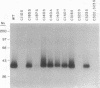
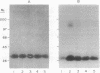
Abstract
Previously, bovine rhodopsin has been shown to be palmitoylated at cysteine residues 322 and 323. Here we report on palmitoylation of bovine opsin in COS-1 cells following expression of the synthetic wild-type opsin gene and several of its cysteine mutants in the presence of [3H]palmitic acid. Two moles of palmitic acid are introduced per wild-type opsin molecule in thioester linkages. Palmitoylation is abolished when both Cys-322 and Cys-323 are replaced by serine residues. Replacement of Cys-322 by serine prevents palmitoylation at Cys-323, whereas replacement of the latter with serine allows palmitoylation at Cys-322. Opsin mutants that evidently do not contain a Cys-110/Cys-187 disulfide bond and presumably remain in the endoplasmic reticulum are not palmitoylated. Replacement of Cys-140 or Cys-185 reduces the extent of palmitoylation of the opsin. Lack of palmitoylation at Cys-322 and/or Cys-323 does not affect 11-cis-retinal binding, absorption maximum or extinction coefficient of the chromophore, the bleaching behavior of the chromophore, or the light-dependent binding and activation of transducin. Mutants containing serine substitutions at Cys-140 or Cys-323 showed reduced light-dependent phosphorylation by rhodopsin kinase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharya S., Ridge K. D., Knox B. E., Khorana H. G. Light-stable rhodopsin. I. A rhodopsin analog reconstituted with a nonisomerizable 11-cis retinal derivative. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6763–6769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke R. R., Sakmar T. P., Oprian D. D., Khorana H. G. A single amino acid substitution in rhodopsin (lysine 248----leucine) prevents activation of transducin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2119–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G., Olson E. N. Fatty acylated proteins as components of intracellular signaling pathways. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2623–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G. Assembly of functional rhodopsin requires a disulfide bond between cysteine residues 110 and 187. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17520–17524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Sakmar T. P., Chen H. B., Khorana H. G. Cysteine residues 110 and 187 are essential for the formation of correct structure in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8459–8463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Krangel M. S., Strominger J. L. Cysteines in the transmembrane region of major histocompatibility complex antigens are fatty acylated via thioester bonds. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7230–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleanthous C., Shaw W. V. Analysis of the mechanism of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase by steady-state kinetics. Evidence for a ternary-complex mechanism. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):211–220. doi: 10.1042/bj2230211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., Arendt A., McDowell J. H., Kahlert M., Hargrave P. A., Hofmann K. P. Three cytoplasmic loops of rhodopsin interact with transducin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6878–6882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. F., O'Brien P. J., Pepperberg D. R. Depalmitylation with hydroxylamine alters the functional properties of rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20118–20123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T. A., Khorana H. G. Mapping of the amino acids in membrane-embedded helices that interact with the retinal chromophore in bovine rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4269–4275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. J., St Jules R. S., Reddy T. S., Bazan N. G., Zatz M. Acylation of disc membrane rhodopsin may be nonenzymatic. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5210–5215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. J., Zatz M. Acylation of bovine rhodopsin by [3H]palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5054–5057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Palmitoylation of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mutation of Cys341 in the carboxyl tail leads to an uncoupled nonpalmitoylated form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7564–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprian D. D., Molday R. S., Kaufman R. J., Khorana H. G. Expression of a synthetic bovine rhodopsin gene in monkey kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8874–8878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Bogachuk A. S. Two adjacent cysteine residues in the C-terminal cytoplasmic fragment of bovine rhodopsin are palmitylated. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papac D. I., Thornburg K. R., Büllesbach E. E., Crouch R. K., Knapp D. R. Palmitylation of a G-protein coupled receptor. Direct analysis by tandem mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16889–16894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Orci L., Glick B. S., Amherdt M., Arden S. R., Malhotra V., Rothman J. E. Fatty acyl-coenzyme A is required for budding of transport vesicles from Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90872-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Franke R. R., Khorana H. G. Glutamic acid-113 serves as the retinylidene Schiff base counterion in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8309–8313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Fatty acylation of proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):411–426. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90013-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault G., Guitard M., Daigneault R. A study of the enzymatic inactivation of chloramphenicol by highly purified chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 7;614(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALD G., BROWN P. K. The molar extinction of rhodopsin. J Gen Physiol. 1953 Nov 20;37(2):189–200. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessling-Resnick M., Johnson G. L. Allosteric behavior in transducin activation mediated by rhodopsin. Initial rate analysis of guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3697–3705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zozulya S. A., Gurevich V. V., Zvyaga T. A., Shirokova E. P., Dumler I. L., Garnovskaya M. N., Natochin MYu, Shmukler B. E., Badalov P. R. Functional expression in vitro of bovine visual rhodopsin. Protein Eng. 1990 Apr;3(5):453–458. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.5.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]