Abstract
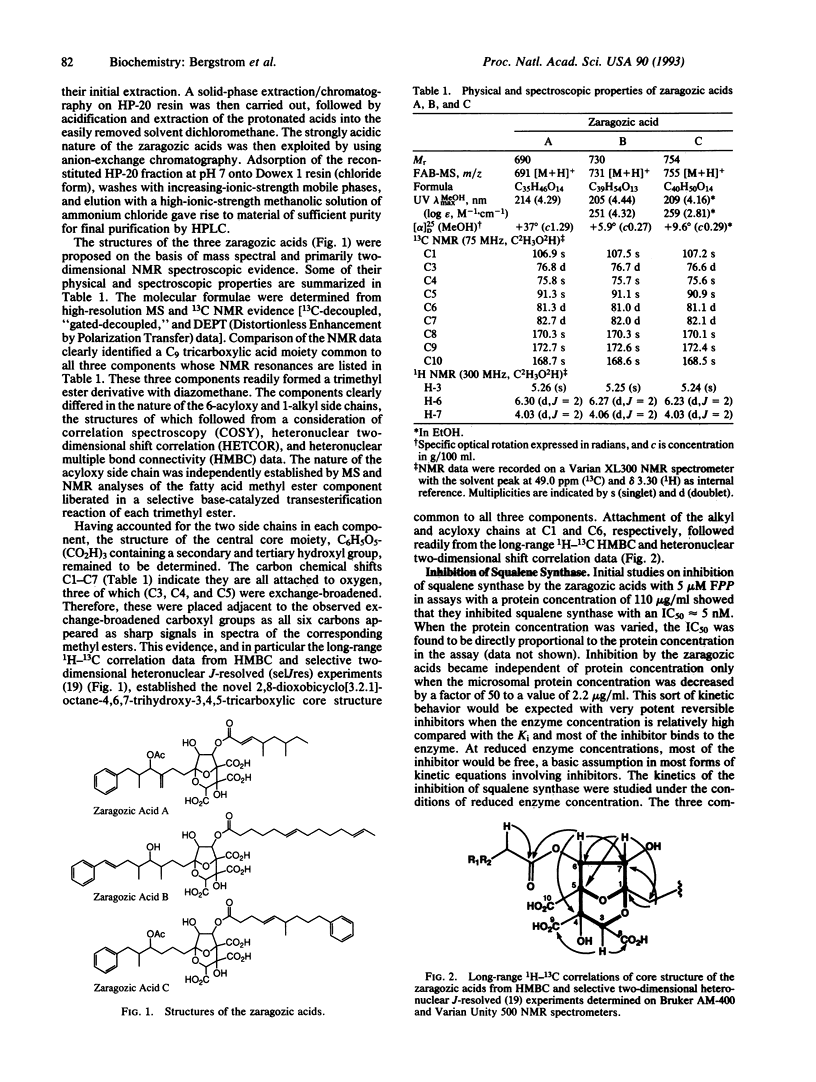
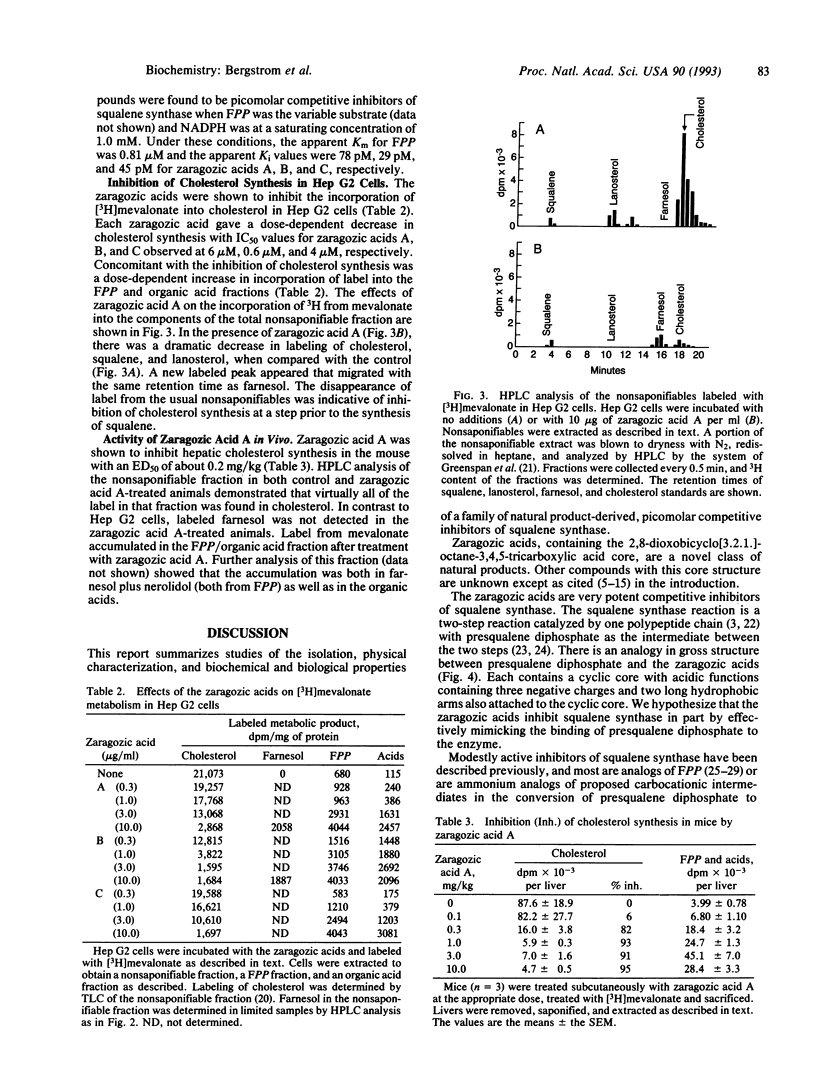
Three closely related fungal metabolites, zaragozic acids A, B, and C, that are potent inhibitors of squalene synthase have been isolated and characterized. Zaragozic acids A, B, and C were produced from an unidentified sterile fungal culture, Sporormiella intermedia, and Leptodontium elatius, respectively. The structures of the zaragozic acids and their trimethyl esters were determined by a combination of physical and chemical techniques. The zaragozic acids are characterized by a novel 2,8-dioxobicyclo[3.2.1]octane-4,6,7- trihydroxyl-3,4,5-tricarboxylic acid core and differ from each other in the structures of the 6-acyl and 1-alkyl side chains. They were found to be potent competitive inhibitors of rat liver squalene synthase with apparent Ki values of 78 pM, 29 pM, and 45 pM, respectively. They inhibited cholesterol synthesis in Hep G2 cells, and zaragozic acid A was an inhibitor of acute hepatic cholesterol synthesis in the mouse (50% inhibitory dose of 200 micrograms/kg of body weight). Inhibition of squalene synthase in cells and in vivo was accompanied by an accumulation of label from [3H]mevalonate into farnesyl diphosphate, farnesol, and organic acids. These data indicate that the zaragozic acids are a previously unreported class of therapeutic agents with potential for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S. Squalene synthetase. Methods Enzymol. 1985;110:359–373. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)10094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter A., Fitzgerald B. J., Hutson J. L., McCarthy A. D., Motteram J. M., Ross B. C., Sapra M., Snowden M. A., Watson N. S., Williams R. J. Squalestatin 1, a potent inhibitor of squalene synthase, which lowers serum cholesterol in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11705–11708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biller S. A., Forster C., Gordon E. M., Harrity T., Rich L. C., Marretta J., Ciosek C. P., Jr Isoprenyl phosphinylformates: new inhibitors of squalene synthetase. J Med Chem. 1991 Jun;34(6):1912–1914. doi: 10.1021/jm00110a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biller S. A., Forster C., Gordon E. M., Harrity T., Scott W. A., Ciosek C. P., Jr Isoprenoid (phosphinylmethyl)phosphonates as inhibitors of squalene synthetase. J Med Chem. 1988 Oct;31(10):1869–1871. doi: 10.1021/jm00118a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. J., Farthing J. E., Marshall P. S., Middleton R. F., O'Neill M. J., Shuttleworth A., Stylli C., Tait R. M., Taylor P. M., Wildman H. G. The squalestatins, novel inhibitors of squalene synthase produced by a species of Phoma. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1992 May;45(5):639–647. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.45.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. W., Rilling H. C. Studies on the mechanism of squalene biosynthesis. The structure of presqualene pyrophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4597–4605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Pacanowska D., Arison B., Havel C. M., Watson J. A. Isopentenoid synthesis in isolated embryonic Drosophila cells. Farnesol catabolism and omega-oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1301–1306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan M. D., Lo C. Y., Hanf D. P., Yudkovitz J. B. Separation and identification of triglycerides, cholesteryl esters, cholesterol, 7-dehydrocholesterol, dolichol, ubiquinone, alpha-tocopherol, and retinol by high performance liquid chromatography with a diode array detector. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jul;29(7):971–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan M. D., Yudkovitz J. B., Lo C. Y., Chen J. S., Alberts A. W., Hunt V. M., Chang M. N., Yang S. S., Thompson K. L., Chiang Y. C. Inhibition of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A synthase by L-659,699. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7488–7492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie M., Tsuchiya Y., Hayashi M., Iida Y., Iwasawa Y., Nagata Y., Sawasaki Y., Fukuzumi H., Kitani K., Kamei T. NB-598: a potent competitive inhibitor of squalene epoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18075–18078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings S. M., Tsay Y. H., Fisch T. M., Robinson G. W. Molecular cloning and characterization of the yeast gene for squalene synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6038–6042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling H. C. A new intermediate in the biosynthesis of squalene. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3233–3236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasiak K., Rilling H. C. Purification to homogeneity and some properties of squalene synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 1;260(2):622–627. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidebottom P. J., Highcock R. M., Lane S. J., Procopiou P. A., Watson N. S. The squalestatins, novel inhibitors of squalene synthase produced by a species of Phoma. II. Structure elucidation. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1992 May;45(5):648–658. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.45.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Montellano P. R., Wei J. S., Castillo R., Hsu C. K., Boparai A. Inhibition of squalene synthetase by farnesyl pyrophosphate analogues. J Med Chem. 1977 Feb;20(2):243–249. doi: 10.1021/jm00212a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



