Abstract
Background
Publication of scientific articles related to khat (Catha edulis) in peer-reviewed journals is considered a measure of research productivity. The principal objectives of this study were to quantify the research contribution related to khat at the global level, as well as to determine its relative growth rate, collaborative measures taken, productivity at the institutional level, and the most prolific journals publishing on the topic.
Methods
On the basis of title words related to khat, publications were identified for all data in Scopus bibliographic database’s history up to December 31, 2014. The research productivity for the top 10 countries was evaluated in relation to the population size and gross domestic product (GDP) in 2013.
Results
The criteria were met by 651documents published in 51 countries. The largest number of articles associated with khat was from the UK (15.2 %), followed by Yemen (10.3 %), the USA (9.7 %) and Ethiopia (9.1 %). Ethiopia, Yemen, and Kenya had the highest productivity of publications after standardization by population size and GDP. Furthermore, Yemen achieved the highest number of collaborations, by having researchers from 19 countries. Ethiopia followed, having researchers from 16 countries.
Conclusions
This bibliometric study provides a demonstration for the worldwide research activity regarding khat. The number of articles related to khat has increased rapidly over the last 10 years. The present study is a good starting point to evaluate research activity in the field of khat. Although the data shows a promising increase in the research activity, the quantity of khat-related research is still too little compared to the massive use of khat in certain countries.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis, Catha edulis, h-index, Khat, Scopus database
Background
Khat (Catha edulis) is a stimulant plant grown commonly in Southern Arabia and East Africa. The leaves of the khat shrub are characterized by an aromatic odour, with an astringent and slightly sweet taste [1]. The leaves and buds of khat are chewed to reach a state of euphoria and excitement [2].
The main active ingredients of khat are cathine and cathinone, thus khat chewing may have various different compounds with different effects [3]. Chewing khat mainly affects the user’s gastro-intestinal system and the central nervous system (CNS). Tolerance to and dependence on khat and its psychiatric symptoms may be observed as effects on the CNS [2–4, 1, 5, 6]. The World Health Organization (WHO) categorized khat as a drug of abuse that can lead to mild to moderate psychological dependence but to a lesser degree than nicotine and alcohol [7], and the WHO does not deem khat to be as dangerously addictive as cocaine [8]. The khat chewing habit has spread with African and Arabian immigrants to Australia, Europe, and Asia, as well as to the United States, and it is becoming a global phenomenon [9]. It is legal for sale and production in some countries but is a controlled or illegal substance in others. The use of khat is accepted within Yemeni, Ethiopian, Eritrean, Djiboutian, Kenyan, Somali and Ugandan cultures [3, 6] but is prohibited in the USA, France, Sweden, and Switzerland. Khat use had been tolerated in the Netherlands and in the UK for a long time, but in 2012, the recreational use of khat was prohibited in the Netherlands, and the UK followed the prohibition in 2014 [10].
Although quite a few bibliometric studies have been carried out on the field of substance abuse [11–17], they have failed to reveal any data concerning the evaluation of scientific research output regarding khat at the global or regional level. The evaluation of scientific research at global, regional, or national levels is necessary to improve its research productivity [18]. The bibliometric approach is a research method used to evaluate the current state of scientific research in certain areas by conducting a precise analysis to obtain statistics that can be considered indicators of achievement that allow researchers to recognise and improve their research [19, 20]. This type of analysis utilizes quantitative methods and statistics to describe publications within a given field, journal, institution, or country [21, 22, 20]. The main objectives of this bibliometric study were to examine the publication pattern of khat at the global level, as well as to determine the publications’ relative growth rate, collaborative measures, productivity at the institutional level, and the most prolific journals publishing on khat, as retrieved from the Scopus database. It is hoped that the results of this study will contribute to quality improvement in future research on khat. This study can be used as a baseline data point to direct national and international policies regarding khat. For example, khat needs to be introduced as one potential substance of abuse in many teaching materials and rehabilitation centres.
Methods
Search strategy
Scientific output was assessed based on a methodology designed and used in previous bibliometric studies [23, 20, 24–30]. SciVerse Scopus was used to collect data pertaining to the current study because it includes all MEDLINE journals, and it contains all authors’ country affiliations, which were needed for seeing international collaborations, institutional phenomena, and countries’ production rates. Furthermore, Scopus is considered to be the largest international multidisciplinary database in the world, and it covers a wider range of journals from developed and developing countries than does MEDLINE or Web of Science [31, 32].
The terminology used for Catha edulis varies between regions and includes names such as qat in Yemen and in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), mirra in Kenya, khat in Ethiopia, and jaad or qaad in Somalia. However, in most of the literature, it is known as khat [33]. The keywords entered into the search engine were retrieved from previous research related to khat [1, 33–35]. All of the following selected keywords were entered in the field for article titles: “khat”, or “jaad”, or “mirra” or “qaad”, or “mairungi” or “qat” or “Catha edulis” or “catha”. The scope of the research went from as far back as Scopus has archived records (1952) through to December 31, 2014. Documents that were published as errata were excluded. In addition, those documents in which the concepts were not related to khat were excluded. Articles from 2015 were excluded because Scopus has not yet archived all of these issues. The collected data were used to create the following measurements: growth rate, collaborative measures, productivity at the institutional level, the most productive authors, the most prolific countries with citation patterns, and the most prolific journals [23, 20, 24, 25]. All of these measurements were ranked according to the order that is now popularly called standard competition ranking (SCR), as in previous similar bibliometric studies [20, 24, 25]. The quality of publications related to khat was measured using the h-index, which was established by Jorge Hirsch in 2005, where index h is defined as the number of papers with a citation number more than or equal to h [36]. Furthermore, the quality of the journals was assessed by two indicators: the impact factor (IF) using the Journal Citation Report (JCR; Web of Knowledge) 2013 and the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR). Additionally, publication activity was adjusted for the top 10 countries by using the adjustment index (AI) formula [37, 24, 28]. The research productivity for the top 10 countries was evaluated in relation to the population size and the gross domestic product (GDP) in 2013 [38].
Statistical analysis
Data were entered in a Microsoft Excel sheet and then transferred to the Statistical Package for Social Science programs (SPSS, V.15) for data management and analyses. Data are presented as medians (with interquartile ranges) or as numbers with percentages.
Results
There were 651 articles meeting the search criteria from 1952 to 2014. We identified 491 (75.4 %) articles of original research, 45 (6.9 %) letters to the editor, 39 (6.0 %) reviews, and 76 (11.7 %) articles that were categorized as other types of publications, such as notes or editorials. The numbers of articles related to khat soared rapidly during the last decade. Before 2002, the number of annual publications related to khat was less than 280 papers, which has grown much more rapidly since 2008 (Fig. 1). The first document related to khat was published by Baird in East African Medical Journal in 1952 [39]. The great majority of articles retrieved were in English (90.2 %). Other relatively frequent languages were French (3.8 %) and German (2.9 %).
Fig. 1.
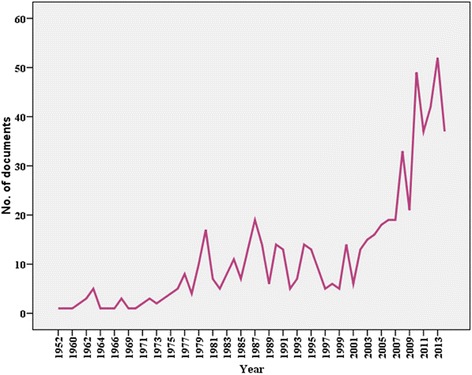
Total articles included in a bibliometric analysis of worldwide publications related to khat from 1952 to 2014
All of the extracted publications were published in 51 countries. The largest number of articles associated with khat was from the UK (15.2 %), followed by Yemen (10.3 %), the USA (9.7 %), and Ethiopia (9.1 %); (Table 1). Ethiopia, Yemen, and Kenya had the highest productivity of publication after standardization by population size and GDP (Table 1). The total number of citations was 7976, giving an average citation per item of 12.3. The median (interquartile range) was 5 (1–16). The highest median (interquartile range) number of citations was 16 (5–28) for Italy, followed by 10 (2–33) for Switzerland. The h-index of the retrieved documents was 44 (44 documents had been cited at least 44times for the period of study). The highest h-index was 22 for the UK, followed by 17 for Yemen and for Switzerland. Furthermore, Yemen achieved the highest number of collaborations, with collaborating researchers from 19 countries. Ethiopia followed, having collaboration among researchers from 16 countries. Yemen had the highest percentage (67.2 %) of documents in collaboration with international authors, followed by 60 % for Egypt, and 53.1 % for Germany (Table 1).
Table 1.
The top 10 ranking of the most productive countries in publishing the largest number of articles associated with khat during the period from 1952 to 2014
| SCR | Countries | No. of articles (%) | h-index | Median (Q1-Q3) of citation | Average of citation | Collaborations with foreign countries | Number (%)a of documents with international authors | Adjustment index b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | UK | 99 (15.2) | 22 | 7 (2–20) | 15.2 | 13 | 27 (27.3) | 2.4 |
| 2nd | Yemen | 67 (10.3) | 17 | 4 (0.0-21) | 12.9 | 19 | 45 (67.2) | 45.5 |
| 3rd | USA | 63 (9.7) | 15 | 5 (1–4) | 10.7 | 10 | 25 (39.7) | 1.2 |
| 4th | Ethiopia | 59 (9.1) | 12 | 1 (0.0-11) | 7.9 | 16 | 20 (33.9) | 116.8 |
| 5th | KSA | 55 (8.4) | 11 | 2 (1–9) | 6.4 | 11 | 16 (29.1) | 2.1 |
| 6th | Switzerland | 47 (7.2) | 17 | 10 (2–33) | 22.6 | 1 | 4 (8.5) | 0.6 |
| 7th | Germany | 32 (4.9) | 12 | 9 (1–24) | 15.8 | 15 | 17 (53.1) | 0.7 |
| 8th | Kenya | 23 (3.5) | 10 | 8 (4–15) | 11.3 | 3 | 6 (26.1) | 18.5 |
| 9th | Egypt | 20 (3.1) | 5 | 1 (0–5.8) | 3.1 | 7 | 12 (60.0) | 6 |
| 10th | Italy | 19 (2.9) | 11 | 16 (5–28) | 18.3 | 6 | 4 (21.1) | 0.5 |
KSA The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, SCR Standard Competition Ranking, USA The United States of America, UK The United Kingdom, Q1–Q3 lower quartile - upper quartile
aPercentage of documents with international authors from the total number of documents for each country
bAn adjustment index (AI) was measured using the following formula: AI = [total number of publications for the country / GDP per capita of the country]*1,000, where GDP per capita = GDP/population of the country
Table 2 shows the data for the most prolific journals in the field of khat. Forty-eight documents (7.4 %) were published in Journal of Ethnopharmacology, whereas 14documents (2.2 %) were published in East African Medical Journal, followed by9 documents (1.4 %) for each of Saudi Medical Journal and Forensic Science International. Four journals from the most prolific journals in the field of khat had no official IF and only four journals had SJR >1 (Table 2).
Table 2.
Ranking of the top 10 journals in which articles associated with khat were published worldwide
| SCRa | Journal | Frequency (%) | IF (2013)b | SJR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Journal of Ethnopharmacology | 48 (7.4) | 2.939 | 1.149 |
| 2nd | East African Medical Journal | 14 (2.2) | NA | 0.152 |
| 3rd | Saudi Medical Journal | 9 (1.4) | 0.554 | 0.269 |
| 3th | Forensic Science International | 9 (1.4) | 2.115 | 1.293 |
| 5th | Bulletin on Narcotics | 8 (1.2) | NA | NA |
| 6th | Lancet | 7 (1.1) | 39.207 | 11.563 |
| 6th | Journal of the Chemical Society Perkin Transactions 1 | 7 (1.1) | NA | NA |
| 6th | BMC Public Health | 7 (1.1) | 2.321 | 1.233 |
| 6th | Planta Medica | 7 (1.1) | 2.339 | 0.791 |
| 6th | Medecine Tropicale | 7 (1.1) | NA | 0.174 |
SCR standard competition ranking; SJR SCImago Journal Rank, NA not available, IF impact factor
aEqual journals have the same ranking number, which leaves a gap in the ranking numbers
bThe impact factor was reported according to the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) journal citation reports (JCR) 2013
Table 3 shows the scientific articles’ areas of interest. Medicine was the most researched topic, represented by 366 (56.2 %) articles. The second most researched topic was pharmacology, toxicology and pharmaceutics, represented by 179 (27.5 %), followed by biochemistry, genetics, and molecular biology with 88 (13.5 %) articles.
Table 3.
Ranking of the top 10 interest areas of the published articles associated with khat
| SCRa | Areas of interest | N (%)b |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Medicine | 366)56.2) |
| 2nd | Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics | 179 (27.5) |
| 3rd | Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology | 88 (13.5) |
| 4th | Social Sciences | 56 (8.6) |
| 5th | Chemistry | 53 (8.1) |
| 6th | Agricultural and Biological Sciences | 43 (6.6) |
| 7th | Neuroscience | 42 (6.5) |
| 8th | Environmental Science | 26 (4.0) |
| 8th | Psychology | 26 (4.0) |
| 10th | Dentistry | 23 (3.5) |
SCR standard competition ranking
aEqual areas of interest have the same ranking number, which leaves a gap in the ranking numbers
bTotal exceeds 100 % as data are overlapping due to multidiscipline interactions
A list of the most cited articles in the field of khat is shown in Table 4 [40–47, 1, 48]. Table 5 presents the 10 institutions producing the most khat research articles. The most productive institution was Sana’a University, Yemen (8.0 % of total publications); followed by Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia (4.5 %), and King Saud University College of Pharmacy, KSA (4.0 %). Table 6 provides the names of the most prolific authors who have contributed at least ten articles in the field of khat.
Table 4.
Top 10 ranking of cited articles in Scopus related to khat worldwide
| SCRa | Authors with year of publication | Title | Source title | Cited by | Article type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Halbach 1972 [40] | Medical aspects of the chewing of khat leaves | Bulletin of the World Health Organization | 145 | Review |
| 2nd | Kalix and Braenden 1985 [41] | Pharmacological aspects of the chewing of khat leaves | Pharmacological Reviews | 142 | Review |
| 3rd | Al-Motarreb et al. 2002 [42] | Khat: Pharmacological and medical aspects and its social use in Yemen | Phytotherapy Research | 128 | Review |
| 4th | Brenneisen et al. 1990 [43] | Amphetamine-like effects in humans of the khat alkaloid cathinone | British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology | 116 | Original article |
| 5th | Widler et al. 1994 [44] | Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of khat: A controlled study | Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics | 110 | Original article |
| 6th | Toennes et al. 2003 [45] | Pharmacokinetics of cathinone, cathine and norephedrine after the chewing of khat leaves | British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology | 104 | Original article |
| 7th | Kalix 1990 [46] | Pharmacological properties of the stimulant khat | Pharmacology and Therapeutics | 90 | Review |
| 8th | Luqman and Danowski 1976 [47] | The use of khat (Catha edulis) in Yemen. Social and medical observations | Annals of Internal Medicine | 84 | Review |
| 9th | Cox and Rampes 2003 [1] | Adverse effects of khat: A review | Advances in Psychiatric Treatment | 82 | Review |
| 10th | Odenwald et al. 2005 [48] | Khat use as risk factor for psychotic disorders: A cross-sectional and case–control study in Somalia | BMC Medicine | 77 | Original article |
SCR standard competition ranking
aEqually cited articles have the same ranking number, which leaves a gap in the ranking numbers
Table 5.
Ranking top 10 highly productive institutions that most frequently published articles associated khat worldwide
| SCRa | Institution, country | No. of documents (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Sana’a University, Yemen | 52 (8.0) |
| 2nd | Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia | 29 (4.5) |
| 3rd | King Saud University, KSA | 26 (4.0) |
| 4th | University of Nairobi, Kenya | 20 (3.1) |
| 4th | Universite de Geneve, Switzerland | 20 (3.1) |
| 6th | University of Minnesota, USA | 19 (2.9) |
| 7th | Jazan University, KSA | 15 (2.3) |
| 8th | University of Nottingham, UK | 14 (2.2) |
| 9th | Jimma University, Ethiopia | 12 (1.8) |
| 10th | University of Kent, UK | 10 (1.5) |
| 10th | Universitat Bern, Switzerland | 10 (1.5) |
SCR standard competition ranking, KSA The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, UK The United Kingdom
aEqual institutions have the same ranking number, which leaves a gap in the ranking numbers
Table 6.
The 10 most-productive authors
| SCRa | Author name | Total number of articles (%) | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Kalix, P. | 32 (4.9) | Universite de Geneve Faculte de Medecine, Department of Pharmacology, Geneve, Switzerland |
| 2nd | Al’Absi, M. | 17 (2.6) | University of Minnesota Twin Cities, Department of Family & Community Medicine, Minneapolis, USA |
| 3rd | Al-Meshal, I.A. | 16 (2.5) | King Saud University College of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmacognosy, Riyadh, KSA |
| 4th | Al-Habori, M. | 14 (2.2) | Sana’a University, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Sana’a, Yemen |
| 5th | Brenneisen, R. | 13 (2.0) | Universitat Bern, Department of Clinical Research (DCR), Bern, Switzerland |
| 5th | Murray-Lyon, I.M. | 13 (2.0) | Department of Gastroenterology, Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, 369 Fulham Road, London SW10 9NH, UK |
| 5th | Crombie, L. | 13 (2.0) | University of Nottingham, Department of Chemistry, Nottingham, UK |
| 5th | Tariq, M. | 13 (2.0) | Department of Pharmacology, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, P.O. Box 2457, Riyadh-11451, KSA |
| 9th | Whiting, D.A. | 11 (1.7) | University of Nottingham, Department of Chemistry, Nottingham, UK |
| 10th | Nakajima, M. | 10 (1.5) | University of Minnesota Medical School, 1035 University Drive, Duluth, Minnesota 55812, USA |
| 10th | Ageel, A.M. | 10 (1.5) | King Saud University, College of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmacology, Riyadh, KSA |
SCR standard competition ranking, KSA The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, USA The United States of America, UK The United Kingdom
a Equal authors have the same ranking number, which leaves a gap in the ranking numbers
Discussion
In this study, I obtained some significant points regarding the research productivity throughout the period between 1952 and 2014. The number of articles related to khat has increased rapidly over the last 10 years. As far as I am aware, this is the first study carried out to evaluate the quantity and quality of khat-based research from all countries in the world. The number of published articles was used as an indicator of the quantity of research activity in the field of khat. The number of citations in an h-index and the impact factors were used as quality indicators [49–51]. This bibliometric study focused primarily on assessing the publication pattern of articles about khat at the global level, the productivity of particular institutions, collaborative measures, and the utility of various journals to the field of khat, which is known as a sub-area in the field of substance abuse. Understanding of how research related to khat has progressed is important in reducing morbidity and mortality related to substance abuse. Such understanding of research activity in the field of khat is helpful in developing an effective policy to respond to this progress, as well as it gives an opportunity for policymakers to gain public and political support for their measures [6].
Ina critical review conducted in 2007, Warfa et al. identified a large amount of evidence on khat, most of which related to khat and to mental health, its adverse effects, and its harms to users and to society [52]. The current bibliometric study also adds to the bibliometric literature in the field of substance abuse [11–15, 17, 16].
It is interesting to note that research performance in the field of khat has been neglected in some countries. However, researcher should grow because khat use has an increasing global market and a documented economic value similar to other harvests, such as coffee, cacao, and tea. During the last few decades, khat use has an increased global importance due to migration, leading to an increase in health problems among its users. The khat trade has a complex delivery system, and thus efforts to prohibit it would need information about the probable risks of a black market developing if khat becomes criminalized [53].
The most obvious finding to emerge from the analysis is that research collaborations in the field of khat, compared to other fields, has been neglected or low in most countries [54, 23–25]. Contributions in research output from collaboration of different world regions with Yemen and Ethiopia were evident. Several studies have found that there is a positive correlation between international collaboration and research output [55–57]. The benefits of increasing collaborations are that it leads to easier access to financing, more opportunities to achieve a higher research productivity [58–60], and it facilitates translation research expertise to countries that require such [28, 24, 61]. As the world faces the truth of khat use as a phenomenon, efforts to put it under global principles and achievable control at national levels should increase. However, these attempts will involve comprehensively reflecting on all the aspects that the expansion of khat consumption and production highlight as a global phenomenon [53]. We need more collaboration in research in order to recognize the actual size and the reasons related to the rapid increase of khat use in some countries such as Yemen and Ethiopia. Continuous research for evaluating the outcomes is another important aspect of knowing more regarding the community status before and after the application of health education programs, public awareness, and information campaigns.
The results of this study show that publications related to khat were 12.3 citations per article. This result is in line with those of previous studies, especially on those that were published in toxicological journals [62–64, 29, 28], and within the average citation range of integrative and complementary medicine journals [65–70]. Several recent studies using the same bibliometric technique indicated that the average citation rate for publications on electronic cigarettes was 6.4 citations per article [20]; on calcium channel blockers, 9.1 [27]; on paracetamol,12.3 [28]; and on narghile tobacco smoking, 13 [23].
The 10 most prolific countries that published articles on khat include many new countries that are usually not as recognizable to readers as other scientific research productivity rankings [71]. As shown in this study, the behaviour of each country, in terms of scientific research output, differs. In countries such as the UK, the total number of scientific publications related to khat output accounted for more than 15.2 % of the global research output. Therefore, this research activity might be dependent on the population size, the GDP, and the level of research activity [72, 28]. In this study, after adjusting for economy and population power, the ranking of countries’ research productivity differed clearly from those based on absolute research production. After adjusting for the national GDP per capita and population, Ethiopia, Yemen, and Kenya had the highest research productivity. No similar study has been found in the literature to this point, thus I was unable to interpret this finding in light of other results. Based on these results, countries with rapidly growing economies and with large population sizes were found to be among the main factors related to research productivity. These findings suggest that rapid economic growth in these countries may result in more research investments and funding support, and may lead to enhance research activity related to khat. The sale and consumption of khat are legal in some countries, including Ethiopia, Kenya and Yemen, which fact might contribute to scientific research productivity.
A bibliometric study was conducted in 10 European countries to examine publications in the field of addiction in comparing to the same type of published data from the USA during the years 2001–2011 [11]. It was found that the absolute increase in publications in the field of addiction was higher in Europe as a whole (an increase on average of 113.8 papers per year) than in the USA. A bibliometric study was also conducted by a number of scholars to examine the worldwide scientific research output in the field of alcohol drinking and alcohol-related problems during the years 2001–2011 [16]. The researchers found that research about alcohol is an integrated field, with an average of 4820 documents published each year in Scopus and in MEDLINE. The bibliometric analysis in this study showed that scientific research output in the field of khat is lagging behind in substance abuse research and the sharing to global research in substance abuse is low.
The present study has several limitations that need to be stated, most of which were mentioned in previous similar bibliometric studies [70, 37, 29, 30]. Studies on khat that were indexed in databases other than Scopus may not have been included. Gaillard demonstrated that some African researchers have published their work in local journals that are not indexed in the international citation databases [73]. Another limitation is that some articles did not mention khat or related expressions in their titles, so it is possible that not all articles about khat were considered.
Conclusions and research-policy considerations
In conclusion, this bibliometric study provides a demonstration of worldwide research activity on khat. The number of articles related to khat has increased rapidly for the last 10 years. The present study is a good starting point to evaluate research activity in the field of khat. Although the data shows a promising increase in the research activity, the quantity of khat-related research is still too little compared to the massive use of khat in certain countries. The quantity and quality of khat research can be enhanced by providing more collaboration with international research projects related to khat use.
Governments of countries in which khat is being used, such as Ethiopia, Yemen, and Kenya, need to implement policies regarding the cultivation of khat and restriction on the areas that are used for khat cultivation. Furthermore, the shipping of khat to other countries, even for personal use, must be considered a legal violation and needs to be prohibited at the global level. Governments need to launch awareness programs and campaigns to fight this social phenomenon, which has surpassed tobacco smoking in some countries. Finally, it is recommend that (i) more research efforts be invested in khat regarding its neuronal and oral health impacts; (ii) communities need to implement new regulations to limit khat use among individuals (iii) and finally, countries make efforts to change their citizens’ khat chewing behaviour by implementing community-based primary prevention activities and by improving the community economic status.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank An-Najah National University for giving the opportunities to access most recent information sources such as Scopus database.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Abbreviations
- AI
Adjustment index
- CNS
Central nervous system
- GDP
Gross domestic product
- IFs
Impact factors
- ISI
Institute for Scientific Information
- JCR
Journal Citation Report
- KSA
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Q1–Q3
Lower quartile upper quartile
- SCR
Standard competition ranking
- SJR
SCImago Journal Rank
- SPSS
Statistical Package for Social Sciences
- USA
United States of America
- UK
United Kingdom
Footnotes
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
SZ has conceived of the study, carried out the overall design and execution of the study, provided the statistical analysis and interpretation, wrote the manuscript, and served as the lead author of the manuscript. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- 1.Cox G, Rampes H. Adverse effects of khat: A review. Adv Psychiatr Treat. 2003;9(6):456–63. doi: 10.1192/apt.9.6.456. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wabe NT. Chemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of khat (catha edulis forsk): a review. Addict Health. 2011;3(3–4):137–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thomas S, Williams T. Khat (Catha edulis): A systematic review of evidence and literature pertaining to its harms to UK users and society. Drug Science, Policy Law. 2013;1:1–25. doi: 10.1177/2050324513498332. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Al-Habori M. The potential adverse effects of habitual use of Catha edulis (khat) Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2005;4(6):1145–54. doi: 10.1517/14740338.4.6.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pennings EJM, Opperhuizen A, van Amsterdam JGC. Risk assessment of khat use in the Netherlands: A review based on adverse health effects, prevalence, criminal involvement and public order. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2008;52(3):199–207. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2008.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.World Health Organization (WHO) Expert Committee on Drug Dependence. Assessment of khat (Catha edulis Forsk). 2006. http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/quality_safety/4.4KhatCritReview.pdf. Accessed May 1st 2014.
- 7.Nutt D, King LA, Saulsbury W, Blakemore C. Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse. Lancet. 2007;369(9566):1047–53. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60464-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Al-Mugahed L. Khat chewing in Yemen: turning over a new leaf. Bull World Health Organ. 2008;86(10):741–2. doi: 10.2471/BLT.08.011008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sheikh KA, El-Setouhy M, Yagoub U, Alsanosy R, Ahmed Z. Khat chewing and health related quality of life: cross-sectional study in Jazan region. Kingdom Saudi Arabia Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014;12:44. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-12-44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Klein A. Framing the Chew: Narratives of Development, Drugs and Danger with Regard to Khat (Catha edulis) In: Labate BC, Cavnar C, editors. Prohibition, Religious Freedom, and Human Rights: Regulating Traditional Drug Use. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer; 2014. pp. 131–47. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bramness JG, Henriksen B, Person O, Mann K. A bibliometric analysis of European versus USA research in the field of addiction. Research on alcohol, narcotics, prescription drug abuse, tobacco and steroids 2001–2011. Eur Addict Res. 2014;20(1):16–22. doi: 10.1159/000348260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sanchez-Carbonell X, Guardiola E, Belles A, Beranuy M. European Union scientific production on alcohol and drug misuse (1976–2000) Addiction. 2005;100(8):1166–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2005.01135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Helinski S, Spanagel R. Publication trends in addiction research. Addict Biol. 2011;16(4):532–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.González-Alcaide G, Valderrama-Zurián JC, Navarro-Molina C, Alonso-Arroyo A, Bolaños-Pizarro M, Aleixandre-Benavent R. Gender analysis of Spanish scientific publications in the area of substance abuse in biomedicine 1999–2004. Adicciones. 2007;19(1):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.González Alcaide G, Bolaños Pizarro M, Navarro Molina C, De Granda Orive JI, Aleixandre Benavent R, Valderrama Zurián JC. An analysis of Spanish scientific productivity in substance abuse according to disciplinary collaboration. Adicciones. 2008;20(4):337–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gonzalez-Alcaide G, Castello-Cogollos L, Castellano-Gomez M, Agullo-Calatayud V, Aleixandre-Benavent R, Alvarez FJ, et al. Scientific publications and research groups on alcohol consumption and related problems worldwide: authorship analysis of papers indexed in PubMed and Scopus databases (2005 to 2009) Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013;37(Suppl 1):E381–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Valderrama-Zurian JC, Bolanos-Pizarro M, Bueno-Canigral FJ, Alvarez FJ, Ontalba-Ruiperez JA, Aleixandre-Benavent R. An analysis of abstracts presented to the college on problems of drug dependence meeting and subsequent publication in peer review journals. Subst Abuse Treat Prev Policy. 2009;4:19. doi: 10.1186/1747-597X-4-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lin JY, Rosenblatt D. Shifting patterns of economic growth and rethinking development. J Econ Policy Reform. 2012;15(3):171–94. doi: 10.1080/17487870.2012.700565. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.De Battisti F, Salini S. Robust analysis of bibliometric data. Statistical Methods Applications. 2012;22(2):269–83. doi: 10.1007/s10260-012-0217-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM. Worldwide research productivity in the field of electronic cigarette: a bibliometric analysis. BMC Public Health. 2014;14(1):667. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tan J, Fu H-Z, Ho Y-S. A bibliometric analysis of research on proteomics in Science Citation Index Expanded. Scientometrics. 2013;98(2):1473–90. doi: 10.1007/s11192-013-1125-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Smith DR. Impact factors, scientometrics and the history of citation-based research. Scientometrics. 2012;92(2):419–27. doi: 10.1007/s11192-012-0685-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM. Bibliometric analysis of scientific publications on waterpipe (narghile, shisha, hookah) tobacco smoking during the period 2003–2012. Tob Induc Dis. 2014;12(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1617-9625-12-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM, Awang R. A bibliometric analysis of toxicology research productivity in Middle Eastern Arab countries during a 10-year period (2003–2012) Health Res Policy Syst. 2014;12(1):4. doi: 10.1186/1478-4505-12-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM, Awang R. A Scopus-based examination of tobacco use publications in Middle Eastern Arab countries during the period 2003–2012. Harm Reduct J. 2014;11(1):14. doi: 10.1186/1477-7517-11-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sweileh WM, Al-Jabi SW, Zyoud SH, Sawalha AF. Bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: research activity in Arab countries. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2014;9(1):38. doi: 10.1186/2049-6958-9-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zyoud S, Al-Jabi S, Sweileh W, Waring W. Scientific research related to calcium channel blockers poisoning: Bibliometric analysis in Scopus, 1968–2012. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015:Article in Press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM. Worldwide research productivity of paracetamol (acetaminophen) poisoning: a bibliometric analysis (2003–2012) Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015;34(1):12–23. doi: 10.1177/0960327114531993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM, Awang R. A bibliometric analysis of research productivity of Malaysian publications in leading toxicology journals during a 10-year period (2003–2012) Hum Exp Toxicol. 2014;33(12):1284–93. doi: 10.1177/0960327113514101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sweileh WM, Awang R. Assessing the scientific research productivity of a leading toxicology journal: A case study of Human & Experimental Toxicology from 2003 to 2012. SAGE Open Medicine. 2014;2:2050312114523424. doi: 10.1177/2050312114523424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008;22(2):338–42. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9492LSF. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kulkarni AV, Aziz B, Shams I, Busse JW. Comparisons of citations in Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar for articles published in general medical journals. JAMA. 2009;302(10):1092–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Alsanosy RM, Mahfouz MS, Gaffar AM. Khat chewing habit among school students of Jazan region. Saudi Arabia PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e65504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Magdum SS. An overview of khat. Addictive Disorders Treatment. 2011;10(2):72–83. doi: 10.1097/ADT.0b013e3181f002db. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Corkery JM, Schifano F, Oyefeso A, Ghodse AH, Tonia T, Naidoo V, et al. ‘Bundle of fun’ or ‘bunch of problems’? Case series of khat-related deaths in the UK. Drugs Education, Prevention Policy. 2011;18(6):408–25. doi: 10.3109/09687637.2010.504200. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46):16569–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507655102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sweileh WM, Zyoud SH, Sawalha AF, Abu-Taha A, Hussein A, Al-Jabi SW. Medical and biomedical research productivity from Palestine, 2002–2011. BMC Res Notes. 2013;6:41. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.World Bank Group. Countries and Economies 2013. 2014. http://data.worldbank.org/country. Accessed June 20 2015.
- 39.Baird DA. A case of optic neuritis in a qat addict. East Afr Med J. 1952;29(8):325–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Halbach H. Medical aspects of the chewing of khat leaves. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;47(1):21–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kalix P, Braenden O. Pharmacological aspects of the chewing of khat leaves. Pharmacol Rev. 1985;37(2):149–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Al-Motarreb A, Baker K, Broadley KJ. Khat: pharmacological and medical aspects and its social use in Yemen. Phytother Res. 2002;16(5):403–13. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brenneisen R, Fisch HU, Koelbing U, Geisshusler S, Kalix P. Amphetamine-like effects in humans of the khat alkaloid cathinone. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30(6):825–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb05447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Widler P, Mathys K, Brenneisen R, Kalix P, Fisch HU. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of khat: a controlled study. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;55(5):556–62. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Toennes SW, Harder S, Schramm M, Niess C, Kauert GF. Pharmacokinetics of cathinone, cathine and norephedrine after the chewing of khat leaves. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;56(1):125–30. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kalix P. Pharmacological properties of the stimulant khat. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(3):397–416. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Luqman W, Danowski TS. The use of khat (Catha edulis) in Yemen. Social and medical observations. Ann Intern Med. 1976;85(2):246–9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-2-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Odenwald M, Neuner F, Schauer M, Elbert T, Catani C, Lingenfelder B, et al. Khat use as risk factor for psychotic disorders: a cross-sectional and case–control study in Somalia. BMC Med. 2005;3:5. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-3-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Luo X, Liang Z, Gong F, Bao H, Huang L, Jia Z. Worldwide productivity in the field of foot and ankle research from 2009–2013: a bibliometric analysis of highly cited journals. J Foot Ankle Res. 2015;8:12. doi: 10.1186/s13047-015-0070-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sweileh WM, Zyoud SH, Al-Jabi SW, Sawalha AF. Quantity and quality of obesity-related research in Arab countries: assessment and comparative analysis. Health Res Policy Syst. 2014;12:33. doi: 10.1186/1478-4505-12-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Joshi MA. Bibliometric indicators for evaluating the quality of scientifc publications. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2014;15(2):258–62. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Warfa N, Klein A, Bhui K, Leavey G, Craig T, Alfred SS. Khat use and mental illness: a critical review. Soc Sci Med. 2007;65(2):309–18. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.04.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Balint EE, Falkay G, Balint GA. Khat - a controversial plant. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2009;121(19–20):604–14. doi: 10.1007/s00508-009-1259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Huamani C, Rey de Castro J, Gonzalez-Alcaide G, Polesel DN, Tufik S, Andersen ML. Scientific research in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: bibliometric analysis in SCOPUS, 1991–2012. Sleep Breath. 2015;19(1):109–14. doi: 10.1007/s11325-014-0969-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bordons M, Gómez I, Fernández MT, Zulueta MA, Méndez A. Local, Domestic and International Scientific Collaboration in Biomedical Research. Scientometrics. 1996;37(2):279–95. doi: 10.1007/BF02093625. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bozeman B, Corley E. Scientists’ collaboration strategies: implications for scientific and technical human capital. Res Policy. 2004;33(4):599–616. doi: 10.1016/j.respol.2004.01.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wagner CS. Six case studies of international collaboration in science. Scientometrics. 2005;62(1):3–26. doi: 10.1007/s11192-005-0001-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Abramo G, D’Angelo CA, Di Costa F. Research collaboration and productivity: is there correlation? High Educ. 2008;57(2):155–71. doi: 10.1007/s10734-008-9139-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Adams J, Gurney K, Hook D, Leydesdorff L. International collaboration clusters in Africa. Scientometrics. 2014;98(1):547–56. doi: 10.1007/s11192-013-1060-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gazni A, Sugimoto CR, Didegah F. Mapping world scientific collaboration: Authors, institutions, and countries. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. 2012;63(2):323–35. doi: 10.1002/asi.21688. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.McKee M, Stuckler D, Basu S. Where there is no health research: What can be done to fill the global gaps in health research? PLoS Medicine. 2012;9(4):e1001209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 62.Jang DH, Rusyniak DE. Hard impact: journal impact factor and JMT. J Med Toxicol. 2011;7(4):256–8. doi: 10.1007/s13181-011-0171-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bird SB. Journal impact factors, h indices, and citation analyses in toxicology. J Med Toxicol. 2008;4(4):261–74. doi: 10.1007/BF03161211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Delirrad M, Rashidi A, Karimi S. A bibliometric analysis of toxicology publications of Iran and Turkey in ISI Web of Science. Iranian J Toxicol. 2013;6(19):735–45. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Danell JAB. Reception of integrative and complementary medicine (ICM) in scientific journals: a citation and co-word analysis. Scientometrics. 2014;98(2):807–21.
- 66.Danell JAB, Danell R. Publication activity in complementary and alternative medicine. Scientometrics. 2009;80(2):539–51. doi: 10.1007/s11192-008-2078-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fu JY, Zhang X, Zhao YH, Huang MH, Chen DZ. Bibliometric analysis of complementary and alternative medicine research over three decades. Scientometrics. 2011;88(2):617–26. doi: 10.1007/s11192-011-0391-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Tam WWS, Wong ELY, Wong FCY, Cheung AWL. Citation classics in the integrative and complementary medicine literature: 50 frequently cited articles. European J Integrative Med. 2012;4(1):e77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2011.12.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Chiu W-T, Ho Y-S. Bibliometric analysis of homeopathy research during the period of 1991 to 2003. Scientometrics. 2005;63(1):3–23. doi: 10.1007/s11192-005-0201-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Li XQ, Tao KM, Zhou QH, Ling CQ. Scientific publications from mainland China, Taiwan, and Hong Kong in integrative and complementary medicine journals: a ten-year literature survey. Am J Chin Med. 2011;39(4):639–49. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X11009081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Essential Science Indicators. Top 20 Countries in ALL FIELDS, 2001-August 31, 2011. 2012. http://archive.sciencewatch.com/dr/cou/2011/11decALL/. Accessed 20, September 2013.
- 72.Miro O, Montori E, Ramos X, Galicia M, Nogue S. Trends in research activity in toxicology and by toxicologists in seven European countries. Toxicol Lett. 2009;189(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.04.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gaillard J. Science Policies and Cooperation in Africa: Trends in the Production and Utilization of Knowledge. Sci Commun. 1992;14(2):212–33. doi: 10.1177/107554709201400212. [DOI] [Google Scholar]


