specific low expression of Eras in PS and mesoderm (figure 1a–f), we assumed that the downregulated expression of this gene also may be important for the specification of PS and mesoderm. Compared with ground ESCs, ESCs cultured in LIF/serum medium have distinct transcriptome and epigenome profiles [38]. These cells represent a relatively primed and metastable state without ERK inhibition, and recapitulate the overall methylation pattern of epiblast cells [39–41]. In our experiments, we also observed increased epiblast markers (Fgf5 and Tcf15) expression in ESCs cultured in LIF/serum (electronic supplementary material, figure S3a). Furthermore, we performed spontaneous differentiation of control and Eras knockdown ESCs in serum containing medium, starting from ESCs cultured in 2i/LIF and LIF/serum. Primitive steak marker (T) expression showed more rapid upregulation in Eras knockdown ESCs differentiated from the LIF/serum condition (electronic supplementary material, figure S3b,c), supporting that ESCs cultured in LIF/serum represent a relatively primed state [39]. Considering that Eras functions in the ESC commitment from ground into primed state (figure 2), it might not be appropriate to use ground state ESCs for Eras functional analysis during germ layer specification. Therefore, we used ESCs cultured in LIF/serum medium as an original condition to investigate the role of Eras on germ layer specification during embryoid body (EB) formation and cytokine-induced differentiation.
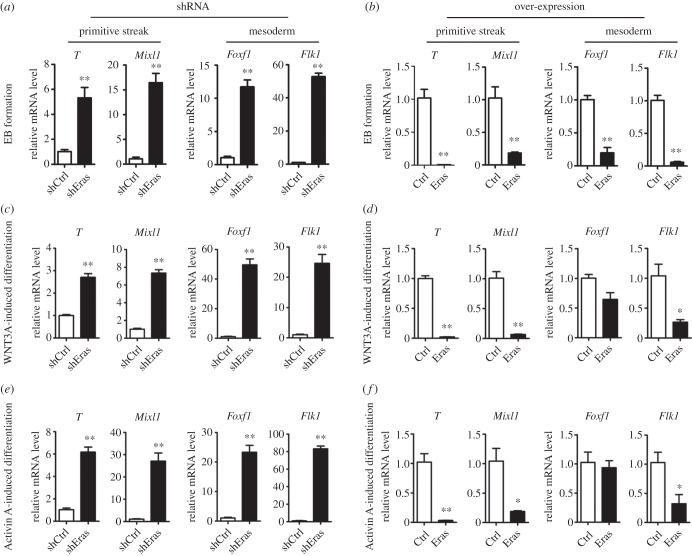
Although there were some differences in the cell growth, Eras over-expression and knockdown ESCs formed grossly normal EBs (data not shown). Compared with the control, Eras knockdown dramatically increased the expression of markers in of PS (T and Mixl1), mesoderm (Flk1 and Foxf1) and endoderm (Sox17 and Foxa2), and decreased neuroectoderm markers (Sox1 and Pax6) expression during EB formation (figure 3a; electronic supplementary material, figure S4a). In addition, over-expressed Eras significantly decreased the expression of mesoderm and PS markers in this ESC differentiation system (figure 3b), but the neuroectoderm and endoderm markers were not affected significantly (electronic supplementary material, figure S4b). These results suggest that downregulated expression of Eras facilitates the differentiation of PS and mesoderm cells.
Figure 3.
Eras negatively regulated the differentiation of ESCs into primitive streak and mesoderm. (a) Eras knockdown promoted the differentiation of ESCs into primitive streak and mesoderm during EB formation. (b) Eras over-expression inhibited the differentiation of ESCs into primitive streak and mesoderm during EB formation. (c–f) Eras negatively regulated the differentiation of ESCs into primitive streak and mesoderm induced by WNT3A and Activin A, respectively. Primitive streak markers: T and Mixl1; mesoderm markers: Flk1 and Foxf1 (Student's t-test; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05).
To further confirm the role of ERAS on the formation of PS and mesoderm, we employed a cytokine-induced differentiation system [42]. WNT3A and Activin A were used to induce ESC differentiation into PS and mesoderm lineages [43]. In these systems, the expression of PS and mesoderm markers was significantly increased during cytokine-induced differentiation in Eras knowndown ESCs. In contrast, the expression of PS and mesoderm markers was significantly decreased in the ESCs with over-expressed Eras during the differentiation (figure 3c–f).
Although the inhibition of PI3K did not affect the activity of ERK in ESCs (electronic supplementary material, figure S2), the inhibition of PI3K and AKT was reported to promote the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells [44–46]. We then examined the role of Ly294002 on cytokine-induced differentiation of mouse ESCs. Ly294002 efficiently promoted the specification of PS and mesoderm after WNT3A or Activin A treatment (figure 4a,b). Furthermore, we found that Eras knockdown also decreased AKT phosphorylation and promoted PS marker (T) expression in mouse EpiSCs, without effect on ERK activity (figure 4c). Consistently, Ly294002 treatment decreased AKT phosphorylation and increased T expression in mouse EpiSCs (figure 4d). Thus, these results suggest that Eras functions through AKT during the formation of PS and mesoderm.
Figure 4.
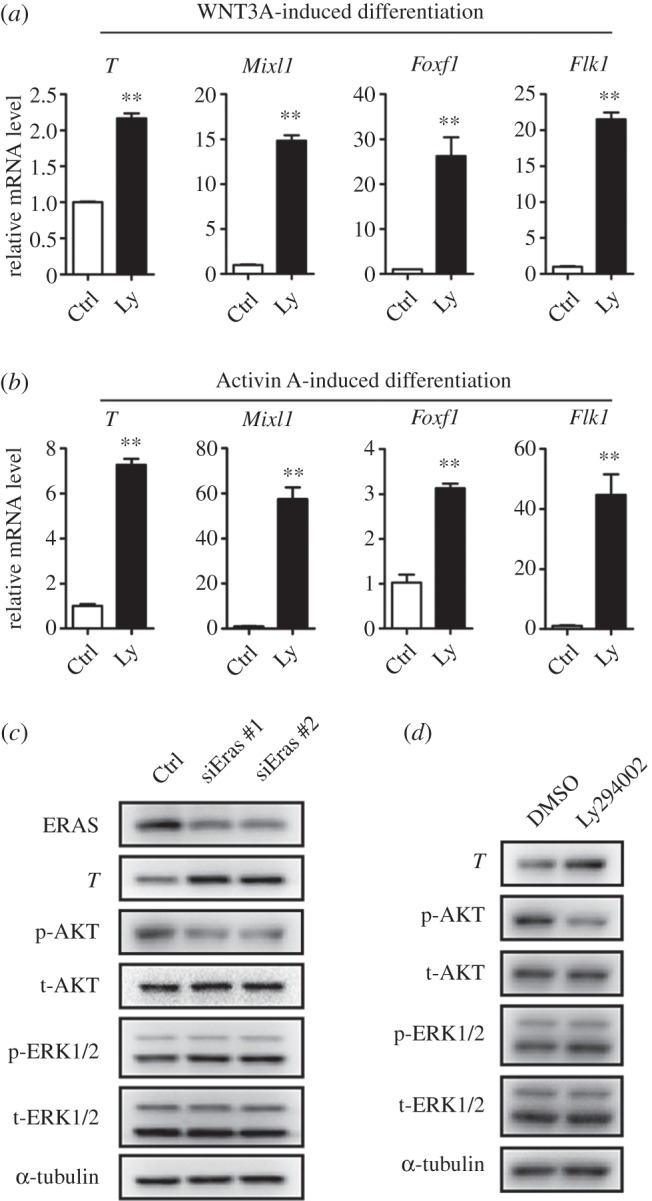
Eras inhibited the differentiation of ESCs and EpiSCs into primitive streak and mesoderm through AKT activation. (a,b) Inhibition of AKT by Ly294002 (Ly, 10 µM) promoted WNT3A or Activin A induced primitive streak and mesoderm differentiation (Student's t-test; **p < 0.01). (c) Eras knockdown facilitated primitive streak differentiation in EpiSCs and inhibited AKT activity. (d) Inhibition of AKT by Ly294002 (10 µM) promoted primitive streak marker T expression in EpiSCs.
Altogether, these results with different ESC differentiation systems consistently support that Eras downregulation is important for the formation of PS and mesoderm, suggesting the role of downregulated Eras during mouse early embryonic development.
2.5. Eras is negatively regulated by β-catenin in stem cells
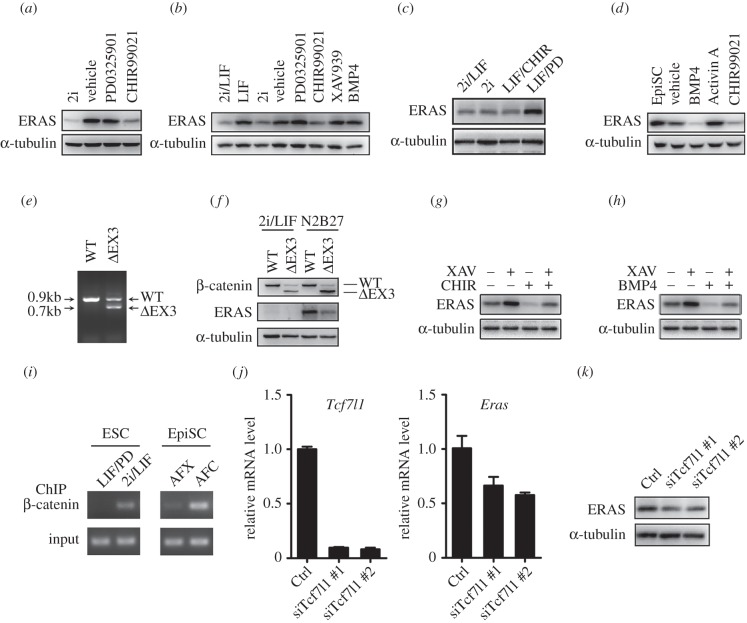
The dynamic expression pattern of Eras during embryonic development and the important roles of this gene during cell growth and specification prompted us to investigate the regulation of ERAS expression. Eras was inhibited in 2i medium (CHIR99021 and PD0325901) (figure 1g,h), indicating these two inhibitors regulated the expression of Eras. To investigate this possibility, we cultured the ESCs in N2B27 with 2i, CHIR99021 or PD0325901. We found ERAS was inhibited by CHIR99021, but not PD0325901, in N2B27 medium (figure 5a). Furthermore, in the ESCs cultured in DMEM/serum medium, CHIR99021, but not other factors, was found to significantly inhibit ERAS expression (figure 5b). In order to exclude the indirect effect of differentiation on ERAS expression, we detected ERAS expression in the undifferentiated ESCs by mixing two of three factors (PD0325901, CHIR99021 and LIF). ERAS was also decreased in the presence of CHIR99021 (figure 5c), indicating the effect of CHIR99021 on ERAS expression was not dependent on the differentiation state. However, in EpiSCs, not only CHIR99021 but also BMP4 could dramatically inhibit ERAS expression (figure 5d). Thus, CHIR99021 is a major factor for the downregulation of Eras in both ESCs and EpiSCs.
Figure 5.
ERAS expression was negatively regulated by β-catenin in ESCs and EpiSCs. (a) ERAS expression was inhibited by CHIR99021 in ESCs cultured in N2B27 medium. ESCs were treated with the inhibitors for 24 h. (b) ERAS expression in ESCs was inhibited by CHIR99021 treatment in DMEM/serum medium. ESCs were treated with indicated cytokines or inhibitors for 24 h. (c) ERAS expression was decreased in the presence of CHIR99021 in undifferentiated ESCs by mixing of two factors. (d) ERAS expression in EpiSCs was inhibited by CHIR99021 and BMP4 treatment for 24 h. (e) Genotyping of wild-type and Catnb(ΔEx3/+) ES cell lines. β-catenin with exon 3 deletion created a constitutive activated form of β-catenin. Wild-type = 0.9 kb, ΔEx3 = 0.7 kb. (f) ERAS protein was decreased in Catnb(ΔEx3/+) ESCs cultured in N2B27 for 24 h. (g) The inhibitory effect of CHIR99021 on ERAS expression was attenuated by XAV939 treatment in EpiSCs. (h) The inhibitory effect of BMP4 on ERAS expression was partially counteracted by XAV939 treatment in EpiSCs. (i) β-Catenin was recruited to the Eras promoter after GSK3 inhibition. ESCs were cultured in LIF/PD or 2i/LIF. EpiSCs were cultured in AFX (Activin A, FGF2 and XAV939) or AFC (Activin A, FGF2 and CHIR99021). (j,k) After Tcf7l1 knockdown for 24 h, Eras mRNA and protein were decreased in EpiSCs. Cytokines and inhibitors were used at the indicated final concentrations: PD0325901 (1 µM), CHIR99021 (3 µM), XAV939 (2 µM), LIF (1000 units ml−1), BMP4 (10 ng ml−1) and Activin A (20 ng ml−1).
CHIR99021, a specific inhibitor for GSK3, functions in cells by regulating metabolic activity and controlling β-catenin transcription factor activity [12]. To investigate how CHIR99021 regulates the expression of Eras, we established a Catnb(ΔEX3/+) ESC line (figure 5e,f), which expressed active β-catenin constitutively [47]. Consistent with our previous findings (figure 1g,h), ERAS showed low expression in wild-type and Catnb(ΔEX3/+) ESCs cultured in 2i/LIF medium (figure 5f). However, compared with the control, ERAS expression was dramatically decreased in Catnb(ΔEX3/+) ESCs cultured in N2B27 medium (figure 5f). These results indicate active β-catenin inhibits ERAS expression in ESCs.
Catnb(ΔEX3/+) EpiSCs could not be established because of an early embryonic lethal effect (data not shown). XAV939 is a tankyrase (TNKS) inhibitor which retains β-catenin in the cytoplasm to antagonize WNT signalling in EpiSCs [48]. To further investigate whether CHIR99021 inhibits Eras expression through β-catenin in EpiSCs, we cultured EpiSCs in CHIR/XAV conditions and examined the expression of ERAS. XAV939 increased the expression of ERAS and restored the ERAS expression inhibited by CHIR99021 (figure 5g). These results indicated β-catenin regulates the expression of Eras in EpiSCs.
In EpiSCs, ERAS was also downregulated by BMP4 (figure 5c). Consistent with this observation, BMP4 dramatically inhibited Eras expression in wild-type EpiLCs (epiblast-like cells), but not in Wnt3 knockout cells during germ cell differentiation in vitro [49] (electronic supplementary material, figure S5), indicating BMP4 may regulate Eras expression through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in EpiSCs. To this end, we treated EpiSCs with BMP4 and XAV939. We observed that XAV939 partially counteracted the inhibition by BMP4 of ERAS expression in EpiSCs (figure 5h). These results indicate BMP4 inhibits Eras expression through the β-catenin pathway in EpiSCs, consistent with a previous report that β-catenin signalling was induced by BMP4 in EpiSCs [50].
In order to confirm the transcriptional regulation of Eras by β-catenin, chromatin immunoprecipitation was used to detect the interaction between β-catenin and Eras promoter. ESCs were cultured in LIF/PD or 2i/LIF (GSK3 inhibition). EpiSCs were cultured in AFX (Activin A, FGF2 and XAV939) or AFC (Activin A, FGF2 and CHIR99021; GSK3 inhibition). β-Catenin was recruited to the promoter of Eras in both ESCs and EpiSCs after GSK3 inhibition by CHIR99021 (figure 5i). Inhibition of GSK3 supports mouse ESC self-renewal by modulating β-catenin–TCF3 interaction (Tcf7l1 was known as Tcf3 previously) [51–53]. After knocking down Tcf7l1 in ESCs, Eras mRNA and protein was decreased (figure 5j,k), indicating Tcf7l1 is involved in Eras expression.
In conclusion, these results suggest the expression of Eras is negatively regulated by β-catenin in stem cells.
2.6. Eras is downregulated by β-catenin in early mouse embryos
To explore the role of β-catenin on Eras expression physically, we cultured E6.5 embryos in medium containing CHIR99021 for 15 h and examined the Eras expression by whole-mount in situ hybridization and real-time RT-PCR. It was reported that Sox2 expression was inhibited by CHIR99021 in embryonic ectoderm but not extraembryonic ectoderm [54]. However, upon the treatment with CHIR99021, Eras expression in the embryos was decreased in both embryonic and extraembryonic ectoderm (figure 6a). Combining with the inhibitory effect of CHIR99021 on Eras also in both ESCs and EpiSCs, we conclude the regulation of Eras expression in these cells may be conserved. Real-time RT-PCR results also showed that Eras expression was significantly decreased in the embryos after the treatment with CHIR99021 (figure 6b). To examine if β-catenin regulates Eras expression in pre-implantation embryos, blastocysts recovered from normal mice at E3.5 were treated with CHIR99021 for 24 h. Compared with the control, Eras mRNA was significantly decreased in the blasocysts treated with CHIR99021 (figure 6c). In accordance with the downregulation of Eras expression by CHIR99021 and the low expression of Eras in PS and mesoderm, β-catenin was observed to be specifically activated in these cell lineages [55]. These results indicate that the activated β-catenin downregulates the expression of Eras in mouse early embryos.
Figure 6.
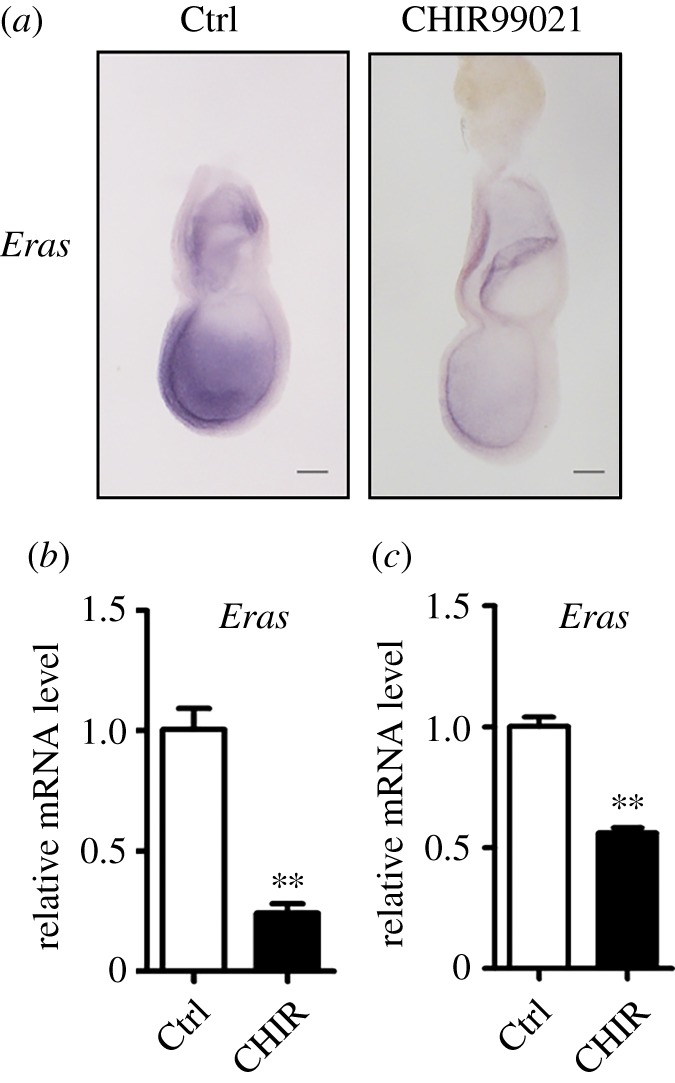
Eras expression in embryos was inhibited by CHIR99021 treatment. (a) In situ hybridization showed that Eras mRNA was decreased in E6.5 embryos treated with CHIR99021 (30 µM) for 15 h. Scale bar, 100 µm. (b) Eras mRNA was detected with real-time RT-PCR in E6.5 embryos treated with CHIR99021 (30 µM) for 15 h. (c) CHIR99021 (3 µM) treatment for 24 h decreased Eras expression in blastocysts cultured in vitro. (Student's t-test; **p < 0.01).
3. Discussion
After mouse embryo implantation, cell number was dramatically increased accompanying cell differentiation [56], suggesting some specific regulators function during this process. Although mouse transgenesis tremendously advances the molecular insights into mammalian early embryonic development, the researches on numerous genes whose mutations in mice do not result in obvious phenotypes are hindered by these analyses [57]. Eras was initially screened as a Ras family protein specifically expressed in ESCs, and its mutation does not lead to an obvious phenotype in mice [26]. However, Eras does play an important role in ESC growth [26] and promotes somatic cell reprogramming [27], suggesting its possible roles in mouse early embryonic development [28]. In this study, we find that Eras is highly expressed in early mouse peri-implantation embryos, while it is specifically downregulated in PS and mesoderm of E7.5 embryos. Beyond its role on cell growth, upregulated Eras facilitates the differentiation of ESCs from ground to primed state, and also downregulated Eras expression is important for the formation of PS and mesoderm. In addition, we find the expression of Eras is tightly regulated by the β-catenin pathway in ESCs and mouse early embryos. Thus, these results indicate that Eras probably coordinates cell proliferation and cell differentiation during mouse early embryonic development.
The ERK pathway plays a critical role during the commitment of ground state ESCs into the primed state. The inhibition of this pathway maintains the ground state of ESCs, and the activation of ERK signalling triggers the transition of ESCs from self-renewal to lineage commitment [12,15,17,58]. However, how the ERK pathway is regulated during the ESC commitment from ground into primed state is still largely unclear. Interestingly, we find that over-expressed Eras stimulates ERK phosphorylation and knockdown of Eras significantly decreases the phosphorylation of ERK during ESC commitment from ground into primed state, suggesting that ERAS is an important regulator that is involved in the ERK pathway in this process. Currently, ERAS is only known to bind to PI3K (p110δ) and increase AKT phosphorylation to promote ESC growth and the formation of iPSCs [26,27]. In accordance with these observations, we find that over-expressed Eras stimulates the phosphorylation of AKT and Eras knockdown decreases AKT phosphorylation. However, Ly294002, a specific inhibitor of PI3K, significantly inhibits phosphorylation of AKT but not ERK phosphorylation in ESCs. Thus, these results indicate that Eras probably regulates ERK activity through an unknown mechanism.
AKT inhibitor has been widely used for mesendoderm induction in human embryonic stem cells [44–46], but developmental evidence for using this inhibitor is still lacking. In this study, we find over-expressed Eras dramatically increases AKT phosphorylation and inhibits the formation of PS and mesoderm. In addition, knockdown Eras significantly decreases AKT activity and promotes the formation of PS and mesoderm. It is well known that β-catenin regulates the formation of mesoderm during mouse early embryonic development [59,60]. Considering that over-expression of Eras inhibited the differentiation of PS and mesoderm induced by WNT3A (figure 3d), ERAS may link the β-catenin and AKT pathways in the formation of PS during mouse early embryonic development. As described above, ERAS regulates both AKT and ERK activities in ESCs, while regulating only AKT activity and not ERK activity at later development stages. How ERAS achieves the specificity during these processes deserves to be further investigated.
Over-expressed Eras has been shown to increase tumour formation in NIH 3T3 cells [26]. Increased ERAS expression is also observed in human gastric carcinoma and neuroblastoma cells, and its expression is significantly associated with metastasis to the lymph nodes and liver. Neuroblastoma cells transfected with ERAS expression vector showed resistance to chemotherapeutic agents and promotion of transforming activity [29–32]. Thus, ERAS may be an important regulator for some types of human cancer. We find that CHIR99021 and BMP4 significantly decrease the expression of Eras, suggesting these pathways may be candidates for the treatment of some types of human cancer.
The emerging iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cell) technology has solved the ethical issues, may overcome the immunogenicity of cell therapy and promotes the application of stem cells in clinics [61,62]. Directed differentiation of ESCs/iPSCs into cells safe for clinical use is the next challenge in stem cell research. Manipulating the key pathways that regulate the formation of germ layers of mouse embryos resulted in the induction of endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm cells from ESCs [43,63]. Recently, pancreatic β cells have been successfully generated from human pluripotent stem cells by a specific process during which the first step is the generation of definitive endoderm by manipulating Wnt and Nodal pathways [64]. Thus, understanding the molecular mechanisms of germ layer specification during early embryonic development will significantly accelerate the strategy of directing ESC differentiation into specific cell lineages in vitro [65]. Our findings described here show the dynamic expression of ERAS during the cell specification of mouse early embryos and ESC differentiation. The precise regulation of ERAS expression is important for ESC growth and commitment from ground to primed state, and PS and mesoderm formation. Thus, also, ERAS may be an important target for the differentiation of ESCs into specific lineage cells.
Although ERAS knockdown affects ESC growth and differentiation, no overt developmental phenotype was observed in Eras-deficient mice [26]. The plasticity of mouse early embryonic development and the redundancy of Ras family genes may account for this [28]. It should also be noted that numerous genes involved in ESC function are not essential for mouse early development. For example, the bHLH transcription factor Tfe3 mutant mice are viable and fertile [66], while later research showed that Tfe3 is very important for the exiting of ESCs from the ground state [67].
In conclusion, our results illustrate that Eras is important for early cell lineage specification and provide new molecular insights into mouse early embryonic development and how Eras may contribute to ESC differentiation.
4. Material and methods
4.1. Antibodies and reagents
Antibodies against phospho (Ser473)-AKT1 (#9018), AKT1 (#2938), phospho (Thr202/Tyr204)-ERK1/2 (#4370), ERK1/2 (#4695), phospho (Ser465/467)-SMAD2 (#3108), SMAD2 (#5339) and α-tubulin (#2144) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. Anti-ERAS (sc-51072) was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Anti-β-catenin antibody (ab6302) was from Abcam Company. Inhibitors and cytokines include Ly294002 (#9901, CST), PD0325901 (P-9688, LC Laboratories), CHIR99021 (C-6556, LC Laboratories), XAV939 (X3004, Sigma), LIF (ESG1107, Millipore), BMP4 (5020-BP-010/CF, R&D Systems), Activin A (120-14, Peprotech) and FGF2 (233-FB-025, R&D Systems).
4.2. Mice maintaining and germ layer separation
CD1 mice were housed under specific-pathogen-free (SPF) conditions (12 L : 12 D cycles) in the animal facilities at the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. They were raised with standard laboratory food and water.
Embryos from E5.5 to E7.5 were dissected from the deciduas in DMEM buffered with 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) containing 10% FBS. Reichert's membrane was removed with fine forceps. The embryonic region was cut off using a glass scalpel. The embryonic region was rinsed in Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS), and incubated in pancreatic/trypsin enzyme solution (a solution of 0.5% trypsin and 2.5% pancreatin in Ca2+/Mg2+-free Tyrode Ringer's saline, pH 7.6–7.7) at 4°C for 8–12 min. After the treatment, the embryonic region was transferred into DMEM buffered with 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) containing 10% FBS. The germ layers were separated carefully with Pasteur pipette and glass needles as previously reported [68,69].
4.3. RNA isolation and real-time RT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated by an RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen). Concentration of RNA was measured using a NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher). The reverse transcription reaction was performed using PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (RR037A, TaKaRa). Real-time PCR was performed using a SYBR Premix Ex Taq kit (DRR041S, TaKaRa), and Hprt was used as an internal reference. The 2−ΔΔCt method was used for data analysis [70]. Primer sequences for real-time RT-PCR are listed in the electronic supplementary material, table S1.
4.4. Whole-mount in situ hybridization
E7.5 embryos from CD1 pregnant mice were dissected from the deciduas, and Reichert's membrane was removed. The embryos were fixed in a clean vial containing fresh 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS at 4°C overnight and dehydrated through methanol series. Antisense probes for Eras were labelled with DIG RNA Labeling Kit (Roche). The procedure of whole-mount in situ hybridization and sectioning was performed as previously reported [71].
4.5. Western blot
Cells were rinsed in PBS, and then lysed with RIPA lysis buffer containing complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) and phosphatase inhibitors (NaF and Na3VO4). Sample viscosity was reduced by sonication for 10 s to shear DNA. BCA reagent kit (Beyotime) was used to measure protein concentration. Normalized samples were run on a 12% PAGE gel and transferred onto PVDF membranes. After blocking for 1 h in 5% non-fat milk, the membranes were incubated with primary antibodies (1 : 1000) at 4°C overnight. After three washes in TBST, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase at room temperature for 1 h. The signals were developed with Pierce ECL Western Blot Substrate in Bio-RAD Chemi DocTMXRs+ (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA) with Quantity One software.
4.6. Mouse embryonic stem cells culture and differentiation
Mouse embryonic stem cell line (CMTI-1, Millipore) was routinely cultured in the dishes coated with MEF (mouse embryonic fibroblasts) feeder treated with mitomycin C under 5% CO2 at 37°C. The ESC culture medium included DMEM supplemented with 15% ESC-qualified FBS (Millipore), 2 mM l-glutamine, 100 units ml−1 penicillin/streptomycin, 0.1 mM non-essential amino acids, 0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 1 mM sodium pyruvate and 1000 units ml−1 LIF (Esgro, Cat# ESG1107, Millipore). The ground state ESCs were cultured in gelatin-coated dishes without feeder with 2i/LIF medium, which included N2B27 medium supplemented with PD0325901 (1 µM), CHIR99021 (3 µM) and LIF (1000 units ml−1) [12].
The EB formation was performed in a hanging drop culture system [72]. Briefly, ESCs were dissociated with trypsin-EDTA (0.25%) and replated to remove the feeders. After an initial culture for 1 h, ESCs were collected and diluted to 2.0 × 104 cells ml−1 in standard ESC culture medium lacking LIF. Then the ESCs were allowed to aggregate in hanging droplets (30 µl) and cultured for 3 days before being harvested for mRNA analysis.
Cytokine-induced differentiations were performed as previous reports [42]. After removing MEF feeder, to start monolayer differentiation, ESCs were plated at a density of 1 × 104 cells cm−2 in N2B27 medium overnight on gelatin-coated culture dishes to form a monolayer, and then were treated with Activin A (20 ng ml−1) and WNT3A (10 ng ml−1) respectively to induce differentiation for 3 days. The differentiated cells were collected for RNA and protein analyses. The medium with Activin A or WNT3A was changed every day until RNA and protein isolation.
4.7. Establishing epiblast stem cell line and Catnb(ΔEX3/+) ES cell line
Mouse E5.75 embryos (129S2 × C57BL/6, F1) were dissected from uteri and epiblasts were obtained through enzyme digestion and micromanipulation as previously described [69,73]. The epiblasts were cultured on MEF feeder in N2B27 medium containing Activin A (20 ng ml−1, Peprotech), bFGF (FGF2, 12 ng ml−1, R&D), XAV939 (2 µM, Sigma-Aldrich) and 20% KSR (Gibco) [54,74]. After 2–3 days of culture, the epiblast outgrowths were ready for passage. For routine passage, EpiSCs were split 1 : 4–1 : 6 every 2–3 days by dissociating with collagenase IV (1 mg ml−1, Gibco) as cell clumps.
To verify the function the Eras in EpiSCs, the cells were plated in matrigel-coated dishes for Eras knockdown. Transfection was performed with lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instruction. Eras siRNAs were ordered from Invitrogen according to the sequences (#1, 5′ GAGGCTACATTCTAAATGT 3′; #2, 5′ GCTTCGTGAAAGACCATGA 3′). After transfection for 6 h, the medium was changed with N2B27 containing 2 ng ml−1 Activin A for PS induction. Protein samples were collected for western blot analysis after 24 h differentiation. For Tcf7l1 knockdown, Tcf7l1 siRNA sequences were synthesized according to the following sequences (#1, 5′ GCACCTACCTACAGATGAA 3′; #2, 5′ GCCTTCATGTTGTATATGA 3′).
For Catnb(ΔEX3/+) ESC line establishment, C57BL/6 wild-type female mice were mated with male Catnblox(ex3)·Prm-Cre mice (specific knockout in the male germ line), and blastocysts were cultured in 2i/LIF medium [12]. After a 5-day culture, the colonies were dissociated with TrypLE (Gibco) and transferred to a 96-well plate with MEF feeder. Routine passage was performed for clonal expansion of the ESCs. Genotype was confirmed by PCR with specific primers (GF2: 5′ GGACAATGGCTACTCAAGGTTTGTG 3′ and AS: 5′ ACGTGTGGCAAGTTCCGCGTCATCC 3′) and western blot with rabbit anti-β-catenin antibody (ab6302).
4.8. Establishing knockdown and over-expressed Eras ES cell lines
For Eras knockdown, Eras RNAi sequences (#1, 5′ GAGGCTACATTCTAAATGT 3′; #2, 5′ GCTTCGTGAAAGACCATGA 3′) were cloned into psicoR lenti-virus vector, respectively. Eras CDS region was cloned into pHIV-EGFP (Addgene) lenti-virus vector for Eras over-expression. Lenti-virus was produced by co-transfection of expression vector, envelop plasmid pMD2G and packaging plasmid psPAX2 in 293-FT cells and concentrated by centrifugation at 20 000 rpm for 2 h. EGFP positive ESC clones were screened with flow cytometry for stable expression. The expression and RNAi efficiency was determined by real-time RT-PCR with primers (electronic supplementary material, table S1) for Eras and western blot with rabbit anti-ERAS (sc-51072).
4.9. ES cell differentiation from ground state and AP staining
ESCs were plated in 2i/LIF medium on matrigel-coated plates at 1.5 × 104 cells cm−2. The next day, cells were washed with DPBS to remove the residual inhibitors and LIF, and the medium was changed to N2B27 without 2i/LIF. After 3 days of differentiation, the undifferentiated ESCs were assayed by AP staining. For AP staining, cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and then incubated with BCIP/NBT for 15 min in AP1 solution (0.1 M NaCl, 0.1 M Tris pH 9.5, 50 mM MgCl2, Tween 0.1%). Integrated optical density (IOD) and area were analysed with IMAGE-PRO PLUS software. Mean density was calculated by (IOD SUM)/area.
4.10. Chromatin immunoprecipitation
ESCs and EpiSCs were cross-linked with formaldehyde. The chromatin was sheared by sonication with eight rounds of 15 1-s pulses at 60% power output [75]. The following procedure was performed as previously reported [76]. Anti-non-phospho (active) β-catenin (1 : 100, #8814, CST) was used for chromatin immunoprecipitation. RT-PCR was performed for semi-quantitative analysis. Primers for Eras promoter (−2395 to −2277) amplification are as follows: Eras-ChIP-F: AACAGAAGAGGGGTATTGGGTAG; Eras-ChIP-R: TGGGCATTGACATAGCGACT.
4.11. Mouse embryo culture
E6.5 Embryos from CD1 pregnant mice were dissected from the deciduas. After Reichert's membrane was removed, the embryos were cultured in CMRL 1066 (Gibco) containing 50% rat serum (derived from dorsal aorta) in the presence or absence of 30 µM CHIR99021. After 15 h culture, the embryos were collected for whole-mount in situ hybridization and real-time RT-PCR analysis. E3.5 blastocysts were flushed from uteri, cultured in N2B27 containing 3 µM CHIR99021 for 24 h and were examined by real-time RT-PCR with specific primers for Eras.
4.12. Statistical analyses
Quantitative analyses were based on at least three independent biological samples and expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. Statistics were calculated using SPSS 18.0. The data were subjected to Student's t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), with a significance level of p < 0.05.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Makoto Mark Taketo for kindly providing Catnblox(ex3) mice, and members of the Li laboratory for advice.
Ethics
All animal experiments were in accordance with the guidelines for the Use of Animals in Research issued by the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Data accessibility
Relevant data supporting this article have been uploaded as part of the electronic supplementary material.
Authors' contributions
Z.-A.Z. designed and performed experiments including major western blot experiments and cytokine-induced differentiation, analysed the data and wrote the manuscript; Y.Y. established cell lines, and performed EB formation and ESC commitment assay; H.-X.M performed whole-mount in situ hybridization, EB formation and real-time RT-PCR; X.-X.W, X.L, Y.Z. and X.Z. performed some western blot and RT-PCR experiments. H.W. analysed the data. L.L. initiated, organized and designed the study, analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Competing interests
We declare we have no competing interests.
Funding
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA01010103 to L.L.) and the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB944501, 2012CB944401 to L.L.) This study was also supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471353 and 31230047 to L.L.; 81100423 to X.Z.).
References
- 1.Rossant J, Tam PP. 2009. Blastocyst lineage formation, early embryonic asymmetries and axis patterning in the mouse. Development 136, 701–713. (doi:10.1242/dev.017178) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nichols J, Smith A. 2009. Naive and primed pluripotent states. Cell Stem Cell 4, 487–492. (doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.05.015) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lawson KA, Meneses JJ, Pedersen RA. 1991. Clonal analysis of epiblast fate during germ layer formation in the mouse embryo. Development 113, 891–911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Singh AM, Dalton S. 2009. The cell cycle and Myc intersect with mechanisms that regulate pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 5, 141–149. (doi:10.1016/j.stem.2009.07.003) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Evans MJ, Kaufman MH. 1981. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292, 154–156. (doi:10.1038/292154a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Martin GR. 1981. Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 78, 7634–7638. (doi:10.1073/pnas.78.12.7634) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Welling M, Geijsen N. 2013. Uncovering the true identity of naive pluripotent stem cells. Trends Cell Biol. 23, 442–448. (doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.004) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boroviak T, Loos R, Bertone P, Smith A, Nichols J. 2014. The ability of inner-cell-mass cells to self-renew as embryonic stem cells is acquired following epiblast specification. Nat. Cell Biol. 16, 516–528. (doi:10.1038/ncb2965) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chambers I, et al. 2007. Nanog safeguards pluripotency and mediates germline development. Nature 450, 1230–1234. (doi:10.1038/nature06403) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wray J, Kalkan T, Smith AG. 2010. The ground state of pluripotency. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 38, 1027–1032. (doi:10.1042/BST0381027) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Martello G, Smith A. 2014. The nature of embryonic stem cells. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 30, 647–675. (doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100913-013116) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ying QL, Wray J, Nichols J, Batlle-Morera L, Doble B, Woodgett J, Cohen P, Smith A. 2008. The ground state of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Nature 453, 519–523. (doi:10.1038/nature06968) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nichols J, Jones K, Phillips JM, Newland SA, Roode M, Mansfield W, Smith A, Cooke A. 2009. Validated germline-competent embryonic stem cell lines from nonobese diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 15, 814–818. (doi:10.1038/nm.1996) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tong C, Huang G, Ashton C, Li P, Ying QL. 2011. Generating gene knockout rats by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nat. Protoc. 6, 827–844. (doi:10.1038/nprot.2011.338) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kunath T, Saba-El-Leil MK, Almousailleakh M, Wray J, Meloche S, Smith A. 2007. FGF stimulation of the Erk1/2 signalling cascade triggers transition of pluripotent embryonic stem cells from self-renewal to lineage commitment. Development 134, 2895–2902. (doi:10.1242/dev.02880) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Findlay GM, et al. 2013. Interaction domains of Sos1/Grb2 are finely tuned for cooperative control of embryonic stem cell fate. Cell 152, 1008–1020. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.056) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Burdon T, Stracey C, Chambers I, Nichols J, Smith A. 1999. Suppression of SHP-2 and ERK signalling promotes self-renewal of mouse embryonic stem cells. Dev. Biol. 210, 30–43. (doi:10.1006/dbio.1999.9265) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lowe LA, Yamada S, Kuehn MR. 2001. Genetic dissection of nodal function in patterning the mouse embryo. Development 128, 1831–1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liu P, Wakamiya M, Shea MJ, Albrecht U, Behringer RR, Bradley A. 1999. Requirement for Wnt3 in vertebrate axis formation. Nat. Genet. 22, 361–365. (doi:10.1038/11932) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Winnier G, Blessing M, Labosky PA, Hogan BL. 1995. Bone morphogenetic protein-4 is required for mesoderm formation and patterning in the mouse. Genes Dev. 9, 2105–2116. (doi:10.1101/gad.9.17.2105) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Irion S, Nostro MC, Kattman SJ, Keller GM. 2008. Directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells: from developmental biology to therapeutic applications. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 73, 101–110. (doi:10.1101/sqb.2008.73.065) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Burdsal CA, Damsky CH, Pedersen RA. 1993. The role of E-cadherin and integrins in mesoderm differentiation and migration at the mammalian primitive streak. Development 118, 829–844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Carver EA, Jiang R, Lan Y, Oram KF, Gridley T. 2001. The mouse snail gene encodes a key regulator of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 8184–8188. (doi:10.1128/MCB.21.23.8184-8188.2001) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ciruna B, Rossant J. 2001. FGF signaling regulates mesoderm cell fate specification and morphogenetic movement at the primitive streak. Dev. Cell. 1, 37–49. (doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(01)00017-X) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tam PP, Loebel DA. 2007. Gene function in mouse embryogenesis: get set for gastrulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 368–381. (doi:10.1038/nrg2084) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Takahashi K, Mitsui K, Yamanaka S. 2003. Role of ERas in promoting tumour-like properties in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature 423, 541–545. (doi:10.1038/nature01646) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yu Y, et al. 2013. Stimulation of somatic cell reprogramming by Eras-Akt-Foxo1 signaling axis. Stem Cells 32, 349–363. (doi:10.1002/stem.1447) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bedzhov I, Graham SJ, Leung CY, Zernicka-Goetz M. 2014. Developmental plasticity, cell fate specification and morphogenesis in the early mouse embryo. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 369, 20130538 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2013.0538) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang F, Tang JM, Wang L, Shen JY, Zheng L, Wu PP, Zhang M, Yan ZW. 2010. Detection of beta-catenin, gastrokine-2 and embryonic stem cell expressed ras in gastric cancers. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 3, 782–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kaizaki R, Yashiro M, Shinto O, Yasuda K, Matsuzaki T, Sawada T, Hirakawa K. 2009. Expression of ERas oncogene in gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 29, 2189–2193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Aoyama M, Kataoka H, Kubota E, Tada T, Asai K. 2010. Resistance to chemotherapeutic agents and promotion of transforming activity mediated by embryonic stem cell-expressed Ras (ERas) signal in neuroblastoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 37, 1011–1016. (doi:10.3892/ijo_00000752) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kubota E, et al. 2010. Role of ES cell-expressed Ras (ERas) in tumorigenicity of gastric cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 177, 955–963. (doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.091056) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Niwa H, Burdon T, Chambers I, Smith A. 1998. Self-renewal of pluripotent embryonic stem cells is mediated via activation of STAT3. Genes Dev. 12, 2048–2060. (doi:10.1101/gad.12.13.2048) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Moodie SA, Willumsen BM, Weber MJ, Wolfman A. 1993. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science 260, 1658–1661. (doi:10.1126/science.8503013) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne PH, Dhand R, Vanhaesebroeck B, Gout I, Fry MJ, Waterfield MD, Downward J. 1994. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature 370, 527–532. (doi:10.1038/370527a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Greber B, et al. 2010. Conserved and divergent roles of FGF signaling in mouse epiblast stem cells and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 6, 215–226. (doi:10.1016/j.stem.2010.01.003) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Davies OR, Lin CY, Radzisheuskaya A, Zhou X, Taube J, Blin G, Waterhouse A, Smith AJ, Lowell S. 2013. Tcf15 primes pluripotent cells for differentiation. Cell Rep. 3, 472–484. (doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.01.017) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Marks H, et al. 2012. The transcriptional and epigenomic foundations of ground state pluripotency. Cell 149, 590–604. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.026) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wu H, Zhang Y. 2014. Reversing DNA methylation: mechanisms, genomics, and biological functions. Cell 156, 45–68. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.019) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Veillard AC, et al. 2014. Stable methylation at promoters distinguishes epiblast stem cells from embryonic stem cells and the in vivo epiblasts. Stem Cells Dev. 23, 2014–2029. (doi:10.1089/scd.2013.0639) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hackett JA, Dietmann S, Murakami K, Down TA, Leitch HG, Surani MA. 2013. Synergistic mechanisms of DNA demethylation during transition to ground-state pluripotency. Stem Cell Rep. 1, 518–531. (doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2013.11.010) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fei T, Zhu S, Xia K, Zhang J, Li Z, Han JD, Chen YG. 2010. Smad2 mediates Activin/Nodal signaling in mesendoderm differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Res. 20, 1306–1318. (doi:10.1038/cr.2010.158) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Murry CE, Keller G. 2008. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells to clinically relevant populations: lessons from embryonic development. Cell 132, 661–680. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.008) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bernardo AS, et al. 2011. BRACHYURY and CDX2 mediate BMP-induced differentiation of human and mouse pluripotent stem cells into embryonic and extraembryonic lineages. Cell Stem Cell 9, 144–155. (doi:10.1016/j.stem.2011.06.015) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cheung C, Bernardo AS, Trotter MW, Pedersen RA, Sinha S. 2012. Generation of human vascular smooth muscle subtypes provides insight into embryological origin-dependent disease susceptibility. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 165–173. (doi:10.1038/nbt.2107) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.McLean AB, et al. 2007. Activin A efficiently specifies definitive endoderm from human embryonic stem cells only when phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling is suppressed. Stem Cells 25, 29–38. (doi:10.1634/stemcells.2006-0219) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Harada N, Tamai Y, Ishikawa T, Sauer B, Takaku K, Oshima M, Taketo MM. 1999. Intestinal polyposis in mice with a dominant stable mutation of the beta-catenin gene. EMBO J. 18, 5931–5942. (doi:10.1093/emboj/18.21.5931) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kim H, Wu J, Ye S, Tai CI, Zhou X, Yan H, Li P, Pera M, Ying QL. 2013. Modulation of beta-catenin function maintains mouse epiblast stem cell and human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Nat. Commun. 4, 2403 (doi:10.1038/ncomms3403) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Aramaki S, et al. 2013. A mesodermal factor T, specifies mouse germ cell fate by directly activating germline determinants. Dev. Cell 27, 516–529. (doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2013.11.001) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kurek D, et al. 2015. Endogenous WNT signals mediate BMP-induced and spontaneous differentiation of epiblast stem cells and human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rep. 4, 114–128. (doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.11.007) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Martello G, Sugimoto T, Diamanti E, Joshi A, Hannah R, Ohtsuka S, Gottgens B, Niwa H, Smith A. 2012. Esrrb is a pivotal target of the Gsk3/Tcf3 axis regulating embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Cell Stem Cell 11, 491–504. (doi:10.1016/j.stem.2012.06.008) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yi F, Pereira L, Hoffman JA, Shy BR, Yuen CM, Liu DR, Merrill BJ. 2011. Opposing effects of Tcf3 and Tcf1 control Wnt stimulation of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 762–770. (doi:10.1038/ncb2283) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cole MF, Johnstone SE, Newman JJ, Kagey MH, Young RA. 2008. Tcf3 is an integral component of the core regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells. Genes Dev. 22, 746–755. (doi:10.1101/gad.1642408) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sumi T, Oki S, Kitajima K, Meno C. 2013. Epiblast ground state is controlled by canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the postimplantation mouse embryo and epiblast stem cells. PLoS ONE 8, e63378 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063378) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ferrer-Vaquer A, Piliszek A, Tian G, Aho RJ, Dufort D, Hadjantonakis AK. 2010. A sensitive and bright single-cell resolution live imaging reporter of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the mouse. BMC Dev. Biol. 10, 121 (doi:10.1186/1471-213X-10-121) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Snow MH, Bennett D. 1978. Gastrulation in the mouse: assessment of cell populations in the epiblast of tw18/tw18 embryos. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 47, 39–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nichols J, Smith A. 2012. Pluripotency in the embryo and in culture. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4, a008128 (doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a008128) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nichols J, Silva J, Roode M, Smith A. 2009. Suppression of Erk signalling promotes ground state pluripotency in the mouse embryo. Development 136, 3215–3222. (doi:10.1242/dev.038893) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Morkel M, et al. 2003. Beta-catenin regulates Cripto- and Wnt3-dependent gene expression programs in mouse axis and mesoderm formation. Development 130, 6283–6294. (doi:10.1242/dev.00859) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Haegel H, Larue L, Ohsugi M, Fedorov L, Herrenknecht K, Kemler R. 1995. Lack of beta-catenin affects mouse development at gastrulation. Development 121, 3529–3537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. 2006. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S. 2007. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131, 861–872. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Keller G. 2005. Embryonic stem cell differentiation: emergence of a new era in biology and medicine. Genes Dev. 19, 1129–1155. (doi:10.1101/gad.1303605) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pagliuca FW, Millman JR, Gurtler M, Segel M, Van Dervort A, Ryu JH, Peterson QP, Greiner D, Melton DA. 2014. Generation of functional human pancreatic beta cells in vitro. Cell 159, 428–439. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.040) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rossant J. 2011. The impact of developmental biology on pluripotent stem cell research: successes and challenges. Dev. Cell 21, 20–23. (doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.010) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Steingrimsson E, Tessarollo L, Pathak B, Hou L, Arnheiter H, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA. 2002. Mitf and Tfe3, two members of the Mitf-Tfe family of bHLH-Zip transcription factors, have important but functionally redundant roles in osteoclast development. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 4477–4482. (doi:10.1073/pnas.072071099) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Betschinger J, Nichols J, Dietmann S, Corrin PD, Paddison PJ, Smith A. 2013. Exit from pluripotency is gated by intracellular redistribution of the bHLH transcription factor Tfe3. Cell 153, 335–347. (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.012) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Brons IG, et al. 2007. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature 448, 191–195. (doi:10.1038/nature05950) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tesar PJ, Chenoweth JG, Brook FA, Davies TJ, Evans EP, Mack DL, Gardner RL, McKay RD. 2007. New cell lines from mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem cells. Nature 448, 196–199. (doi:10.1038/nature05972) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25, 402–408. (doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Piette D, Hendrickx M, Willems E, Kemp CR, Leyns L. 2008. An optimized procedure for whole-mount in situ hybridization on mouse embryos and embryoid bodies. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1194–1201. (doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.103) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.ten Berge D, Koole W, Fuerer C, Fish M, Eroglu E, Nusse R. 2008. Wnt signaling mediates self-organization and axis formation in embryoid bodies. Cell Stem Cell 3, 508–518. (doi:10.1016/j.stem.2008.09.013) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Chenoweth JG, Tesar PJ. 2010. Isolation and maintenance of mouse epiblast stem cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 636, 25–44. (doi:10.1007/978-1-60761-691-7_2) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hayashi K, Surani MA. 2009. Self-renewing epiblast stem cells exhibit continual delineation of germ cells with epigenetic reprogramming in vitro. Development 136, 3549–3556. (doi:10.1242/dev.037747) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Nelson JD, Denisenko O, Bomsztyk K. 2006. Protocol for the fast chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) method. Nat. Protoc. 1, 179–185. (doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.27) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Lee TI, Johnstone SE, Young RA. 2006. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarray-based analysis of protein location. Nat. Protoc. 1, 729–748. (doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.98) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Relevant data supporting this article have been uploaded as part of the electronic supplementary material.