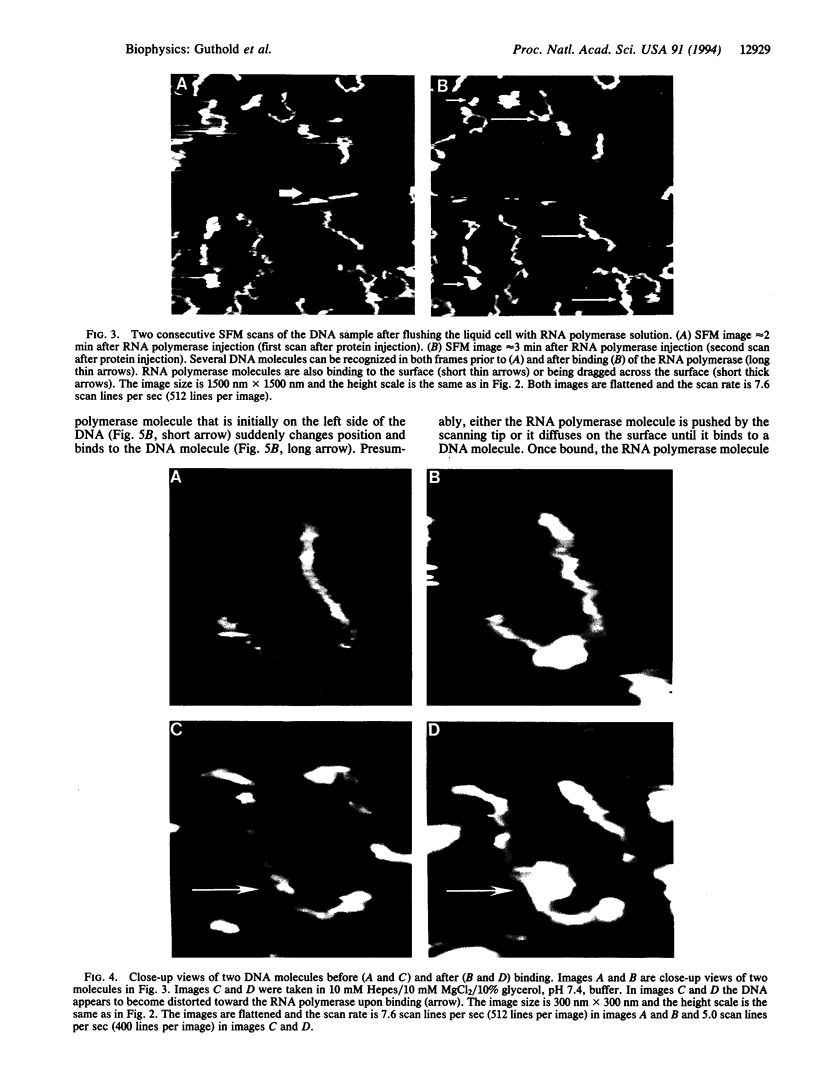
Abstract
The capability of the scanning force microscope (SFM) to image molecules in aqueous buffers has opened the exciting possibility of following processes of molecular assembly in real time and in near-physiological environments. This capability is demonstrated in this paper by following the assembly process of RNA polymerase-DNA complexes. DNA fragments deposited on mica and imaged in Hepes/MgCl2 are shown before and after Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme is injected in the SFM liquid chamber. The protein can recognize and bind to these DNA fragments within several seconds after injection, suggesting that the protein and the DNA retain their native configuration after deposition and during SFM imaging. A time-lapse sequence depicting the process of assembly of RNA polymerase-DNA complexes is shown. These results represent the first step for acquiring the capabilities to monitor complex biomolecular processes as they take place in ionic solutions and to characterize their spatial organization.
Full text
PDF
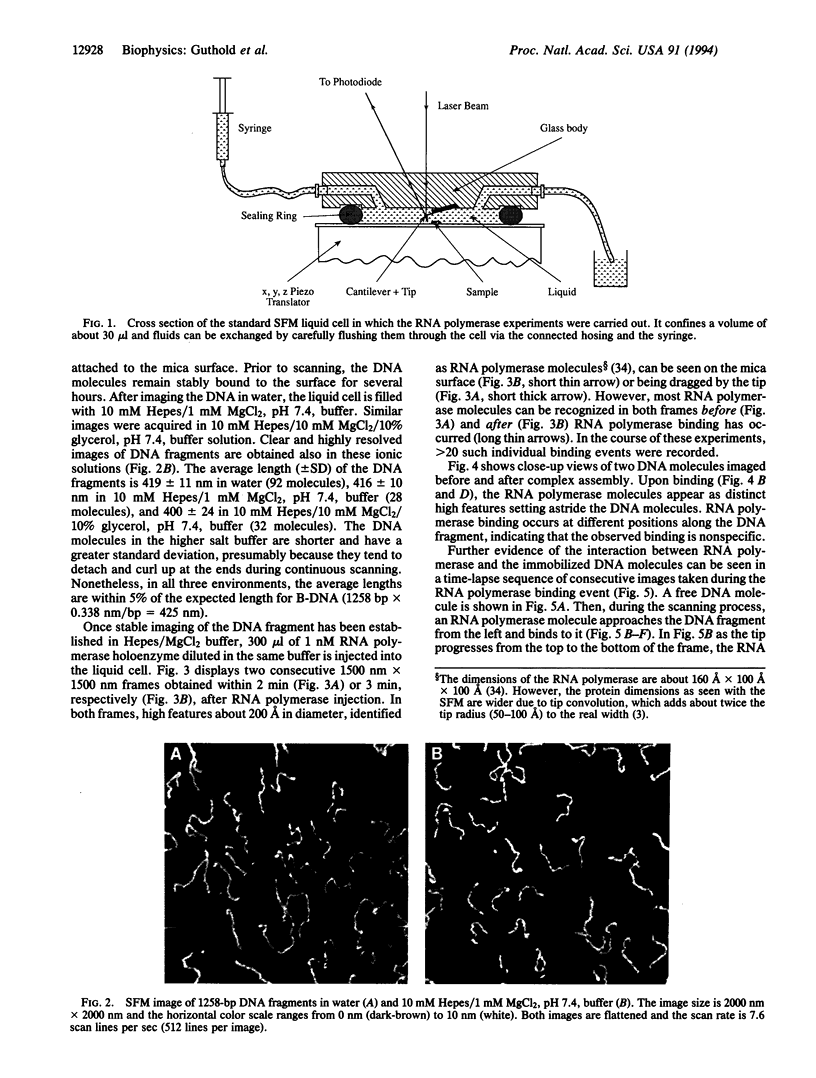


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbee K. A., Davies P. F., Lal R. Shear stress-induced reorganization of the surface topography of living endothelial cells imaged by atomic force microscopy. Circ Res. 1994 Jan;74(1):163–171. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-controlled macromolecular interactions. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:131–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C., Vesenka J., Tang C. L., Rees W., Guthold M., Keller R. Circular DNA molecules imaged in air by scanning force microscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):22–26. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darst S. A., Kubalek E. W., Kornberg R. D. Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme determined by electron crystallography. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):730–732. doi: 10.1038/340730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edstrom R. D., Meinke M. H., Yang X. R., Yang R., Elings V., Evans D. F. Direct visualization of phosphorylase-phosphorylase kinase complexes by scanning tunneling and atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1437–1448. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82489-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. Biological applications of scanning probe microscopes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Bezanilla M., Zenhausern F., Adrian M., Sinsheimer R. L. Atomic force microscopy of DNA in aqueous solutions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):505–512. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Vesenka J., Siegerist C., Kelderman G., Morrett H., Sinsheimer R. L., Elings V., Bustamante C., Hansma P. K. Reproducible imaging and dissection of plasmid DNA under liquid with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1180–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. Imaging and nanodissection of individual supercoiled plasmids by atomic force microscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):445–447. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Hansma P. K. Atomic force microscopy for high-resolution imaging in cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):208–213. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90248-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Lal R., John S. A., Revel J. P., Arnsdorf M. F. Atomic force microscopy and dissection of gap junctions. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1405–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.1910206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrasch S., Hegerl R., Hoh J. H., Baumeister W., Engel A. Atomic force microscopy produces faithful high-resolution images of protein surfaces in an aqueous environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):836–838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S. M., Nagahara L. A., Thundat T., Knipping U., Rill R. L., Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Hansma P. K. STM and AFM images of nucleosome DNA under water. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1989 Oct;7(2):279–287. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1989.10507771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S. M., Tao N. J., DeRose J. A., Oden P. I., Lyubchenko YuL, Harrington R. E., Shlyakhtenko L. Potentiostatic deposition of DNA for scanning probe microscopy. Biophys J. 1992 Jun;61(6):1570–1584. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81961-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubchenko Y. L., Oden P. I., Lampner D., Lindsay S. M., Dunker K. A. Atomic force microscopy of DNA and bacteriophage in air, water and propanol: the role of adhesion forces. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1117–1123. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnesorge F., Binnig G. True atomic resolution by atomic force microscopy through repulsive and attractive forces. Science. 1993 Jun 4;260(5113):1451–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.260.5113.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnesorge F., Heckl W. M., Häberle W., Pum D., Sara M., Schindler H., Schilcher K., Kiener A., Smith D. P., Sleytr U. B. Scanning force microscopy studies of the S-layers from Bacillus coagulans E38-66, Bacillus sphaericus CCM2177 and of an antibody binding process. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1236–1242. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90429-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees W. A., Keller R. W., Vesenka J. P., Yang G., Bustamante C. Evidence of DNA bending in transcription complexes imaged by scanning force microscopy. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1646–1649. doi: 10.1126/science.8503010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe J. H., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Kinetics and mechanism of the interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with the lambda PR promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):495–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samorí B., Siligardi G., Quagliariello C., Weisenhorn A. L., Vesenka J., Bustamante C. J. Chirality of DNA supercoiling assigned by scanning force microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3598–3601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr J. M. The one-dimensional diffusion coefficient of proteins absorbed on DNA. Hydrodynamic considerations. Biophys Chem. 1979 May;9(4):413–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesenka J., Guthold M., Tang C. L., Keller D., Delaine E., Bustamante C. Substrate preparation for reliable imaging of DNA molecules with the scanning force microscope. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1243–1249. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90430-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenhorn A. L., Drake B., Prater C. B., Gould S. A., Hansma P. K., Ohnesorge F., Egger M., Heyn S. P., Gaub H. E. Immobilized proteins in buffer imaged at molecular resolution by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1251–1258. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82465-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Takeyasu K., Shao Z. Atomic force microscopy of DNA molecules. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 20;301(2):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81241-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Tamm L. K., Tillack T. W., Shao Z. New approach for atomic force microscopy of membrane proteins. The imaging of cholera toxin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):286–290. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenhausern F., Adrian M., ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Emch R., Jobin M., Taborelli M., Descouts P. Imaging of DNA by scanning force microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;108(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deHaseth P. L., Lohman T. M., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Nonspecific interactions of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with native and denatured DNA: differences in the binding behavior of core and holoenzyme. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1612–1622. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]