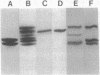
Abstract
We describe the isolation and characterization of proteasomes from recently established immortalized ovarian granulosa cell lines and their intracellular distribution during mitosis and during cAMP-induced differentiation, as revealed by immunofluorescence microscopy. In interphase, proteasomes were localized in small clusters throughout the cytoplasm and the nuclear matrix. In prophase, a substantial increase in proteasomal staining was observed in the perichromosomal area. A dramatic increase occurred in metaphase and in early anaphase; the chromosomes remained unstained. In late anaphase, intensive staining remained associated mainly with the spindle fibers. In telophase and early interphase of the daughter cells, intensive staining of proteasomes persisted in the nuclei. In contrast, in cells stimulated to differentiate by forskolin, which substantially elevates intracellular cAMP in these cell lines, only a weak staining of proteasomes was revealed in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Double staining of nondividing cells with antibodies to proteasomes and to tubulin did not show colocalization of proteasomes and microtubules. In contrast, dividing cells show a preferential concentration of proteasomes around spindle microtubules during metaphase and anaphase. The observed spatial and temporal distribution pattern of proteasomes during mitosis is highly reminiscent of the behavior of cyclins [Pines, J. & Hunter, T. (1991) J. Cell Biol. 115, 1-17]. Since proteasome accumulation appears to coincide with disappearance of cyclins A and B1 from the spindle apparatus, it is suggested that proteasomes may play a role in termination of mitosis by degrading the cyclins, which act as regulatory elements.
Full text
PDF

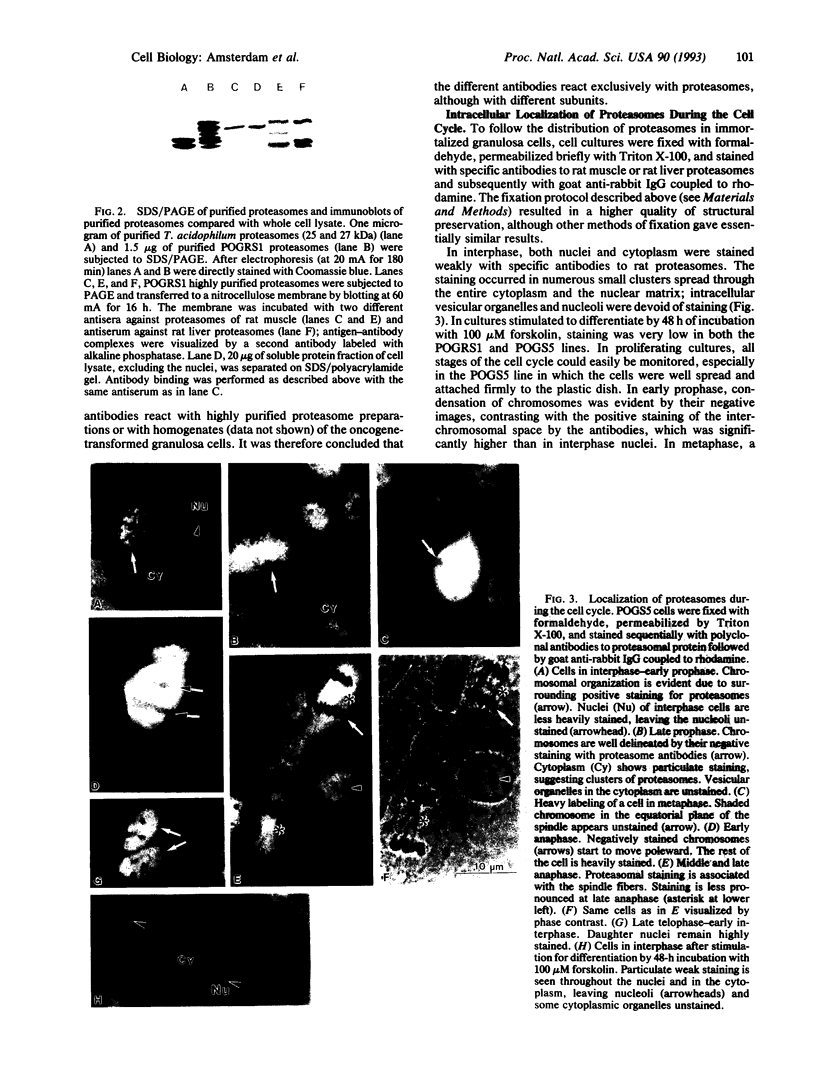


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsterdam A., Zauberman A., Meir G., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Suh B. S., Oren M. Cotransfection of granulosa cells with simian virus 40 and Ha-RAS oncogene generates stable lines capable of induced steroidogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7582–7586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum G., Suh B. S., Amsterdam A., Ben-Ze'ev A. Regulation of tropomyosin expression in transformed granulosa cell lines with steroidogenic ability. Dev Biol. 1990 Nov;142(1):115–128. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90155-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister W., Dahlmann B., Hegerl R., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Pfeifer G. Electron microscopy and image analysis of the multicatalytic proteinase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. G., Driscoll J., Monaco J. J. Structural and serological similarity of MHC-linked LMP and proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase) complexes. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):355–357. doi: 10.1038/353355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Niedel B., Pfeifer G., Hegerl R., Baumeister W. The multicatalytic proteinase (prosome) is ubiquitous from eukaryotes to archaebacteria. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81441-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Kuehn L., Rutschmann M., Reinauer H. Purification and characterization of a multicatalytic high-molecular-mass proteinase from rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):161–170. doi: 10.1042/bj2280161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H. The possible autocrine/paracrine and endocrine roles of insulin-like growth factors of human tumors. Endocrinology. 1990 Jul;127(1):1–4. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deverson E. V., Gow I. R., Coadwell W. J., Monaco J. J., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. MHC class II region encoding proteins related to the multidrug resistance family of transmembrane transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):738–741. doi: 10.1038/348738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Cola D., Pratt G., Rechsteiner M. Multicatalytic and 26 S ubiquitin/ATP-stimulated proteases in maturing rabbit red blood cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 11;280(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80222-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domae N., Harmon F. R., Busch R. K., Spohn W., Subrahmanyam C. S., Busch H. Donut-shaped "miniparticles" in nuclei of human and rat cells. Life Sci. 1982 Feb 1;30(5):469–477. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90464-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll J., Goldberg A. L. The proteasome (multicatalytic protease) is a component of the 1500-kDa proteolytic complex which degrades ubiquitin-conjugated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4789–4792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eytan E., Ganoth D., Armon T., Hershko A. ATP-dependent incorporation of 20S protease into the 26S complex that degrades proteins conjugated to ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7751–7755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Pal J. K., Grossi de Sa M. F., Beetschen J. C., Scherrer K. Differential cytolocalization of prosomes in axolotl during oogenesis and meiotic maturation. J Cell Sci. 1988 Aug;90(Pt 4):543–553. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.4.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynne R., Powis S. H., Beck S., Kelly A., Kerr L. A., Trowsdale J. A proteasome-related gene between the two ABC transporter loci in the class II region of the human MHC. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):357–360. doi: 10.1038/353357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi de Sa M. F., Martins de Sa C., Harper F., Coux O., Akhayat O., Pal J. K., Florentin Y., Scherrer K. Cytolocalization of prosomes as a function of differentiation. J Cell Sci. 1988 Feb;89(Pt 2):151–165. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi de Sa M. F., Martins de Sa C., Harper F., Olink-Coux M., Huesca M., Scherrer K. The association of prosomes with some of the intermediate filament networks of the animal cell. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1517–1530. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grziwa A., Baumeister W., Dahlmann B., Kopp F. Localization of subunits in proteasomes from Thermoplasma acidophilum by immunoelectron microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Pesold-Hurt B., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Kloetzel P. M. The Drosophila PROS-28.1 gene is a member of the proteasome gene family. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90185-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Suh B. S., Himmelhoch S., Amsterdam A. Induction and mitochondrial localization of cytochrome P450scc system enzymes in normal and transformed ovarian granulosa cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1373–1381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegerl R., Pfeifer G., Pühler G., Dahlmann B., Baumeister W. The three-dimensional structure of proteasomes from Thermoplasma acidophilum as determined by electron microscopy using random conical tilting. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80567-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemeyer W., Kleinschmidt J. A., Saidowsky J., Escher C., Wolf D. H. Proteinase yscE, the yeast proteasome/multicatalytic-multifunctional proteinase: mutants unravel its function in stress induced proteolysis and uncover its necessity for cell survival. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):555–562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A. The ubiquitin pathway for protein degradation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jul;16(7):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90101-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hügle B., Kleinschmidt J. A., Franke W. W. The 22 S cylinder particles of Xenopus laevis. II. Immunological characterization and localization of their proteins in tissues and cultured cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;32(1):157–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikai A., Nishigai M., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Electron microscopy of 26 S complex containing 20 S proteasome. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80824-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanayama H., Tanaka K., Aki M., Kagawa S., Miyaji H., Satoh M., Okada F., Sato S., Shimbara N., Ichihara A. Changes in expressions of proteasome and ubiquitin genes in human renal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6677–6685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara H., Yokosawa H. Cell cycle-dependent change of proteasome distribution during embryonic development of the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Dev Biol. 1992 May;151(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Powis S. H., Glynne R., Radley E., Beck S., Trowsdale J. Second proteasome-related gene in the human MHC class II region. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):667–668. doi: 10.1038/353667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein U., Gernold M., Kloetzel P. M. Cell-specific accumulation of Drosophila proteasomes (MCP) during early development. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2275–2282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumatori A., Tanaka K., Inamura N., Sone S., Ogura T., Matsumoto T., Tachikawa T., Shin S., Ichihara A. Abnormally high expression of proteasomes in human leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7071–7075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez C. K., Monaco J. J. Homology of proteasome subunits to a major histocompatibility complex-linked LMP gene. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):664–667. doi: 10.1038/353664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. W. Characterization of the active site of human multicatalytic proteinase. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):479–484. doi: 10.1042/bj2650479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C. Pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Specificity of components and aspects of proteolytic activity. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9270–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M. The multicatalytic proteinase complex, a major extralysosomal proteolytic system. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 13;29(45):10289–10297. doi: 10.1021/bi00497a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Navarrete V., Seelig A., Gernold M., Frentzel S., Kloetzel P. M., Hämmerling G. J. Subunit of the '20S' proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase) encoded by the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):662–664. doi: 10.1038/353662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal J. K., Gounon P., Grossi de Sa M. F., Scherrer K. Presence and distribution of specific prosome antigens change as a function of embryonic development and tissue-type differentiation in Pleurodeles waltl. J Cell Sci. 1988 Aug;90(Pt 4):555–567. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. Antigen presentation. Half of a peptide pump. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):271–272. doi: 10.1038/351271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclins A and B1 are differentially located in the cell and undergo cell cycle-dependent nuclear transport. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):1–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pühler G., Weinkauf S., Bachmann L., Müller S., Engel A., Hegerl R., Baumeister W. Subunit stoichiometry and three-dimensional arrangement in proteasomes from Thermoplasma acidophilum. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1607–1616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M. Natural substrates of the ubiquitin proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):615–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennert H., Amsterdam A., Billheimer J. T., Strauss J. F., 3rd Regulated expression of sterol carrier protein 2 in the ovary: a key role for cyclic AMP. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 26;30(47):11280–11285. doi: 10.1021/bi00111a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivett A. J. High molecular mass intracellular proteases. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2630625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. Antigen processing. Proteasomes in the pathway. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):300–301. doi: 10.1038/353300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Kloetzel P. M., Kuehn L., Dahlmann B. Molecular interaction of the proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase). Evidence that the proteasome is not a constituent of the '26 S' multienzyme complex. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):225–232. doi: 10.1042/bj2800225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Bahram S., Arnold D., Blanck G., Mellins E., Pious D., DeMars R. A gene in the human major histocompatibility complex class II region controlling the class I antigen presentation pathway. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):744–747. doi: 10.1038/348744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Kumatori A., Ii K., Ichihara A. Direct evidence for nuclear and cytoplasmic colocalization of proteasomes (multiprotease complexes) in liver. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):34–41. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Tamura T., Fujiwara T., Kumatori A., Ichihara A. Possible mechanism of nuclear translocation of proteasomes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80367-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Hanson I., Mockridge I., Beck S., Townsend A., Kelly A. Sequences encoded in the class II region of the MHC related to the 'ABC' superfamily of transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):741–744. doi: 10.1038/348741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hostos E. L., Bradtke B., Lottspeich F., Guggenheim R., Gerisch G. Coronin, an actin binding protein of Dictyostelium discoideum localized to cell surface projections, has sequence similarities to G protein beta subunits. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4097–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]