The crystal structure of enantiopure (3aS,4S,5R,7aR)-2,2,7-trimethyl-3a,4,5,7a- tetrahydro-1,3-benzodioxole-4,5-diol shows that the absolute configuration determined from the synthesis pathway agrees with that determined by X-ray analysis.
Keywords: crystal structure, epoxycyclohexenones, absolute configuration, chiral crystal, chemoenzymatic strategy
Abstract
The absolute configuration of the title compound, C10H16O4, determined as 3aS,4S,5R,7aR on the basis of the synthetic pathway, was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The molecule contains a five- and a six-membered ring that adopt twisted and envelope conformations, respectively. The dihedral angle between the mean planes of the rings is 76.80 (11)° as a result of their cis-fusion. In the crystal, molecules are linked by two pairs of O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [010]. These chains are further connected by weaker C—H⋯O interactions along [100], creating (001) sheets that interact only by weak van der Waals forces.
Chemical context
Compounds containing an epoxycyclohexenone skeleton are very interesting, not only because of their wide spectrum of biological activities, but also because of their synthetically challenging chemical structures (Pandolfi et al., 2013 ▸). A biotransformation of toluene leads to a chiral diol (see Fig. 1 ▸) which is used as a precursor in enantioselective syntheses of epoxycyclohexenone compounds. Model compounds of the central core of ambuic acid (Labora et al., 2008 ▸), (+)- and (−)-bromoxone (Labora et al., 2010 ▸), an epoxyquinol analog (Heguaburu et al., 2010 ▸), gabosine A, ent-epoformin and ent-epiepoformin (Labora et al., 2011 ▸) have been prepared starting from the same precursor. The title compound, diol (3) (see Fig. 1 ▸) has been prepared from iodohydrin (1), which, as indicated earlier, can be easily synthesized via biotransformation of toluene (Carrera et al., 2007 ▸).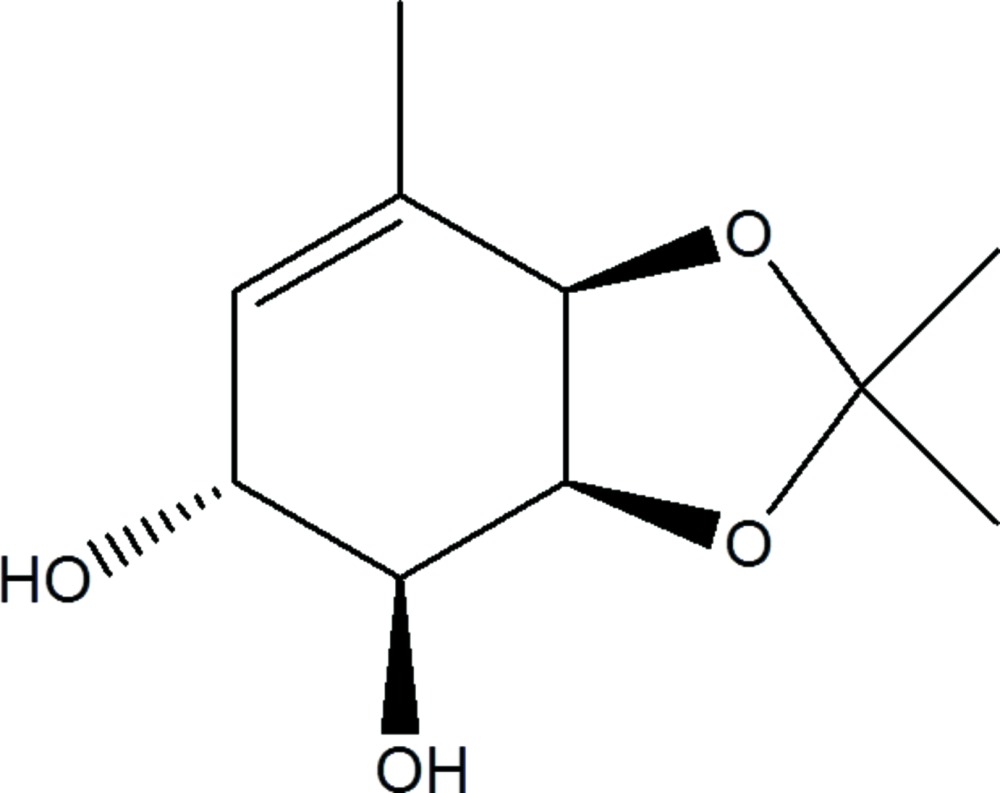
Figure 1.
Synthesis pathway and structural scheme of the chiral C10H16O4 compound.
Structural commentary
Fig. 2 ▸ shows the molecule of the title compound. The absolute configuration of the title compound, determined as 3aS,4S,5R,7aR on the basis of the synthetic pathway, was confirmed by X-ray diffraction on the basis of anomalous dispersion of light atoms only. The five-membered ring (O1–C2–O3–C3A–C7A) adopts a twisted conformation with puckering parameters Q(2) = 0.342 (2) Å and φ = 122.1 (3)°. The six-membered ring (C3A–C4–C5–C6–C7–C7A) adopts an envelope conformation with atom C4 as the flap. In this case, the puckering parameters are Q = 0.466 (2) Å, θ = 52.1 (2) and φ = 50.8 (3)°. The fused rings are nearly perpendicular with a dihedral angle of 76.20 (11)° as a result of their cis-fusion.
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the anisotropic displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal structure, the molecules are connected in the three crystallographic directions by intermolecular interactions of different strengths (Table 1 ▸). In the [010] direction hydrogen bonds O41—H41⋯O3i and O51—H51⋯O41i [symmetry code: (i) −x, y +  , −z +
, −z +  ] join molecules into chains that are further connected by weaker C7A—H7A⋯O51ii [symmetry code: (ii) x + 1, y, z] hydrogen bonds along [100], forming (001) sheets. Hydrogen bonds of the O—H⋯O type generate
] join molecules into chains that are further connected by weaker C7A—H7A⋯O51ii [symmetry code: (ii) x + 1, y, z] hydrogen bonds along [100], forming (001) sheets. Hydrogen bonds of the O—H⋯O type generate  (10) motifs (Fig. 3 ▸). There are only weak van der Waals forces acting between neighbouring (001) sheets.
(10) motifs (Fig. 3 ▸). There are only weak van der Waals forces acting between neighbouring (001) sheets.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O41H41O3i | 0.82(3) | 2.04(3) | 2.849(2) | 171(3) |
| O51H51O41i | 0.80(3) | 2.04(3) | 2.826(2) | 167(2) |
| C7AH7AO51ii | 0.98 | 2.44 | 3.299(3) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Figure 3.
Packing of the title compound, viewed along [100], showing hydrogen-bonded chains of molecules
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD Version 5.36 with one update; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) of the 3a,4,5,7a-tetrahydro-1,3-benzodioxole skeleton gave 30 hits, of which only 20 had no additional fused rings. In all cases, the six-membered ring displays an envelope conformation with atom C4 as a flap. The orientation of the flap with respect to the plane of the envelope can be determined from the C7—C7A—C3A—C4 or the H7A—C7A—C3A—H3A torsion angles (with very similar values due to the geometry of the cis-fused rings). The C7—C7A—C3A—C4 torsion angle is positive if the flap atom is located on the opposite side of the plane (defined by the remaining five atoms of the cyclohexene ring) to O1 and O3 of the 1,3-dioxole ring, as observed in the title compound [33.5 (2)°]. 12 of the 20 mentioned structures, show a positive torsion angle with minimum and maximum values of 17.2 and 36.4°, respectively. From analysis of the above-mentioned torsion angle and the equatorial/axial orientation of the C4 and C5 substituents in the 20 structures, there is no clear trend that allows the relative orientation of the flap to be predicted based only on the size or kind of the substituents.
Synthesis and crystallization
The synthesis of the title compound was carried out through the intermediate epoxide (2) (see Fig. 1 ▸). Iodohydrin (1) (0.6 mmol, 0.18 g) was dissolved in dry dichloromethane (5 mL) and 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-en (DBU) (0.8 mmol, 0.12 g) was added at room temperature. The reaction was stirred for 24 h After completion of the reaction, the mixture was diluted with saturated NH4Cl solution (20 mL) and extracted with dichloromethane (3 x 10 mL). The combined organic layers were washed with saturated NaCl solution (10 mL), dried (Na2SO4) and filtered. Concentration of the filtrate, followed by flash chromatography (hexanes:ethyl acetate 93:7) yielded (2) (0.063 g, 60%). FT–IR (KBr): 2983, 2926, 2856, 1672, 1371. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 6.01 (m, 1H), 4.40 (m, 2H), 3.58 (m, 1H), 3.42 (t, J = 4.0 Hz, 1H), 1.91 (s, 3H), 1.53 (s, 3H), 1.41 (s, 1H). For the synthesis of diol (3), epoxide (2) (0.27 mmol, 0.05 g) was dissolved in THF (25 mL) and 10% KOH (aq., 25 mL) was added. This mixture was refluxed for 4 h. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was diluted with dichloromethane (20 mL) and the organic phase was washed with 10% HCl until neutralization, washed with saturated NaCl solution (10 mL), dried with (Na2SO4) and filtered. Concentration of the filtrate, followed by flash chromatography (ethyl acetate:hexanes 4:6) yielded (3) (0.02g, 52%). Crystals suitable for X-ray structure analysis were obtained by dissolving (3) in the minimum volume of ethyl acetate, adding hexanes until the solution became slightly turbid and slowly evaporating the solvent at room temperature. (m.p. = 385–386 K). FT–IR (KBr): 3402, 1637, 1371. 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 5.45 (s, 1H), 4.48 (m, 2H), 4.33 (m, 1H), 3.59 (m, 1H), 2.52 (bs, 1H), 2.30 (bs, 1H), 1.79 (s, 3H), 1.38 (s, 3H), 1.35 (s, 3H).
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. H atoms bonded to C were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters set to 1.2–1.5 times of the U eq of the parent atom. H atoms belonging to OH groups were located in ΔF maps and freely refined.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C10H16O4 |
| M r | 200.23 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P212121 |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c () | 6.1230(13), 7.5163(17), 23.347(5) |
| V (3) | 1074.5(4) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu K |
| (mm1) | 0.79 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.28 0.18 0.14 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 Venture/Photon 100 CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.643, 0.752 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 29451, 1967, 1951 |
| R int | 0.030 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.603 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.029, 0.078, 1.18 |
| No. of reflections | 1967 |
| No. of parameters | 139 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.14, 0.11 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 782 quotients [(I +)(I )]/[(I +)+(I )] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.01(3) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015014590/gk2644sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015014590/gk2644Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015014590/gk2644Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1416687
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank ANII (EQC_2012_07), CSIC and the Facultad de Química for funds to purchase the diffractometer and the financial support of OPCW and PEDECIBA. MM and GT also thank ANII for their respective postdoctoral contracts (PD_NAC_2014_1_102409 and PD_NAC_2014_1_102498).
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C10H16O4 | F(000) = 432 |
| Mr = 200.23 | Dx = 1.238 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | θ = 3.8–66.7° |
| a = 6.1230 (13) Å | µ = 0.79 mm−1 |
| b = 7.5163 (17) Å | T = 293 K |
| c = 23.347 (5) Å | Parallelepiped, colorless |
| V = 1074.5 (4) Å3 | 0.28 × 0.18 × 0.14 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 Venture/Photon 100 CMOS diffractometer | 1967 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Cu Incoatec microsource | 1951 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Helios X-ray optical focusing and monochromatization module | Rint = 0.030 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4167 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 68.4°, θmin = 3.8° |
| π and ω scans | h = −7→6 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.643, Tmax = 0.752 | l = −28→28 |
| 29451 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0278P)2 + 0.2133P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.078 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.18 | Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3 |
| 1967 reflections | Δρmin = −0.11 e Å−3 |
| 139 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0063 (9) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 782 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Absolute structure parameter: 0.01 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O3 | 0.1718 (2) | 0.02424 (17) | 0.83031 (6) | 0.0431 (4) | |
| C3A | 0.2609 (3) | 0.1964 (3) | 0.81761 (8) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.3868 | 0.1850 | 0.7919 | 0.045* | |
| O1 | 0.4078 (3) | 0.0973 (2) | 0.90222 (7) | 0.0562 (5) | |
| C7A | 0.3342 (3) | 0.2591 (3) | 0.87622 (8) | 0.0405 (5) | |
| H7A | 0.4583 | 0.3403 | 0.8719 | 0.049* | |
| H41 | −0.026 (5) | 0.337 (4) | 0.7201 (12) | 0.066 (9)* | |
| H51 | −0.197 (5) | 0.545 (4) | 0.8006 (10) | 0.051 (8)* | |
| O41 | 0.0349 (3) | 0.2538 (2) | 0.73585 (6) | 0.0499 (4) | |
| O51 | −0.2609 (3) | 0.4552 (2) | 0.80767 (7) | 0.0488 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.1596 (4) | 0.3484 (3) | 0.91126 (8) | 0.0403 (5) | |
| C6 | −0.0366 (3) | 0.3793 (3) | 0.88973 (8) | 0.0415 (5) | |
| H6 | −0.1387 | 0.4344 | 0.9133 | 0.050* | |
| C23 | 0.4527 (6) | −0.1837 (4) | 0.85765 (13) | 0.0778 (9) | |
| H23A | 0.5376 | −0.2248 | 0.8896 | 0.117* | |
| H23B | 0.5475 | −0.1307 | 0.8297 | 0.117* | |
| H23C | 0.3769 | −0.2824 | 0.8407 | 0.117* | |
| C2 | 0.2898 (4) | −0.0479 (3) | 0.87792 (9) | 0.0484 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.0914 (3) | 0.3159 (3) | 0.79142 (8) | 0.0358 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.1557 | 0.4347 | 0.7873 | 0.043* | |
| C5 | −0.1064 (3) | 0.3320 (2) | 0.83012 (9) | 0.0370 (4) | |
| H5 | −0.1771 | 0.2152 | 0.8317 | 0.044* | |
| C71 | 0.2246 (5) | 0.3979 (4) | 0.97104 (10) | 0.0621 (7) | |
| H71A | 0.1042 | 0.4554 | 0.9898 | 0.093* | |
| H71B | 0.3471 | 0.4775 | 0.9698 | 0.093* | |
| H71C | 0.2639 | 0.2925 | 0.9919 | 0.093* | |
| C22 | 0.1246 (6) | −0.1199 (4) | 0.91968 (12) | 0.0762 (9) | |
| H22A | 0.1985 | −0.1646 | 0.9530 | 0.114* | |
| H22B | 0.0437 | −0.2145 | 0.9019 | 0.114* | |
| H22C | 0.0263 | −0.0266 | 0.9308 | 0.114* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O3 | 0.0525 (8) | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0444 (8) | 0.0017 (6) | −0.0105 (7) | −0.0019 (6) |
| C3A | 0.0346 (9) | 0.0391 (10) | 0.0400 (10) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0044 (8) | −0.0027 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0621 (10) | 0.0478 (9) | 0.0587 (9) | 0.0118 (8) | −0.0243 (8) | −0.0051 (7) |
| C7A | 0.0353 (9) | 0.0407 (10) | 0.0455 (10) | −0.0020 (9) | −0.0032 (9) | −0.0026 (9) |
| O41 | 0.0668 (11) | 0.0458 (8) | 0.0372 (7) | 0.0157 (8) | −0.0080 (7) | −0.0020 (7) |
| O51 | 0.0369 (8) | 0.0452 (9) | 0.0643 (10) | 0.0056 (7) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0124 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0482 (12) | 0.0349 (10) | 0.0377 (10) | −0.0064 (9) | 0.0036 (9) | −0.0010 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0428 (11) | 0.0414 (11) | 0.0405 (10) | 0.0022 (9) | 0.0124 (9) | 0.0014 (9) |
| C23 | 0.083 (2) | 0.0651 (17) | 0.0857 (19) | 0.0354 (16) | −0.0191 (16) | −0.0160 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0605 (14) | 0.0390 (11) | 0.0456 (11) | 0.0103 (10) | −0.0116 (10) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0408 (10) | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0343 (9) | 0.0000 (8) | 0.0034 (8) | −0.0004 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0465 (10) | 0.0003 (8) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0047 (8) |
| C71 | 0.0779 (17) | 0.0649 (15) | 0.0436 (12) | 0.0032 (15) | −0.0050 (12) | −0.0076 (11) |
| C22 | 0.102 (2) | 0.0665 (17) | 0.0599 (15) | −0.0030 (18) | 0.0010 (15) | 0.0110 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O3—C2 | 1.433 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C3A | 1.435 (2) | C23—C2 | 1.503 (3) |
| C3A—C4 | 1.503 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.9600 |
| C3A—C7A | 1.515 (3) | C23—H23B | 0.9600 |
| C3A—H3A | 0.9800 | C23—H23C | 0.9600 |
| O1—C2 | 1.427 (3) | C2—C22 | 1.505 (4) |
| O1—C7A | 1.432 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.516 (3) |
| C7A—C7 | 1.504 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9800 |
| C7A—H7A | 0.9800 | C5—H5 | 0.9800 |
| O41—C4 | 1.421 (2) | C71—H71A | 0.9600 |
| O41—H41 | 0.82 (3) | C71—H71B | 0.9600 |
| O51—C5 | 1.424 (2) | C71—H71C | 0.9600 |
| O51—H51 | 0.80 (3) | C22—H22A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C6 | 1.323 (3) | C22—H22B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C71 | 1.498 (3) | C22—H22C | 0.9600 |
| C6—C5 | 1.499 (3) | ||
| C2—O3—C3A | 108.04 (16) | O1—C2—C23 | 108.0 (2) |
| O3—C3A—C4 | 111.11 (16) | O3—C2—C23 | 110.34 (19) |
| O3—C3A—C7A | 101.91 (15) | O1—C2—C22 | 111.0 (2) |
| C4—C3A—C7A | 112.71 (16) | O3—C2—C22 | 107.4 (2) |
| O3—C3A—H3A | 110.3 | C23—C2—C22 | 113.9 (2) |
| C4—C3A—H3A | 110.3 | O41—C4—C3A | 110.06 (15) |
| C7A—C3A—H3A | 110.3 | O41—C4—C5 | 112.08 (17) |
| C2—O1—C7A | 108.78 (15) | C3A—C4—C5 | 110.92 (15) |
| O1—C7A—C7 | 111.85 (17) | O41—C4—H4 | 107.9 |
| O1—C7A—C3A | 102.24 (16) | C3A—C4—H4 | 107.9 |
| C7—C7A—C3A | 114.80 (16) | C5—C4—H4 | 107.9 |
| O1—C7A—H7A | 109.2 | O51—C5—C6 | 112.15 (17) |
| C7—C7A—H7A | 109.2 | O51—C5—C4 | 111.30 (16) |
| C3A—C7A—H7A | 109.2 | C6—C5—C4 | 110.18 (16) |
| C4—O41—H41 | 105.6 (19) | O51—C5—H5 | 107.7 |
| C5—O51—H51 | 107.4 (19) | C6—C5—H5 | 107.7 |
| C6—C7—C71 | 123.5 (2) | C4—C5—H5 | 107.7 |
| C6—C7—C7A | 121.16 (18) | C7—C71—H71A | 109.5 |
| C71—C7—C7A | 115.4 (2) | C7—C71—H71B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 124.75 (18) | H71A—C71—H71B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 117.6 | C7—C71—H71C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 117.6 | H71A—C71—H71C | 109.5 |
| C2—C23—H23A | 109.5 | H71B—C71—H71C | 109.5 |
| C2—C23—H23B | 109.5 | C2—C22—H22A | 109.5 |
| H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 | C2—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C2—C23—H23C | 109.5 | H22A—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 | C2—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 | H22A—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—O3 | 105.92 (16) | H22B—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C2—O3—C3A—C4 | −151.43 (16) | C7A—O1—C2—C23 | 127.8 (2) |
| C2—O3—C3A—C7A | −31.14 (19) | C7A—O1—C2—C22 | −106.6 (2) |
| C2—O1—C7A—C7 | 95.1 (2) | C3A—O3—C2—O1 | 14.5 (2) |
| C2—O1—C7A—C3A | −28.2 (2) | C3A—O3—C2—C23 | −102.1 (2) |
| O3—C3A—C7A—O1 | 35.64 (18) | C3A—O3—C2—C22 | 133.2 (2) |
| C4—C3A—C7A—O1 | 154.80 (17) | O3—C3A—C4—O41 | −68.3 (2) |
| O3—C3A—C7A—C7 | −85.7 (2) | C7A—C3A—C4—O41 | 178.01 (16) |
| C4—C3A—C7A—C7 | 33.5 (2) | O3—C3A—C4—C5 | 56.3 (2) |
| O1—C7A—C7—C6 | −120.5 (2) | C7A—C3A—C4—C5 | −57.4 (2) |
| C3A—C7A—C7—C6 | −4.6 (3) | C7—C6—C5—O51 | −147.6 (2) |
| O1—C7A—C7—C71 | 59.4 (2) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | −23.0 (3) |
| C3A—C7A—C7—C71 | 175.29 (19) | O41—C4—C5—O51 | −60.8 (2) |
| C71—C7—C6—C5 | 179.8 (2) | C3A—C4—C5—O51 | 175.69 (16) |
| C7A—C7—C6—C5 | −0.3 (3) | O41—C4—C5—C6 | 174.10 (15) |
| C7A—O1—C2—O3 | 9.6 (2) | C3A—C4—C5—C6 | 50.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O41—H41···O3i | 0.82 (3) | 2.04 (3) | 2.849 (2) | 171 (3) |
| O51—H51···O41i | 0.80 (3) | 2.04 (3) | 2.826 (2) | 167 (2) |
| C7A—H7A···O51ii | 0.98 | 2.44 | 3.299 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) x+1, y, z.
References
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Carrera, I., Brovetto, M. & Seoane, G. (2007). Tetrahedron, 63, 4095–4107.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Heguaburu, V., Schapiro, V. & Pandolfi, E. (2010). Tetrahedron Lett. 51, 6921–6923.
- Labora, M., Heguaburu, V., Pandolfi, E. & Schapiro, V. (2008). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 19, 893–895.
- Labora, M., Pandolfi, E. & Schapiro, V. (2010). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 21, 153–155.
- Labora, M., Schapiro, V. & Pandolfi, E. (2011). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 22, 1705–1707.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Pandolfi, E., Schapiro, V., Heguaburu, V. & Labora, M. (2013). Curr. Org. Synth. 71, 2–42.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015014590/gk2644sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015014590/gk2644Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015014590/gk2644Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1416687
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





