Figure 7. RHOB-mediated resistance to PLX4032 is overcomed by combination with an AKT inhibitor.
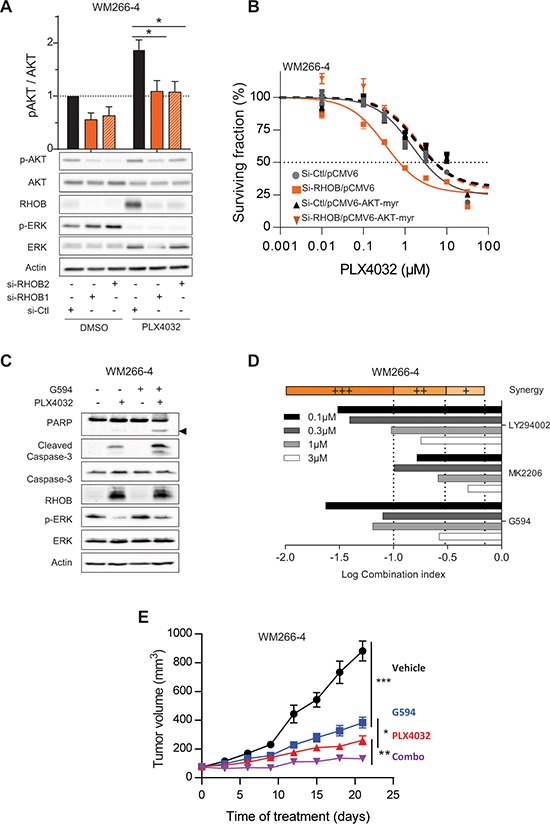
A. WM266-4 cells were transfected with siRNA control (si-Ctl) or targeting RHOB (si-RHOB1 or si-RHOB2) before treatment with 2 μM PLX4032 for 72 h. AKT phosphorylation was analyzed by Western blotting. Total AKT, RHOB, p-ERK and ERK were examined in parallel. Actin was the loading control. Histogram is a quantification of 5 independent experiments. B. WM266-4 cells were co-transfected with siRNAs control (si-Ctl) or targeting RHOB (si-RHOB2) and empty plasmid (pCMV6-Ctl) or encoding AKT-myr (pCMV6-AKT-myr). Cells were then treated with PLX4032 and the viability was assayed 72 h later. C. Western blotting of caspase-3 and PARP cleavage (the cleaved fragment is indicated by the arrowhead) in WM266-4 cells treated with 2 μM PLX4032 and/or 1 μM G594 for 48 h. Total caspase-3, RHOB, p-ERK and ERK were examined in parallel. Actin was the loading control. D. WM266-4 cells were treated with equal amount of PI3K/AKT inhibitors (LY294002, MK2206 or G594) and PLX4032. Viability was assayed 72 h later by MTS assay. Combination indexes (CI) were calculated with CompuSyn (very strong synergism (+++) CI < 0.1; strong synergism (++) 0.1 < CI < 0.3; synergism (+) 0.3 < CI < 0.7). E. Athymic mice were subcutaneously inoculated with WM266-4 cells. Mice were randomized 10 days later in 4 groups (10 mice per group) and treated orally with vehicle, G594 or/and PLX4032 for 21 days. The tumor volume was evaluated every 3 days.
