Abstract
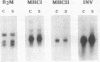
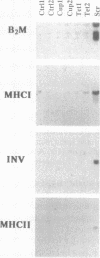
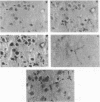
We have examined the expression of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens and related genes in scrapie-infected hamster brain. Both the class I and the class II MHC genes as well as the class II-associated invariant chain were found to have an increased brain expression after scrapie infection. The increased expression of the class I complex was immunohistochemically localized primarily to neurons, though some astrocytes contained much smaller amounts of the class I complex. While there is no detectable immune response to scrapie infection, the possibility that increased MHC expression affords some defense against the scrapie agent is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrill A. M., Blair G. E. Expression of hamster MHC class I antigens in transformed cells and tumours induced by human adenoviruses. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Nov;24(11):1745–1750. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(88)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiken J. M., Marsh R. F. The search for scrapie agent nucleic acid. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):242–246. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.242-246.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiken J. M., Williamson J. L., Borchardt L. M., Marsh R. F. Presence of mitochondrial D-loop DNA in scrapie-infected brain preparations enriched for the prion protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3265–3268. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3265-3268.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Brown H. R., Rudelli R. D., Scala L. J., Goller N. L., Wen G. Y., Kascsak R. J., Cashman N. R., Bolton D. C. Nearly ubiquitous tissue distribution of the scrapie agent precursor protein. Neurology. 1992 Jan;42(1):149–156. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp R. I., Callahan S. M. In vitro interaction of scrapie agent and mouse peritoneal macrophages. Intervirology. 1981;16(1):8–13. doi: 10.1159/000149241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp R. I., Callahan S. M. Scrapie incubation periods and end-point titers in mouse strains differing at the H-2D locus. Intervirology. 1986;26(1-2):85–92. doi: 10.1159/000149685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp R. I., Kascsak R. J., Wisniewski H. M., Merz P. A., Rubenstein R., Bendheim P., Bolton D. The nature of the unconventional slow infection agents remains a puzzle. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1989 Spring-Summer;3(1-2):79–99. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198903010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman N. R., Loertscher R., Nalbantoglu J., Shaw I., Kascsak R. J., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E. Cellular isoform of the scrapie agent protein participates in lymphocyte activation. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. C., Haig D. A. Multiplication of scrapie agent in mouse spleen. Res Vet Sci. 1971 Mar;12(2):195–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen P. R. Scrapie and the sheep MHC: claims of linkage refuted. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(6):414–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00375873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C. Cell-mediated immunity in virus infections of the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:228–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. R., Dinauer M. C. Library subtraction of in vitro cDNA libraries to identify differentially expressed genes in scrapie infection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2789–2792. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. R., Rohwer R. G., Seed B. Isolation of cDNAs of scrapie-modulated RNAs by subtractive hybridization of a cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5738–5742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser H., Dickinson A. G. Studies of the lymphoreticular system in the pathogenesis of scrapie: the role of spleen and thymus. J Comp Pathol. 1978 Oct;88(4):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(78)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C. Unconventional viruses and the origin and disappearance of kuru. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):943–960. doi: 10.1126/science.142303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hildebrand W. H., Martinko J. M., Pease L. R. Structural analysis of H-2Kf and H-2Kfm1 by using H-2K locus-specific sequences. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1782–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. D. Scrapie. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):289–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Walker C. Characteristics of a short incubation model of scrapie in the golden hamster. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):295–304. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T. Genetics of response to slow virus (prion) infection. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:115–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Kasper K. C., Stites D. P., Watson J. D., Hogan R. N., Prusiner S. B. Genetic control of scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):491–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlin D. E., Raff M. C., Simpson E., Nehlsen S. H. Scrapie in immunologically deficient mice. Nature. 1971 Oct 1;233(5318):336–336. doi: 10.1038/233336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. J., Mason D. W., Barclay A. N. Sequence of a rat MHC class II-associated invariant chain cDNA clone containing a 64 amino acid thyroglobulin-like domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3983–3984. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Iqbal K. Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(1):63–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00691333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri S., Handa S., Tateishi J. Lack of effect of thymus and spleen on the incubation period of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in mice. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1187–1189. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson T., Maehlen J., Löve A., Klareskog L., Norrby E., Kristensson K. Measles virus infection causes expression of class I and class II MHC antigens in rat brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:486–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:345–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. A., Schöld M., Itakura K., Wallace R. B. Isolation of a cDNA clone for the murine transplantation antigen H-2Kb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3270–3274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Kappler J., Marrack P., Grey H. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. I. Cell-free antigen processing. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):303–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Collins A. B., Colvin R. B., Bhan A. K. The in situ cellular immune response in acute herpes simplex encephalitis. Am J Pathol. 1986 Nov;125(2):332–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Hood L. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex in mouse and man. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):727–733. doi: 10.1126/science.6356354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syha J., Henkes W., Reske K. Complete cDNA sequence coding for the MHC class II RT1.B alpha chain of the Lewis rat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3985–3985. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis A. E., McMaster W. R. Sequence of a cDNA coding for a rat class II A alpha chain: extensive DNA and protein sequence identity to H-2 A alpha and HLA-DC1 alpha chains. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(1):53–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00364475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Jones P. P. Complete sequence of the murine invariant chain (Ii) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):447–448. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):701–702. doi: 10.1038/248701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]