Abstract
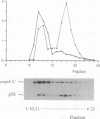
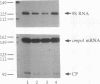
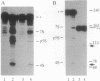
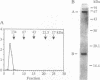
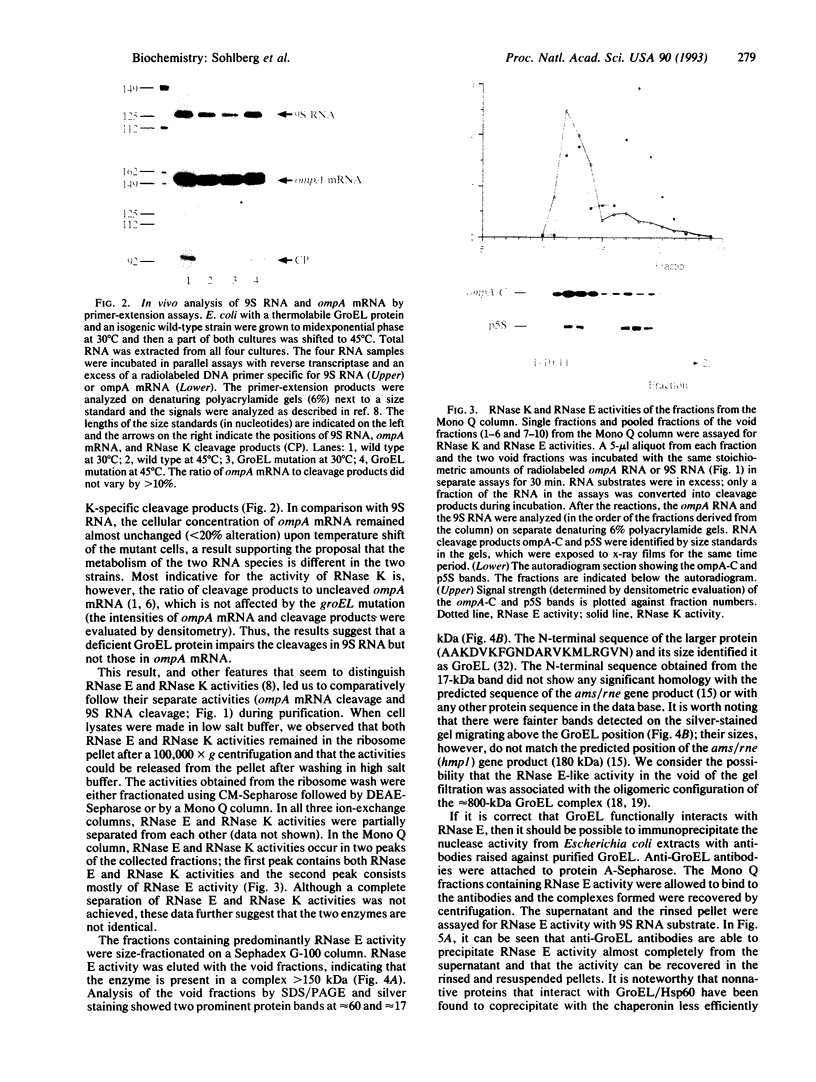
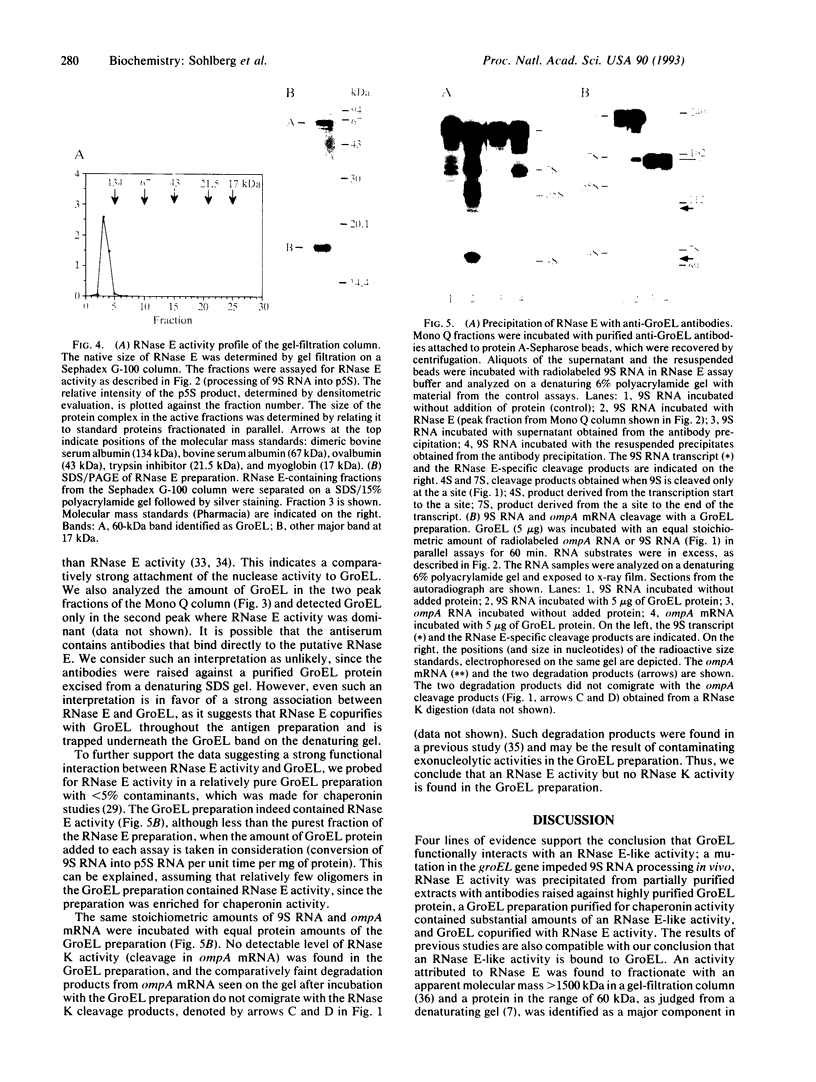
The highly specific endoribonuclease activities of RNase E (which processes ribosomal 9S RNA into p5S RNA) and RNase K (which initiates decay of the ompA mRNA) are inferred to play a central role in RNA processing and mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. In vivo both activities are affected by a conditional mutation of the ams/rne gene that seems to be complemented at nonpermissive temperatures by a fragment of the groEL gene. Analysis of the relationship between the two nucleases and the heat shock protein revealed that GroEL interacts functionally with an RNase E-like activity but not with an RNase K activity, a groEL mutation affected 9S RNA processing but not ompA mRNA cleavage, RNase E activity could be precipitated with an antibody against GroEL, and a highly purified GroEL preparation contained RNase E activity but not RNase K activity. When purifying RNase E activity, we obtained a preparation containing two major proteins of 60 and 17 kDa. The size and the N-terminal sequence identified the 60-kDa protein as GroEL.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chanda P. K., Ono M., Kuwano M., Kung H. Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of alteration of the mRNA stability gene (ams+) of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):446–449. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.446-449.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan A. K., Miczak A., Taraseviciene L., Apirion D. Sequencing and expression of the rne gene of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):125–129. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. H., Emory S. A., Bricker A. L., Bouvet P., Belasco J. G. Structure and function of a bacterial mRNA stabilizer: analysis of the 5' untranslated region of ompA mRNA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4578–4586. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4578-4586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J. The 9S RNA precursor of Escherichia coli 5S RNA has three structural domains: implications for processing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7457–7476. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie-Martin F., Diaz-Torres M. R., Yancey S. D., Kushner S. R. Analysis of the altered mRNA stability (ams) gene from Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence, transcriptional analysis, and homology of its product to MRP3, a mitochondrial ribosomal protein from Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2843–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie-Martin F., Diaz-Torres M. R., Yancey S. D., Kushner S. R. Cloning of the altered mRNA stability (ams) gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5479–5486. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5479-5486.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Marlor C. W., Zaniewski R. RNase T is responsible for the end-turnover of tRNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6427–6430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., van der Vies S. M. Molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:321–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgellis D., Arvidson S., von Gabain A. Decay of ompA mRNA and processing of 9S RNA are immediately affected by shifts in growth rate, but in opposite manners. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5382–5390. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5382-5390.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghora B. K., Apirion D. Structural analysis and in vitro processing to p5 rRNA of a 9S RNA molecule isolated from an rne mutant of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Martin J., Neupert W. Protein folding in the cell: the role of molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp60. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:293–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Purification and properties of groE, a host protein involved in bacteriophage assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Hohn B., Engel A., Wurtz M., Smith P. R. Isolation and characterization of the host protein groE involved in bacteriophage lambda assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):359–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90501-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa N., Yura T., Ueguchi C., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Effects of mutations in heat-shock genes groES and groEL on protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3517–3521. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg U., von Gabain A., Melefors O. Cleavages in the 5' region of the ompA and bla mRNA control stability: studies with an E. coli mutant altering mRNA stability and a novel endoribonuclease. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2731–2741. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07460.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie G. A. Secondary structure of the mRNA for ribosomal protein S20. Implications for cleavage by ribonuclease E. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1054–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning-Krieg U. C., Scherer P. E., Schatz G. Sequential action of mitochondrial chaperones in protein import into the matrix. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Langer T., Boteva R., Schramel A., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U. Chaperonin-mediated protein folding at the surface of groEL through a 'molten globule'-like intermediate. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):36–42. doi: 10.1038/352036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melefors O., von Gabain A. Genetic studies of cleavage-initiated mRNA decay and processing of ribosomal 9S RNA show that the Escherichia coli ams and rne loci are the same. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):857–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melefors O., von Gabain A. Site-specific endonucleolytic cleavages and the regulation of stability of E. coli ompA mRNA. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Apirion D. RNase E, an RNA processing enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11154–11159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd E. A., Krisch H. M., Higgins C. F. RNase E, an endoribonuclease, has a general role in the chemical decay of Escherichia coli mRNA: evidence that rne and ams are the same genetic locus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2127–2135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):75–77. doi: 10.1038/312075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Lundberg U., von Gabain A. In vivo and in vitro identity of site specific cleavages in the 5' non-coding region of ompA and bla mRNA in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2269–2275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann J., Horwich A. L., Neupert W., Hartl F. U. Protein folding in mitochondria requires complex formation with hsp60 and ATP hydrolysis. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):125–130. doi: 10.1038/341125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy M. K., Apirion D. Purification and properties of ribonuclease E, an RNA-processing enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 28;747(3):200–208. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Little R., Bremer H. Control of RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli after a shift to higher temperature. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1425–1432. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1425-1432.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Fujita H., Itikawa H. Genetic suppression of a temperature-sensitive groES mutation by an altered subunit of RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1102–1106. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1102-1106.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada M., Itikawa H. Participation of Escherichia coli K-12 groE gene products in the synthesis of cellular DNA and RNA. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):694–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.694-696.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilstra-Ryalls J., Fayet O., Georgopoulos C. The universally conserved GroE (Hsp60) chaperonins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:301–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]