Abstract
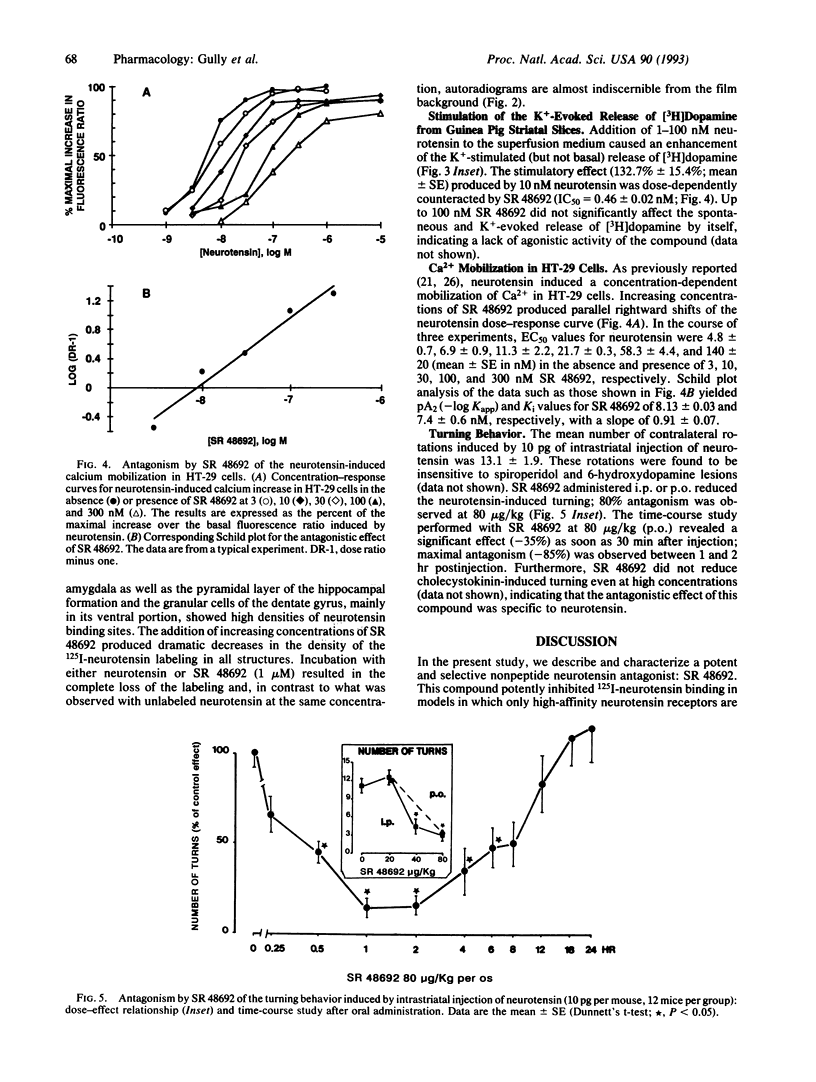
We describe the characteristics of SR 48692, a selective, nonpeptide antagonist of the neurotensin receptor. In vitro, this compound competitively inhibits 125I-labeled neurotensin binding to the high-affinity binding site present in brain tissue from various species with IC50 values of 0.99 +/- 0.14 nM (guinea pig), 4.0 +/- 0.4 nM (rat mesencephalic cells), 7.6 +/- 0.6 nM (COS-7 cells transfected with the cloned high-affinity rat brain receptor), 13.7 +/- 0.3 nM (newborn mouse brain), 17.8 +/- 0.9 nM (newborn human brain), 8.7 +/- 0.7 nM (adult human brain), and 30.3 +/- 1.5 nM (HT-29 cells). It also displaces 125I-labeled neurotensin from the low-affinity levocabastine-sensitive binding sites but at higher concentrations (34.8 +/- 8.3 nM for adult mouse brain and 82.0 +/- 7.4 nM for adult rat brain). In guinea pig striatal slices, SR 48692 blocks K(+)-evoked release of [3H]dopamine stimulated by neurotensin with a potency (IC50 = 0.46 +/- 0.02 nM) that correlates with its binding affinity. In a cell line derived from a human colon carcinoma (HT-29), SR 48692 competitively antagonizes neurotensin-induced intracellular Ca2+ mobilization with a pA2 (-log Kapp) values of 8.13 +/- 0.03, which is consistent with results obtained in binding studies. Moreover, SR 48692 is devoid of any intrinsic agonist activity. This compound is also active in vivo, since it reverses at low dose (80 micrograms/kg) the turning behavior induced by intrastriatal injection of neurotensin in mice with similar potency whatever the route of administration (i.p. or orally) and with a long duration of action (6 hr). Thus, being a potent and selective neurotensin receptor antagonist, SR 48692 may be considered as a powerful tool for investigating the role of neurotensin in physiological and pathological processes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. J., Mahoney P. D., Ferris C. F., Carraway R. E., Leeman S. E. Evidence that neurotensin participates in the central regulation of the preovulatory surge of luteinizing hormone in the rat. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):783–788. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battaini F., Govoni S., Di Giovine S., Trabucchi M. Neurotensin effect on dopamine release and calcium transport in rat striatum: interactions with diphenylalkylamine calcium antagonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;332(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00504865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissette G., Nemeroff C. B., Loosen P. T., Prange A. J., Jr, Lipton M. A. Hypothermia and intolerance to cold induced by intracisternal administration of the hypothalamic peptide neurotensin. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):607–609. doi: 10.1038/262607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozou J. C., Rochet N., Magnaldo I., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Neurotensin stimulates inositol trisphosphate-mediated calcium mobilization but not protein kinase C activation in HT29 cells. Involvement of a G-protein. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 15;264(3):871–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2640871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine, and stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7045–7052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clineschmidt B. V., McGuffin J. C., Bunting P. B. Neurotensin: antinocisponsive action in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 15;54(1-2):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dana C., Pelaprat D., Vial M., Brouard A., Lhiaubet A. M., Rostene W. Characterization of neurotensin binding sites on rat mesencephalic cells in primary culture. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991 Aug 19;61(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(91)90139-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. F., Pan J. X., Singer E. A., Boyd N. D., Carraway R. E., Leeman S. E. Stimulation of luteinizing hormone release after stereotaxic microinjection of neurotensin into the medial preoptic area of rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1984 Feb;38(2):145–151. doi: 10.1159/000123882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herve D., Tassin J. P., Studler J. M., Dana C., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P., Glowinski J., Rostene W. Dopaminergic control of 125I-labeled neurotensin binding site density in corticolimbic structures of the rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6203–6207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasckow J., Nemeroff C. B. The neurobiology of neurotensin: focus on neurotensin-dopamine interactions. Regul Pept. 1991 Oct 29;36(2):153–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90053-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Checler F., Mazella J., Vincent J. P. Pharmacology and biochemistry of neurotensin receptors. Rev Clin Basic Pharm. 1985 Jul-Dec;5(3-4):397–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Rostène W., Dussaillant M., Schotte A., Laduron P. M., Vincent J. P. Two populations of neurotensin binding sites in murine brain: discrimination by the antihistamine levocabastine reveals markedly different radioautographic distribution. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug 21;140(3):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugrin D., Vecchini F., Doulut S., Rodriguez M., Martinez J., Kitabgi P. Reduced peptide bond pseudopeptide analogues of neurotensin: binding and biological activities, and in vitro metabolic stability. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 26;205(2):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90819-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markstein R., Emson P. Effect of neurotensin and its fragments neurotensin-(1-6) and neurotensin-(8-13) on dopamine release from cat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 26;152(1-2):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90846-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazella J., Chabry J., Zsurger N., Vincent J. P. Purification of the neurotensin receptor from mouse brain by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5559–5563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyse E., Rostène W., Vial M., Leonard K., Mazella J., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P., Beaudet A. Distribution of neurotensin binding sites in rat brain: a light microscopic radioautographic study using monoiodo [125I]Tyr3-neurotensin. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff C. B. The interaction of neurotensin with dopaminergic pathways in the central nervous system: basic neurobiology and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1986;11(1):15–37. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(86)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Chiueh C. C., Everist H. D., Pert A. Comparative localization of neurotensin receptors on nigrostriatal and mesolimbic dopaminergic terminals. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 18;327(1-2):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91542-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux F., Kérouac R., Quirion R., St-Pierre S. Mechanisms of the cardiovascular effects of neurotensin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;400:56–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivest R., Marsden C. A. Muscarinic antagonists attenuate neurotensin-stimulated accumbens and striatal dopamine metabolism. Neuroscience. 1992;47(2):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul J. L., Mazella J., Amar S., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P. Preparation of neurotensin selectively iodinated on the tyrosine 3 residue. Biological activity and binding properties on mammalian neurotensin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):812–819. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotte A., Leysen J. E., Laduron P. M. Evidence for a displaceable non-specific [3H]neurotensin binding site in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;333(4):400–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00500016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. T., James-Kracke M. R., Camden J. M. Regulation of the neurotensin receptor and intracellular calcium mobilization in HT29 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jun;253(3):1049–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worms P., Gueudet C., Biziere K. Induction of turning by direct intrastriatal injection of dopaminomimetic drugs in mice: pharmacological analysis of a simple screening model. Life Sci. 1986 Dec 8;39(23):2199–2208. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90397-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsürger N., Chabry J., Coquerel A., Vincent J. P. Ontogenesis and binding properties of high-affinity neurotensin receptors in human brain. Brain Res. 1992 Jul 24;586(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91640-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Quidt M. E., Emson P. C. Neurotensin facilitates dopamine release in vitro from rat striatal slices. Brain Res. 1983 Sep 12;274(2):376–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90722-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]