Figure 6. GSI-I and BTZ effectively suppressed T-LPN xenograft tumor growth.
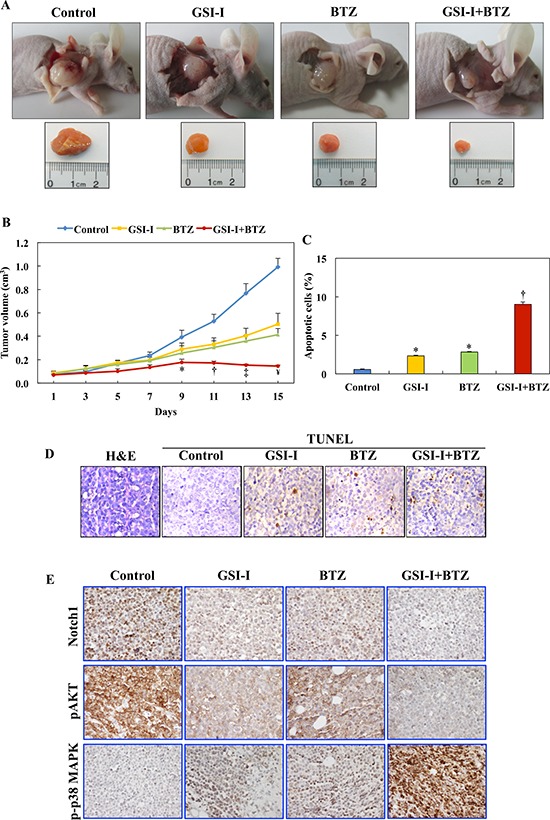
A. In nude mice (examples shown) challenged with subcutaneous injection of Jurkat cells, GSI-I combined with BTZ significantly inhibited tumor growth. B. Quantitative analysis of tumor volume indicates that the combination treatment was superior to treatment with a single drug in suppressing tumor growth. For instance, compared with control mice, combined treatment with GSI-I and BTZ significantly limited tumor growth starting from day 9 after treatment (P < 0.05). In contrast, inhibitory effects were observed at day 11 for BTZ (P < 0.05) and day 13 for GSI-I (P < 0.01). With the progress of the experiment at days 11 through day 15, the regression of tumor volumes was more evident after combined treatment with GSI-I and BTZ. At day 13, combined treatment was associated with more significant inhibitory effects than treatment with GSI-I alone, which became more pronounced at day 15. In addition, at day 15, the combined regimen was more effective than treatment with BTZ alone (*: P < 0.05 vs. control; †: P < 0.001 vs. control; ‡: P < 0.0001 vs. control and P < 0.05 vs. GSI-I; ¥: P < 0.0001 vs. control, P < 0.01 vs. GSI-I, P < 0.05 vs. BTZ). C. Quantitative analysis of TUNEL staining performed on tumor tissues collected at necropsy shows that there was a significant increase in apoptotic cells in tumors tissues from mice treated with GSI-I or BTZ alone compared with tumors collected from control mice. Nonetheless, the highest percentage of apoptotic cells were detected in the mice simultaneously treated with GSI-I and BTZ, and this percentage was not only significantly higher than control tumors but also than tumors from mice treated with either GSI-I or BTZ (*: P < 0.0001 vs. control; †: P < 0.0001 vs. control, GSI-I, and BTZ). Data represent means ± SE. D. Photomicrographs show representative examples of tumor sections collected from a control, untreated mouse stained with H&E (left panel). In addition, representative examples of tumor tissues from the different treatment groups are shown after being stained with TUNEL technique. Tumor tissues from the mouse treated with combined GSI-I and BTZ show more apoptotic cells compared with mice treated with GSI-I or BTZ alone. Original magnification: ×400. E. IHC stain shows pronounced expression of Notch1 and pAKT in the lymphoma xenograft tumors from control mice. Single treatments by GSI-I or BTZ slightly decreased the expression of Notch1 and pAKT. Importantly, combined treatment with the two inhibitors abrogated the expression of Notch1 and pAKT proteins. The expression of p-p38 MAPK was not detected in control lymphoma tumors, whereas treatment with GSI-I or BTZ slightly enhanced its expression. Notably, combined treatment with GSI-I and BTZ significantly increased the expression of p-p38 MAPK in the lymphoma cells. Original magnification: ×400.
