Abstract
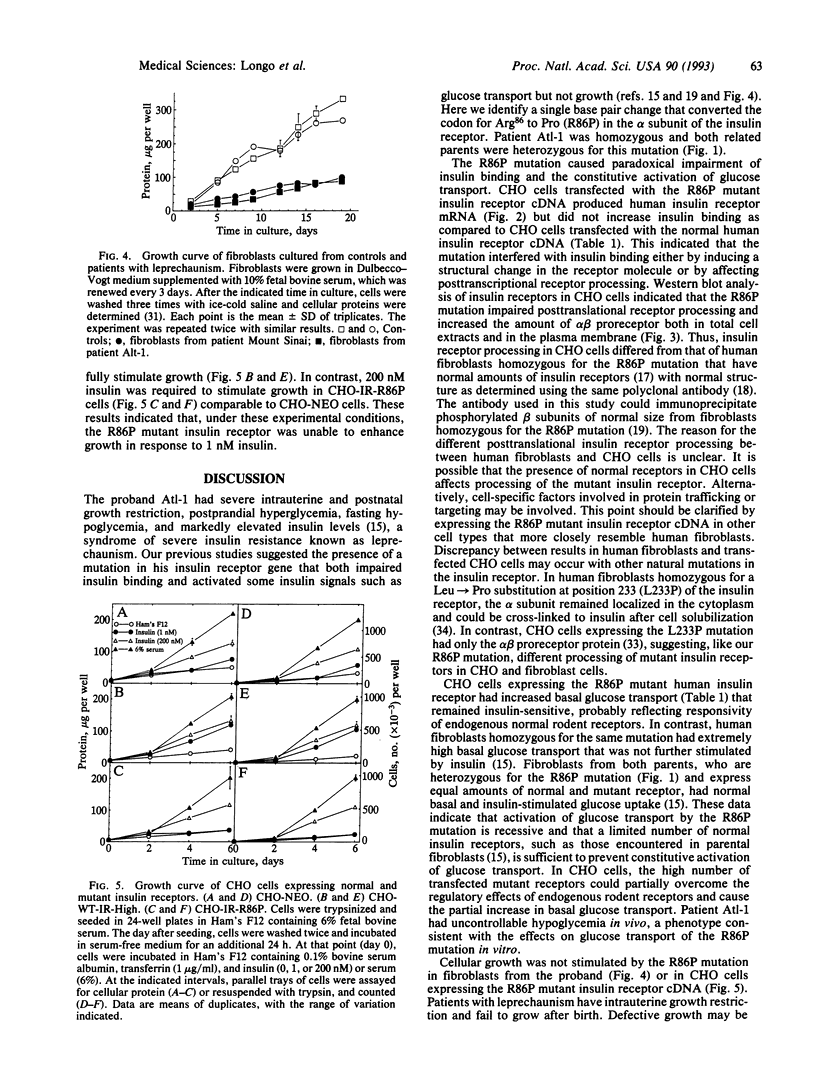
Naturally occurring mutations in the insulin receptor gene cause heritable severe insulin resistance. These mutations usually impair insulin receptor signaling in cells cultured from affected individuals. However, fibroblasts cultured from a patient with intrauterine growth restriction and severe insulin resistance (leprechaun Atl-1) had normal amounts of insulin receptor protein and defective insulin binding but constitutive activation of insulin-receptor autophosphorylation and kinase activity and of glucose transport. In the same fibroblasts, growth was impaired. Homozygosity for a mutation in the insulin receptor gene was suspected, since he inherited identical DNA haplotypes for this gene from both related parents. Here we report that the proband was homozygous and both parents were heterozygous for a point mutation in the insulin receptor gene converting the Arg86 codon (CGA) to Pro (CCA) (R86P). The R86P substitution is contiguous to the hydrophobic beta-sheet of the receptor alpha subunit implicated by DeMeyts et al. [DeMeyts, P., Gu, J.-L., Shymko, R. M., Kaplan, B. E., Bell, G. I. & Whittaker, J. (1990) Mol. Endocrinol. 4, 409-416] in the binding of aromatic residues of the insulin molecule. The R86P mutant insulin receptor cDNA was inserted into a plasmid under control of a simian virus 40 promoter and transfected into Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. In contrast with fibroblasts from patient Atl-1, which had normal insulin receptor processing, CHO cells stably transfected with the R86P mutant cDNA (CHO-R86P) had altered posttranslational processing. The R86P mutant receptor failed to bind insulin but caused a significant increase in basal glucose transport in CHO cells. As in fibroblasts cultured from the patient, the R86P mutant insulin receptor did not stimulate growth in transfected CHO cells. These results suggest that the R86P mutation in the insulin receptor activates glucose transport without promoting cell growth and that distinct cell types process this mutant insulin receptor differently.
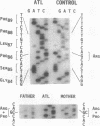
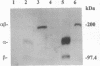
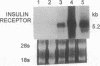
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajaj M., Waterfield M. D., Schlessinger J., Taylor W. R., Blundell T. On the tertiary structure of the extracellular domains of the epidermal growth factor and insulin receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 26;916(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Read L. C., Gunn J. M. Protein synthesis and breakdown rates associated with the insulin resistance of fibroblasts from patients with leprechaunism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Dec;61(6):1146–1151. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-6-1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E., Groelke J., Plet A. Leprechaunism: studies of the relationship among hyperinsulinism, insulin resistance, and growth retardation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):495–502. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P., Gu J. L., Shymko R. M., Kaplan B. E., Bell G. I., Whittaker J. Identification of a ligand-binding region of the human insulin receptor encoded by the second exon of the gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):409–416. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debant A., Clauser E., Ponzio G., Filloux C., Auzan C., Contreres J. O., Rossi B. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 does not alter the mitogenic effect of the hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8032–8036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Morgan D. O., Clauser E., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. A membrane-anchored cytoplasmic domain of the human insulin receptor mediates a constitutively elevated insulin-independent uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., 2nd, Longo N., Langley S., Griffin L. D., Shuster R. C. Molecular genetics of severe insulin resistance. Yale J Biol Med. 1989 Sep-Oct;62(5):533–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Endo F., Strumlauf E., Elders J., Priest J. H. Leprechaunism: an inherited defect in a high-affinity insulin receptor. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;37(1):73–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Longo N., Fotion T. R., Langley S. Comparison of the insulin receptor gene and insulin binding in families with severe insulin resistance. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1988;101:137–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo F., Nagata N., Priest J. H., Longo N., Elsas L. J., 2nd Structural analysis of normal and mutant insulin receptors in fibroblasts cultured from families with leprechaunism. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;41(3):402–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry M., Schaefer E., Ellis L., Kojro E., Fahrenholz F., Brandenburg D. Detection of a new hormone contact site within the insulin receptor ectodomain by the use of a novel photoreactive insulin. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8950–8956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Bevins C. L., Cama A., Ojamaa K., Marcus-Samuels B., Kadowaki H., Beitz L., McKeon C., Taylor S. I. Two mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene in a patient with extreme insulin resistance. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):787–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2834824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Rechler M. M., Serrano-Rios M., Roth J., Gorden P., Taylor S. I. Five mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene in patients with genetic forms of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):254–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI114693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Taylor S. I. A nonsense mutation causing decreased levels of insulin receptor mRNA: detection by a simplified technique for direct sequencing of genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Pariza M. W., Becker J. E., Potter V. R. A method using 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and phloretin for the determination of intracellular water space of cells in monolayer culture. Anal Biochem. 1975 Oct;68(2):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90649-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkhamer M. P., Groen N. A., van der Zon G. C., Lindhout D., Sandkuyl L. A., Krans H. M., Möller W., Maassen J. A. A leucine-to-proline mutation in the insulin receptor in a family with insulin resistance. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2503–2507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A. B., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Nissley S. P. Stimulation of glucose incorporation and amino acid transport by insulin and an insulin-like growth factor in fibroblasts with defective insulin receptors cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Griffin L. D., Elsas L. J. Influx and efflux of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose by cultured human fibroblasts. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):C628–C633. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.5.C628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Griffin L. D., Shuster R. C., Langley S., Elsas L. J. Increased glucose transport by human fibroblasts with a heritable defect in insulin binding. Metabolism. 1989 Jul;38(7):690–697. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Langley S. D., Griffin L. D., Elsas L. J., 2nd Reduced mRNA and a nonsense mutation in the insulin-receptor gene produce heritable severe insulin resistance. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):998–1007. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Shuster R. C., Griffin L. D., Elsas L. J. Insulin-receptor autophosphorylation and kinase activity are constitutively increased in fibroblasts cultured from a patient with heritable insulin-resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1229–1234. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90655-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Shuster R. C., Griffin L. D., Langley S. D., Elsas L. J. Activation of insulin receptor signaling by a single amino acid substitution in the transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12416–12419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Klinkhamer M. P., van der Zon G. C., Sips H., Möller W., Krans H. M., Lindhout D., Beemer F. A. Fibroblasts from a leprechaun patient have defects in insulin binding and insulin receptor autophosphorylation. Diabetologia. 1988 Aug;31(8):612–617. doi: 10.1007/BF00264769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Van der Vorm E. R., Van der Zon G. C., Klinkhamer M. P., Krans H. M., Möller W. A leucine to proline mutation at position 233 in the insulin receptor inhibits cleavage of the proreceptor and transport to the cell surface. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10778–10783. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzino V., Papa V., Trischitta V., Brunetti A., Goodman P. A., Treutelaar M. K., Williams J. A., Maddux B. A., Vigneri R., Goldfine I. D. Human insulin receptor radioimmunoassay: applicability to insulin-resistant states. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):E451–E457. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.3.E451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzio G., Contreres J. O., Debant A., Baron V., Gautier N., Dolais-Kitabgi J., Rossi B. Use of an anti-insulin receptor antibody to discriminate between metabolic and mitogenic effects of insulin: correlation with receptor autophosphorylation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4111–4117. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Downing J. R., Rettenmier C. W., Sherr C. J. A point mutation in the extracellular domain of the human CSF-1 receptor (c-fms proto-oncogene product) activates its transforming potential. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):979–988. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Seino M., Bell G. I. Human insulin-receptor gene. Partial sequence and amplification of exons by polymerase chain reaction. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):123–128. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Tryptic activation of the insulin receptor. Proteolytic truncation of the alpha-subunit releases the beta-subunit from inhibitory control. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4852–4860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y., Webster N. J., Olefsky J. M. Mutation of the two carboxyl-terminal tyrosines results in an insulin receptor with normal metabolic signaling but enhanced mitogenic signaling properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9135–9139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thies R. S., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Augmented mitogenesis and impaired metabolic signaling mediated by a truncated insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12820–12825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Smith R. L. Lowry determination of protein in the presence of Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):414–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Ullrich A. Gene for human insulin receptor: localization to site on chromosome 19 involved in pre-B-cell leukemia. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.3873110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vorm E. R., van der Zon G. C., Möller W., Krans H. M., Lindhout D., Maassen J. A. An Arg for Gly substitution at position 31 in the insulin receptor, linked to insulin resistance, inhibits receptor processing and transport. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]