Abstract
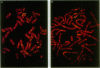
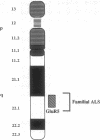
Genomic clones of the human non-N-methyl-D-aspartate (non-NMDA) glutamate receptor subunit GluR5 were isolated by high-stringency screening of a cosmid library using the rat cDNA as a probe. The chromosomal localization of the human GluR5 gene has been established. Southern hybridization of DNA isolated from mapping panels of Chinese hamster-human hybrid cell lines and high-resolution in situ suppression hybridization localize the GluR5 gene to chromosome 21q21.1-22.1. This coincides with the localization of a mutant gene causing familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), as Siddique et al. established by linkage analyses [Siddique, T., Figlewicz, D. A., Pericak-Vance, M. A., Haines, J. L., Rouleau, G., Jeffers, A. J., Sapp, P., Hung, W. Y., Bebout, J., McKenna-Yasek, D., Deng, G., Horvitz, H. R., Gusella, J. F., Brown, R. H. & Roses, A. D. (1991) N. Engl. J. Med. 324, 1381-1384]. Convergent evidence from other investigators suggests that chronic pathologic activation of motor neurons via non-NMDA glutamate receptors might induce excitotoxic injury of motor neurons, culminating in ALS. Together with the demonstration that GluR5 transcripts are expressed in the ventral horn of the spinal cord, the region in which susceptible motor neurons reside, the chromosomal localization suggests that a mutated GluR5 gene may be responsible for the familial form of ALS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bettler B., Boulter J., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Deneris E. S., Moll C., Borgmeyer U., Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloning of a novel glutamate receptor subunit, GluR5: expression in the nervous system during development. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90213-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Egebjerg J., Sharma G., Pecht G., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Moll C., Stevens C. F., Heinemann S. Cloning of a putative glutamate receptor: a low affinity kainate-binding subunit. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90292-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Hartley M., Deneris E., Maron C., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1033–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2168579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks J. H., Altherr M., Wagner-McPherson C., McPherson J. D., Wasmuth J. J., Evans G. A. Localization of the D5 dopamine receptor gene to human chromosome 4p15.1-p15.3, centromeric to the Huntington's disease locus. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90442-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite G., Garthwaite J. Neurotoxicity of excitatory amino acid receptor agonists in rat cerebellar slices: dependence on calcium concentration. Neurosci Lett. 1986 May 15;66(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headley P. M., Grillner S. Excitatory amino acids and synaptic transmission: the evidence for a physiological function. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 May;11(5):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90116-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herb A., Burnashev N., Werner P., Sakmann B., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herb A., Burnashev N., Werner P., Sakmann B., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Cloning by functional expression of a member of the glutamate receptor family. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):643–648. doi: 10.1038/342643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume R. I., Dingledine R., Heinemann S. F. Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1028–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.1653450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCAS D. R., NEWHOUSE J. P. The toxic effect of sodium L-glutamate on the inner layers of the retina. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1957 Aug;58(2):193–201. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1957.00940010205006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomeli H., Wisden W., Köhler M., Keinänen K., Sommer B., Seeburg P. H. High-affinity kainate and domoate receptors in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80753-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. O., Eubanks J. H., McPherson J. D., Wasmuth J. J., Evans G. A., Heinemann S. F. Chromosomal localization of human glutamate receptor genes. J Neurosci. 1992 Jul;12(7):2555–2562. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-07-02555.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder D. W., Kurland L. T., Offord K. P., Beard C. M. Familial adult motor neuron disease: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology. 1986 Apr;36(4):511–517. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.4.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W. Inciting excitotoxic cytocide among central neurons. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;203:631–645. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7971-3_48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Misra C. H., de Gubareff T. Cysteine-S-sulfate: brain damaging metabolite in sulfite oxidase deficiency. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1975 Mar;34(2):167–177. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197503000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaitakis A., Constantakakis E., Smith J. The neuroexcitotoxic amino acids glutamate and aspartate are altered in the spinal cord and brain in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1988 Sep;24(3):446–449. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman S. M., Thurston J. H., Hauhart R. E. Delayed neurotoxicity of excitatory amino acids in vitro. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90347-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. D., Martin L. J., Kuncl R. W. Decreased glutamate transport by the brain and spinal cord in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 28;326(22):1464–1468. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205283262204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. D., Tsai G., Kuncl R. W., Clawson L., Cornblath D. R., Drachman D. B., Pestronk A., Stauch B. L., Coyle J. T. Abnormal excitatory amino acid metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jul;28(1):18–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Morita T., Kushiya E., Mishina M. Primary structure and expression of the gamma 2 subunit of the glutamate receptor channel selective for kainate. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90293-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T., Figlewicz D. A., Pericak-Vance M. A., Haines J. L., Rouleau G., Jeffers A. J., Sapp P., Hung W. Y., Bebout J., McKenna-Yasek D. Linkage of a gene causing familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis to chromosome 21 and evidence of genetic-locus heterogeneity. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1381–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Burnashev N., Verdoorn T. A., Keinänen K., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A glutamate receptor channel with high affinity for domoate and kainate. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1651–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Nunn P. B., Hugon J., Ludolph A. C., Ross S. M., Roy D. N., Robertson R. C. Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia linked to a plant excitant neurotoxin. Science. 1987 Jul 31;237(4814):517–522. doi: 10.1126/science.3603037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Roy D. N., Ludolph A., Hugon J., Dwivedi M. P., Schaumburg H. H. Lathyrism: evidence for role of the neuroexcitatory aminoacid BOAA. Lancet. 1986 Nov 8;2(8515):1066–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Lewis K. A., Ruiz J. C., Rothenberg B., Zhao J., Evans G. A. Cosmid vectors for rapid genomic walking, restriction mapping, and gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. H., Koh J. Y., Choi D. W. Neurotoxicity of beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and beta-N-oxalylamino-L-alanine (BOAA) on cultured cortical neurons. Brain Res. 1989 Sep 11;497(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90970-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner P., Voigt M., Keinänen K., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Cloning of a putative high-affinity kainate receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampal CA3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):742–744. doi: 10.1038/351742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]