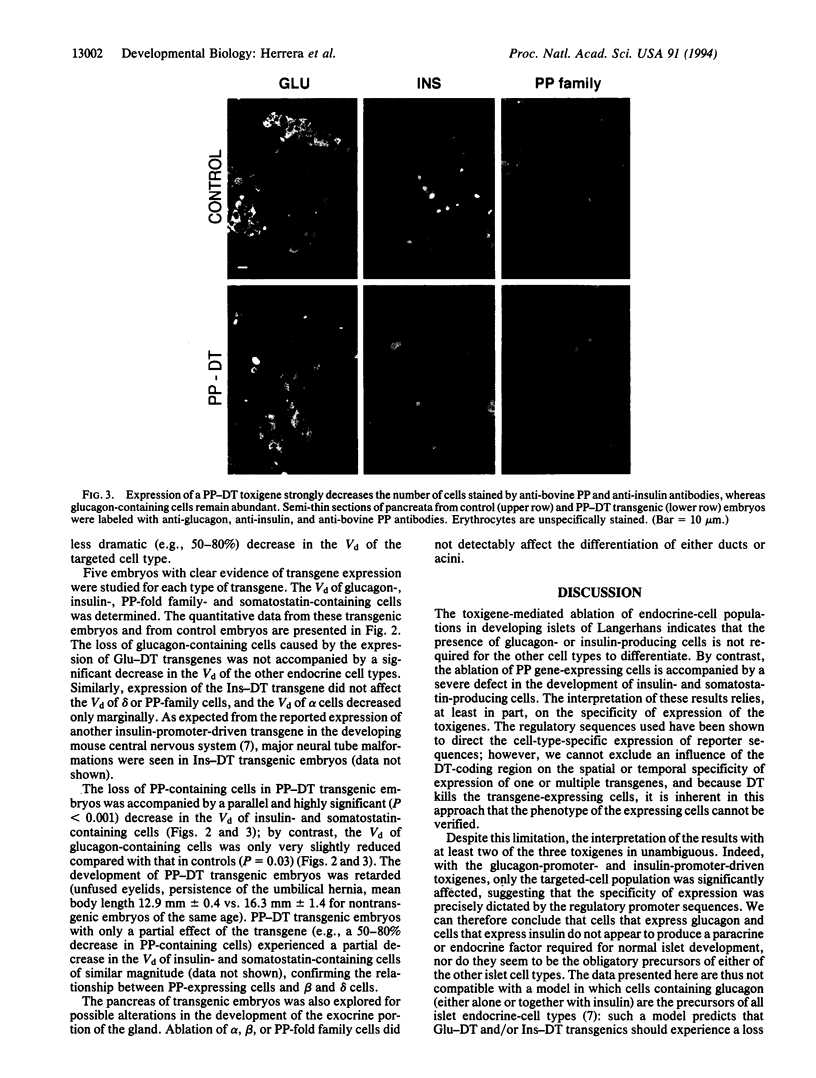
Abstract
Ontogenic relationships between the different types of endocrine cells in the islets of Langerhans were explored by generating transgenic mouse embryos in which cells transcribing the glucagon, insulin, or pancreatic polypeptide genes were destroyed through the promoter-targeted expression of the diphtheria toxin A chain. Embryos lacking glucagon- or insulin-containing cells did not exhibit alterations in the development of the nontargeted islet cell types, whereas embryos lacking pancreatic polypeptide gene-expressing cells also lacked pancreatic insulin- and somatostatin-containing cells. These results show that neither glucagon nor insulin gene-expressing cells are essential for the differentiation of the other islet endocrine-cell types. These results also suggest that pancreatic polypeptide gene-expressing cells are indispensable for the differentiation of islet beta and delta cells because the former produce a necessary paracrine or endocrine factor and/or operate through a cell-lineage relationship.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Mathews L. S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Dwarf mice produced by genetic ablation of growth hormone-expressing cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):453–461. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., Breitman M. Genetic ablation in transgenic mice. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Dec;6(6):523–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman M. L., Clapoff S., Rossant J., Tsui L. C., Glode L. M., Maxwell I. H., Bernstein A. Genetic ablation: targeted expression of a toxin gene causes microphthalmia in transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1563–1565. doi: 10.1126/science.3685993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. J., Philippe J., Jepeal L., Habener J. F. Glucagon gene 5'-flanking sequences promote islet cell-specific gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15659–15665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Teitelman G., Anwar M., Ruggiero D., Hanahan D. Glucagon gene regulatory region directs oncoprotein expression to neurons and pancreatic alpha cells. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A. Dissecting mouse development with toxigenics. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):259–263. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittes G. K., Rutter W. J. Onset of cell-specific gene expression in the developing mouse pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera P. L., Huarte J., Sanvito F., Meda P., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Embryogenesis of the murine endocrine pancreas; early expression of pancreatic polypeptide gene. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1257–1265. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur S., Key B., Stock J., McNeish J. D., Akeson R., Potter S. S. Targeted ablation of alpha-crystallin-synthesizing cells produces lens-deficient eyes in transgenic mice. Development. 1989 Mar;105(3):613–619. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.3.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall S. K., Saunders T. L., Jin L., Lloyd R. V., Glode L. M., Nett T. M., Keri R. A., Nilson J. H., Camper S. A. Targeted ablation of pituitary gonadotropes in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2025–2036. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zijderveld A., Linders K., Rudnicki M. A., Jaenisch R., Berns A. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4293–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson K., Edlund T. IPF1, a homeodomain-containing transactivator of the insulin gene. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4251–4259. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. Macro- and micro-domains in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):538–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Behringer R. R., Quaife C. J., Maxwell F., Maxwell I. H., Brinster R. L. Cell lineage ablation in transgenic mice by cell-specific expression of a toxin gene. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pictet R. L., Clark W. R., Williams R. H., Rutter W. J. An ultrastructural analysis of the developing embryonic pancreas. Dev Biol. 1972 Dec;29(4):436–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Alpert S., Polak J. M., Martinez A., Hanahan D. Precursor cells of mouse endocrine pancreas coexpress insulin, glucagon and the neuronal proteins tyrosine hydroxylase and neuropeptide Y, but not pancreatic polypeptide. Development. 1993 Aug;118(4):1031–1039. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.4.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Linkage of the brain-skin-gut axis: islet cells originate from dopaminergic precursors. Peptides. 1981;2 (Suppl 2):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(81)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upchurch B. H., Aponte G. W., Leiter A. B. Expression of peptide YY in all four islet cell types in the developing mouse pancreas suggests a common peptide YY-producing progenitor. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):245–252. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Evans J. Ultrastructural studies of early morphogenesis and cytodifferentiation in the embryonic mammalian pancreas. Dev Biol. 1968 Apr;17(4):413–446. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. F., Parker R. A., Kendrick J. S. The box plot: a simple visual method to interpret data. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Jun 1;110(11):916–921. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-11-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura H., Nata K., Watanabe T., Kurashina Y., Yamamoto H., Okamoto H. Mosaic evolution of prepropancreatic polypeptide. II. Structural conservation and divergence in pancreatic polypeptide gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2990–2997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]