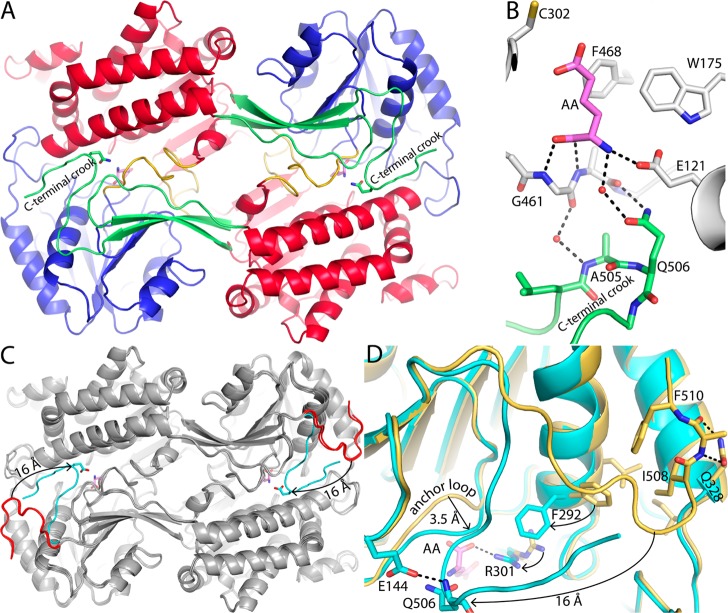
Figure 5.
Conformational variation of the C-terminus. (A) Dimer of ALDH7A1 complexed with AA (pink). The domains are colored as in Figure 2A, with the NAD+-binding domain colored red, the catalytic domain blue, and the oligomerization domain green. Gln506 is shown as sticks. (B) Close-up of the quaternary structural interactions that stabilize the aldehyde-binding site in the AA complex. One protomer of the dimer is colored white with bound AA colored pink. The C-terminus of the other protomer is colored green. (C) Superposition of the dimers of the ALDH7A1–AA complex (gray with a cyan C-terminus), apo ALDH7A1 in space group C2 (gray with a red C-terminus), and the ALDH7A1–NAD+ complex in space group C2 (also gray with a red C-terminus). The arrow indicates the 16 Å movement of the C-terminus from the open conformation (AA-free) to the closed conformation (AA-bound). (D) Close-up of a superposition of the AA complex (cyan) and the apoenzyme in space group C2 (gold). The arrows indicate movement of the active site from the open conformation (AA-free) to the closed conformation (AA-bound). AA is colored pink.