Abstract
In the title compound, C11H12N2O2·C4H4O4·H2O, the l-tryptophan molecule crystallized as a zwitterion, together with a neutral fumaric acid molecule and a water solvent molecule. In the crystal, the three components are linked by a series of N—H⋯O, O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming slabs lying parallel to (001). The slabs are connected by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, involving inversion-related fumaric acid groups, leading to the formation of a three-dimensional structure.
Keywords: crystal structure, l-tryptophan, fumaric acid, hydrogen bonding, three-dimensional structure
Related literature
For literature on the UV spectroscopy of proteins, see: Demchenko (1986 ▸). For the different polymorphic forms of fumaric acid, see: Reis & Schneider (1928 ▸); Yardley (1925 ▸); Bednowitz & Post (1966 ▸). For the nonlinear optical properties of organic molecules, see: Chemla & Zyss (1987 ▸); Zyss & Ledoux (1994 ▸); Zyss & Nicoud (1996 ▸). For the common conformations of l-tryptophan, see: Bye et al. (1973 ▸); Bakke & Mostad (1980 ▸). The bond lengths and angles in l-trypophan, see, for example: Gorbitz (2006 ▸); Gorbitz et al. (2012 ▸), and for fumaric acid, see: Goswami et al. (1999 ▸). For the crystal structure of l-tryptophan formic acid solvate, see: Hubschle et al. (2002 ▸). For details of the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Groom & Allen (2014 ▸).
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H12N2O2·C4H4O4·H2O
M r = 338.31
Monoclinic,

a = 11.3928 (8) Å
b = 6.6476 (4) Å
c = 21.4219 (13) Å
β = 95.801 (3)°
V = 1614.07 (18) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▸) T min = 0.898, T max = 0.978
10737 measured reflections
3157 independent reflections
2731 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.084
S = 1.04
3157 reflections
242 parameters
4 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▸); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▸); data reduction: SAINT and XPREP (Bruker, 2004 ▸); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1994 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▸) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL2014 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176fig2.tif
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
b . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176fig3.tif
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the b axis. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
CCDC reference: 1417535
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1H1O3i | 0.85(3) | 2.11(3) | 2.912(3) | 158(3) |
| N2H2AO7 | 0.92(4) | 1.94(4) | 2.845(3) | 170(3) |
| N2H2BO1ii | 0.94(3) | 2.30(3) | 3.085(3) | 140(2) |
| N2H2BO3 | 0.94(3) | 2.28(3) | 2.901(3) | 123(2) |
| N2H2CO2iii | 0.96(3) | 1.87(3) | 2.832(3) | 174(3) |
| O4H4OO1ii | 0.82 | 1.74 | 2.559(2) | 178 |
| O5H5OO6iv | 0.82 | 1.81 | 2.630(3) | 174 |
| O7H7AO1v | 0.88(2) | 2.60(3) | 3.261(3) | 133(3) |
| O7H7AO2v | 0.88(2) | 1.97(2) | 2.824(3) | 165(3) |
| O7H7BO2vi | 0.85(2) | 2.53(3) | 3.347(3) | 162(3) |
| C3H3BO3vii | 0.97 | 2.66 | 3.255(3) | 120 |
| C5H5O7i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.491(3) | 166 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  ; (vi)
; (vi)  ; (vii)
; (vii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The scientific support extended by the Sophisticated Analytical Instruments Facility, Indian Institute of Technology IITM, Chennai, in solving the crystal structure is greatly appreciated. The authors personally thank Professor E. M. Subramanian, retired Professor of Chemistry, Pachayappas College, Kanchipuram, Tamilnadu, for valuable suggestions.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
Natural aromatic amino acids, particularly tryptophan, have near UV absorption and emission properties which are utilized extensively in solution phase investigations of structure-function relationships (Demchenko, 1986). Fumaric acid is known to exist in two different polymorphic forms viz. cis and trans ( Reis & Schneider, 1928; Yardley, 1925; Bednowitz & Post, 1966).
In conjunction with our ongoing work on non-linear optical organic crystals among the 20 naturally occurring amino acids, we have directed our interest to tryptophan (Trp), one of the essential amino acids for humans. The non-linear optical properties of organic molecules and crystals have been reviewed by Zyss (Chemla & Zyss, 1987; Zyss & Ledoux, 1994; Zyss & Nicoud, 1996). For similar properties and most the common confirmations of L-tryptophan have been reported (Bye et al., 1973; Bakke & Mostad, 1980). Compared with other amino acids, there are less than 30 tryptophan structures listed in the Cambridge Structural Database (Groom & Allen, 2014), due to the difficulty of obtaining good optical quality crystals; as noted by (Hubschle et al., 2002) who studied the crystal structure of L-tryptophan formic acid solvate. We successfully obtained good quality hard golden-yellow single crystals of L-tryptophan fumaric acid monohydrate, and we report herein on its synthesis and crystal structure.
In the title compound, Fig. 1, L-tryptophan is zwitterionic, as are most amino acids in the solid state, and fumaric acid is neutral. The bond lengths and angles in L-trypophan and fumaric acid are similar to those reported previously (Gorbitz, 2006; Gorbitz et al., 2012; Goswami et al., 1999).
In the crystal, the three components are linked by a series of O—H···O, N—H···O and C—H···O hydrogen bonds forming slabs lying parallel to (001); Table 1 and Fig. 2. The slabs are connected by O—H···O hydrogen bonds, involving inversion related fumaric acid groups, leading to the formation of a three-dimensional structure; Table 1 and Fig. 3.
S2. Synthesis and crystallization
An aqueous solution of L-tryptophan and fumaric acid in a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio was stirred at room temperature for 6 h. The resulting yellow solution was filtered and kept in a Petri dish. Yellow prismatic-shaped hard crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained over a period of 5 days.
S3. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2. The N-bound, acid and water H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map. The NH and NH3 H atoms were freely refined. The water H atoms were refined with distance restraints: O—H = 0.86 (2) Å, H···H = 1.388 (20) Å with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O). The acid (OH) H atoms and the C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding atoms: Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O,C) for OH and methyl H atoms and 1.2Ueq(C) for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
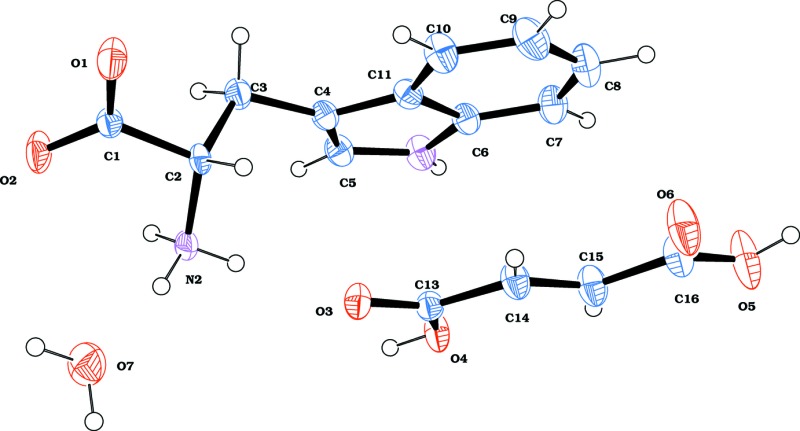
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level.
Fig. 2.

The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
Fig. 3.

The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the b axis. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
Crystal data
| C11H12N2O2·C4H4O4·H2O | F(000) = 712 |
| Mr = 338.31 | Dx = 1.392 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.3928 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 5033 reflections |
| b = 6.6476 (4) Å | θ = 2.8–27.9° |
| c = 21.4219 (13) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 95.801 (3)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1614.07 (18) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2731 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: Sealed X-ray tube | Rint = 0.025 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.898, Tmax = 0.978 | k = −8→8 |
| 10737 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
| 3157 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.084 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0458P)2 + 0.2154P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3157 reflections | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 242 parameters | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0069 (11) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.75082 (19) | 0.1813 (4) | 0.77433 (10) | 0.0380 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.825 (3) | 0.191 (5) | 0.7735 (13) | 0.047 (8)* | |
| N2 | 0.5095 (2) | 0.4264 (3) | 0.91895 (10) | 0.0276 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.472 (3) | 0.534 (5) | 0.9350 (15) | 0.056 (10)* | |
| H2B | 0.563 (3) | 0.476 (5) | 0.8921 (14) | 0.049 (8)* | |
| H2C | 0.554 (3) | 0.365 (4) | 0.9546 (15) | 0.047 (9)* | |
| O1 | 0.24153 (16) | 0.1425 (3) | 0.89730 (8) | 0.0483 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.35274 (17) | 0.2275 (3) | 0.98224 (8) | 0.0485 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.50562 (13) | 0.6533 (3) | 0.80307 (7) | 0.0334 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.69014 (13) | 0.6700 (3) | 0.77851 (7) | 0.0381 (4) | |
| H4O | 0.7050 | 0.6615 | 0.8167 | 0.057* | |
| O5 | 0.63962 (18) | 0.6937 (5) | 0.54724 (8) | 0.0706 (7) | |
| H5O | 0.6080 | 0.6855 | 0.5112 | 0.106* | |
| O6 | 0.45352 (18) | 0.6884 (4) | 0.57018 (8) | 0.0595 (6) | |
| O7 | 0.37013 (19) | 0.7265 (3) | 0.97085 (11) | 0.0532 (6) | |
| H7A | 0.304 (2) | 0.705 (5) | 0.9880 (16) | 0.080* | |
| H7B | 0.382 (3) | 0.852 (4) | 0.9713 (18) | 0.080* | |
| C1 | 0.3327 (2) | 0.2159 (3) | 0.92463 (10) | 0.0263 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.4263 (2) | 0.2860 (3) | 0.88365 (10) | 0.0244 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.3876 | 0.3556 | 0.8468 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 0.4928 (2) | 0.1034 (4) | 0.86179 (12) | 0.0328 (6) | |
| H3A | 0.5345 | 0.0401 | 0.8983 | 0.039* | |
| H3B | 0.4354 | 0.0073 | 0.8432 | 0.039* | |
| C4 | 0.5792 (2) | 0.1458 (4) | 0.81563 (11) | 0.0302 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.6979 (2) | 0.1602 (4) | 0.82805 (11) | 0.0357 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.7379 | 0.1562 | 0.8681 | 0.043* | |
| C6 | 0.6657 (2) | 0.1816 (4) | 0.72436 (11) | 0.0333 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.6742 (2) | 0.1930 (5) | 0.66020 (12) | 0.0445 (7) | |
| H7 | 0.7471 | 0.2041 | 0.6445 | 0.053* | |
| C8 | 0.5720 (3) | 0.1874 (5) | 0.62093 (12) | 0.0508 (7) | |
| H8 | 0.5756 | 0.1951 | 0.5778 | 0.061* | |
| C9 | 0.4630 (2) | 0.1705 (5) | 0.64405 (13) | 0.0507 (7) | |
| H9 | 0.3951 | 0.1677 | 0.6160 | 0.061* | |
| C10 | 0.4529 (2) | 0.1579 (5) | 0.70688 (11) | 0.0417 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.3792 | 0.1472 | 0.7216 | 0.050* | |
| C11 | 0.5557 (2) | 0.1615 (4) | 0.74880 (11) | 0.0312 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.57628 (19) | 0.6648 (4) | 0.76415 (10) | 0.0286 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.5377 (2) | 0.6733 (4) | 0.69680 (10) | 0.0365 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.4570 | 0.6672 | 0.6848 | 0.044* | |
| C15 | 0.6070 (2) | 0.6888 (5) | 0.65258 (11) | 0.0418 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.6880 | 0.6994 | 0.6632 | 0.050* | |
| C16 | 0.5603 (2) | 0.6899 (5) | 0.58582 (11) | 0.0447 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0245 (11) | 0.0520 (14) | 0.0381 (12) | 0.0037 (12) | 0.0067 (9) | −0.0028 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0274 (12) | 0.0345 (12) | 0.0219 (11) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0072 (9) | 0.0000 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0374 (11) | 0.0818 (15) | 0.0254 (9) | −0.0268 (11) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0006 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0834 (16) | 0.0183 (9) | −0.0273 (11) | 0.0045 (7) | −0.0019 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0300 (9) | 0.0449 (10) | 0.0260 (8) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0056 (7) | 0.0031 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0278 (9) | 0.0651 (11) | 0.0216 (8) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0003 (10) |
| O5 | 0.0548 (13) | 0.133 (2) | 0.0237 (9) | −0.0004 (17) | 0.0058 (9) | −0.0012 (15) |
| O6 | 0.0464 (12) | 0.1044 (17) | 0.0265 (9) | 0.0027 (13) | −0.0027 (8) | 0.0012 (12) |
| O7 | 0.0511 (13) | 0.0543 (13) | 0.0578 (13) | 0.0096 (11) | 0.0227 (10) | 0.0010 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0249 (12) | 0.0323 (13) | 0.0220 (11) | −0.0021 (10) | 0.0034 (10) | −0.0003 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0250 (13) | 0.0331 (12) | 0.0149 (11) | 0.0015 (10) | 0.0011 (9) | 0.0015 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0399 (15) | 0.0318 (13) | 0.0275 (13) | 0.0034 (11) | 0.0073 (12) | −0.0007 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0304 (12) | 0.0315 (12) | 0.0295 (12) | 0.0041 (12) | 0.0074 (9) | −0.0047 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0371 (14) | 0.0387 (13) | 0.0312 (13) | 0.0068 (13) | 0.0029 (10) | −0.0028 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0327 (13) | 0.0365 (13) | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0040 (12) | 0.0076 (10) | −0.0033 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0416 (15) | 0.0558 (17) | 0.0384 (14) | 0.0055 (15) | 0.0158 (12) | −0.0013 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0600 (19) | 0.0640 (19) | 0.0291 (13) | 0.0095 (18) | 0.0084 (13) | 0.0003 (15) |
| C9 | 0.0446 (16) | 0.0678 (19) | 0.0374 (14) | 0.0066 (17) | −0.0071 (12) | −0.0061 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0301 (13) | 0.0578 (16) | 0.0373 (14) | 0.0054 (15) | 0.0033 (11) | −0.0047 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0286 (12) | 0.0331 (12) | 0.0323 (12) | 0.0049 (12) | 0.0056 (9) | −0.0043 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0286 (12) | 0.0313 (12) | 0.0257 (11) | −0.0016 (12) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0003 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0328 (13) | 0.0500 (15) | 0.0263 (12) | −0.0002 (14) | 0.0002 (10) | −0.0013 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0339 (14) | 0.0630 (18) | 0.0278 (13) | 0.0024 (15) | −0.0002 (11) | −0.0004 (14) |
| C16 | 0.0429 (16) | 0.0637 (19) | 0.0279 (13) | 0.0031 (16) | 0.0053 (11) | −0.0018 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C5 | 1.359 (3) | C3—H3A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C6 | 1.370 (3) | C3—H3B | 0.9700 |
| N1—H1 | 0.85 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.355 (3) |
| N2—C2 | 1.482 (3) | C4—C11 | 1.433 (3) |
| N2—H2A | 0.92 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N2—H2B | 0.94 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.390 (3) |
| N2—H2C | 0.96 (3) | C6—C11 | 1.413 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.240 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.366 (4) |
| O2—C1 | 1.235 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C13 | 1.219 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.387 (4) |
| O4—C13 | 1.303 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O4—H4O | 0.8200 | C9—C10 | 1.365 (4) |
| O5—C16 | 1.285 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| O5—H5O | 0.8200 | C10—C11 | 1.401 (3) |
| O6—C16 | 1.229 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| O7—H7A | 0.88 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.466 (3) |
| O7—H7B | 0.85 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.297 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.521 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.529 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.475 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9800 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.491 (3) | ||
| C5—N1—C6 | 108.8 (2) | N1—C5—H5 | 124.4 |
| C5—N1—H1 | 123.6 (19) | N1—C6—C7 | 131.2 (2) |
| C6—N1—H1 | 127.6 (19) | N1—C6—C11 | 107.1 (2) |
| C2—N2—H2A | 113 (2) | C7—C6—C11 | 121.7 (2) |
| C2—N2—H2B | 109.4 (19) | C8—C7—C6 | 117.9 (2) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 108 (3) | C8—C7—H7 | 121.1 |
| C2—N2—H2C | 113.4 (17) | C6—C7—H7 | 121.1 |
| H2A—N2—H2C | 105 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 121.4 (2) |
| H2B—N2—H2C | 108 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.3 |
| C13—O4—H4O | 109.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.3 |
| C16—O5—H5O | 109.5 | C10—C9—C8 | 121.6 (3) |
| H7A—O7—H7B | 107 (3) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.2 |
| O2—C1—O1 | 123.9 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.2 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 119.2 (2) | C9—C10—C11 | 118.9 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 116.79 (19) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.6 |
| N2—C2—C1 | 110.35 (18) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.6 |
| N2—C2—C3 | 110.2 (2) | C10—C11—C6 | 118.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 109.37 (19) | C10—C11—C4 | 134.3 (2) |
| N2—C2—H2 | 109.0 | C6—C11—C4 | 107.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 109.0 | O3—C13—O4 | 123.4 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 109.0 | O3—C13—C14 | 121.5 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 115.7 (2) | O4—C13—C14 | 115.07 (19) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 108.4 | C15—C14—C13 | 125.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 108.4 | C15—C14—H14 | 117.4 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 108.4 | C13—C14—H14 | 117.4 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 108.4 | C14—C15—C16 | 121.5 (2) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 107.4 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C5—C4—C11 | 105.8 (2) | C16—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 126.6 (2) | O6—C16—O5 | 124.5 (2) |
| C11—C4—C3 | 127.4 (2) | O6—C16—C15 | 121.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—N1 | 111.1 (2) | O5—C16—C15 | 114.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 124.4 | ||
| O2—C1—C2—N2 | −21.1 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.3 (5) |
| O1—C1—C2—N2 | 161.6 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | 1.1 (4) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | 100.3 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C4 | −177.8 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −77.0 (3) | N1—C6—C11—C10 | 179.9 (3) |
| N2—C2—C3—C4 | −64.7 (3) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | −1.5 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 173.8 (2) | N1—C6—C11—C4 | −0.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 101.2 (3) | C7—C6—C11—C4 | 177.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C11 | −84.9 (3) | C5—C4—C11—C10 | 180.0 (3) |
| C11—C4—C5—N1 | −0.7 (3) | C3—C4—C11—C10 | 5.1 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 174.2 (2) | C5—C4—C11—C6 | 1.0 (3) |
| C6—N1—C5—C4 | 0.1 (3) | C3—C4—C11—C6 | −173.9 (2) |
| C5—N1—C6—C7 | −177.9 (3) | O3—C13—C14—C15 | 178.9 (3) |
| C5—N1—C6—C11 | 0.5 (3) | O4—C13—C14—C15 | −1.3 (4) |
| N1—C6—C7—C8 | 179.2 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 178.1 (3) |
| C11—C6—C7—C8 | 1.0 (4) | C14—C15—C16—O6 | 4.4 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.1 (5) | C14—C15—C16—O5 | −175.9 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.3 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O3i | 0.85 (3) | 2.11 (3) | 2.912 (3) | 158 (3) |
| N2—H2A···O7 | 0.92 (4) | 1.94 (4) | 2.845 (3) | 170 (3) |
| N2—H2B···O1ii | 0.94 (3) | 2.30 (3) | 3.085 (3) | 140 (2) |
| N2—H2B···O3 | 0.94 (3) | 2.28 (3) | 2.901 (3) | 123 (2) |
| N2—H2C···O2iii | 0.96 (3) | 1.87 (3) | 2.832 (3) | 174 (3) |
| O4—H4O···O1ii | 0.82 | 1.74 | 2.559 (2) | 178 |
| O5—H5O···O6iv | 0.82 | 1.81 | 2.630 (3) | 174 |
| O7—H7A···O1v | 0.88 (2) | 2.60 (3) | 3.261 (3) | 133 (3) |
| O7—H7A···O2v | 0.88 (2) | 1.97 (2) | 2.824 (3) | 165 (3) |
| O7—H7B···O2vi | 0.85 (2) | 2.53 (3) | 3.347 (3) | 162 (3) |
| C3—H3B···O3vii | 0.97 | 2.66 | 3.255 (3) | 120 |
| C5—H5···O7i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.491 (3) | 166 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, y−1/2, z; (ii) x+1/2, y+1/2, z; (iii) −x+1, y, −z+2; (iv) −x+1, y, −z+1; (v) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+2; (vi) x, y+1, z; (vii) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU5176).
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Burla, M. C., Polidori, G. & Camalli, M. (1994). J. Appl. Cryst. 27, 435.
- Bakke, O., Mostad, A., Grynfarb, M., Bartfai, T. & Enzell, C. R. (1980). Acta Chem. Scand. 34b, 559–570.
- Bednowitz, A. L. & Post, B. (1966). Acta Cryst. 21, 566–571.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bye, E., Mostad, A., Rømming, C., Husebye, S., Klaeboe, P. & Swahn, C. (1973). Acta Chem. Scand. 27, 471–484.
- Chemla, D. S. & Zyss, J. (1987). In Nonlinear optical properties of organic molecules and crystals, Vol. 1–2. Orlando, New York: Academic Press.
- Demchenko, A. P. (1986). In Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Proteins. Berlin: Springer.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Görbitz, C. H. (2006). Acta Cryst. C62, o328–o330. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Görbitz, C. H., Törnroos, K. W. & Day, G. M. (2012). Acta Cryst. B68, 549–557. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S., Mahapatra, A. K., Nigam, G. D., Chinnakali, K., Fun, H.-K. & Razak, I. A. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 583–585.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hübschle, C. B., Dittrich, B. & Luger, P. (2002). Acta Cryst. C58, o540–o542. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Reis, A. & Schneider, E. (1928). Z. Kristallogr. 68, 543–545.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yardley, J. (1925). J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 127, 2207–2219.
- Zyss, J. & Ledoux, I. (1994). Chem. Rev. 94, 77–105.
- Zyss, J. & Nicoud, J. F. (1996). Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1, 533–546.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176fig2.tif
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
b . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901501484X/su5176fig3.tif
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the b axis. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details).
CCDC reference: 1417535
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


