Abstract
Sepsis causes mitochondrial oxidative injury and swelling. Ethyl pyruvate (EP) is a cytoprotective agent, while aquaporin-8 (AQP8) is a mitochondrial water channel that can induce mitochondrial swelling. We assessed whether EP protects mitochondria during sepsis, and whether AQP8 contributes to the underlying mechanisms. A cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) sepsis model was established in Sprague-Dawley rats, randomized to 3 groups: sham (n=20), CLP (n=59) and CLP+EP (n=51). All rats received postoperative intraperitoneal fluid resuscitation (30 ml/kg); the CLP+EP group also received intraperitoneal EP (100 mg/kg). Survival was assessed at 24 hours. Hepatic mitochondrial ultrastructure was characterized by electron microscopy. The membrane potential of isolated hepatic mitochondria was determined using JC-1 and flow cytometry. Mitochondrial AQP8 expression and cytochrome C (Cyt C) release were measured by Western blotting (values normalized to ß-actin). Survival in the sham, CLP and CLP+EP groups was 100%, 21% and 41%, respectively. Mitochondrial cross-sectional area was smaller in the CLP+EP group than in the CLP group (0.231±0.110 vs. 0.641±0.460 µm2; P<0.001), with a tendency for a lower form factor (a measure of contour irregularity) in the CLP+EP group. Mitochondrial depolarization by CLP was inhibited by EP. Mitochondrial Cyt C release was higher in the CLP group than in the sham (1.211±0.24 vs. 0.48±0.03) or CLP+EP (0.35±0.39) groups. AQP8 expression was similar between groups, with a trend for lower expression in the CLP+EP group compared with the CLP group. EP improves sepsis outcome by targeting the mitochondrion, possibly through modulation of AQP8 expression.
Keywords: Sepsis, mitochondrial swelling, ultrastructure, ethyl pyruvate, aquaporin 8, rat
Introduction
Sepsis is defined by the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) and Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) as the presence of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) caused by infection [1]. However, although our understanding of the mechanisms underlying sepsis has increased over recent years, this has not resulted in the development of novel therapies for this potentially life-threatening condition. In the past few decades, it has become clear that many of the pathophysiologic changes that underlie sepsis occur in the microcirculation, and numerous studies have demonstrated that microcirculatory and mitochondrial dysfunction form an essential part of these pathophysiologic changes [2]. Mitochondrial injury during sepsis is believed to progress from reversible (during the early stages) to irreversible, and hence it is thought that targeting of mitochondrial dysfunction will improve the outcomes of patients with sepsis [3].
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA), or Krebs, cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, and as a result, mitochondria generate substantial quantities of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under pathologic conditions, such as sepsis, these ROS can cause oxidative damage. In a rat model of sepsis, it has been shown that superoxide production by hepatic mitochondria can lead to mitochondrial oxidative damage, dysfunction, swelling, and cytochrome C (Cyt C) release [4]. Interestingly, sepsis seems to result in a mixed population of mitochondria, with some hyperfunctional (and hence generating substantial ROS) and others hypofunctional (due to injury) [5].
The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (PTP) is a protein pore formed under pathologic conditions (such as sepsis) that is thought to allow the movement of ROS from the mitoplast to the cytoplasm, but that also leads to mitochondrial swelling and apoptosis. The PTP is formed as a complex of the adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT; in the inner membrane), the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC; in the outer membrane) and cyclophilin-D, at the junction of the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes [6,7]. However, there has been some debate as to whether PTP underlies the mitochondrial swelling that occurs under pathologic conditions, and alternative candidates have been proposed, including the aquaporin family of proteins that has been well characterized over the past decade [8]. Aquaporin-8 (AQP8) has been detected on the mitochondrial membrane, and shown to be capable of generating mitochondrial swelling in vitro [9,10]. In light of this, we have hypothesized that AQP8 may contribute to sepsis-induced mitochondrial swelling.
Pyruvate plays a key role in glycometabolism, and is one of the primary sources of acetyl-CoA for the TCA cycle. As long ago as 1904, pyruvate was recognized as being a non-enzymatic scavenger for H2O2 [11,12], and since then it has been studied for its potential as a cytoprotective agent. Ethyl pyruvate (EP) is a more stable form of pyruvate that is 10-fold to 100-fold more potent as a cytoprotective agent [13]. Several in vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated EP to be an anti-oxidant that protects organs and tissues during sepsis. However, it is not currently known whether these beneficial actions of EP involve effects on the mitochondrion and its membrane. Therefore, we have examined the effects of EP on the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane during sepsis, and investigated whether AQP8 may contribute to the pathophysiologic processes in the mitochondria that, at least in part, underlie sepsis.
Materials and methods
Animals
The experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China, and all procedures followed the Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, formulated by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. One hundred and thirty male Sprague-Dawley rats (7 weeks of age, weighing 180-150 g) were obtained from the Animal Experiment Center of Sun Yat-Sen University. The animals were fed on standard rat chow and were allowed to drink ad libitum. Prior to the experiments, all animals were allowed to acclimate to the laboratory environment for at least one week. A summary of the experimental protocol is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
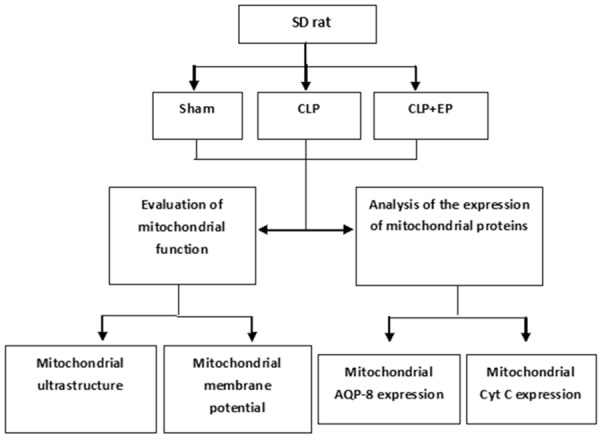
Flow chart illustrating the experimental protocol. CLP, cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis; EP, ethyl pyruvate. The total number of rats used was 130 (20 in the sham group, 59 in the CLP group, and 51 in the CLP+EP group).
Cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis
A cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) model of sepsis was used for these studies. The rat was anesthetized with intraperitoneal (i.p.) chloral hydrate (10%, 10 mg/kg), and a 2-cm midline incision made in the abdominal wall. The cecum was exposed and tightly ligated at a position 1 cm above its base, using a 3-0 silk suture; care was taken to avoid obstruction of neighboring bowel. The cecum was then punctured with an 18-gauge needle. The cecum was gently squeezed until feces were just visible through the puncture, and placed back into the abdominal cavity. The incision was closed with a 3-0 silk suture. At the end of the operation and 6 hours after surgery, intraperitoneal fluid resuscitation was administered (Ringer’s solution, 30 mL/kg), with or without EP (100 mg/kg; Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany).
Since the mortality following CLP was expected to be high, a total of 130 rats were assigned to the three experimental groups: 20 in the sham (S) group, 59 in the CLP (C) group and 51 in the CLP+EP (E) group. The surviving rats were sacrificed (by dislocation of the cervical vertebra) at 6, 12 or 24 hours post-surgery.
Survival was evaluated at 24 hours post-CLP in rats scheduled for sacrifice at this time point (i.e., rats scheduled for sacrifice at 6 or 12 hours was not included in the survival analysis).
Preparation of samples for electron microscopy
Tissue samples were taken from the liver immediately after the rat was sacrificed. Each sample was washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; 4°C), fixed in cold 2.5% glutaraldehyde with 0.1 mol/L cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4), post-fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide, dehydrated, and then embedded in Epon embedding resin. Using the standard stereological principle of randomization, ultrathin sections (60-80 nm) were cut randomly, regardless of the orientation, and mounted on copper grids. Each section was stained with lead citrate and uranyl acetate, and then viewed at a final magnification of approximately 5000×, using an FEI Tecnai G2 transmission electron microscope equipped with a Gatan 832 CCD camera (Gatan, Pleasanton, CA, USA).
Analysis of mitochondrial ultrastructure
Electron micrographs were obtained randomly and sequentially from one section per rat. Thirty photographs were analyzed. Analysis of mitochondrial ultrastructure was undertaken using a computerized image analysis system (Image Pro Plus ver. 6.0, Media Cybernetics, Silver Springs, MD, USA). Mitochondria were identified by an experienced pathologist trained in the Department of Electronic Microscopy, Sun Yat-Sen University. Using the image analysis software, each identified mitochondrion was encircled by a cursor to allow computerized determination of the cross-sectional area and perimeter.
Every complete mitochondrion in each micrograph was assessed qualitatively. Approximately 100 mitochondria per animal were evaluated (at a magnification of approximately 5000×). The mitochondrial form factor was calculated from measurements of the area and perimeter of each individual mitochondrion, using the standard stereological formula: form factor = perimeter2/4× area [13-15]. The form factor bears a linear relationship to the degree of the contour irregularity; it gives an indication of the irregularity of a mitochondrion, independent of its actual size. The minimal value is 1 (for a perfect circle); the value increases as the perimeter increases relative to the area, indicating an irregular shape. A decrease in the value of the form factor suggests the rounding up or swelling of a mitochondrion.
The histological measurements (mitochondrial dimensions and form factor) obtained in the current investigation are presented as median values.
Analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential
5,5’,6,6’-tetrachloro-1,1’,3,3’-tetraethylbenzimidazolocarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) is a cationic lipophilic dye that is widely utilized in apoptosis studies to monitor mitochondrial membrane potential in order to distinguish between apoptotic and healthy cells [16,17]. For these experiments, tissue blocks were pre-heated (0.25 M sucrose, 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 45°C), homogenized (in PBS, 0-4°C), and filtered through a copper strainer (74 μm). The pellet obtained was diluted in PBS to a final concentration of approximately 1×106 cells/mL. The cells were stained using the commercially available Mitochondria Staining Kit (JC-1; MultiSciences Biotech Co., Ltd, Hangzhou, China). Cytofluorometric analysis (Epics XL-MCL flow cytometer; Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA) was performed within 30 min of staining. The samples were monitored using the FL1 photomultiplier tube sensor (excitation 488 nm; emission 525 nm bandpass).
Isolation and preparation of mitochondria
For Western blot analysis of AQP8 and Cyt C, the liver tissue blocks obtained after sacrifice of the animal were stored immediately under liquid nitrogen in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 2%), used as an anti-freezing agent [18]. For the experiments, the sample was first heated (0.25 M sucrose, 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 45°C) and homogenized (pH 7.5, 0-4°C), and the homogenate then centrifuged (20 min, 1200×g, 0-4°C). The supernatant obtained was filtered through two layers of gauze and then centrifuged (15 min, 26000×g, 0-4°C). The mitochondrial pellet obtained was re-suspended in sucrose buffer (0.25 M sucrose, 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.5), and centrifuged (30 min, 1200×g, 0-4°C). Finally, the pellet was re-suspended in sucrose buffer for determination of AQP8, and the filtrate used for Cyt C analysis.
Immunoblotting of mitochondrial proteins
For immunoblotting experiments, mitochondrial suspensions and filtrates were collected as described above. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE on 15% acrylamide Laemmli minigels, and transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes overnight at 4°C. Blots were blocked with 3% non-fat dry milk and incubated overnight at 4°C with primary anti-Cyt C (1:250 dilution; MAB897; R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) or anti-AQP8 (1:400 dilution; ab85909; Abcam, Pak Shek Kok, Hong Kong). After incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:10,000) for 1 h at 4°C, the blots were developed using luminol reagent (sc-2048; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA), and the signals visualized on X-ray film. The blots were scanned digitally (JS-780; Beijing Technology, Beijing, China) and analyzed with Image Pro Plus ver. 6.0 software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Springs, MD, USA). β-actin was used as a loading control.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS software (version 13.0). Ratios are expressed as medians and interquartile ranges, while other data are expressed as means ± standard errors of the mean (SEM). Ordinal data were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis test, and ratio data were compared using the χ2-test. Statistical significance was accepted with a 2-tailed P value <0.05 (α=0.05).
Results
Survival
To determine whether EP suppresses the mechanisms underlying sepsis in the CLP model, survival was assessed 24 hours after the surgical procedure. As expected, survival in the CLP group (21.21%) was much lower than that in the sham group (100%). Interestingly, survival in the CLP+EP group (41.38%) was higher than that in the CLP group, indicative of a beneficial effect of EP.
Mitochondrial ultrastructure
Morphometric analysis was performed on all electron micrographs (at a magnification of approximately 5000×) to determine the effects of CLP on mitochondrial morphology, and establish whether EP was able to influence any such effects of CLP. Figure 2 presents representative photographs obtained by electron microscopy, and Tables 1 and 2 summarize the main findings of the morphometric analysis.
Figure 2.
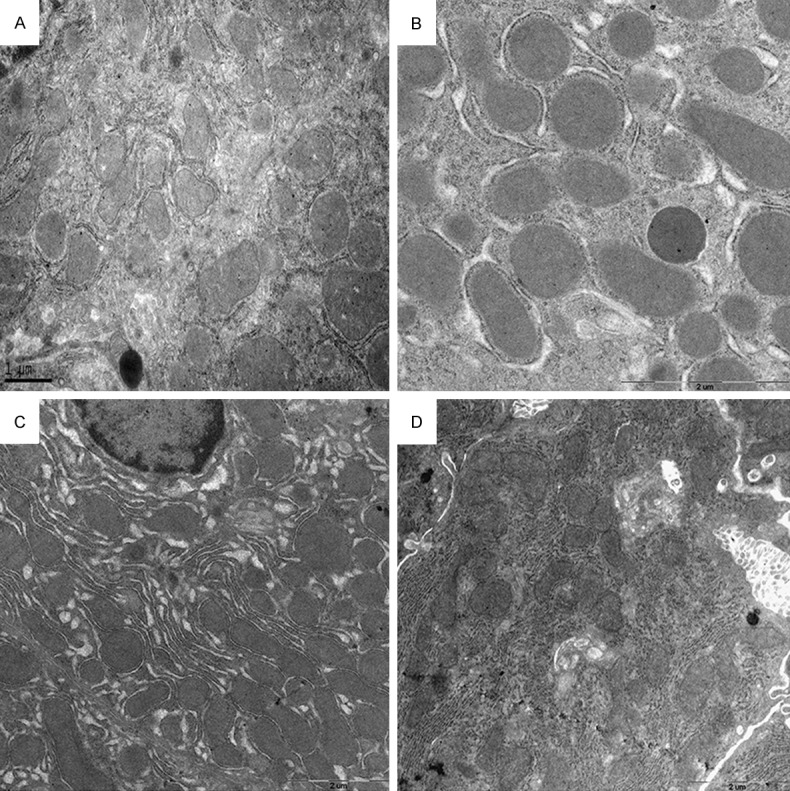
Representative electron micrographs, obtained at a magnification of 3000-5000×. A: CLP group, 24 hours after surgery. B: CLP+EP group, 6 hours after surgery. C: CLP+EP group, 12 hours after surgery. D: CLP+EP group, 24 hours after surgery. No obvious differences in mitochondrial shape or the electron-dense matrix were observed between these groups.
Table 1.
Morphometric analyses of mitochondria, 24 hours after CLP surgery
| Group | SSA | FF | CSA (µm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLP | 0.027 (0.018, 0.035) | 1.162 (1.117, 1.278) | 0.641±0.460 |
| CLP+EP | 0.029 (0.024, 0.039) | 1.300 (1.130, 1.543) | 0.231±0.110* |
Values are shown as median (interquartile range) for SSA and FF, and mean ± SEM for CSA. SSA, specific surface area; FF, form factor; CSA, cross-sectional area.
P<0.001.
Table 2.
Morphometric analyses of mitochondria in the CLP+EP group at varying times after CLP surgery
| Time after CLP surgery | SSA | FF | CSA (µm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 hours | 0.038 (0.021, 0.068) | 1.111 (1.068, 1.265)b | 0.621±0.347d |
| 12 hours | 0.991 (0.764, 1.322)a | 1.124 (1.074, 1.344) | 0.295±0.278 |
| 24 hours | 0.029 (0.024, 0.039) | 1.300 (1.130, 1.543)c | 0.231±0.110 |
Values are shown as median (interquartile range) for SSA and FF, and mean ± SEM for CSA. SSA, specific surface area; FF, form factor; CSA, cross-sectional area.
P<0.001 compared with the values at 6 and 24 hours;
P=0.008, compared with the value at 12 h;
P=0.028 compared with the value at 12 h;
P<0.001 compared with the values at 12 and 24 hours.
Twenty-four hours after surgery, mitochondrial cross-sectional area was significantly smaller in the CLP+EP group than in the CLP group (0.231±0.110 vs. 0.641±0.460 µm2, P<0.001; Table 1). There also appeared to be a trend for the form factor to be lower in the CLP+EP group (1.162 [1.117, 1.278]) than in the CLP group (1.300 [1.130, 1.543]), although statistical significance was not reached (P=0.096). There was no significant difference in the specific surface areas between the two groups (Table 1).
In order to characterize the time course of the effect of EP on these morphometric variables, measurements were made at 6, 12 and 24 hours post-CLP surgery. As shown in Table 2, there was a significant improvement in the form factor over time in the CLP+EP group. Furthermore, mitochondrial CSA was significantly higher 6 hours post-surgery than at the later time points, while mitochondrial SSA was significantly increased at 12 hours post-surgery compared with the other time points (see Table 2).
Taken together, these data suggest that mitochondrial swelling in the rat CLP model of sepsis was alleviated by EP.
Mitochondrial membrane potential
Figures 3 and 4 show the results of experiments designed to measure membrane potential in rat liver mitochondria, in order to identify any detrimental effects of CLP on mitochondrial membrane potential and any beneficial effects of EP. Figure 3 presents control experiments on rat liver hepatocytes, used to characterize the effects of apoptosis. The cells were either treated (POS, Figure 3) or not treated (NEG) with an inducer of apoptosis, carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP; 1 µL of 50 mmol/L stock solution per 1×106 cells, as recommended by the manufacturer) (MultiSciences Biotech Co., Ltd, Hangzhou, China). By comparing the traces obtained in the absence and presence of CCCP, it may be seen that mitochondrial depolarization accompanying apoptosis resulted in the appearance of deflections (arrow in the left-hand panel of Figure 3) in the log 102-103 region. In cells not treated with CCCP, the major signal was in the log 101 region.
Figure 3.
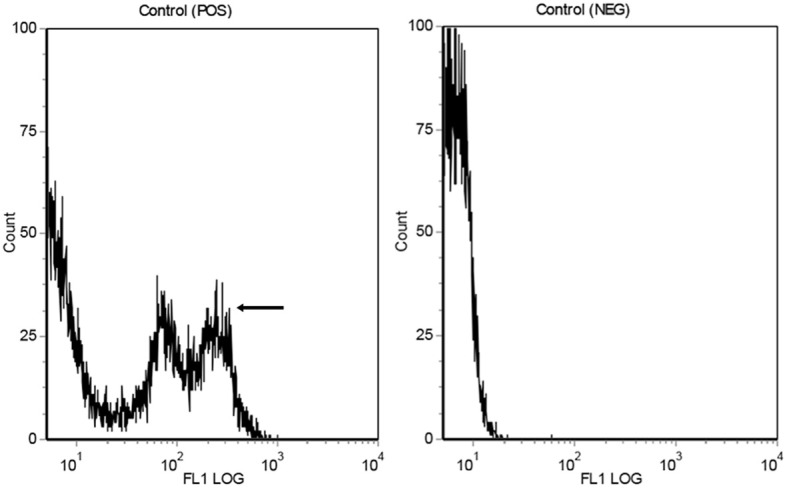
Representative flow cytometry traces to show measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential. POS (left-hand panel): rat liver cells were treated with CCCP to induce apoptosis; the peaks in the 102-103 region (arrow) reflect mitochondrial depolarization. NEG (right-hand panel): cells not treated with CCCP; note the lack of peaks in the 102-103 region.
Figure 4.
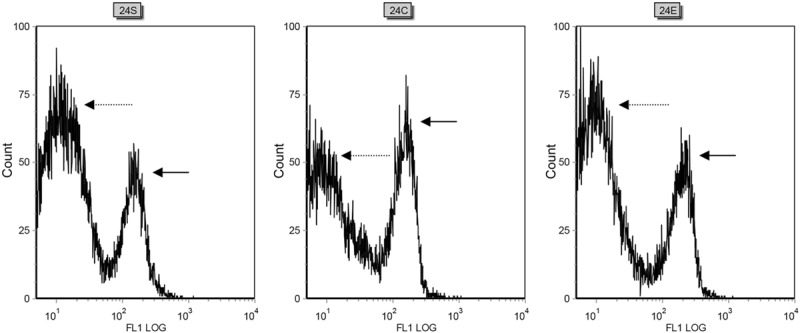
Representative flow cytometry traces to show measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential in the three experimental groups (sham, CLP and CLP+EP). 24S: Measurements made 24 hours after surgery in the sham group show a peak in the 101 region (broken arrow), representing cells without mitochondrial depolarization, and a second peak in the 102-103 region (solid arrow), indicating mitochondrial depolarization. 24C: 24 hours after surgery, the CLP group showed a higher peak in the 102-103 region (solid arrow) and a lower peak in the 101 region (broken arrow), compared with the sham group, reflecting an increase in mitochondrial depolarization. 24E: The CLP+EP group showed a reduced peak in the 102-103 region (solid arrow) and a corresponding enhanced peak in the 101 region (broken arrow), compared with the CLP group, such that the trace resembled that for the sham group. This is consistent with EP reducing mitochondrial injury and depolarization following CLP-induced sepsis.
As shown in Figure 4, a signal in the log 102-103 region was detected even in the sham group (24 hours post-surgery), although most of the signal was in the log 101 region. A much larger peak in the log 102-103 region was found for cells in the CLP group, with a corresponding reduction in the signal in the log 101 region. Importantly, the CLP+EP group showed a smaller signal in the log 102-103 region than that seen in the CLP group, indicating less mitochondrial depolarization that likely reflects a reduction in mitochondrial injury.
Expression of AQP8 and Cyt C
To assess the possibility that AQP8 may be involved in the beneficial actions of EP to reduce mitochondrial injury, the expression levels of this protein were measured (Figure 5). The protein expression of liver mitochondrial AQP8 (relative to β-actin) was not significantly different between the sham and CLP group (sham, 0.76±0.23; CLP, 0.71±0.12). Interestingly, AQP8 protein expression in the CLP+EP group (0.31±0.27) appeared to be lower than that of the other two groups, although statistical significance was not reached (P=0.260).
Figure 5.
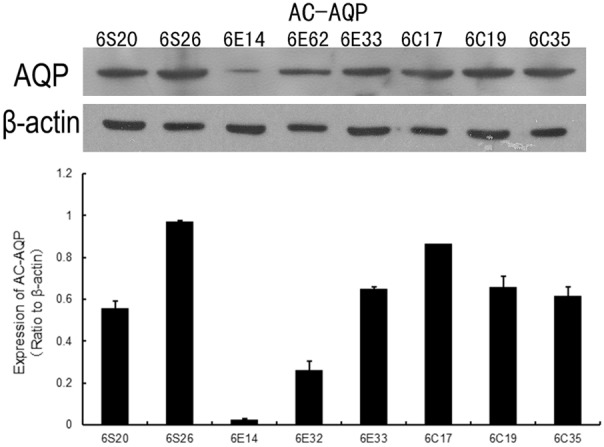
Mitochondrial expression of AQP-8, assessed 6 hours post-surgery using the Western blot technique. β-actin was used as a loading control. The upper panel shows representative immunoblots for AQP8 and β-actin proteins. The lower panel shows data for the sham (6S20 and 6S26), CLP (6C17, 6C19 and 6C35) and CLP+EP (6E14, 6E32 and 6E33) groups, normalized to the β-actin loading control.
Mitochondrial release of Cyt C was also assessed using the Western blot technique, as a measure of mitochondrial injury (Figure 6). The expression of Cyt C (relative to β-actin) was higher in the CLP group (1.211±0.24) than in the sham group (0.48±0.03). Consistent with an action of EP to reduce mitochondrial damage following CLP, Cyt C expression in the CLP+EP group (0.35±0.39) was lower than that in the CLP group.
Figure 6.
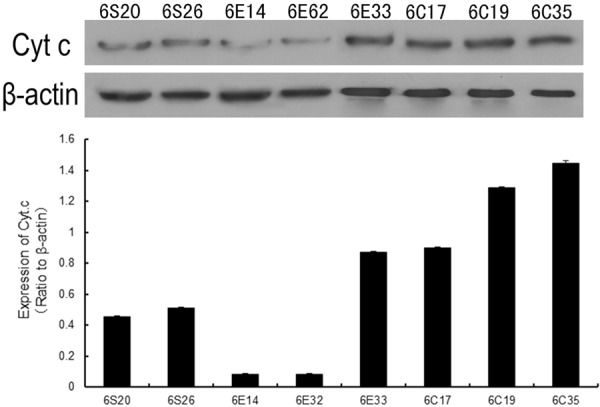
Mitochondrial release of Cyt C into the cytoplasm, assessed 6 hours post-surgery using the Western blot technique. β-actin was used as a loading control. The upper panel shows representative immunoblots for Cyt C and β-actin proteins. The lower panel shows data for the sham (6S20 and 6S26), CLP (6C17, 6C19 and 6C35) and CLP+EP (6E14, 6E32 and 6E33) groups, normalized to the β-actin loading control.
Discussion
Since mitochondrial dysfunction may contribute to the pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying sepsis [2-5], and since EP has been reported to have cytoprotective actions, the aim of the present study was to determine whether EP has beneficial effects in a rat CLP model of sepsis. In addition, we explored whether changes in AQP8 expression contribute to these actions of EP. The major findings of our study were that administration of EP approximately doubled the survival rate of rats 24 hours after CLP surgery, and reduced mitochondrial swelling (assessed by morphometric analyses) and dysfunction (assessed from mitochondrial membrane potential changes and Cyt C release into the cytoplasm). In addition, there was evidence of a trend toward reduced mitochondrial expression of AQP8. Taken together, these data indicate that EP may be a useful therapy targeted at mitochondria to inhibit mitochondrial injury during sepsis, and that these effects may, at least in part, involve changes in AQP8 expression.
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is the end-stage of sepsis, and this highlights the need for aggressive hemodynamic support and optimization of oxygen delivery to maintain tissue perfusion and prevent organ injury during sepsis. Early goal-directed therapy (EGDT) has been shown to improve the outcomes of patients with sepsis [19]; nevertheless, there is still debate concerning certain aspects of EGDT, such as the optimal balance between oxygen delivery and utility [20,21]. The development of an effective strategy to evaluate this balance has become a focus of research in this area. Mitochondria are the principal subcellular organelles that utilize oxygen, and are therefore markedly affected by pathophysiologic processes associated with the host’s response to invading pathogens. The observation that sepsis may lead to a mixture of hyperfunctional and hypofunctional mitochondria [5] highlights the challenges faced when attempting to develop novel therapeutic strategies.
It has been suggested that an adaptive state may develop during multiple organ failure following sepsis, in which the functions of various organs of the body are temporarily inhibited in order to protect these organs from insult [22]. As these normal metabolic functions ‘shut down’, cytopathic hypoxia would be expected to cause mitochondrial dysfunction. In addition, mitochondrial injury exacerbates oxidative stress [23]. Therefore, advanced therapeutic strategies need to have anti-oxidant properties as well as confer protection to the mitochondria.
Animal models of sepsis and endotoxemia have identified numerous mechanisms that may contribute to the underlying pathophysiology. Investigations of cardiac mitochondria in such models have revealed that an impaired mitochondrial defense against oxidation (reduced levels of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase) and mitochondrial oxidative damage (with enhanced lipid and protein oxidation) is associated with nuclear factor kappa-B activation [24], and that a mitochondrial tyrosine kinase (src) and phosphatase (SHP2) may play a role [25]. Furthermore, various interventions have been shown to confer protection against mitochondrial injury and cardiac dysfunction, including scavenging of ROS with melatonin [26], supporting oxidative phosphorylation with glutamine [27], and inhibition of the mitoK (ATP) channel [28]. In addition, stress response proteins have also been implicated as relevant to endotoxemia [29]. Nonetheless, although advances have been made in our understanding of the underlying pathologic processes, the mechanisms have yet to be fully elucidated.
The structure of the mitochondrial membranes limits the ability of typical lipophilic anti-oxidants to ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction, necessitating the development of novel therapies that target mitochondria in order to augment organ function following sepsis [30]. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate plays a key role in intermediary metabolism as a product of glycolysis, entering the mitochondria to undergo oxidative decarboxylation in a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme complex. In models of hemorrhagic shock, the effects of pyruvate and EP have been found to be qualitatively similar, but with EP being 10-100-fold more potent [31,32]. EP has also been used as an experimental therapeutic to effectively protect animals from sepsis, through its anti-oxidative and inflammation-modulating actions [33,34]. In our experiments, administration of EP resulted in a marked improvement in rat survival at 24 hours post-CLP surgery, and this was associated with an alleviation of mitochondrial injury (based on observations made using ultrastructural, membrane potential and protein expression studies). These findings indicate that EP may exert an anti-oxidative action in mitochondria, and that this may be an essential mechanism by which it alleviates the cellular damage otherwise caused by sepsis. In view of these observations, we propose that EP may be a potential therapy for sepsis that targets mitochondria.
Mitochondrial permeability has been found to play an important role in necrosis and apoptosis, with the PTP thought to be a major inducer of cell death. The PTP is formed from a complex of the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), the adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) and cyclophilin-D (CyP-D), at the contact site between the mitochondrial outer and inner membranes. The pathophysiologic activity of the PTP complex corresponds well with the transition of oxidant substances during mitochondrial dysfunction [30,35]. However, the PTP is rarely formed physiologically, and the mechanisms underlying its pathophysiologic induction are still under debate [36]. Our hypothesis was that there may be some other structure or substances that induce mitochondrial swelling and cause the mitochondria to become morphologically abnormal, thereby modifying the elements of the PTP to result in formation of the complex.
AQPs are a family of integral membrane proteins that facilitate the movement of water and certain small solutes across cellular membranes. Interestingly, there are several published studies describing the involvement of AQPs in animal models of sepsis/endotoxemia. Downregulation of AQP2 in certain segments of the renal nephron has been reported to occur during sepsis/endotoxemia [37-40], and there is evidence from a DNA microarray study that AQP5 may be downregulated in the lung [41]. Decreased hepatic expression of AQP8 has also been observed, possibly due to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated post-transcriptional downregulation [42]. Calamita et al. were the first to report that AQP8-mediated water transport may be particularly important for rapid expansion of the mitochondrial volume [43,44]. We therefore speculated that AQP8 may be involved in the pathophysiologic mechanisms that contribute to mitochondrial swelling during sepsis. As described above, we found a tendency for AQP8 protein expression to decrease following EP administration. Since EP also reduced mitochondrial dysfunction (assessed with our other experimental approaches), it is possible that the cytoprotective action of EP may, in part, be due to an action on AQP8 expression to reduce mitochondrial swelling.
Our study is not without its limitations. Although there appeared to be a trend for AQP8 expression to be reduced following EP administration, statistical significance was not reached. Therefore, additional studies, examining protein as well as mRNA expression, are required to confirm whether this effect was real. This study also did not elucidate the mechanisms linking EP to a possible alteration in AQP8 expression, and was limited to one animal model of sepsis. Further research is merited to address these limitations.
In summary, we propose that AQP8 may be an important protein that contributes to the induction of mitochondrial swelling during the early phase of sepsis. As the infection exacerbates, expansion of the mitochondrial volume causes mitochondrial dysfunction and a stimulation of PTP formation, eventually leading to MODS.
Conclusion
EP improves the outcome of sepsis by targeting the mitochondrion, and this effect may involve modulation of the expression of AQP8. Further studies are merited to explore this possibility further.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by The Guangdong Nature Science Foundation (8451008901000719). We thank Fang Rong MD and Li Ying MD for their kind assistance with the experiments.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ruggieri AJ, Levy RJ, Deutschman CS. Mitochondrial dysfunction and resuscitation in sepsis. Crit Care Clin. 2010;26:567–575. x–xi. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2010.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Balestra GM, Legrand M, Ince C. Microcirculation and mitochondria in sepsis: getting out of breath. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2009;22:184–190. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e328328d31a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zapelini PH, Rezin GT, Cardoso MR, Ritter C, Klamt F, Moreira JC, Streck EL, Dal-Pizzol F. Antioxidant treatment reverses mitochondrial dysfunction in a sepsis animal model. Mitochondrion. 2008;8:211–218. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2008.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kantrow SP, Taylor DE, Carraway MS, Piantadosi CA. Oxidative metabolism in rat hepatocytes and mitochondria during sepsis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1997;345:278–288. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1997.0264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Crompton M. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem J. 1999;341:233–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB, Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A, Nielsen S. Aquaporin water channels--from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol. 2002;542:3–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.020818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Crompton M, Virji S, Ward JM. Cyclophilin-D binds strongly to complexes of the voltage-dependent anion channel and the adenine nucleotide translocase to form the permeability transition pore. Eur J Biochem. 1998;258:729–735. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2580729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee WK, Bork U, Gholamrezaei F, Thevenod F. Cd(2+)-induced cytochrome c release in apoptotic proximal tubule cells: role of mitochondrial permeability transition pore and Ca(2+) uniporter. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;288:F27–39. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00224.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Soria LR, Fanelli E, Altamura N, Svelto M, Marinelli RA, Calamita G. Aquaporin-8-facilitated mitochondrial ammonia transport. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;393:217–221. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Holleman MAF. Notice sur l’action de l’eau oxygénée sur les acétoniques et sur le dicétones1.2. Recl Trav Chim Pays-bas Belg. 1904;23:169–171. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kao KK, Fink MP. The biochemical basis for the anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective actions of ethyl pyruvate and related compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;80:151–159. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pomar F, Cosin J, Portoles M, Faura M, Renau-Piqueras J, Hernandiz A, Andres F, Colomer JL, Graullera B. Functional and ultrastructural alterations of canine myocardium subjected to very brief coronary occlusions. Eur Heart J. 1995;16:1482–1490. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a060768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fang X, Huang Z, Zhu J, Jiang L, Li H, Fu Y, Sun S, Tang W. Ultrastructural evidence of mitochondrial abnormalities in postresuscitation myocardial dysfunction. Resuscitation. 2012;83:386–394. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2011.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yu T, Robotham JL, Yoon Y. Increased production of reactive oxygen species in hyperglycemic conditions requires dynamic change of mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:2653–2658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511154103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Reers M, Smith TW, Chen LB. J-aggregate formation of a carbocyanine as a quantitative fluorescent indicator of membrane potential. Biochemistry. 1991;30:4480–4486. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cossarizza A, Salvioli S. Flow cytometric analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential using JC-1. Curr Protoc Cytom. 2001 doi: 10.1002/0471142956.cy0914s13. Chapter 9: Unit 9.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fleischer S, Kervina M. Long-term preservation of liver for subcellular fractionation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:3–6. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Intensive Care Med. 2008;34:17–60. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0934-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rampal T, Jhanji S, Pearse RM. Using oxygen delivery targets to optimize resuscitation in critically ill patients. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2010;16:244–249. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0b013e328338a929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rivers EP, Katranji M, Jaehne KA, Brown S, Abou Dagher G, Cannon C, Coba V. Early interventions in severe sepsis and septic shock: a review of the evidence one decade later. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012;78:712–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Azevedo LC. Mitochondrial dysfunction during sepsis. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2010;10:214–223. doi: 10.2174/187153010791936946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang Q, Raoof M, Chen Y, Sumi Y, Sursal T, Junger W, Brohi K, Itagaki K, Hauser CJ. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature. 2010;464:104–107. doi: 10.1038/nature08780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li L, Hu BC, Chen CQ, Gong SJ, Yu YH, Dai HW, Yan J. Role of mitochondrial damage during cardiac apoptosis in septic rats. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013;126:1860–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zang QS, Martinez B, Yao X, Maass DL, Ma L, Wolf SE, Minei JP. Sepsis-induced cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction involves altered mitochondrial-localization of tyrosine kinase Src and tyrosine phosphatase SHP2. PLoS One. 2012;7:e43424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang H, Liu D, Wang X, Chen X, Long Y, Chai W, Zhou X, Rui X, Zhang Q, Wang H, Yang Q. Melatonin improved rat cardiac mitochondria and survival rate in septic heart injury. J Pineal Res. 2013;55:1–6. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Groening P, Huang Z, La Gamma EF, Levy RJ. Glutamine restores myocardial cytochrome C oxidase activity and improves cardiac function during experimental sepsis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2011;35:249–254. doi: 10.1177/0148607110383040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chopra M, Golden HB, Mullapudi S, Dowhan W, Dostal DE, Sharma AC. Modulation of myocardial mitochondrial mechanisms during severe polymicrobial sepsis in the rat. PLoS One. 2011;6:e21285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Metukuri MR, Reddy CM, Reddy PR, Reddanna P. Bacterial LPS-mediated acute inflammation-induced spermatogenic failure in rats: role of stress response proteins and mitochondrial dysfunction. Inflammation. 2010;33:235–243. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Galley HF. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis. Br J Anaesth. 2011;107:57–64. doi: 10.1093/bja/aer093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cai B, Deitch EA, Grande D, Ulloa L. Anti-inflammatory resuscitation improves survival in hemorrhage with trauma. J Trauma. 2009;66:1632–1639. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a5b179. discussion 1639-1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cai B, Brunner M, Wang H, Wang P, Deitch EA, Ulloa L. Ethyl pyruvate improves survival in awake hemorrhage. J Mol Med (Berl) 2009;87:423–433. doi: 10.1007/s00109-009-0441-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang Y, Li M, Meng M, Qin C. Effect of ethyl pyruvate on physical and immunological barriers of the small intestine in a rat model of sepsis. J Trauma. 2009;66:1355–1364. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31817d0568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kung CW, Lee YM, Cheng PY, Peng YJ, Yen MH. Ethyl pyruvate reduces acute lung injury via regulation of iNOS and HO-1 expression in endotoxemic rats. J Surg Res. 2011;167:e323–331. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2011.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Otero-Anton E, Gonzalez-Quintela A, Lopez-Soto A, Lopez-Ben S, Llovo J, Perez LF. Cecal ligation and puncture as a model of sepsis in the rat: influence of the puncture size on mortality, bacteremia, endotoxemia and tumor necrosis factor alpha levels. Eur Surg Res. 2001;33:77–79. doi: 10.1159/000049698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lee WK, Thevenod F. A role for mitochondrial aquaporins in cellular life-and-death decisions? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;291:C195–202. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00641.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cui WY, Tian AY, Bai T. Protective effects of propofol on endotoxemia-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011;38:747–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Olesen ET, de Seigneux S, Wang G, Lutken SC, Frokiaer J, Kwon TH, Nielsen S. Rapid and segmental specific dysregulation of AQP2, S256-pAQP2 and renal sodium transporters in rats with LPS-induced endotoxaemia. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:2338–2349. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Versteilen AM, Heemskerk AE, Groeneveld AB, van Wijhe M, van Lambalgen AA, Tangelder GJ. Mechanisms of the urinary concentration defect and effect of desmopressin during endotoxemia in rats. Shock. 2008;29:217–222. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e3180ca9e53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Grinevich V, Knepper MA, Verbalis J, Reyes I, Aguilera G. Acute endotoxemia in rats induces down-regulation of V2 vasopressin receptors and aquaporin-2 content in the kidney medulla. Kidney Int. 2004;65:54–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chinnaiyan AM, Huber-Lang M, Kumar-Sinha C, Barrette TR, Shankar-Sinha S, Sarma VJ, Padgaonkar VA, Ward PA. Molecular signatures of sepsis: multiorgan gene expression profiles of systemic inflammation. Am J Pathol. 2001;159:1199–1209. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62505-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lehmann GL, Marinelli RA. Peritoneal sepsis downregulates liver expression of Aquaporin-8: a water channel involved in bile secretion. Liver Int. 2009;29:317–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Calamita G, Ferri D, Gena P, Liquori GE, Cavalier A, Thomas D, Svelto M. The inner mitochondrial membrane has aquaporin-8 water channels and is highly permeable to water. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:17149–17153. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C400595200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Calamita G, Gena P, Meleleo D, Ferri D, Svelto M. Water permeability of rat liver mitochondria: A biophysical study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:1018–1024. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


