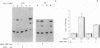Abstract
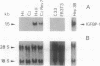
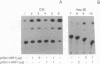
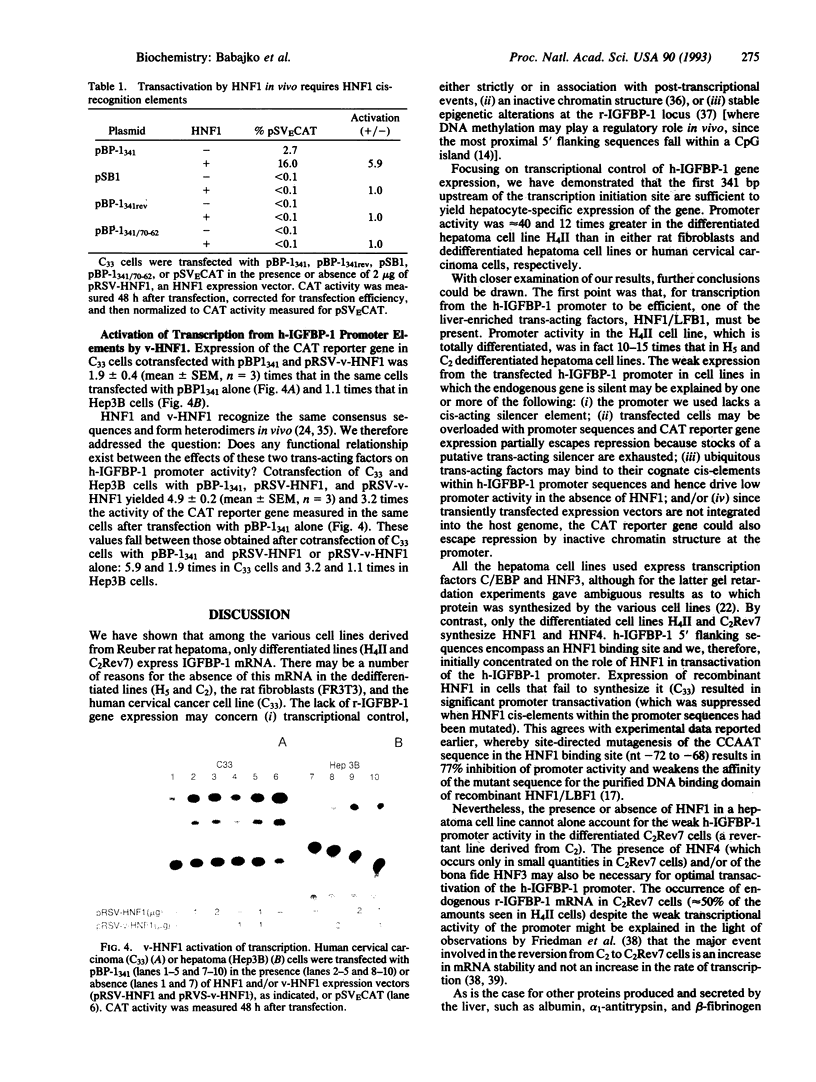
Tissue-specific expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1) in the liver has been studied using differentiated (H4II and C2Rev7) and dedifferentiated (H5 and C2) rat hepatoma cell lines. Northern blot analysis showed that endogenous IGFBP-1 mRNA was expressed only in the differentiated cell lines. The first 341 base pairs 5' to the transcription initiation site of the human IGFBP-1 gene were inserted upstream of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene (pBP-1(341)). Expression of this gene from the human IGFBP-1 promoter was 10-16 times more efficient in the H4II line than in the other hepatoma cell lines and 40 and approximately 12 times more so than in rat fibroblasts (FR3T3) and a human cervical carcinoma cell line (C33), respectively. Cotransfection of pBP-1(341) and pRSV-HNF1 and/or pRSV-v-HNF1 (eukaryotic expression vectors that drive the synthesis of the liver-enriched trans-acting factor HNF1 or of v-HNF1, a related form) in C33 recipient cells yielded a 6-fold increase in IGFBP-1 promoter activity by HNF1 and a 2-fold increase by v-HNF1. These increases were dependent on the integrity of an HNF1 binding site located 58-74 nucleotides upstream of the cap site. Stimulation of promoter activity by cotransfection of both HNF1 and v-HNF1 fell between these values. Our results indicate that HNF1 is instrumental in human IGFBP-1 promoter activity in vivo and that v-HNF1 modulates this functional role.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman A., Groffen C. A., Kortleve D. J., Drop S. L. Organization of the gene encoding the insulin-like growth factor binding protein IBP-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):898–907. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80959-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman A., Groffen C., Kortleve D. J., Geurts van Kessel A., Drop S. L. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IBP-1). EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2417–2423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby W. H., Snyder D. K., Clemmons D. R. Radioimmunoassay of a 26,000-dalton plasma insulin-like growth factor-binding protein: control by nutritional variables. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Dec;67(6):1225–1230. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-6-1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Yaniv M., Cortese R. Hepatocyte dedifferentiation and extinction is accompanied by a block in the synthesis of mRNA coding for the transcription factor HNF1/LFB1. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2257–2263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouard T., Blumenfeld M., Bach I., Vandekerckhove J., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. A distal dimerization domain is essential for DNA-binding by the atypical HNF1 homeodomain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5853–5863. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon H. G., Weiss M. C. A quantitative comparison of formation of spontaneous and virus-produced viable hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):852–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubbage M. L., Suwanichkul A., Powell D. R. Structure of the human chromosomal gene for the 25 kilodalton insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 May;3(5):846–851. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-5-846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):68–91. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., De Magistris L., Lazzaro D., Gerstner J., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. LFB3, a heterodimer-forming homeoprotein of the LFB1 family, is expressed in specialized epithelia. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1435–1443. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Moore E. E., Dubois M., Cassio D., Weiss M. C. Dedifferentiated variants of a rat hepatoma: analysis by cell hybridization. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):697–718. doi: 10.1007/BF01542636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Weiss M. C. Characterization of differentiated and dedifferentiated clones from a rat hepatoma. Biochimie. 1974;56(11-12):1603–1611. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Babiss L. E., Weiss M., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatoma variants (C2) are defective for transcriptional and post-transcriptional actions from both endogenous and viral genomes. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1727–1731. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Nielsch U., Sladek F., Lai E., Babiss L. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Differential regulation of hepatocyte-enriched transcription factors explains changes in albumin and transthyretin gene expression among hepatoma cells. New Biol. 1991 Mar;3(3):289–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):445–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F. Transcriptional activators in hepatocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Jan;1(1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Koistinen R., Aalto-Setälä K., Seppälä M., Jänne O. A., Kontula K. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein/placental protein 12 and tissue-specific expression of its mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Koistinen R., Suikkari A. M., Seppälä M., Jänne O. A. Identification by hybridization histochemistry of human endometrial cells expressing mRNAs encoding a uterine beta-lactoglobulin homologue and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 May;4(5):700–707. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-5-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassarre C., Hardouin S., Daffos F., Forestier F., Frankenne F., Binoux M. Serum insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in the human fetus. Relationships with growth in normal subjects and in subjects with intrauterine growth retardation. Pediatr Res. 1991 Mar;29(3):219–225. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Powell D. R., Styne D. M., Hintz R. L. Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding proteins in the developing rhesus monkey. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Apr;72(4):905–911. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-4-905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Orlowski C. C., Brown A. L., Becker R. E., Unterman T. G., Rechler M. M. Different tissue distribution and hormonal regulation of messenger RNAs encoding rat insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins-1 and -2. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):321–328. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski C. C., Ooi G. T., Rechler M. M. Dexamethasone stimulates transcription of the insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 gene in H4-II-E rat hepatoma cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1592–1599. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITOT H. C., PERAINO C., MORSE P. A., Jr, POTTER V. R. HEPATOMAS IN TISSUE CULTURE COMPARED WITH ADAPTING LIVER IN VIVO. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1964 Apr;13:229–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Campos J., Chouard T., Yaniv M., Cereghini S. vHNF1 is a homeoprotein that activates transcription and forms heterodimers with HNF1. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1445–1457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritvos O., Ranta T., Jalkanen J., Suikkari A. M., Voutilainen R., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human decidua inhibits the binding and biological action of IGF-I in cultured choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2150–2157. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanichkul A., Cubbage M. L., Powell D. R. The promoter of the human gene for insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1. Basal promoter activity in HEP G2 cells depends upon liver factor B1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21185–21193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. S., Lim J., English J., Irvine L., Chard T. The concentration of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in human umbilical cord serum at delivery: relation to fetal weight. J Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;129(3):459–464. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1290459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]