Abstract
Previous studies showed that administration of ascorbate to glutathione (GSH)-deficient newborn rats and guinea pigs prevented toxicity and mortality and led to increased tissue and mitochondrial GSH levels; ascorbate thus spares GSH. In the present work, we tried to answer the converse question: Does administration of GSH spare ascorbate? Because administered GSH is not well transported into most cells, we gave GSH monoethyl ester (which is readily transported and converted into GSH intracellularly) to guinea pigs fed an ascorbate-deficient diet. We found that treatment with GSH ester significantly delays appearance of the signs of scurvy and that this treatment spares ascorbate; thus, the decrease of tissue levels of ascorbate was delayed. The findings support the conclusions that (i) GSH is essential for the physiological function of ascorbate because it is required in vivo for reduction of dehydroascorbate and (ii) there is metabolic redundancy and overlap of the functions of these antioxidants. The sparing effect of GSH in scurvy may be mediated through an increase in the reduction of dehydroascorbate (which would otherwise be degraded) and to antioxidant effects of GSH that are also produced by ascorbate. Other studies indicate that GSH deficiency in adult mice stimulates ascorbate synthesis in liver. During this work we found that administration of GSH itself is highly toxic to ascorbate-deficient guinea pigs when given in divided i.p. doses totaling 3.75 mmol/kg daily.
Full text
PDF
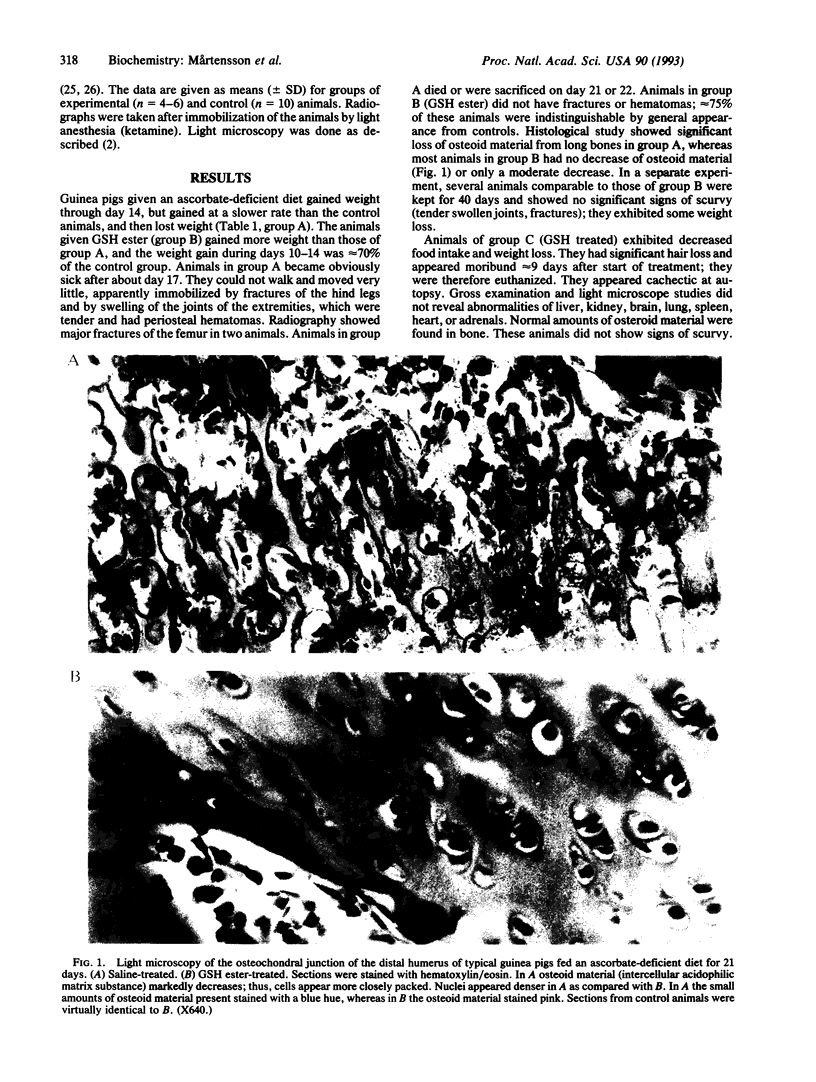
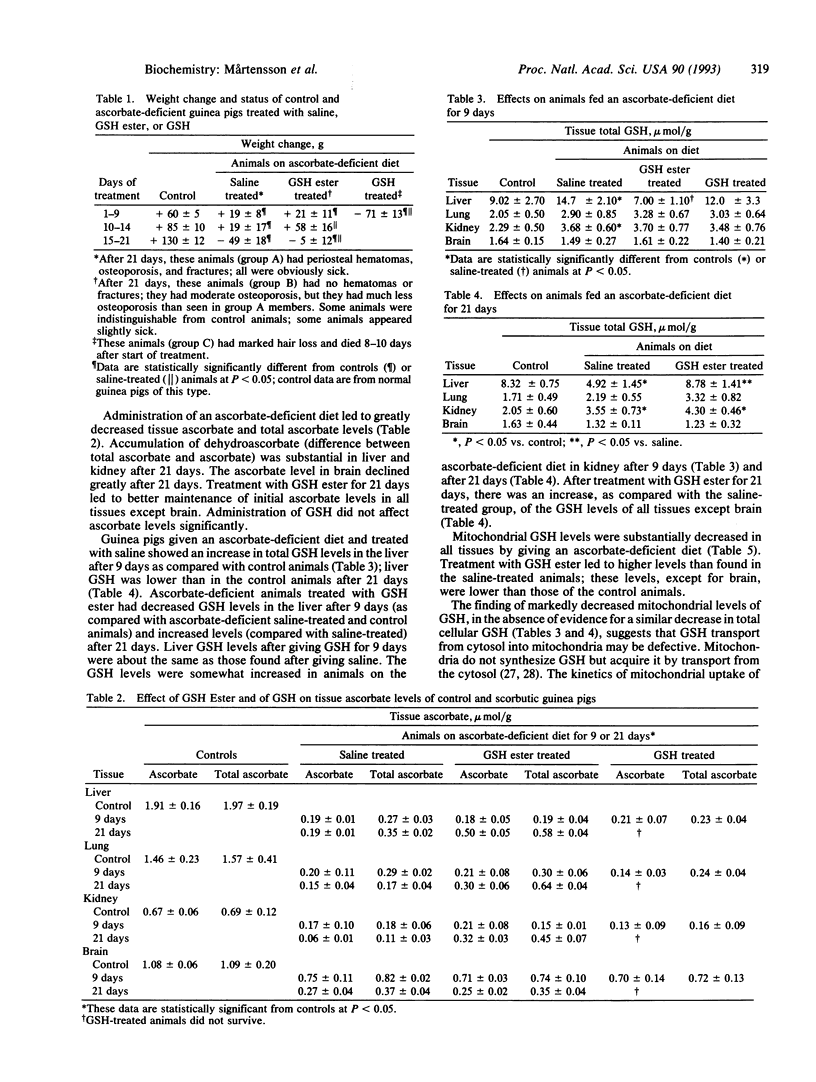


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. E., Meister A. Glutathione monoesters. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. E., Powrie F., Puri R. N., Meister A. Glutathione monoethyl ester: preparation, uptake by tissues, and conversion to glutathione. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jun;239(2):538–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90723-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin H. I., Medvedovsky C., Worgul B. V. Near-total glutathione depletion and age-specific cataracts induced by buthionine sulfoximine in mice. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):553–555. doi: 10.1126/science.3726547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell E. B., Griffith O. W. Glutathione monoethyl ester: high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis and direct preparation of the free base form. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Anderson M. E., Meister A. Inhibition of glutathione biosynthesis by prothionine sulfoximine (S-n-propyl homocysteine sulfoximine), a selective inhibitor of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1205–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W. Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 15;106(1):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Origin and turnover of mitochondrial glutathione. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4668–4672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Potent and specific inhibition of glutathione synthesis by buthionine sulfoximine (S-n-butyl homocysteine sulfoximine). J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7558–7560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain A., Mårtensson J., Mehta T., Krauss A. N., Auld P. A., Meister A. Ascorbic acid prevents oxidative stress in glutathione-deficient mice: effects on lung type 2 cell lamellar bodies, lung surfactant, and skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5093–5097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain A., Mårtensson J., Stole E., Auld P. A., Meister A. Glutathione deficiency leads to mitochondrial damage in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1913–1917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. C., Clark J. B. Preparation of synaptic and nonsynaptic mitochondria from mammalian brain. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:51–60. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mãrtensson J., Meister A., Mrtensson J. Glutathione deficiency decreases tissue ascorbate levels in newborn rats: ascorbate spares glutathione and protects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4656–4660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson J., Jain A., Frayer W., Meister A. Glutathione metabolism in the lung: inhibition of its synthesis leads to lamellar body and mitochondrial defects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5296–5300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson J., Jain A., Meister A. Glutathione is required for intestinal function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1715–1719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson J., Jain A., Stole E., Frayer W., Auld P. A., Meister A. Inhibition of glutathione synthesis in the newborn rat: a model for endogenously produced oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9360–9364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson J., Lai J. C., Meister A. High-affinity transport of glutathione is part of a multicomponent system essential for mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7185–7189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson J., Meister A. Glutathione deficiency increases hepatic ascorbic acid synthesis in adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11566–11568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson J., Meister A. Mitochondrial damage in muscle occurs after marked depletion of glutathione and is prevented by giving glutathione monoester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):471–475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson J., Steinherz R., Jain A., Meister A. Glutathione ester prevents buthionine sulfoximine-induced cataracts and lens epithelial cell damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8727–8731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard J., Cannon B. Overview--preparation and properties of mitochondria from different sources. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:3–28. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omaye S. T., Turnbull J. D., Sauberlich H. E. Selected methods for the determination of ascorbic acid in animal cells, tissues, and fluids. Methods Enzymol. 1979;62:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)62181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri R. N., Meister A. Transport of glutathione, as gamma-glutamylcysteinylglycyl ester, into liver and kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5258–5260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeev I. N., Arkhapchev Y. P., Spirichev V. B. Ascorbic acid effects on vitamin D hormone metabolism and binding in guinea pigs. J Nutr. 1990 Oct;120(10):1185–1190. doi: 10.1093/jn/120.10.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal R. K., Anderson M. E., Meister A. Glutathione, a first line of defense against cadmium toxicity. FASEB J. 1987 Sep;1(3):220–223. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.3.2887478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):502–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellner V. P., Anderson M. E., Puri R. N., Jensen G. L., Meister A. Radioprotection by glutathione ester: transport of glutathione ester into human lymphoid cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4732–4735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



