Abstract
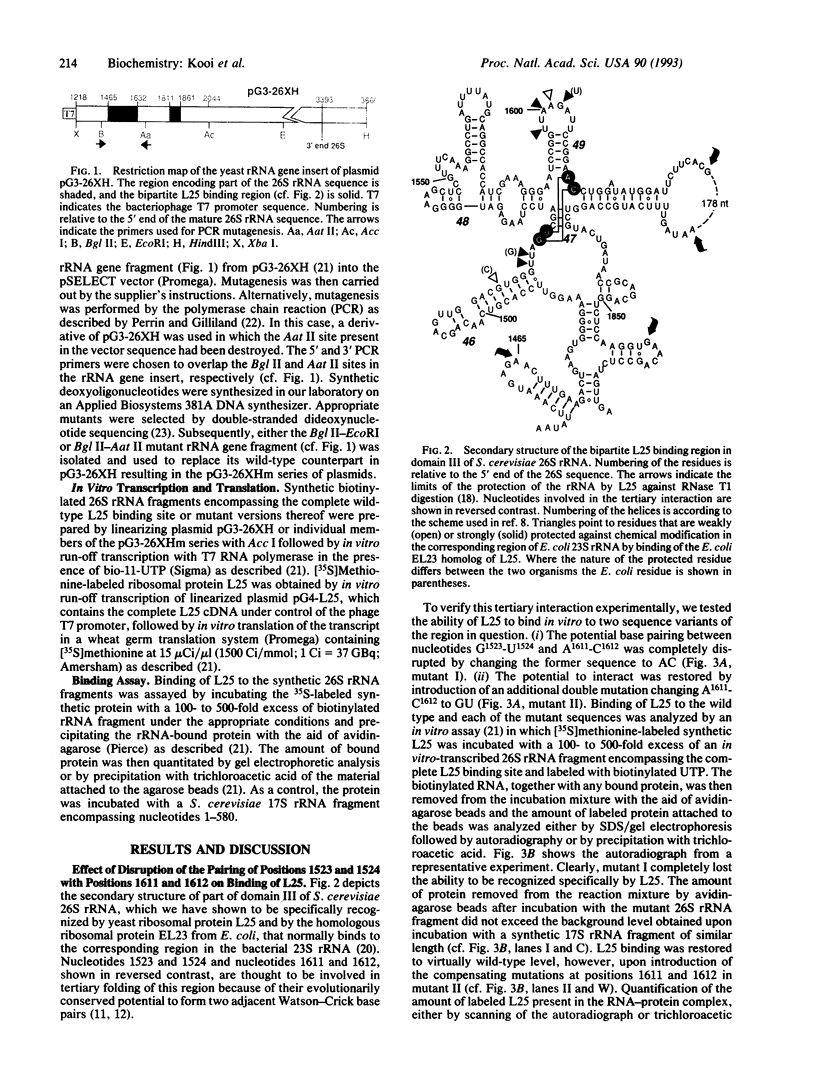
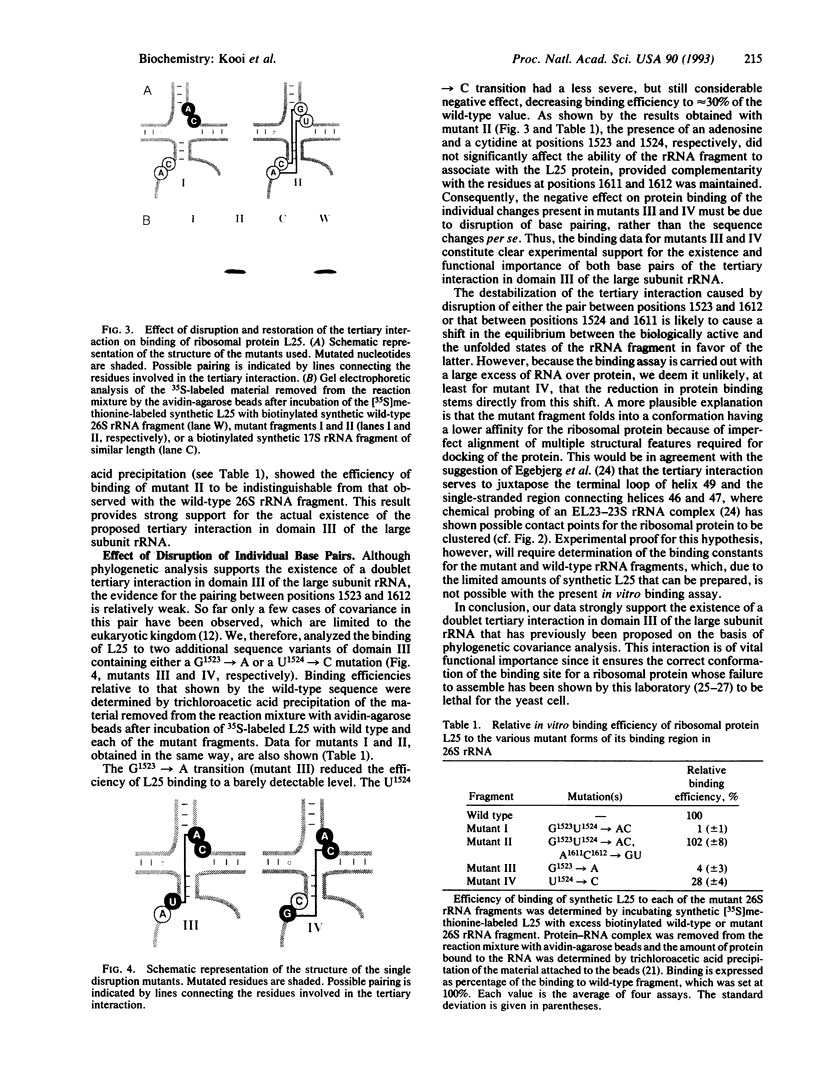
Previous phylogenetic analysis of rRNA sequences for covariant base changes has identified approximately 20 potential tertiary interactions. One of these is present in domain III of the large subunit rRNA and consists of two adjacent Watson-Crick base pairs that, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae 26S rRNA, connect positions 1523 and 1524 to positions 1611 and 1612. This interaction would strongly affect the structure of an evolutionarily highly conserved region that acts as the binding site for the early-assembling ribosomal proteins L25 and EL23 of S. cerevisiae and Escherichia coli, respectively. To assess the functional importance of this tertiary interaction, we determined the ability of synthetically prepared S. cerevisiae ribosomal protein L25 to associate in vitro with synthetic 26S rRNA fragments containing sequence variations at positions 1523 and 1524 and/or positions 1611 and 1612. Mutations that prevent the formation of both base pairs abolished L25 binding completely, whereas the introduction of compensatory mutations fully restored protein binding. Disruption of only the U1524.A1611 pair reduced L25 binding to approximately 30% of the value shown by the wild-type 26S rRNA fragment, whereas disruption of the G1523.C1612 base pair resulted in almost complete loss of protein binding. These results strongly support the existence and functional importance of the proposed doublet tertiary interaction in domain III of the large subunit rRNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Egebjerg J., Christiansen J., Garrett R. A. Attachment sites of primary binding proteins L1, L2 and L23 on 23 S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):251–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90210-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Fox G. E. A compilation of large subunit RNA sequences presented in a structural format. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r175–r269. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Woese C. R. Higher order structural elements in ribosomal RNAs: pseudo-knots and the use of noncanonical pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruiswijk T., Planta R. J. Analysis of the protein composition of yeast ribosomal subunits by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Sep;1(7):409–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00385674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Kjems J., Ostergaard L., Larsen N., Garrett R. A. Evolutionary relationships amongst archaebacteria. A comparative study of 23 S ribosomal RNAs of a sulphur-dependent extreme thermophile, an extreme halophile and a thermophilic methanogen. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Hoffarth V., Zimniak L. Unusual resistance of peptidyl transferase to protein extraction procedures. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1416–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1604315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Ribosomal RNA and translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:191–227. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin S., Gilliland G. Site-specific mutagenesis using asymmetric polymerase chain reaction and a single mutant primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7433–7438. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Noller H. F. A functional pseudoknot in 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2203–2214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Klootwijk J., Musters W. Evolutionary conservation of structure and function of high molecular weight ribosomal RNA. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;51(2):77–129. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Otaka E., Suzuki K. Structural comparison of 26S rRNA-binding ribosomal protein L25 from two different yeast strains and the equivalent proteins from three eubacteria and two chloroplasts. J Mol Evol. 1989 May;28(5):418–426. doi: 10.1007/BF02603077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers C. A., Rientjes J. M., van 't Riet J., Raué H. A. rRNA binding domain of yeast ribosomal protein L25. Identification of its borders and a key leucine residue. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90719-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers C. A., Schaap P. J., van 't Riet J., Woldringh C. L., Raué H. A. In vivo and in vitro analysis of structure-function relationships in ribosomal protein L25 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90144-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan P. C., Draper D. E. Detection of a key tertiary interaction in the highly conserved GTPase center of large subunit ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6308–6312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P. J., van't Riet J., Woldringh C. L., Raué H. A. Identification and functional analysis of the nuclear localization signals of ribosomal protein L25 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80216-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt F. J., Thompson J., Lee K., Dijk J., Cundliffe E. The binding site for ribosomal protein L11 within 23 S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12301–12305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Weiser B., Noller H. F. Model for the three-dimensional folding of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):447–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90588-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vester B., Garrett R. A. Structure of a protein L23-RNA complex located at the A-site domain of the ribosomal peptidyl transferase centre. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 5;179(3):431–452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Baradi T. T., Raué H. A., de Regt V. C., Verbree E. C., Planta R. J. Yeast ribosomal protein L25 binds to an evolutionary conserved site on yeast 26S and E. coli 23S rRNA. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2101–2107. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Baradi T. T., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Nierhaus K. H., Raué H. A. Interaction of ribosomal proteins L25 from yeast and EL23 from E. coli with yeast 26S and mouse 28S rRNA. Biochimie. 1987 Sep;69(9):939–948. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]