Abstract
Escherichia coli AW1.7 is a heat resistant food isolate and the occurrence of pathogenic strains with comparable heat resistance may pose a risk to food safety. To identify the genetic determinants of heat resistance, 29 strains of E. coli that differed in their of heat resistance were analyzed by comparative genomics. Strains were classified as highly heat resistant strains, exhibiting a D60-value of more than 6 min; moderately heat resistant strains, exhibiting a D60-value of more than 1 min; or as heat sensitive. A ~14 kb genomic island containing 16 predicted open reading frames encoding putative heat shock proteins and proteases was identified only in highly heat resistant strains. The genomic island was termed the locus of heat resistance (LHR). This putative operon is flanked by mobile elements and possesses >99% sequence identity to genomic islands contributing to heat resistance in Cronobacter sakazakii and Klebsiella pneumoniae. An additional 41 LHR sequences with >87% sequence identity were identified in 11 different species of β- and γ-proteobacteria. Cloning of the full length LHR conferred high heat resistance to the heat sensitive E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 and DH5α. The presence of the LHR correlates perfectly to heat resistance in several species of Enterobacteriaceae and occurs at a frequency of 2% of all E. coli genomes, including pathogenic strains. This study suggests the LHR has been laterally exchanged among the β- and γ-proteobacteria and is a reliable indicator of high heat resistance in E. coli.
Keywords: STEC, VTEC, EHEC, O157, heat resistance, beef, Cronobacter, Klebsiella
Introduction
Escherichia coli are commensals in the human and animal gut but the species also comprises intestinal and extraintestinal pathogens. The ecological versatility of E. coli is reflected in its genome plasticity. The average E. coli genome is approximately 5.16 Mb, encoding an average of 5190 genes. The core genome of E. coli comprises about 1700 genes (Kaas et al., 2012); however, the pan-genome of E. coli contains more than 18,000 genes and is still considered to be open (Rasko et al., 2008; Touchon et al., 2009; Kaas et al., 2012).
Lateral gene transfer promotes the evolution and diversity of E. coli, and allows acquisition of virulence factors (Dobrindt et al., 2004; Croxen et al., 2013; Gordienko et al., 2013). Genes responsible for colonization, toxin production and antibiotic resistance are encoded on mobile genetic elements and are transmitted between strains of E. coli (Croxen et al., 2013). One prominent example is the Shiga toxin (stx1 or stx2), carried on the genomes of lambdoid prophages (O'Brien et al., 1984). The horizontal transfer of large gene clusters, called genomic islands, also provides accessory genes for niche adaptation and pathogenicity (reviewed in Schmidt and Hensel, 2004; Rasko et al., 2008; Croxen et al., 2013). The locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) is a 35-kb genomic island coding for virulence genes for attachment and effacement of intestinal epithelial cells and other pathogenic traits (McDaniel et al., 1995). Novel combinations of accessory genes present significant challenges to public health. Transduction of an E. coli by a Shiga toxin-converting phage resulted in a new pathovar, enteroaggregative hemorrhagic E. coli, which caused a large foodborne outbreak in summer 2011 (Bielaszewska et al., 2011).
Pathovars of E. coli are characterized by their virulence gene profile, mechanisms for cellular adhesions, and site of colonization, and include enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC), enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC), enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC), enteroaggregative hemorrhagic E. coli (EAHEC), enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), and uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) (Agarwal et al., 2012; Croxen et al., 2013). Due to the severity of infections and the low infectious dose, EHEC and EAHEC are particularly of concern for both public health and the food industry (Bielaszewska et al., 2011; Scallan et al., 2011; Croxen et al., 2013). EHEC carry stx genes and are also referred to as Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) (Croxen et al., 2013). STEC causes an estimated 175,000 food-borne infections per year in the United States (Scallan et al., 2011). The most frequent serotype of STEC in North America is O157:H7, but other serotypes have also been implicated in STEC infections and are food adulterants in the U.S. (USDA, 2012).
Ruminants including cattle are the primary reservoir for STEC (Lainhart et al., 2009; Croxen et al., 2013). The beef processing industry applies thermal intervention methods such as steam pasteurization and hot water washes to reduce STEC contamination of meat. However, heat resistance in E. coli is highly variable and some strains exhibit a stable thermotolerant phenotype (Rudolph and Gebendorfer, 2010). While most strains of E. coli have D60 values of less than 1 min, moderately or exceptionally heat resistant strains exhibit D60 values of more than 1 and more than 10 min, respectively (Hauben et al., 1997; Dlusskaya et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2015). The beef isolate E. coli AW1.7 has a D60 value of more than 60 min and survives in beef patties grilled to a core temperature of 71°C or “well done” (Dlusskaya et al., 2011). Heat resistance in E. coli AW1.7 has been attributed to the accumulation of compatible solutes (Pleitner et al., 2012) and membrane transport proteins including the outer membrane porin NmpC (Ruan et al., 2011); however, the genetic determinants of heat resistance remain unknown. This study aimed to identify genetic determinants of heat resistance in E. coli by comparative genomic analysis of heat sensitive, moderately heat resistant, and extremely heat resistant strains of E. coli. Analyses focused on food and clinical isolates of E. coli and included Shiga-toxin producing strains.
Materials and methods
Strain selection and heat treatments
The 29 strains of E. coli used in this study included previously characterized heat resistant and sensitive food and clinical isolates (Ruan et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2015). Strains were selected to include isolates differing in their heat resistance, and to include the phylogenetic variability in the species E. coli. All strains were grown overnight in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth at 37°C with 200 rpm agitation. To determine the heat resistance, E. coli strains were treated at 60°C for 5 min as previously described (Dlusskaya et al., 2011). After heating, the cultures were serially diluted, plated onto LB agar and incubated aerobically overnight at 37°C. Strains were classified into phenotypic groups based on their survival after heating. Strains with a reduction in cell counts of more than 5 log (cfu mL−1) after 5 min at 60°C were classified as heat sensitive. Strains demonstrating a reduction in cell counts of 1 to 5 log (cfu mL−1) were classified as moderately heat resistant while strains with reductions less than 1 log (cfu mL−1) designated as highly heat resistant.
Genomic DNA isolation, genome sequencing, assembly, and annotation
DNA for genome sequencing was isolated from overnight cultures of E. coli grown in 5 ml of LB broth. Genomic DNA was isolated using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit (Promega, Madisson, Wisconsin, USA) following the manufacturer's guidelines. The quality and quantity of each sample was assessed using gel electrophoresis and a NanoDrop® 2000c spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, Delaware, USA). DNA samples were sequenced using Illumina HiSeq2000 with an insert size of 300 bp by Axeq Technologies (Seoul, South Korea). The quality of the 100-bp paired-end reads was assessed using the FastQC tool (http://www.bioinformatics.bbsrc.ac.uk/projects/fastqc) and low quality reads were filtered by Quake (Kelley et al., 2010). Assemblies were obtained using ABySS 1.3.4 (Assembly By Short Sequence; Simpson et al., 2009) with the most optimal k-mer value for each genome. Genomes were annotated automatically by the RAST server. For O157:H7 strains, the genomes assemblies were improved by scaffolding the contigs using the reference genomes of strains EDL933 (Accession: NC002655) and Sakai (Accession: NC002695). All genomic sequences of the 29 strains used in this current study are deposited to the NCBI wgs database under BioProject PRJNA277539.
Core genome phylogenetic analysis and identification of orthologous genes unique to different phenotypes
To construct a core-genome phylogenetic tree, the 28 sequenced genomes obtained in this study were combined with 48 reference genomes obtained from NCBI Genbank (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome) for a total of 76 E. coli and Shigella genomes. Reference genomes were selected to prioritize closed genomes over whole genome shotgun sequences, and to represent the phylogroups A, B1, B2, D, E, and Shigella. Construction of the core genome phylogenetic tree employed the previously described workflow (Touchon et al., 2009; Hazen et al., 2013) including genome alignment to identify the core genome, extraction of nucleotide sequences of the core genome, and calculation of a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree. The genomes were aligned with Mugsy with default parameters (Angiuoli and Salzberg, 2011). Homologous blocks present in each genome were extracted and concatenated using an in-house Perl script. The most disordered regions were eliminated using Gblocks with default parameters (Talavera and Castresana, 2007). The core genome size of the 76 genomes was approximately 2.7 Mbp. A maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed by RaxML with default parameters (Stamatakis, 2014) using bootstrapping for 1000 replicates.
To identify orthologous genes unique to the different phenotypic groups, protein sequences from all 29 genomes were combined and searched using all-against-all BLAST. The protein sequences with identities and coverage above 70% were clustered into families using the program OrthoMCL (Li et al., 2003). The inflation value of 2 was used for the MCL clustering. Sequence identity and comparisons of open reading frames (ORFs) were analyzed in Geneious (Biomatters, Auckland, New Zealand).
For phylogenetic analysis of the locus of heat resistance, genomes containing homologous sequences with >80% coverage of the ~14 kb LHR nucleotide sequence from E. coli AW1.7 were retrieved from NCBI. Sequences with homology to the LHR of E. coli AW1.7 were manually extracted and aligned with ClustalW implemented in MEGA6 (Tamura et al., 2013). The MEGA6 oftware package was used to construct a maximum-likelihood tree with default parameters. Bootstrap support values were calculated from 100 replicates.
To assess frequency of the locus of heat resistance in E. coli, a BLAST search of both the NCBI Genomes and whole-genome shotgun assemblies (wgs) database was performed. For each study, the number of strains containing sequence corresponding to >80% coverage was counted and totaled to give an approximate percentage of strains that were positive for the locus. Bioinformatic characterization of the genetic island was completed using BPROM (Solovyev and Salamov, 2011) and ARNold (Gautheret and Lambert, 2001) to identify putative promoters and rho-independent terminator sequences, respectively.
Genetic complementation of the LHR
To construct a plasmid-borne copy of the LHR, primers were designed in Geneious to selectively amplify the entire genomic island in 3 separate fragments. All primers and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. PCR reactions were carried out using Phusion High-Fidelity DNA polymerase (Thermo Scientific) according to manufacturer guidelines. F1 (~6 kb) was amplified using primer pair HR-R1/HR-R1 and included the native putative promoter sequence. F2 (~3.3 kb) and F3 (~7 kb) were amplified by primer pairs HR-F2.1/HR-R2 and HR-F3/HR-R3, respectively. F1 and F2 were cloned separately into pUC19 as KpnI/XbaI inserts, while F3 was inserted as a XbaI/HindIII fragment, yielding recombinant vectors pUCF1, pUCF2, and pUCF3 (Table 1). All 3 fragments were sequenced and subsequently sub-cloned into the low-copy plasmid, pRK767 (Gill and Warren, 1988), generating pRF1, pRF2, and pRF3 (Table 1). To construct the entire LHR on a plasmid, F1 was ligated into pUCF2 as a KpnI/SmaI fragment, resulting in pUCF1-2. The 8.3 kb insert, F1-2, was sub-cloned to pRK767 as a KpnI/XbaI fragment. The new recombinant vector, pRF1-2, and F3 were digested with BglII and HindIII and ligated to form pRF1-2-3, or simply, pLHR. The plasmids pRF1, pRF2, pRF3, and pLHR were electroporated into E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1, a heat sensitive derivative of AW1.7 (Pleitner et al., 2012). The resulting strains, as well as the DH5α strains used for cloning, were assayed for heat resistance as previously described (Liu et al., 2015). All transformants carrying either pUC19- or pRK767-based recombinant vectors were plated on LB media containing 50 mg l−1 ampicillin or 15 mg l−1 tetracycline, respectively.
Table 1.
Primers and plasmids used in this study.
| Primer | Sequence (5′ → 3′) | References |
|---|---|---|
| HR-F1 | TTAGGTACCGCTGTCCATTGCCTGA | This study |
| HS-R1 | AGACCAATCAGGAAATGCTCTGGACC | This study |
| HR-R1 | TATCTAGAGTCGCGTGCCAATACCAGTTC | This study |
| HR-F2.1 | AGGGTACCAGCGATATCCGTCAATTGACT | This study |
| HR-F2.2 | GAGGTACCTGTCTTGCCTGACAACGTTG | This study |
| HR-R2 | TATCTAGAATGTCATTTCTATGGAGGCATGAATCG | This study |
| HR-F3 | TATCTAGAGATGGTCAGCGCAGCG | This study |
| HS-F1 | GCAATCCTTTGCCGCAGCTATT | This study |
| HR-R3 | GTCAAGCTTCTAGGGCTCGTAGTTCG | This study |
| Plasmids | Description | References |
| pUC19 | High-copy cloning vector | Sigma |
| pRK767 | Low-copy cloning vector | Gill and Warren, 1988 |
| pUCF1 | LHR fragment 1 in pUC19 | This study |
| pUCF2 | LHR fragment 2 in pUC19 | This study |
| pUCF3 | LHR fragment 3 in pUC19 | This study |
| pUCF1-2 | LHR fragments 1-2 in pUC19 | This study |
| pRF1 | LHR fragment 1 in pRK767 | This study |
| pRF2 | LHR fragment 2 in pRK767 | This study |
| pRF3 | LHR fragment 3 in pRK767 | This study |
| pRF1-2 | LHR fragments F1-2 in pRK767 | This study |
| pLHR | The entire LHR sequence, F1-F2-F3, in pRK767 | This study |
PCR screening of beef isolates for heat resistance
A set of 55 strains of E. coli that were previously isolated from a beef processing plant (Dlusskaya et al., 2011) was screened for heat resistance with primers targeting the locus of heat resistance. E. coli AW1.7 and its heat sensitive derivative E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 (Pleitner et al., 2012) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Primers (Table 1) were designed and used to selectively target 3 separate regions (size ranging 1.8–2.8 kb) of the locus of heat resistance. The primer pairs HR-F1/HS-R1 and HR-F2.2/HR-R2 amplified regions A (~1.8 kb) and B (~2.8 kb), respectively. Primers HS-F1 and HR-R3 were used to amplify region C (~2.8 kb). Recombinant Taq® DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Burlington, Ontario) was used to amplify products in a standard colony PCR reaction mixture and amplicons were visualized by staining with SYBRsafe (Invitrogen, Burlington, Ontario) after agarose gel electrophoresis. Heat resistance for strains E. coli MB1.8, DM19.2, AW1.1, GM12.6, MB 16.6, MB 3.5, GM9.1, and AW 12.2 (Dlusskaya et al., 2011) was determined by incubation at 60°C for 5 min and enumeration of surviving cells as described above.
Results
Heat resistance of E. coli
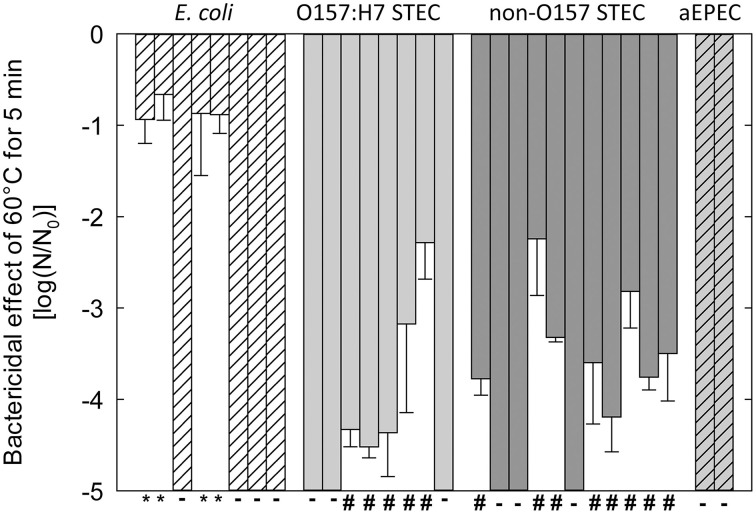
Strains of E. coli were selected for genome sequencing to obtain a wide range of heat resistance despite the limited number of strains (Figure 1). In Figure 1, strains are grouped based on their virulence profiles. O157:H7 STEC and non-O157 STEC were grouped based on serotype and the presence of stx1 or stx2 coding for Shiga toxins (Liu et al., 2015). Strains from four groups included heat sensitive strains (Figure 1), in agreement with the heat sensitivity of a majority of strains of E. coli (Hauben et al., 1997; Dlusskaya et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2015). Both O157:H7 STEC and non-O157:H7 STEC included moderately heat resistant strains (Figure 1). Four non-pathogenic strains of E. coli including E. coli AW1.7 were highly heat resistant. All of these strains were obtained from a beef processing facility (Dlusskaya et al., 2011).
Figure 1.
Reduction of cell counts of strains of E. coli after heating at 60°C for 5 min in LB broth. Strains are separated based on pathotypes: no virulence factors (E. coli); O157:H7 STEC and non-O157 STEC); eae+ stx− (atypical EPEC or aEPEC). - indicates strains that were designated as “heat sensitive” because cell counts were reduced by more than 5 log (cfu mL−1). #Indicates strains that were designated as “moderately heat resistant” because the reduction of cell counts was less than 5 log (cfu mL−1). *Indicates strains that were designated as “highly heat resistant” because the reduction of cell counts was less than 1 log (cfu mL−1). The figure includes data from Liu et al. (2015).
Genome sequences and characteristics
The 29 E. coli genomes sequences obtained in this study included genomes from 4 highly heat resistant strains, 13 moderately resistant strains, and 12 heat sensitive strains (Figure 1, Table 2). Genebank accession numbers of the 29 genomes sequenced in this study are indicated in Table 2. The number of contigs larger than 500 bp per genome ranged from 95 to 277, with max sequence lengths ranging from 204263–435416 bp (Table 2).
Table 2.
E. coli strain used in this study and features of their genome sequences.
| Accession Numbers | Strain (references); phylogenetic group | Coverage (X)a | Number of contigs assembled | Max contig size (bp) | Number of putative proteinsb | Heat Resistance | EHEC Virulence Factors | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDYI00000000 | AW1.3 (1); A | 579.12 | 184 | 317424 | 5041 | High | n.d.c | Beef |
| LDYL00000000 | DM18-3 (2); A | 469.26 | 111 | 353387 | 4700 | High | n.d. | Beef |
| LDYM00000000 | GM16-6 (2); A | 442.89 | 164 | 209077 | 4678 | High | n.d. | Beef |
| LDYJ00000000 | AW1.7 (1); A | 494.63 | 165 | 245564 | 4971 | High (1) | n.d. | Beef |
| LDYK00000000 | AW1.7ΔpHR1; A | 519.61 | 152 | 246187 | 4952 | Sensitive (3) | n.d. | AW1.7 mutant |
| LECO00000000 | O103:H2 PARC444 (2); B1 | 471.64 | 98 | 356993 | 4864 | Sensitive (2) | n.d. | Unknown |
| LECG00000000 | O103:H2 PARC445 (2); B1 | 584.81 | 158 | 327869 | 5096 | Sensitive (2) | n.d. | Unknown |
| LECL00000000 | O44:H18 PARC450 (2); E | 458.44 | 146 | 343811 | 4951 | Sensitive (2) | n.d. | Unknown |
| LEAF00000000 | O157:H7 CO6CE1353 (2); D | 484.64 | 205 | 376588 | 5572 | Moderate (2) | stx1 stx2 eae | Clinical |
| LEAG00000000 | O157:H7 CO6CE1943 (2); D | 477.76 | 185 | 374853 | 5436 | Moderate (2) | stx1 stx2 eae | Clinical |
| LEAH00000000 | O157:H7 CO6CE2940 (2); D | 475.57 | 197 | 376618 | 5537 | Moderate (2) | stx2 eae | Clinical |
| LEAE00000000 | O157:H7 CO6CE900 (2); D | 470.23 | 225 | 376513 | 5554 | Moderate (2) | stx2 eae | Clinical |
| LEAJ00000000 | O157:H7 E0122 (2); D | 480.56 | 189 | 399998 | 5478 | Moderate (2) | stx2 eae | Cattle |
| LEAD00000000 | O157:H7 1935 (2); D | 502.88 | 194 | 393069 | 5523 | Sensitive (2) | stx1 stx2 eae | Human |
| LEAI00000000 | O157:H7 CO283 (2); D | 531.16 | 184 | 376583 | 5296 | Sensitive (2) | stx1 stx2 eae | Cattle |
| LEAK00000000 | O157:H7 LCDC7236 (2); D | 492.65 | 181 | 376583 | 5461 | Sensitive (2) | stx1 stx2 eae | Human |
| LDYN00000000 | O26:H11 05-6544 (2) | 426.65 | 280 | 219684 | 5691 | Moderate (2) | stx1 eae | Human |
| LECF00000000 | O103:H25 338 (2); B1 | 439.31 | 218 | 376897 | 5321 | Moderate (2) | stx1 eae | Clinical |
| LECH00000000 | O104:H4 11-3088 (2); B1 | 515.77 | 173 | 320350 | 5254 | Moderate (2) | stx2d | Human |
| LECI00000000 | O111:NM 583 (2); B1 | 492.35 | 185 | 323305 | 5067 | Moderate (2) | stx1 eae | Clinical |
| LECK00000000 | O113:H4 09-0525 (2); A | 475.86 | 165 | 254878 | 5275 | Moderate (2) | stx1 stx2 | Unknown |
| LDZZ00000000 | O121:H19 03-2832 (2); B1 | 457.58 | 213 | 434838 | 5272 | Moderate (2) | stx2 eae | Human |
| LEAA00000000 | O121:NM 03-4064 (2); B1 | 568.02 | 221 | 435416 | 5298 | Moderate (2) | stx2 eae | Human |
| LEAB00000000 | O145:NM 03-6430 (2); n.a. | 528.20 | 210 | 359240 | 5371 | Moderate (2) | stx1 eae | Human |
| LECM00000000 | O45:H2 05-6545 (2); B1 | 508.74 | 263 | 261384 | 5352 | Sensitive (2) | stx1 eae | Human |
| LECN00000000 | O76:H19 09-0523 (2); B1 | 456.09 | 191 | 404223 | 5432 | Sensitive (2) | stx1 stx2 | Unknown |
| LECJ00000000 | O111:NM PARC447 (2); B1 | 544.42 | 200 | 376589 | 5672 | Sensitive (2) | stx1 stx2 eae | Unknown |
| LDYO00000000 | O26:H11 PARC448; B1 | 489.45 | 240 | 204263 | 5429 | Sensitive (2) | eae | Unknown |
| LEAC00000000 | O145:NM PARC449 (2); n.a. | 502.50 | 181 | 328848 | 5390 | Sensitive (2) | eae | Unknown |
n.a., not assigned;
Based on the Lander-Waterman equation using an average size of E. coli genome (5.16 Mb);
Based on OrthoMCL analysis of all annotated genes;
n.d., not detected;
Carries at least the beta lactamase gene present on pHUSEC2011-2 present in EAEC. Other genes on this plasmid includes factors for adhesion.
Genome sequence data confirmed the presence or absence of stx1/stx2 and eae that was determined earlier by PCR (Liu et al., 2015, Table 2). The atypical EPEC (aEPEC) carried the eae gene, but no pEAF-encoded bfp (bundle-forming pilus) genes (Trabulsi et al., 2002). Other strains of E. coli were negative for eae, stx1/2 and bfp. None of the highly heat resistant strains of E. coli carried any virulence factors (Table 2). The genomes of E. coli AW1.7 and its heat-sensitive derivative E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 (Pleitner et al., 2012) were virtually identical; however, in addition to the loss of the 4842 bp plasmid pHR1, two additional deletions of 21768 and 16248 bp were identified in the heat sensitive E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1. Of the 19 STEC, 16 possessed the eae gene/LEE pathogenicity island; the remaining 3 STEC were categorized as LEE negative STECs (Table 2), which still have the ability to cause disease (Newton et al., 2009). The 19 STEC included moderately heat resistant and heat sensitive strains (Table 2). A moderately heat resistant STEC isolate from the 2011 Germany outbreak, O104:H4 11-3088, carried stx2, as well as a gene encoding a β-lactamase from the EHEC plasmid, pHUSEC2011. This plasmid also encodes EAEC virulence factors such as the aaf and agg genes (Estrada-Garcia and Navarro-Garcia, 2012).
Phylogenetic distribution of heat resistant isolates
To assess the phylogenetic relationships of the heat resistant and sensitive strains, a core genome phylogenetic tree was constructed with the genomes from this study, and 48 obtained from the NCBI database. The E. coli phylogenetic groups A, B1, B2, D and E (Jaureguy et al., 2008; Touchon et al., 2009) were well supported by our core genome tree (Figure 2).
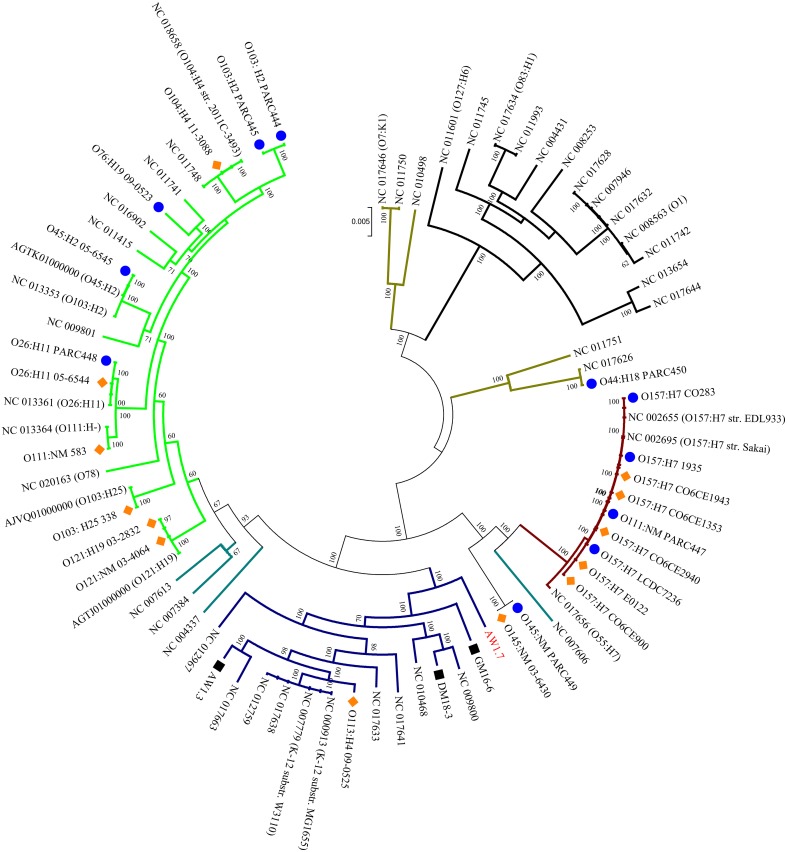
Figure 2.
Phylogenomic distribution of strains of E. coli and Shigella spp. A core genome phylogenetic tree was constructed using the 28 sequenced genomes from this project, indicated by strain numbers and serotype as applicable, and 48 genome sequences from NCBI, indicated by serotype and Accession numbers. The strain numbers of the 48 strains are indicated in Table S2. The phylogenetic groups of E. coli are color coded: A, Blue; B1, Green; B2, Black; D, Brown; and E, Maroon; Shigella spp. (indicated by teal colored branches) were included in the phylogenetic tree because this genus is considered a host-adapted pathovar of E. coli. Bootstrapping values are indicated for each branch. The sequenced genomes from this project are coded by blue circles and orange diamonds indicating heat sensitive and moderately heat resistant strains, respectively. Black squares represent highly heat resistant strains.
Moderately heat resistant strains were found in the phylogenetic groups A, B1, and E (Figure 2). Resistant and sensitive strains of the serotype O157H7 and O26:H11, 05-6544 and PARC448, respectively, group together near NCBI strains of similar serotypes. This grouping of heat resistant and sensitive isolates occurs with O145:NM isolates as well, however, these strains are found distinctly separate from other phylogenetic groups (Figure 2). Some moderately resistant, non-O157 STEC are located on branches with pathogenic E. coli including O104:H4 11-3088 (Figure 2). The overall genomic similarity of sensitive and resistant strains may illustrate the ease of acquiring genetic variations to become moderately heat resistant. Particularly strains within phylogenetic group E, comprising O157:H7 STEC (Figure 2), are highly related and therefore the differences in the accessory genes, content or sequence, accounts for differences in heat resistance.
All four highly resistant strains were assigned to group A. The highly heat resistant strains E. coli AW1.7 and GM16.6 are located in divergent branches separate from other E. coli in this group (Figure 2). E. coli AW1.3 shares a high degree of sequence similarity to E. coli P12b, a model strain for flagellar studies (Ratiner et al., 2010), while E. coli DM18.3 is closely related to the commensal E. coli strain HS (Levine et al., 1978). The phylogenetic diversity of highly heat resistant strains indicates that these strains do not share a common ancestor (Figure 2).
Identification the locus of heat resistance (LHR)
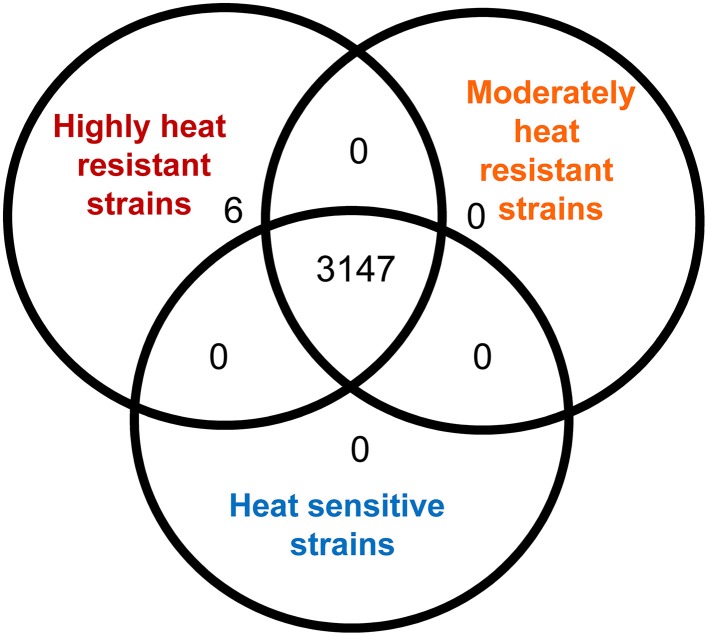
To identify differences in gene content conferring high heat resistance, the genomes were separated into their phenotypic groups: highly resistant; moderately resistant; and sensitive. An OrthoMCL analysis found 3147 orthologs shared among all 28 genomes, however, none of these were unique to heat sensitive or moderately heat resistant strains (Figure 3). A set of 6 genes was unique to the highly heat resistant strains (Figure 3); all of these genes are located on a 14,469 bp genomic island present in E. coli AW1.7, AW1.3, DM18.3, and GM16.6 (Figure 4). The 6 genes specific to the highly heat resistant group are scattered among an additional 10 ORFs in this genomic island (Figure 4). Remarkably, this genomic island was absent in E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1. The plasmid curing protocol used to generate E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 (Pleitner et al., 2012) thus also resulted in a 16,248 bp deletion encompassing the genomic island and the flanking mobile genetic elements. This operon was previously identified in heat resistant strains of Cronobacter sakazakii (Gajdosova et al., 2011) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (Bojer et al., 2010). Due to its presence in highly heat resistant E. coli, the genomic island was named the locus of heat resistance (LHR).
Figure 3.
Analysis of orthologous protein coding sequences identified in highly heat resistant, moderately heat resistant and heat sensitive E. coli strains by OrthoMCL. The Venn diagram indicates the number of protein coding sequences that are shared by all strains analysed in this study, the number of protein coding sequences that were shared between any two of the phenotypic groups, and the number of protein coding sequences that were found only in one of the three phenotypic groups.
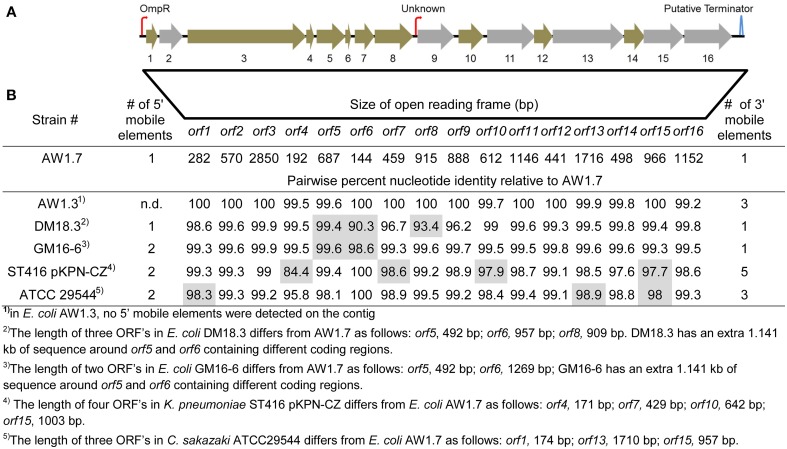
Figure 4.
Representation of the locus of heat resistance (LHR) in E. coli AW1.7, AW1.3, DM18.3, and GM16-6, K. pneumoniae ST416 pKPN-CZ and C. sakazaki ATCC29544. (A) Representation of the LHR in highly heat resistant strains. The figure is scaled to the locus of heat resistance in E. coli AW1.7 (14.469 kb in size). Putative promoters and terminators sequences are indicated with hooked arrows and stem-loops, respectively. Open reading frames (ORFs) shaded in gray were identified as unique orthologs in highly heat resistant strains. The GC content of the genetic island is 61.8% while the genome average for AW1.7 is 51.1%. (B) Pairwise nucleotide identity of ORFs in E. coli AW1.3, DM18.3, and GM16-6, K. pneumoniae ST416 pKPN-CZ and C. sakazaki ATCC29544 to the corresponding ORFs in E. coli AW1.7. ORFs that differ in size from E. coli AW1.7 are shaded in gray and the size is indicated in footnotes. Mobile genetic elements were detected in all strains upstream and downstream of the locus of heat resistance; the number of mobile genetic elements is also indicated.
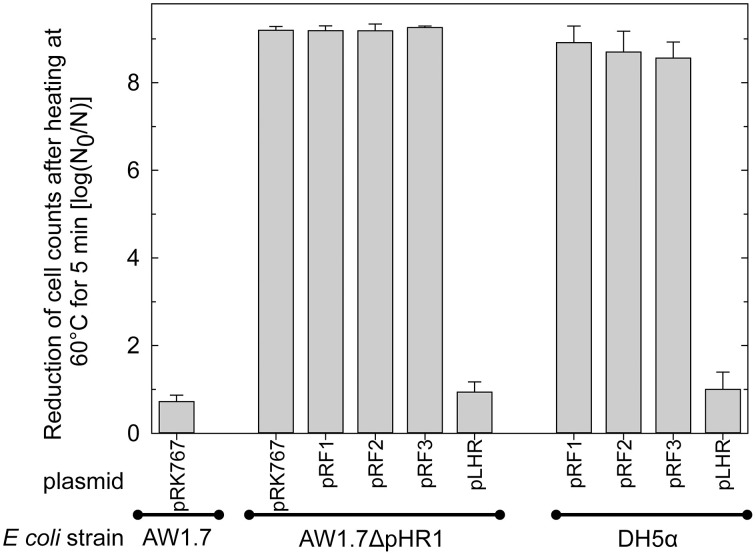
LHR confers high heat resistance to heat sensitive E. coli
To verify that high heat resistance in E. coli is mediated by proteins encoded by the LHR, the heat sensitive E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 and DH5α were complemented with LHR or fragments of LHR. LHR or LHR fragments were introduced in E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 and DH5α after cloning into the low-copy vector pRK767. Fragments F1, F2 and F3 encompassed about 6, 3.3, and 8 kbp, respectively. Cloning of the empty plasmid pRK767 served as control and the heat resistance of the resulting derivatives of E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 and DH5α was compared to the wild type strains (Figure 5). Cloning the low copy number plasmid pRK767 into E. coli AW1.7 did not affect the strain's heat resistance (Figures 1, 5). Strains expressing the full length LHR were as heat resistant as E. coli AW1.7 while strains with plasmids containing only a portion of the LHR remained heat sensitive (Figure 5). Complementation of E. coli AW1.7ΔpHR1 with the plasmid pHR1 did not alter heat resistance of the strain (Bédié et al., 2012 and data not shown), confirming that the loss of the LHR rather than the loss of the plasmid pHR1 are responsible for the heat sensitive phenotype of this strain.
Figure 5.
Heat resistance of E. coli AW1.7, AW1.7ΔpHR1, and DH5α carrying the vector pRK767 or derivatives of this vector with the full length LHR or the LHR fragments F1, F2, or F3. Data are shown as means ± standard deviation of triplicate independent experiments.
Genes encoded by the LHR
The LHR codes for 16 putative ORFs (Figure 4A, Table S1): 2 small heat-shock proteins (sHSPs); a Clp protease (Bojer et al., 2013); several hypothetical proteins with predicted transmembrane domains; a putative sodium/hydrogen exchanger; and several peptidases. Figure 4 compares the operons in E. coli, C. sakazakii, and K. pneumonia. The predicted function and the conserved functional and transmembrane domains of the predicted proteins are shown in Table S1. The conservation of the ORFs among E. coli, C. sakazakii, and K. pneumonia is remarkable; most ORFs share more than 99% nucleotide identity to the corresponding genes in E. coli AW1.7 (Figure 4B). E. coli AW1.7 and AW1.3 share 100% nucleotide identity for 10 of the 16 ORFs (Figure 4B). In E. coli AW1.7, the strongest predicted promoter was located 63 bp upstream from ORF1. BPROM analysis predicted that the transcription factor OmpR interacts with this promoter. Another putative promoter is located 26 bp upstream from ORF 9 (Figure 4A). One predicted rho-independent terminator was oriented in the same direction as the ORFs and located 177 bp downstream from ORF 16 (Figure 4A).
In all four strains of E. coli, the LHR is flanked by mobile elements or putative transposases (Figure 4B and data not shown). Accordingly, the GC content of the island is 61.8%, substantially higher than the E. coli average of ~50% (Figure 4A). In C. sakazakii and K. pneumonia, the LHR is located on plasmids (Bojer et al., 2010; Gajdosova et al., 2011); however, none of the E. coli strains in this study possess plasmids larger than 14 kb (data not shown) and the LHR can thus be assumed to be encoded by the chromosome in the strains of E. coli analyzed here. The high degree of sequence identity of the LHR in different species of Enterobacteriaceae, the presence of mobile genetic elements adjacent to the LHT, and the divergent GC content suggest that the LHR was acquired by lateral gene transfer.
Presence of LHR in E. coli and other pathogenic species
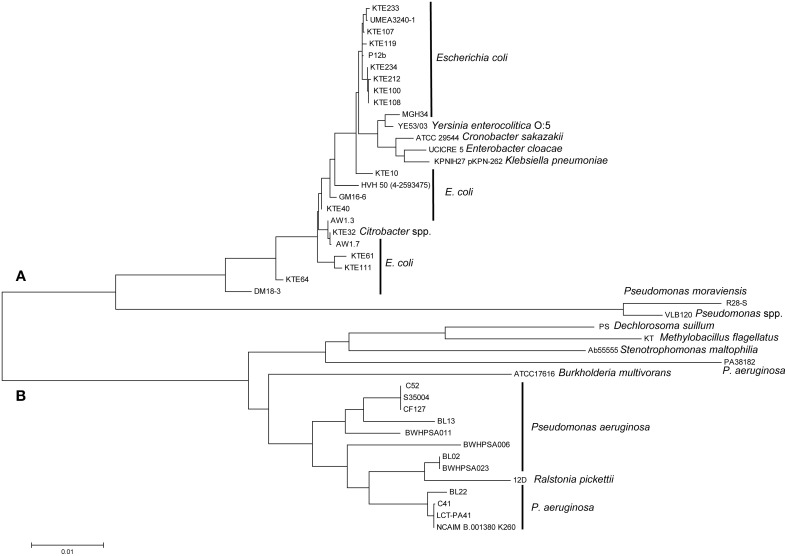
Our study and prior studies with K. pneumonia and C. sakazakii reported a correlation of the presence of the LHR and heat resistance (Figures 1, 4, 5, Bojer et al., 2010; Gajdosova et al., 2011). The LHR may thus be a marker for heat resistance in Enterobacteriaceae and related organisms. To determine the presence of the LHR in bacterial genomes, we performed a BLAST search using the entire LHR, excluding adjacent transposases, against the NCBI Genomes database. This analysis retrieved 41 sequences with more than 80% coverage from several species in the β- and γ-proteobacteria, including pathogenic strains of Yersinia entercolitica, Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter sp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and 16 strains of E. coli. The sequences were used to calculate a maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree (Figure 6) that shows remarkable differences from the phylogenetic tree of the bacterial species shown in the tree. The tree is divided into 2 large groups; group A is exclusively composed of sequences γ-proteobacteria (Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas spp.) while group B includes sequences from β - and γ-proteobacteria (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree generated from an alignment of LHR sequences (>80% coverage of AW1.7) of disparate species of γ- and β-proteobacteria. The tree is separated into cluster (A), represented by Enterobacteriaceae, and cluster (B), represented primarily by strains of P. aeruginosa. Genebank accession numbers of genomes with LHR sequences are indicated in Table S3.
Group A includes sequences from strains of E. coli isolated from urinary tract infections (e.g., KTE#) and food isolates of E. coli. The conserved sequence identity between the most distantly related sequences from E. coli, DM18.3 and KTE233, is 98.9%, suggesting recent lateral transfer of the LHR. LHR sequences from E. coli AW1.3 and P12b, two strains that are phylogenetically closely related, cluster in separate branches of group A while LHR sequences from phylogenetically unrelated strains, e.g., E. coli AW1.3 and AW1.7, cluster closely together. LHR sequences from Yersinia enterocolitica, Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter spp., K. pneumonia, and C. sakazakii are interspersed with LHR sequences from E. coli (Figure 6). The most divergent LHR sequences in group A belong to 2 Pseudomonas spp. (Figure 6).
LHR sequences in group B are represented by 13 strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. LHR sequences from other pulmonary pathogens include sequences from Ralstonia pickettii, Burkoholderia multivorans, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (Figure 6). Dechlorosoma suillum (now Azospira suillum; Byrne-Bailey and Coates, 2012) and Methylobacillus flagellatus (Chistoserdova et al., 2007) are found in freshwater and sewage and represent the most divergent LHR sequences in group B. The nucleotide identity between the most distant species from group A (E. coli KTE233) and group B (Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCAIM B.001380 K260) is 87.2% over >80% of the entire LHR sequence. These data provide evidence that the LHR is highly conserved and has been laterally exchanged within the β- and γ-proteobacteria.
To determine the frequency of the LHR in E. coli more accurately, we searched the NCBI whole-genome shotgun assemblies (wgs) database in addition to the NCBI Genome database. This analysis retrieved additional LHR sequences predominantly from clinical isolates including UPEC and ETEC (Table 3). Sequences covering >80% of the LHR were identified in 66 out of 3347 strains, with an additional 15 strains found to possess 60–80% of the LHR (Table 3). All sequences are more than 99% identical to the LHR sequence of E. coli AW1.7. Including genome sequences obtained in this study, the proportion of LHR-positive strains of E. coli is approximately 2% (Table 3).
Table 3.
Frequency of LHR in E. coli. This table lists E. coli genomes or whole genome shotgun sequences containing the locus of heat resistance.
| Origin of E. coli strains sequenced (ref) | # of genome sequences | # genomes with LHR 80% (60%) coveragea |
|---|---|---|
| NCBI genome databaseb | 2263 | 16 |
| Patients with urinary tract infections or bacteremia (1) | 317 | 3 (1) |
| Clinical isolates of enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) (2) | 218 | 13 (4) |
| Patients with urinary tract infections (3) | 236 | 15c |
| Clinical isolates after antibiotic treatment (4) | 247 | 21 (9) |
| Water isolates of O157:H12 (5) | 1 | 1 |
| ETEC (6) | 5 | 1 |
| Woman with recurrent urinary tract infections (7) | 27 | 3 (1) |
| Intensive care unit patients (8) | 5 | 2 (0) |
| Clinical and food isolates (this study) | 28 | 4 (0) |
| Total # of genomes 3347 | Total LHR 66 (81) | |
| % positive 2.0 (2.4) |
> 80% coverage and > 95% pairwise nucleotide identity when compared to E. coli AW1.7; values in brackets indicate BLAST hits with 60–80% coverage and > 95% nucleotide identity when compared to E. coli AW1.7.
Accessed on Aug 11th, 2014.
13 of these E. coli strains are included in the NCBI genome database.
(1) E.coli UTI Bacteremia initiative, Broad Institute (broadinstitute.org) Accessed Aug 11th, 2014; (2) http://genomesonline.org/project?id=16624 Accessed Aug 11th, 2014; (3) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/193500 Accessed Aug 11th, 2014; (4) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/233951 Accessed Aug 11th, 2014; (5) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA51127 Accessed Aug 11th, 2014; (6) Sahl et al., 2010; (7); Chen et al., 2013; (8) Hazen et al., 2014.
PCR targeting the LHR as a predictor and screening tool for highly heat resistant E. coli
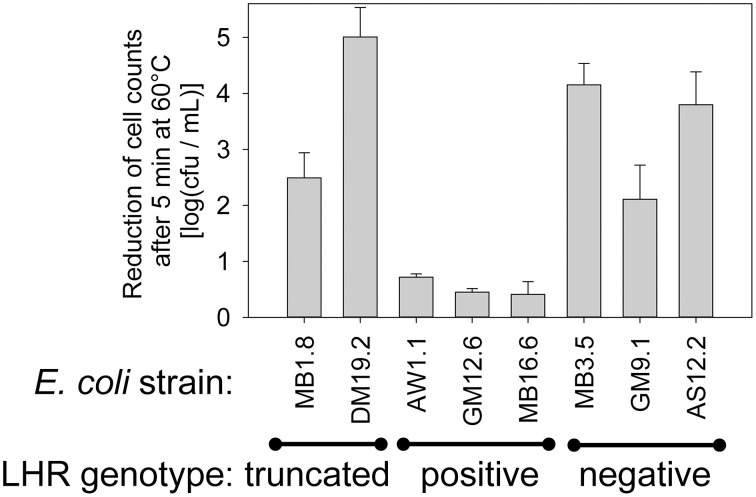
To determine whether PCR screening for the LHR reliably identifies highly heat resistant strains of E. coli, 55 beef isolates of E. coli (Dlusskaya et al., 2011) were screened by PCR using primers targeting 3 different regions of the LHR, spanning several ORF's that are unique to highly heat resistant E. coli (Figure S1). Out of the 55 strains of E. coli, 13 strains were positive for all 3 LHR amplicons (Figure S1) and 2 strains were positive for 2 of the 3 LHR fragments (Figure S1). We selected 3 LHR positive, 3 LHR negative and the 2 strains containing a partial LHR for evaluation of heat resistance at 5 min at 60°C (Figure 7). All LHR positive strains were highly heat resistant but the 2 strains containing a truncated LHR and LHR-negative strains were moderately heat resistant (Figure 7C). The results support the hypothesis that the presence of the complete LHR sequence is required for high heat resistance in E. coli.
Figure 7.
Correlation of the LHR positive genotype to heat resistance in E. coli. Three fragments of the LHR were amplified with PCR (Figure S1) to identify strains with a full length LHR and strains with a full length LHR. Heat resistance of 8 strains of E. coli representing 3 LHR-positive and negative strains, respectively, and two strains in which a truncated LHR was detected. Data are shown as means ± standard deviation of triplicate independent experiments.
Discussion
The resistance of food-borne pathogens to thermal intervention mechanisms challenges the food industry and public heath sectors, requiring a better understanding of the frequency, distribution and detection of heat resistance. This study employed comparative genomics to identify a genetic island, the LHR, which provides exceptional heat resistance in E. coli. Core-genome phylogenetic analysis and phylogenetic analysis of the LHR support the conclusion that the LHR is transmitted via lateral gene transfer. Transfer of the LHR occurred between diverse species in the β- and γ-proteobacteria, including enteric and pulmonary pathogens. Screening of food isolates yielded a number of LHR positive strains, and demonstrated that the LHT is a suitable target for identifying heat resistant E. coli.
The LHR mediates heat resistance in Enterobacteriaceae
Presence of the LHR in C. sakazakii and K. pneumoniae correlated to heat resistance of the strains (Bojer et al., 2010; Gajdosova et al., 2011). Of the 36 strains of E. coli that were analyzed both with respect to heat resistance and the presence of the LHR, all highly resistant strains carried the LHR and all strains carrying the full length LHR were highly heat resistant. Orthologs of 10 of the 16 ORFs are present in moderately resistant and heat sensitive strains, and a truncated LHR provides only moderate heat resistance. However, presence of the full length locus is unique to highly heat resistant E. coli. Complementation with the LHR conferred heat resistance to sensitive strains of E. coli only if the entire genomic island was cloned. Heat resistance of E. coli is thus dependent on the entire genomic island, and not on the function of a single protein.
The LHR comprises ORFs that are predicted to encode proteins with putative functions in cell envelope maintenance, turnover of misfolded proteins, and heat shock. The predicted products of 5 ORFs possess highly conserved functional domains, including sHSPs (Han et al., 2008) and several proteases. Eight ORFs contain predicted transmembrane domains, including Orfs8-10 and the proteases Orf15 and Orf16. One putative gene, orf13, is predicted to encode a sodium/hydrogen antiporter, which corresponds to the interplay of osmotic and heat stress in strains expressing the LHR (Pleitner et al., 2012; Orieskova et al., 2013). Orf16, a predicted membrane protease, possesses a similar domain structure to DegS, a protease involved in the activation of the σE stress pathway in E. coli (Alba and Gross, 2004). DegS types of proteases are members of the HtrA (high temperature requirement A) family of proteins, which play a role in protein turnover in the periplasm and are induced by heat shock (Kim and Kim, 2005).
The expression of orf3, designated as a Clp protease ClpK, increased heat resistance in E. coli DH5α; however, transfer of the entire LHR was required for heat resistance in a clpP mutant strain (Bojer et al., 2013), suggesting an interplay of ClpP and other proteins encoded within the LHR. Heterologous expression of orf7-orf10 from C. sakazakii in E. coli also resulted in an increase in thermotolerance (Gajdosova et al., 2011), but the heat resistance of the resulting transgenic strains was substantially lower than the level of resistance that was observed in E. coli AW1.7 carrying the entire LHR (Figures 1, 5, 7). Deletion of the LHR substantially reduced the resistance of C. sakazakii to heat (Orieskova et al., 2013).
The LHR was suggested to be transcribed as a single poly-cistronic mRNA in K. pneumonia and C. sakazakii (Gajdosova et al., 2011; Bojer et al., 2013). We identified a strong putative promoter upstream of orf1 which is conserved in both K. pneumoniae and C. sakazakii. The promoter was predicted to interact with the OmpR, a transcription factor coordinating gene expression in response to osmotic stress (Mizuno and Mizushima, 1990). The LHR is over-expressed in response to osmotic stress (Riedel and Lehner, 2007), which corresponds to the observation that E. coli AW1.7 is resistant to heat only when incubated in growth media containing 1–4% NaCl (Ruan et al., 2011; Pleitner et al., 2012), as well as the observation that deletion of the LHR reduces the tolerance of C. sakazakii to osmotic stress (Orieskova et al., 2013). The LHR may thus function in response to osmotic and heat stress and its function may be partially dependent on the extracellular concentration of compatible solutes.
The LHR is transmitted by lateral gene transfer between β - and γ-proteobacteria
The nucleotide identity of the LHR in the Enterobacteriaceae is ~99% and the LHR is consistently flanked by mobile genetic elements. Both imply recent lateral gene transfer. The differences in the phylogenetic relationship between strains E. coli AW1.3 and P12b support this notion. Based on core-genome sequences, E. coli AW1.3 and P12b are highly related and have a recent ancestor. However, their LHR sequences are much more evolutionarily distant; suggesting the strains independently acquired the LHR. Transfer of large genomic elements is well described for genomic islands encoding virulence factors, for example the LEE (Schmidt, 2010). Comparative genomics analysis of the fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda indicated that the LEE of E. coli is also transmitted to other Enterobacteriaceae (Nakamura et al., 2013). Genomic islands that are transmitted by lateral gene transfer also possess environmental relevance (Juhas et al., 2009) and provide genes for sugar metabolism (Chouikha et al., 2006) or degradation of aromatic compounds (Gaillard et al., 2006). Acquiring multiple genes that require coordinated expression and protein function, e.g., LEE and LHR, can increase the overall fitness of the species.
Genomic islands do not always encode self-transfer capabilities (Shoemaker et al., 2000) and the LHR is located on the chromosome or on plasmids (Bojer et al., 2010; Gajdosova et al., 2011; this study), which may allow exchange through conjugation. Species carrying the LHR occupy similar environmental niches, such as the gastrointestinal tract (E. coli, Citrobacter and Yersinia), the urinary tract (UPEC and Yersinia), and sewage/fresh water (Enterobacteriaceae). Remarkably, transfer of the LHR is not restricted to Enterobacteriaceae but includes Pseudomonas spp. and β-proteobacteria. The GC content and predicted function of the ORFs do suggest a thermophillic origin of the LHR.
The LHR is present in approximately 2% of strains of E. coli, including food isolates and pathogens
This study, in combination with past studies, has identified 7 LHR-positive and highly heat resistant strains (Dlusskaya et al., 2011; Ruan et al., 2011). None of these strains carry virulence factors; however, bioinformatic analyses revealed that about 2% of all the E. coli genome sequences or whole genome shotgun sequences contain the LHR with more than 80% coverage and more than 95% nucleotide identity. All studies on the heat resistance of LHR positive strains of E. coli, Cronobacter, and Klebsiella confirmed that the full length LHR is a reliable predictor of heat resistance. LHR positive strains of E. coli include UPEC and ETEC. Because both the LHR and genes coding for virulence factors are highly mobile, highly heat resistant strains of other pathovars likely also exist. A screening of about 100 strains of STEC has not identified highly heat resistant pathogens (Liu et al., 2015), but screening of 100 strains may not suffice to identify a genetic and physiological trait that is present in about 2% of strains. The identification of the genetic determinants of heat resistance provides a rapid screening tool to identify heat resistant E. coli in food or clinical isolates. A broader screening of strains and the assessment of their heat resistance will enable to assess the public health significance of heat resistance in E. coli.
This study observed a high frequency of LHR-positive and highly heat resistant strains in beef isolates (Dlusskaya et al., 2011). Beef is an important vector for transmission of STEC (Scallan et al., 2011; USDA, 2012) and highly heat resistant E. coli are recovered in high numbers from inoculated beef patties that are cooked medium rare and even survive in burger patties that are cooked “well done,” corresponding to an internal temperature of 71°C (Dlusskaya et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2015). To date, the transmission of STEC was attributed to undercooked meat (Schmidt et al., 2002); however, LHR-positive heat resistant pathogens may additionally contribute to foodborne disease. Because these organisms may survive in beef that is cooked to a core temperature of 71°C, cooking meat to a “well done” stage may not always eliminate all pathogenic E. coli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Linda Chui, University of Alberta, and Alexander Gill, Health Canada, for providing bacterial strains, and to Andrew Lang, Memorial University, for providing plasmid pRK767. Petr Miller and Gerard Bedié are acknowledged for providing the sequence of plasmid pHR1. Alberta Innovates Bio-Solutions (grant number AI-BIO FSC-12-015) and Alberta Livestock and Meat Agency Ltd (grant number 2013R048R) are acknowledged for funding.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00932
References
- Agarwal J., Srivastava S., Singh M. (2012). Pathogenomics of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 30, 141–149. 10.4103/0255-0857.96657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alba B. M., Gross C. A. (2004). Regulation of the Escherichia coli sigma-dependent envelope stress response. Mol. Microbiol. 52, 613–619. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2003.03982.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angiuoli S. V., Salzberg S. L. (2011). Mugsy: fast multiple alignment of closely related whole genomes. Bioinformatics 27, 334–344. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bédié G., Liu Y., Miller P., Ruan L. F., McMullen L., Gänzle M. G. (2012). Identification of pHR1 as a major factor in heat and pressure resistance of E. coli AW1.7. Book of Abstracts, in 7th International Conference on High Pressure Bioscience and Biotechnology (Otsu).
- Bielaszewska M., Mellmann A., Zhang W., Köck R., Fruth A., Bauwens A., et al. (2011). Characterization of the Escherichia coli strain associated with an outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Germany, 2011: a microbiological study. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 11, 671–676. 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70165-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojer M. S., Struve C., Ingmer H., Hansen D. S., Krogfelt K. A. (2010). Heat resistance mediated by a new plasmid encoded Clp ATPase, ClpK, as a possible novel mechanism for nonsocomial persistence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 5:e15467. 10.1371/journal.pone.0015467 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojer M. S., Struve C., Ingmer H., Krogfelt K. A. (2013). ClpP-dependent and –independent activities encoded by the polycistronic clpK-encoding locus contribute to heat shock survival in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Res. Microbiol. 164, 205–210. 10.1016/j.resmic.2012.11.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne-Bailey K. G., Coates J. D. (2012). Complete genome sequence of the anaerobic perchlorate-reducing bacterium Azospira suillum strain PS. J. Bacteriol. 194, 2767–2768. 10.1128/JB.00124-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. L., Wu M., Henderson J. P., Hooton T. M., Hibbing M. E., Hultgren S. J., et al. (2013). Genomic diversity and fitness of E. coli strains recovered from the intestinal and urinary tracts of women with recurrent urinary tract infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 5, 184ra60 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chistoserdova L., Lapidus A., Han C., Goodwin L., Saunders L., Brettin T., et al. (2007). Genome of Methylobacillus flagellatus, molecular basis for obligated methylotrophy, and polyphyletic origin of methylotrophy. J. Bacteriol. 189, 4020–4027. 10.1128/JB.00045-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouikha I., Germon P., Brée A., Gilot P., Moulin-Schouleur M., Schouler C. (2006). A selC-associated genomic island of the extraintestinal avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain DEN2908 is involved in carbohydrate uptake and virulence. J. Bacteriol. 188, 977–987. 10.1128/JB.188.3.977-987.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croxen M. A., Law R. J., Scholz R., Keeney K. M., Wlodarska M., Finlay B. B. (2013). Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 26, 22–880. 10.1128/cmr.00022-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlusskaya E. A., McMullen L. M., Gänzle M. G. (2011). Characterization of an extremely heat-resistant Escherichia coli obtained from a beef processing facility. J. Appl. Microbiol. 110, 840–849. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.04943.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrindt U., Hochhut B., Hentschel U., Hacker J. (2004). Genomic islands in pathogenic and environmental microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2, 414–424. 10.1038/nrmicro884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Garcia T., Navarro-Garcia F. (2012). Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli pathotype: a genetically heterogeneous emerging foodborne enteropathogen. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 66, 281–298. 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2012.01008.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard M., Vallaeys T., Vorhölter F. J., Minoia M., Werlen C., Sentchilo V., et al. (2006). The clc element of Pseudomonas sp. strain B13, a genomic island with various catabolic properties. J. Bacteriol. 188, 1999–2013. 10.1128/JB.188.5.1999-2013.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdosova J., Benedikovicova K., Kamodyova N., Tothova L., Kaclikova E., Stuchlik S., et al. (2011). Analysis of the DNA region mediating increased thermotolerance at 58°C in Cronobacter sp. and other enterobacterial strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100, 279–289. 10.1007/s10482-011-9585-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautheret D., Lambert A. (2001). Direct RNA motif definition and identification from multiple sequence alignments using secondary structure profiles. J. Mol. Biol. 313, 1003–1011. 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. R., Jr., Warren G. J. (1988). An iron-antagonized fungistatic agent that is not required for iron assimilation from a fluorescent rhizosphere pseudomonad. J. Bacteriol. 170, 163–170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordienko E. N., Kazanov M. D., Gelfand M. S. (2013). Evolution of pan-genomes of Escherichia coli, Shigella spp., and Salmonella enterica. J. Bacteriol. 195, 2786–2792. 10.1128/JB.02285-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M. J., Yun H., Lee S. Y. (2008). Microbial small heat shock proteins and their use in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 26, 591–609. 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauben K. J., Bartlett D. H., Soontjens C. C., Cornelis K., Wuytack E. Y., Michiels W. E. (1997). Escherichia coli mutants resistant to inactivation by high hydrostatic pressure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 945–950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. H., Sahl J. W., Fraser C. M., Donnenberg M. S., Scheutz F., Rasko D. A. (2013). Refining the pathovar paradigm via phylogenomics of the attaching and effacing Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 12810–12815. 10.1073/pnas.1306836110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. H., Zhao L., Boutin M. A., Stancil A., Robinson G., Harris A. D., et al. (2014). Comparative genomics of an IncA/C multidrug resistance plasmid from Escherichia coli and Klebsiella isolates from intensive care unit patients and the utility of whole-genome sequencing in health care settings. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 4814–4825. 10.1128/AAC.02573-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaureguy F., Landraud L., Passet V., Diancourt L., Frapy E., Guigon G., et al. (2008). Phylogenetic and genomic diversity of human bacteremic Escherichia coli strains. BMC Genomics 9:560. 10.1186/1471-2164-9-560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhas M., van der Meer J. R., Gaillard M., Harding R. M., Hood D. W., Crook D. W. (2009). Genomic islands: tools of bacterial horizontal gene transfer and evolution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 33, 376–393. 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00136.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaas R. S., Friis C., Ussery D. W., Aarestrup F. M. (2012). Estimating variation within the genes and inferring the phylogeny of 186 sequenced diverse Escherichia coli genomes. BMC Genomics 13:577. 10.1186/1471-2164-13-577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. R., Schatz M. C., Salzberg S. L. (2010). Quake: quality-aware detection and correction of sequencing errors. Genome Biol. 11:R116. 10.1186/gb-2010-11-11-r116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. Y., Kim K. K. (2005). Structure and function of HtrA family proteins, the key players in protein quality control. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 38, 266–274. 10.5483/BMBRep.2005.38.3.266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lainhart W., Stolfa G., Koudelka G. B. (2009). Shiga toxin as a bacterial defense against a eukaryotic predator, Tetrahymena thermophila. J. Bacteriol. 191, 5116–5122. 10.1128/JB.00508-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., et al. (1978). Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet 311, 1119–1122. 10.1016/S0140-6736(78)90299-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Stoeckert C. J., Jr., Roos D. S. (2003). OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res. 13, 2178–2189. 10.1101/gr.1224503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Gill A., McMullen L. M., Gänzle M. G. (2015). Variation in heat and pressure resistance of verotoxigenic and non-toxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Food. Prot. 78, 111–120. 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel T. K., Jarvis K. G., Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. (1995). A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 1664–1668. 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1664 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Mizushima S. (1990). Signal transduction and gene regulation through the phosphorylation of two regulatory components: the molecular basis for the osmotic regulation of the porin genes. Mol. Microbiol. 4, 1077–1082. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00681.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Takano T., Yasuike M., Sakai T., Matsuyama T., Sano M. (2013). Comparative genomics reveals that a fish pathogenic bacterium Edwardsiella tarda has acquired the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) through horizontal gene transfer. BMC Genomics 14:642. 10.1186/1471-2164-14-642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton H. J., Sloan J., Bulach D. M., Seemann T., Allison C. C., Tauschek M., et al. (2009). Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains negative for locus of enterocyte effacement. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 15, 372–380. 10.3201/eid1503.080631 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Newland J. W., Miller S. F., Holmes R. K., Smith H. W., Formal S. B. (1984). Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science 226, 694–696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orieskova M., Gajdosova J., Oslanecova L., Ondreickova K., Kaclikova E., Stuchlik E., et al. (2013). Function of thermotolerance genomic island in increased stress resistance of Cronobacter sakazakii. J. Food Nutr. Res. 52, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pleitner A., Zhai Y., Winter R., Ruan L., McMullen L. M., Gänzle M. G. (2012). Compatible solutes contribute to heat resistance and ribosome stability in Escherichia coli AW1.7. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1824, 1351–1357. 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.07.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasko D. A., Rosovitz M. J., Myers G. S., Mongodin E. F., Fricke W. F., Gajer P., et al. (2008). The pangenome structure of Escherichia coli: comparative genomic analysis of E. coli commensal and pathogenic isolates. J. Bacteriol. 190, 6881–6893. 10.1128/JB.00619-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratiner Y. A., Sihvonen L. M., Liu Y., Wang L., Siitonen A. (2010). Alteration of flagellar phenotype of Escherichia coli strain P12b, the standard type strain for flagellar antigen H17, possessing a new non-fliC flagellin gene flnA, and possible loss of original flagellar phenotype and genotype in the course of subculturing through semisolid media. Arch. Microbiol. 192, 267–278. 10.1007/s00203-010-0556-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel K., Lehner A. (2007). Identification of proteins involved in osmotic stress in Enterobacter sakazakii by proteomics. Proteomics 7, 1217–1231. 10.1002/pmic.200600536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan L., Pleitner A., Gänzle M. G., McMullen L. M. (2011). Solute transport proteins and the outer membrane protein NmpC contribute to heat-resistance of Escherichia coli AW1.7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 2961–2967. 10.1128/AEM.01930-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph B., Gebendorfer K. M. (2010). Evolution of Escherichia coli for growth at high temperatures. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 19029–19034. 10.1074/jbc.M110.103374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl J. W., Steinsland H., Redman J. C., Angiuoli S. V., Nataro J. P., Sommerfelt H., et al. (2010). A comparative genomic analysis of diverse clonal types of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli reveals pathovar-specific conservation. Infect. Immun. 79, 950–960. 10.1128/IAI.00932-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scallan E., Hoekstra R. M., Angulo F. J., Tauxe R. V., Widdowson M. A., Roy S. L., et al. (2011). Foodborne illness acquired in the United States - Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17, 7–14. 10.3201/eid1701.P11101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Hensel M. (2004). Pathogenicity islands in bacterial pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 17, 14–56. 10.1128/CMR.17.1.14-56.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. A. (2010). LEEways: tales of EPEC, ATEC and EHEC. Cell Microbiol. 12, 1544, 1552. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01518.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. B., Keene M. P., Lorenzen C. L. (2002). Improving consumer satisfaction of beef through the use of thermometers and consumer education by wait staff. J. Food Sci. 67, 3190–3193. 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb08880.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Wang G. R., Salyers A. A. (2000). Multiple gene products and sequences required for excision of the mobilizable integrated Bacteroides element NBU1. J. Bacteriol. 182, 928–936. 10.1128/JB.182.4.928-936.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. T., Wong K., Jackman S. D., Schein J. E., Jones S. J., Birol I. (2009). ABySS: a parallel assembler for short read sequence data. Genome Res. 19, 1117–1123. 10.1101/gr.089532.108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solovyev V., Salamov A. (2011). Automatic annotation of microbial genomes and metagenomic sequences, in Metagenomics and its Applications in Agriculture, Biomedicine and Environmental Studies, ed Li R. W. (New York, NY: Nova Science Publishers; ), 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis A. (2014). RAxML Version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30, 1312–1313. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera G., Castresana J. (2007). Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Systematic Biol. 56, 564–577. 10.1080/10635150701472164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Stecher G., Peterson D., Filipski A., Kumar S. (2013). MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725–2729. 10.1093/molbev/mst197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchon M., Hoede C., Tenaillon O., Barbe V., Baeriswyl S., Bidet P., et al. (2009). Organised genome dynamics in the Escherichia coli species results in highly diverse adaptive paths. PLoS Genet. 5:e1000344. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trabulsi L. R., Keller R., Tardelli Gomes T. A. (2002). Typical and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 8, 508–513. 10.3201/eid0805.010385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USDA (2012). Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli in certain raw beef products. Fed. Regist. 77, 31975–31981. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.