Abstract
Objective
Existing criteria for the classification of gout have suboptimal sensitivity and/or specificity, and were developed at a time when advanced imaging was not available. The current effort was undertaken to develop new classification criteria for gout.
Methods
An international group of investigators, supported by the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism, conducted a systematic review of the literature on advanced imaging of gout, a diagnostic study in which the presence of monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) crystals in synovial fluid or tophus was the gold standard, a ranking exercise of paper patient cases, and a multicriterion decision analysis exercise. These data formed the basis for developing the classification criteria, which were tested in an independent data set.
Results
The entry criterion for the new classification criteria requires the occurrence of at least 1 episode of peripheral joint or bursal swelling, pain, or tenderness. The presence of MSU crystals in a symptomatic joint/bursa (i.e., synovial fluid) or in a tophus is a sufficient criterion for classification of the subject as having gout, and does not require further scoring. The domains of the new classification criteria include clinical (pattern of joint/bursa involvement, characteristics and time course of symptomatic episodes), laboratory (serum urate, MSU‐negative synovial fluid aspirate), and imaging (double‐contour sign on ultrasound or urate on dual‐energy computed tomography, radiographic gout‐related erosion). The sensitivity and specificity of the criteria are high (92% and 89%, respectively).
Conclusion
The new classification criteria, developed using a data‐driven and decision analytic approach, have excellent performance characteristics and incorporate current state‐of‐the‐art evidence regarding gout.
This criteria set has been approved by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Board of Directors and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) Executive Committee. This signifies that the criteria set has been quantitatively validated using patient data, and it has undergone validation based on an independent data set. All ACR/EULAR‐approved criteria sets are expected to undergo intermittent updates.
The American College of Rheumatology is an independent, professional, medical and scientific society which does not guarantee, warrant, or endorse any commercial product or service.
Introduction
Gout, which is characterized by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) in synovial fluid and other tissues, is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, with a prevalence of 3.9% in the US 1, 0.9% in France 2, 3, 1.4 – 2.5% in the UK 4, 5, 6, 1.4% in Germany 5, and 3.2% (European ancestry)−6.1% (Maori ancestry) in New Zealand 7. Over the last decade, several new therapies for gout have been approved by regulatory agencies or are being tested 8. The conduct of trials that lead to drug approval, and of observational studies that provide insights into risk factors, genetic associations, and general epidemiology of gout, is critically dependent on appropriate identification of individuals with gout for inclusion in such studies. Classification criteria serve the purpose of enabling standardized assembly of a relatively homogeneous group of individuals with the disease of interest for enrollment into such studies 9.
There are several existing sets of classification criteria or diagnostic rules for gout 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, with the most widely used being the 1977 American Rheumatism Association (now the American College of Rheumatology [ACR]) preliminary criteria for the classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout 10. These preliminary criteria were intended for identifying the acute arthritis of gout and not necessarily for intercritical gout, the spectrum of comparator diseases was limited, and physician diagnosis was the gold standard. In a recent study in which the gold standard was MSU crystal status in synovial fluid or nodule aspirate among individuals with a broad range of diagnoses, the sensitivity of existing criteria sets 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 ranged from 57.6% to 100% (i.e., 100% with MSU crystal identification as sufficient for classification as gout), whereas the specificity ranged from 34.3% to 86.4%, with no single criteria set having both excellent sensitivity and excellent specificity 15, 16. Such findings highlight the need for classification criteria with improved performance characteristics, with higher specificity likely to be favored in order to ensure that individuals enrolled into trials for treatments with unclear efficacy and safety truly have gout.
Accurate classification of gout without crystal documentation for recruitment into studies is also needed, since the majority of cases of gout are managed in primary or acute care settings 17, 18, where synovial fluid aspiration and polarizing microscopy are not commonly performed. Additionally, the existing published criteria were developed at a time when advanced imaging modalities, such as ultrasonography or dual‐energy computed tomography (DECT), had not been studied; their utility for gout classification in the context of other clinical and laboratory parameters is not known.
To address these issues, an international collaborative working group to develop new classification criteria for gout was convened with the support of the ACR and the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) 19. The final results are reported here.
Methods
The major steps taken to develop the new classification criteria are outlined in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
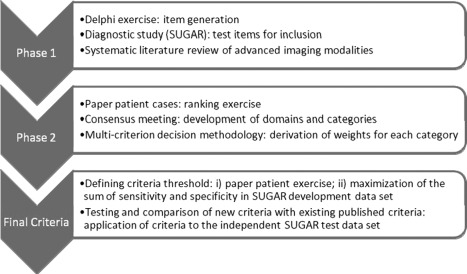
Flow chart of the study process. The major steps taken to develop the new American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism criteria for classification of gout are outlined. SUGAR = Study for Updated Gout Classification Criteria.
Phase 1
To identify factors to be considered for the content of classification criteria for gout, 3 studies were undertaken (Figure 1). First, clinicians with expertise in gout and patients with gout identified factors they believed to discriminate gout from other rheumatic diseases in a Delphi exercise 20. Second, we tested items from this Delphi exercise that were agreed to be potentially discriminatory for gout and items from existing classification criteria in a cross‐sectional diagnostic study (Study for Updated Gout Classification Criteria [SUGAR]) 21. Briefly, this study included 983 consecutive subjects (exceeding the recruitment target of 860) who had had joint swelling or a subcutaneous nodule within the previous 2 weeks, either of which was judged to be conceivably due to gout. These subjects were recruited from rheumatology clinics in 16 countries. All subjects were required to undergo aspiration of the symptomatic joint or nodule, with crystal examination performed by a certified observer 21, 22, and imaging (ultrasound, radiography). Those who were MSU crystal positive were designated as cases while those who were MSU crystal negative were designated as controls, irrespective of clinical diagnosis. Analyses in the SUGAR study were conducted among two‐thirds of the sample (derivation data set; n = 653); the other one‐third (n = 330) were analyzed as the validation data set for the final criteria. Third, we conducted a systematic literature review of advanced imaging modalities for classifying gout 23.
Phase 2
Rationale
It was recognized that the SUGAR study and the imaging review may have some limitations. The SUGAR study might have been prone to selection bias as MSU crystal positivity was required in order for a subject to be considered a case; this may have introduced bias toward larger joints, more severe disease, and/or tophaceous disease. In addition, subjects were recruited from rheumatology clinics, which may have contributed to spectrum bias since most patients with gout are seen in primary care settings. The systematic literature review of imaging was limited by the relative paucity of published data, and comparator diseases included were limited. Thus, Phase 2 was envisioned as a complementary phase that would incorporate the data derived in Phase 1 with clinical expertise to address a broader spectrum of clinical gout.
Approach to identifying domains and categories
In Phase 2, an international panel of expert rheumatologists and primary care physicians used a multicriterion decision analytic consensus methodology, informed by data generated in Phase 1, to determine the factors that best discriminated gout from other rheumatic diseases that could conceivably be considered in the differential diagnosis. Such an approach would lead to expert‐derived, data‐informed weighting of discriminating factors. The specific methods are described below.
Rheumatologists and general internists with an interest in gout submitted paper patient cases of patients for whom gout was in the differential diagnosis, using standardized data collection forms. A subset of 30 paper patient cases was selected to represent a broad spectrum of the probability of gout. Prior to the in‐person expert panel meeting, panel members were given the data from Phase 1 to review, and they were asked to rank‐order the 30 paper patient cases from lowest to highest probability of having gout.
At the in‐person expert panel meeting, held over 2 days (June 9–10, 2014 in Paris, France in advance of the EULAR Congress), 3 concepts were agreed upon a priori. First, the task was to develop criteria that would enable standardized assembly of a well‐defined, relatively homogeneous group of subjects representative of persons with gout, for entry into observational studies or clinical trials. Such criteria are not intended to capture all possible patients, but rather to capture the great majority of patients with shared key features of gout. Second, the classification was to apply to the patient's total disease experience, not to classify individual symptomatic episodes. Third, elements of the criteria could be accrued over time such that individuals could fulfill criteria at a later time point even if they did not at the initial assessment.
Review of the Phase 1 data and the paper patient case ranking exercise formed the basis for in‐depth discussion to identify key features that were pertinent to the probability of gout. Based on these key features, initial formulation of potential criteria was developed, with consideration of entry, sufficient, and exclusion criteria, and more precise definition of domains and their categories. Decisions regarding domains and their categories were supported, where possible, by Phase 1 data and/or any other available published evidence.
Approach to assigning relative weights to domains and categories
Once the Paris panel agreed upon preliminary domains and categories, the members undertook a discrete‐choice conjoint analysis exercise guided by an experienced facilitator (RPN) and aided by a rheumatologist with experience in the process (TN), similar to that used for other classification criteria (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis) 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29. Specifically, we used a computer software program, 1000Minds (www.1000minds.com), which utilizes decision science theory and computer adaptive technology to carry out a series of discrete forced‐choice experiments through pairwise ranking of alternatives that lead to quantified weights of each domain and each category within the domains 28, 30. Briefly, the expert panel was presented with a series of paired scenarios, each of which contained the same 2 domains, but with different combination of the domains’ categories grouped together in each scenario. The panel was instructed to assume that all other parameters were equivalent between the 2 patients represented by the scenarios. The distribution of votes (percent who voted for “A,” “B,” or “equal probability”) was presented for each pair of scenarios after each vote. Discussion occurred after each vote, with re‐voting as necessary. Consensus was considered to have been achieved when all participants either indicated complete agreement as to which scenario represented a higher probability of gout, or indicated that they could accept the majority opinion.
Relative weights were derived with the decision analytic software, based on the voting results of the discrete‐choice scenarios and refined by each successive result. Upon completion of the voting exercise, the relative weights for each category and domain, and the face validity of the resulting rank order of 10 paper patient cases, were reviewed.
After the in‐person meeting, minor scoring simplifications were incorporated and pretested in the SUGAR derivation data set (i.e., the original two‐thirds sample analyzed in Phase 1). A cutoff score that maximized the sum of sensitivity and specificity was determined, to examine misclassification.
Approach to developing final criteria scoring
The raw weights from the scoring system were simplified into whole numbers, with performance characteristics assessed for each simplification.
Approach to defining criteria threshold for classifying gout
The original 30 paper patient cases (except for 3 with demonstrated MSU crystals), in addition to 20 subjects from the SUGAR study analyzed in Phase 1 who had unique scores close to the cutoff score derived as described above, were used for a threshold identification exercise. For these 20 subjects, if synovial fluid microscopy had failed to show MSU crystals, this information was provided. Otherwise, the results of synovial fluid examination were recorded as “not done.” This information was not made known to the expert panel. These cases were arranged according to their score in descending order. In an online exercise, the expert panel indicated whether they would classify the patient as having gout with sufficient confidence to feel comfortable enrolling that patient into a Phase 3 trial of a new urate‐lowering agent.
Testing of the new gout classification criteria and comparison with existing published criteria
The final criteria set was evaluated in the SUGAR validation data set (i.e., the one‐third of the data set that had not been used for any analyses to date [n = 330]); the purpose of this was to enable validation of the newly developed criteria in an independent data set. A secondary analysis was conducted to evaluate how the criteria would perform if only clinical parameters were available (i.e., without MSU determination or imaging). The performance characteristics of the new criteria were compared with those of existing published criteria using logistic regression.
Results
The expert panel (n = 20) comprised 19 physicians with a clinical and/or research interest in gout (17 clinical rheumatologists and 2 primary care physicians) and an epidemiologist/biostatistician; 9 members of the panel were from the US, 8 from Europe, 2 from New Zealand, and 1 from Mexico. One hundred thirty‐three paper cases were submitted by the expert panel and 79 clinical rheumatologists and general internists.
Based on review of the Phase 1 data and the ranking exercise with the 30 cases representing low to high probability of gout, initial key factors that were identified as being important for classifying gout were presence of MSU crystals, pattern of joint involvement, intensity of symptomatic episodes, time to maximal pain and to resolution, episodic nature of symptoms, presence of clinical tophus, level of serum urate, imaging features, response to treatment, family history, and risk factors or associated comorbidities. The last 3 factors were not considered further as they are not features of gout itself despite their association with gout, and inclusion of risk factors or comorbidities in the definition of gout would preclude future studies evaluating their association with gout.
Entry, sufficient, and exclusion criteria
Before embarking upon defining domains and domain categories (the classification criteria), we defined entry, sufficient, and exclusion criteria. The entry criteria were intended to be used to identify the relevant patient population to whom the classification criteria would be applied. Sufficient criteria were intended to define features such as a gold standard that alone could classify gout without further need to apply the classification criteria scoring system. Exclusion criteria were intended to define individuals in whom gout could be ruled out (among those who met entry criteria) and to whom the classification criteria should not be further applied. The expert panel agreed that these classification criteria should be applicable only to people with symptomatic disease because the prognosis of asymptomatic disease is presently not well delineated in the literature, and to enable categorization based on features of symptomatic episodes. The entry criterion was defined as the occurrence of at least 1 episode of swelling, pain, or tenderness in a peripheral joint or bursa. The sufficient criterion was defined as the presence of MSU crystals in a symptomatic joint or bursa (i.e., in synovial fluid) or tophus as observed by a trained examiner. The panel agreed that there would be no exclusion criteria because gout can often coexist with other diseases and because synovial fluid microscopy can sometimes fail to disclose MSU crystals in patients with gout for technical, sampling, or treatment reasons.
Domains and categories
Based on the key features identified initially, Phase 1 data, and available published literature, and with a defined population to whom the criteria would apply, the expert panel further developed the pertinent domains and their respective categories in an iterative process. The expert panel aimed to define relevant clinical and imaging parameters to be as specific as possible for gout.
The domains included clinical parameters (numbers 1 – 4), laboratory parameters (numbers 5 and 6), and imaging parameters (numbers 7 and 8). The specific domains and their respective definitions are summarized in Table 1. The domains were designed to be scored based on the totality of the subjects’ symptomatic disease experience. All of the categories within domains are hierarchical and mutually exclusive, such that if both a higher and a lower category have been fulfilled at different points in time, the higher one should be scored; the highest categories are listed last within each domain.
Table 1.
Definitions and considerations for each domaina
| Domainb | Definitions and special considerations |
|---|---|
| 1. Pattern of joint/bursa involvement during symptomatic episode(s) ever Categories are defined as per the description of the distribution of joints involved |
Distribution of joints: involvement (ever) of
|
|
2. Characteristics of symptomatic episode(s) ever Categories are defined as
|
Characteristics to consider: presence (ever) of
|
|
3. Time course of symptomatic episode(s) ever Categories are defined as
|
“Typical symptomatic episode”: presence (ever) of >2 of the following, irrespective of antiinflammatory treatment
|
|
4. Clinical evidence of tophus Categories are defined as
|
Appearance: draining or chalk‐like subcutaneous nodule under transparent skin, often with overlying vascularity (Figure 2) Location: classic locations—joints, ears, olecranon bursae, finger pads, tendons (e.g., Achilles) |
|
5. Serum urate level, off‐treatment Categories are defined as
|
Which serum urate measurement to use: highest reading on record, off urate‐lowering therapy Special considerations: Ideally, the serum urate level should be scored if tested at a time when the patient was not receiving urate‐lowering therapy and it was >4 weeks from the start of an episode; if practicable, retest under those conditions. If serum urate level is ≥10 mg/dl, no need to retest. |
|
6. Synovial fluid analysis Categories are defined as
|
Location: symptomatic (ever) joint or bursa Special considerations: Assessment should be performed by a trained observer. Note: MSU positive is a sufficient criterion. |
|
7. Imaging evidence of urate deposition Categories are defined as
|
Modality: ultrasound or DECT Appearance: double‐contour sign on ultrasound (Figure 3A)c or urate deposition on DECT (Figure 3B)d Location: symptomatic (ever) joint or bursa |
|
8. Imaging evidence of gout‐related joint damage Categories are defined as
|
Modality: radiography Appearance of gout‐related erosion: cortical break with sclerotic margin and overhanging edge; excludes gull wing appearance (Figure 3C) Location: radiograph of hands and/or feet; excludes distal interphalangeal joints |
Symptomatic (ever) refers to pain and/or swelling.
Categories within each domain are hierarchical; if a subject fulfills more than 1 category, the highest category should be selected.
A false‐positive double‐contour sign (artifact) may appear at the cartilage surface, but should disappear with a change in the insonation angle of the probe 31, 32.
Images should be acquired using a dual‐energy computed tomography (DECT) scanner, with data acquired at 80 kV and 140 kV and analyzed using gout‐specific software with a 2‐material decomposition algorithm that color‐codes urate 33. A positive scan result is defined as the presence of color‐coded urate at articular or periarticular sites. Nailbed, submillimeter, skin, motion, beam hardening, and vascular artifacts should not be interpreted as DECT evidence of urate deposition 34.
Symptomatic episodes were defined as those in which there was swelling, pain, or tenderness in a peripheral joint or bursa. For the pattern of joint involvement, it was agreed that first metatarsophalangeal joint, ankle, or midfoot involvement as part of a polyarticular presentation, though possible in gout, was not specific enough for gout since that pattern could be seen commonly in other disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. The time course of symptomatic episodes was to be considered irrespective of antiinflammatory treatment. For clinical tophus, a precise definition in terms of appearance and location was developed to assist in differentiation from other subcutaneous nodules that may be confused with tophi. Examples of clinically evident tophi are provided in Figure 2. Serum urate was considered a mandatory element of the classification criteria scoring system (i.e., the score cannot be computed without a serum urate value). For the synovial fluid domain, the fluid must be aspirated from a symptomatic (ever) joint or bursa, and assessed by a trained observer. If the synovial fluid aspirate was MSU positive, the individual would have been classified as having gout under the sufficient criterion without evaluating the rest of the classification criteria.
Figure 2.

Examples of tophus. The tophus is defined as a draining or chalk‐like subcutaneous nodule under transparent skin, often with overlying vascularity. Typical locations are the ear (A), the elbow (olecranon bursa) (B), and the finger pulps (C and D). Note the overlying vascularity in D.
For imaging evidence of urate deposition, the imaging modalities with sufficient published data and investigator experience to support their utility in identifying urate deposition accurately were ultrasound and DECT. Magnetic resonance imaging and conventional CT did not have sufficient published data or investigator experience to support their consideration. For ultrasound evidence of urate deposition, the required finding is the double‐contour sign (DCS), defined as hyperechoic irregular enhancement over the surface of the hyaline cartilage that is independent of the insonation angle of the ultrasound beam (note: false‐positive DCS [artifact] may appear at the cartilage surface but should disappear with a change in the insonation angle of the probe) 31, 32. Examples of gout‐related DCS are provided in Figure 3. For DECT, urate deposition is defined as the presence of color‐coded urate at articular or periarticular sites (Figure 3). Images should be acquired using a DECT scanner, with data acquired at 80 kV and 140 kV and analyzed using gout‐specific software with a 2‐material decomposition algorithm that color‐codes urate 33. A positive scan result is defined as the presence of color‐coded urate at articular or periarticular sites. Nailbed, submillimeter size, skin, motion, beam hardening, and vascular artifacts should not be interpreted as DECT evidence of urate deposition 34. The scoring of this imaging domain is applicable only to a symptomatic (ever) joint or bursa (i.e., swelling, pain, or tenderness), and is scored as present on either modality, or absent/not done (i.e., neither modality was performed). That is, if either imaging modality demonstrates the required finding, then urate deposition is considered to be present.
Figure 3.
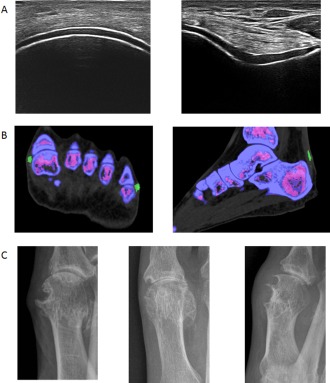
Examples of imaging features included in the classification criteria. A, Double‐contour sign seen on ultrasonography. Left panel shows a longitudinal ultrasound image of the femoral articular cartilage; right panel shows a transverse ultrasound image of the femoral articular cartilage. Both images show hyperechoic enhancement over the surface of the hyaline cartilage (images kindly provided by Dr. Esperanza Naredo, Hospital Universitario Gregorio Marañon, Madrid, Spain). B, Urate deposition seen on dual‐energy computed tomography. Left panel shows urate deposition at the first and fifth metatarsophalangeal joints; right panel shows urate deposition within the Achilles tendon. C, Erosion, defined as a cortical break with sclerotic margin and overhanging edge, seen on conventional radiography of the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
Finally, imaging evidence of gout‐related joint damage is to be scored on the basis of conventional radiography of the hands and/or feet demonstrating at least 1 gout‐related erosion, which is defined as a cortical break with sclerotic margin and overhanging edge (Figure 3). The distal interphalangeal joints and gull wing appearance should be excluded from this evaluation since they can occur in osteoarthritis.
Assigning relative weights to domains and categories
Once the domains and categories were defined, the expert panel undertook a series of discrete‐choice experiments. This work resulted in weights being assigned to each category and domain, such that the highest category of each domain summed to a total of 100%. Any necessary revisions to the categories were made with subsequent repetition of the discrete‐choice experiments after any such changes.
A sample of 10 paper patient cases (from among the original 30 paper cases) was scored and rank‐ordered with this preliminary scoring system. The cases were accurately ranked with reference to the expert panel's premeeting rankings, lending face validity to this preliminary scoring system. The scoring was also repeated without the imaging domains, which resulted in little change in the rank‐ordering. Correlation between premeeting mean ranking and the initial scoring system ranking was high (r2 = 0.71).
Defining criteria threshold for classifying gout
Using a cutoff score that maximized the sum of sensitivity and specificity from the SUGAR data, the percentage of false‐negatives and false‐positives was 13.9% and 10.5%, respectively. Next, the expert panel performed a threshold identification exercise designed to assess the members’ willingness to enroll 47 paper cases, based on having sufficient confidence that the individual has gout, into a Phase 3 randomized clinical trial of a new urate‐lowering agent with unclear efficacy and safety. The score at which the majority considered an individual as having gout or not fell at the same threshold as that identified as the cutoff score that maximized the sum of sensitivity and specificity.
Final criteria scoring
With face validity of the initial scoring system confirmed and a threshold identified, the raw relative weights of the domain categories and the threshold score were rescaled and rounded into whole numbers to make the scoring system as simple as possible, while retaining the relative weighting produced by the expert panel. The maximum possible score in the final criteria is 23. A threshold score of ≥8 classifies an individual as having gout.
A unique aspect of the new classification criteria is that there are 2 categories that elicit negative scores. Specifically, if the synovial fluid is MSU negative, 2 points are subtracted from the total score. Similarly, if the serum urate level is <4 mg/dl (<0.24 mmoles/liter), 4 points are subtracted from the total score. This approach was taken to emphasize that these findings reduce the probability of gout. The lowest category in each domain has a score of 0 and is therefore not explicitly depicted in the final criteria table; however, for serum urate level, the category that receives a score of 0 is 4−<6 mg/dl (0.24−<0.36 mmoles/liter). If imaging is not performed, those categories are also scored as 0. The final criteria are presented in Table 2. A web‐based calculator can be accessed at http://goutclassificationcalculator.auckland.ac.nz, as well as through the ACR and EULAR web sites.
Table 2.
The ACR/EULAR gout classification criteriaa
| Categories | Score | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1: Entry criterion (only apply criteria below to those meeting this entry criterion) | At least 1 episode of swelling, pain, or tenderness in a peripheral joint or bursa | |
| Step 2: Sufficient criterion (if met, can classify as gout without applying criteria below) | Presence of MSU crystals in a symptomatic joint or bursa (i.e., in synovial fluid) or tophus | |
| Step 3: Criteria (to be used if sufficient criterion not met) | ||
| Clinical | ||
| Pattern of joint/bursa involvement during symptomatic episode(s) everb | Ankle or midfoot (as part of monoarticular or oligoarticular episode without involvement of the first metatarsophalangeal joint | 1 |
| Involvement of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (as part of monoarticular or oligoarticular episode) | 2 | |
|
Characteristics of symptomatic episode(s) ever • Erythema overlying affected joint (patient‐ reported or physician‐observed) • Can't bear touch or pressure to affected joint • Great difficulty with walking or inability to use affected joint |
One characteristic | 1 |
| Two characteristics | 2 | |
| Three characteristics | 3 | |
|
Time course of episode(s) ever Presence (ever) of ≥2, irrespective of antiinflammatory treatment: |
One typical episode |
1 2 |
|
• Time to maximal pain <24 hours • Resolution of symptoms in ≤14 days • Complete resolution (to baseline level) between symptomatic episodes |
Recurrent typical episodes | |
|
Clinical evidence of tophus (Figure 2) Draining or chalk‐like subcutaneous nodule under transparent skin, often with overlying vascularity, located in typical locations: joints, ears, olecranon bursae, finger pads, tendons (e.g., Achilles) |
Present | 4 |
| Laboratory | ||
| Serum urate: Measured by uricase method. Ideally should be scored at a time when the patient was not receiving urate‐lowering treatment and it was >4 weeks from the start of an episode (i.e., during intercritical period); if practicable, retest under those conditions. The highest value irrespective of timing should be scored. |
<4 mg/dl (<0.24 mmoles/liter)c
6–<8 mg/dl (0.36–<0.48 mmoles/liter) 8–<10 mg/dl (0.48–<0.60 mmoles/liter) ≥10 mg/dl (≥0.60 mmoles/liter) |
−4234 |
| Synovial fluid analysis of a symptomatic (ever) joint or bursa (should be assessed by a trained observer)d | MSU negative | −2 |
| Imaging (Figure 3)e | ||
| Imaging evidence of urate deposition in symptomatic (ever) joint or bursa: ultrasound evidence of double‐contour signf or DECT demonstrating urate depositiong | Present (either modality) | 4 |
| Imaging evidence of gout‐related joint damage: conventional radiography of the hands and/or feet demonstrates at least 1 erosionh | Present | 4 |
A web‐based calculator can be accessed at: http://goutclassificationcalculator.auckland.ac.nz, and through the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) web sites.
Symptomatic episodes are periods of symptoms that include any swelling, pain, and/or tenderness in a peripheral joint or bursa.
If serum urate level is <4 mg/dl (<0.24 mmoles/liter), subtract 4 points; if serum urate level is ≥4−<6 mg/dl (≥0.24−<0.36 mmoles/liter), score this item as 0.
If polarizing microscopy of synovial fluid from a symptomatic (ever) joint or bursa by a trained examiner fails to show monosodium urate monohydrate (MSU) crystals, subtract 2 points. If synovial fluid was not assessed, score this item as 0.
If imaging is not available, score these items as 0.
Hyperechoic irregular enhancement over the surface of the hyaline cartilage that is independent of the insonation angle of the ultrasound beam (note: false‐positive double‐contour sign [artifact] may appear at the cartilage surface but should disappear with a change in the insonation angle of the probe) (31,32).
Presence of color‐coded urate at articular or periarticular sites. Images should be acquired using a dual‐energy computed tomography (DECT) scanner, with data acquired at 80 kV and 140 kV and analyzed using gout‐specific software with a 2‐material decomposition algorithm that color‐codes urate (33). A positive scan is defined as the presence of color‐coded urate at articular or periarticular sites. Nailbed, submillimeter, skin, motion, beam hardening, and vascular artifacts should not be interpreted as DECT evidence of urate deposition (34).
Erosion is defined as a cortical break with sclerotic margin and overhanging edge, excluding distal interphalangeal joints and gull wing appearance.
The original version of this table contained a typographical error. The online version of the table has been corrected.
Results of testing of the new gout classification criteria and comparison with existing published criteria
In the SUGAR validation data set (n = 330), the sensitivity of the new classification criteria was 0.92, and specificity was 0.89 (Table 3). The performance of the criteria was also tested using only clinical parameters, i.e., without MSU results, scored as 0 (unknown/not done) and without imaging (i.e., radiographic, ultrasound, or DECT imaging) results, scored as 0; this latter scoring was in keeping with similar weighting being given to imaging studies that were negative versus not being performed in the discrete‐choice experiments. In this setting, the sensitivity and specificity were 0.85 and 0.78.
Table 3.
Performance of the gout classification criteria in the Study for Updated Gout Classification Criteria validation data set, in comparison with existing published criteria
| Criteria set (ref.) | Area under the curvea | Sensitivity at published threshold | Specificity at published threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACR/EULAR criteria | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.89 |
| ACR/EULAR criteria (clinical‐only)b | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.78 |
| ACR 1977 criteria (full) 9 | 0.83 | 1.00‡ | 0.51c |
| ACR 1977 (survey) 9 | 0.83 | 0.84‡ | 0.62c |
| Rome 12 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.78c |
| Rome (clinical) 12 | NA | 0.77‡ | 0.78c |
| New York 13 | 0.83 | 1.00‡ | 0.78c |
| New York (clinical) 13 | NA | 0.79‡ | 0.78c |
| Mexico 11 | 0.84 | 1.00‡ | 0.44c |
| Mexico (clinical) 11 | NA | 0.95 | 0.44c |
| Netherlands 10, d | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.59c |
Based on the sum of the number of items present, or the total score in the case of weighted criteria (American College of Rheumatology [ACR]/European League Against Rheumatism [EULAR] criteria and Netherlands criteria). NA = not applicable.
Without synovial fluid microscopy or imaging.
P < 0.05 versus the ACR/EULAR criteria.
The Netherlands criteria set was intended as a diagnostic aid, and has 2 possible cutoffs (see Supplementary Table 1, on the Arthritis & Rheumatology web site at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.39254/abstract); we used the higher cutoff for these analyses because such a score is deemed to suggest gout.
When compared with existing published criteria (using their respective published thresholds), the new classification criteria performed well. For some existing criteria sets, presence of MSU crystals alone is sufficient to fulfill criteria; they are therefore 100% sensitive by definition. The new gout classification criteria also have MSU positivity as a sufficient criterion for classification, but the criteria set was not assessed in that regard, to avoid circularity. When the new classification criteria set was compared in its complete form (i.e., incorporating imaging and MSU data) with other published “full” criteria, some existing criteria had higher sensitivity, but all had lower specificity (Table 3). Additionally, for the clinical‐parameters‐only version of the new criteria, the sensitivity was better than that of all but 1 of the other clinical‐only criteria sets, and the specificity was similar or better. The new gout classification criteria therefore performed well in both the “full” form and the “clinical‐only” form.
Discussion
The new ACR/EULAR gout classification criteria represent an international collaborative effort that incorporates the latest published evidence on imaging modalities, a data‐driven approach with MSU identification as a gold standard to reference key features, and a decision analytic approach to inform the weighting of the scoring system. This classification criteria set will enable a standardized approach to identifying a relatively homogeneous group of individuals who have the clinical entity of gout for enrollment into studies. The criteria permit characterization of an individual as having gout regardless of whether he or she is currently experiencing an acute symptomatic episode and regardless of any comorbidities. The new classification criteria have superior performance characteristics, with high sensitivity and improved specificity compared with previously published criteria. Arguably, specificity (leading to high positive predictive value) is of critical importance in most clinical studies since investigators need to have confidence that individuals who are enrolled in a study truly have the condition of interest.
Gout is unlike other rheumatic diseases in that a gold standard assessment is available, i.e., MSU crystal positivity. While this gold standard has high specificity, its feasibility and sensitivity may be inadequate, because of difficulty with aspiration of joints (particularly small ones) and/or examination of the sample under polarizing microscopy. Thus, although MSU crystal results are extremely helpful when positive, they are not a feasible universal standard, particularly because many potential study subjects are likely to be recruited from nonrheumatology settings. We aimed to develop a new set of criteria that could be flexible enough to enable accurate classification of gout regardless of MSU status; a clinical‐only version can be considered for use in settings in which synovial fluid or tophus aspiration is not feasible. Nonetheless, in recognition of its gold standard status, the expert panel set the presence of MSU crystal positivity in a symptomatic joint or bursa as sufficient for classifying an individual as having gout. It should be recognized that classification criteria are not intended for use in making a diagnosis in a clinical setting 35. Thus, in clinical practice, joint or tophus aspiration remains an essential component of establishing a diagnosis of gout.
As with most diseases, there is a gradient of probability of truly having the disease based on signs and symptoms. The threshold chosen for this classification criteria set yielded the best combination of sensitivity and specificity. While for certain purposes a higher sensitivity (lower score) may be preferable (e.g., general population survey to determine the public health burden of gout for resource planning), a higher specificity (higher score) may be desirable for others (e.g., genetic association studies in which accurate phenotyping is critical). Furthermore, classification criteria are not intended to characterize the severity of disease, but only its presence. Additionally, classification criteria should be applied only to the intended population—those who meet the entry criteria. Performance characteristics of any classification criteria set will necessarily be altered if the criteria are applied to those other than the intended population.
A limitation of our current effort is that there is still a relative paucity of data and of clinical experience to fully test advanced imaging data empirically. As more studies are published, there may be additional imaging signs and/or modalities found to have sufficient specificity for gout that could be incorporated into future criteria. We also realized that some investigators may not have access to imaging and therefore aimed to develop criteria that would still perform well in the absence of imaging data. In the discrete‐choice experiments, the lack of imaging data was weighted the same as for studies performed with negative results, supporting the validity of using the scoring system in the absence of imaging data. We did not address asymptomatic hyperuricemia, since the purpose of classification criteria is to identify individuals with a clinical entity for clinical studies. There is certainly an interest in studying asymptomatic hyperuricemia, but this was beyond the scope of the current activity; the expert panel agreed that its charge was to classify individuals with symptomatic disease as evidence of a clinical condition. The present criteria set represents an attempt to optimize both sensitivity and specificity for enrollment into trials and prospective epidemiologic studies. Further testing of the criteria in additional samples, particularly in settings from which individuals with gout are likely to be recruited (e.g., primary care), and other study types, is warranted.
This study provides a number of insights relating to the likelihood of gout. First, the clinical picture of gout as an episodic disease with stereotypical features and a predilection for lower‐extremity joints, particularly the first metatarsophalangeal joint, was captured in the SUGAR study, despite concerns that the study design might lead to selection bias. Second, there were certain conditions that strongly reduced the likelihood of gout: synovial fluid from a symptomatic joint or bursa that was negative for MSU crystals, and a serum urate level of <4 mg/dl (0.24 mmoles/liter). While such findings would not necessarily rule out gout, they were weighted in the discrete‐choice experiments such that they lower the probability of gout. Third, both the SUGAR subjects and the paper patient cases were derived from a large international pool, supporting generalizability of these criteria. Finally, advanced imaging modalities have been incorporated into classification criteria for gout for the first time.
In summary, the 2015 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for gout represent an advance over previous criteria, with improved performance characteristics and incorporation of newer imaging modalities. These criteria may be considered as inclusion criteria for future studies of clinical gout.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors were involved in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and all authors approved the final version to be published. Dr. Neogi had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Study conception and design. Neogi, Jansen, Dalbeth, Fransen, Schumacher, Taylor.
Acquisition of data. Neogi, Jansen, Dalbeth, Fransen, Schumacher, Berendsen, Brown, Choi, Edwards, Janssen, Lioté, Naden, Nuki, Ogdie, Perez‐Ruiz, Saag, Singh, Sundy, Tausche, Vaques‐Mellado, Yarows, Taylor.
Analysis and interpretation of data. Neogi, Jansen, Dalbeth, Fransen, Schumacher, Berendsen, Brown, Choi, Edwards, Janssen, Lioté, Naden, Nuki, Ogdie, Perez‐Ruiz, Saag, Singh, Sundy, Tausche, Vaques‐Mellado, Yarows, Taylor.
Supporting information
Supporting Information
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the following investigators for contributing additional paper patient cases: Drs. Everardo Alvarez Hernandez, Ruben Burgos, Geraldo Castelar, Marco Cimmino, Tony Dowell, Angelo Gaffo, Rebecca Grainger, Leslie Harrold, Phillip Helliwell, Changtsai Lin, Worawit Louthrenoo, Claudia Schainberg, Naomi Schlesinger, Carlos Scire, Ole Slot, Lisa Stamp, Robert Terkeltaub, Harald Vonkeman, Zeng Xuejun. We would like to thank Dr. Thomas Bardin for participating in ranking of the paper cases. We would like to acknowledge and thank Dr. Esperanza Naredo for her advice regarding standardization of the ultrasound definition of double‐contour sign. We are also grateful to the following additional investigators who collected data for the SUGAR study: Drs. Lorenzo Cavagna, Jiunn‐Horng Chen, Yi‐Hsing Chen, Yin‐Yi Chou, Hang‐Korng Ea, Maxim Eliseev, Martijn Gerritsen, Matthijs Janssen, Juris Lazovskis, Geraldine McCarthy, Francisca Sivera, Ana Beatriz Vargas‐Santos, Till Uhlig, Douglas White, and all of the authors of the SUGAR study (full list in ref. 21). We would like to acknowledge and thank Ian Sayer (Application Specialist, Information Services, Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand) for his work on developing the gout classification calculator web page.
This article is published simultaneously in the October 2015 issue of Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
REFERENCES
- 1. Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2008. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:3136–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Richette P, Clerson P, Bouee S, Chales G, Doherty M, Flipo RM, et al. Identification of patients with gout: elaboration of a questionnaire for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis 2014. E‐pub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bardin T, Bouee S, Clerson P, Chales G, Doherty M, Flipo RM, et al. Prevalence of gout in the adult population of France in 2013 [abstract]. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73 Suppl 2:787–8. 24285489 [Google Scholar]
- 4. Annemans L, Spaepen E, Gaskin M, Bonnemaire M, Malier V, Gilbert T, et al. Gout in the UK and Germany: prevalence, comorbidities and management in general practice 2000‐2005. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:960–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kuo CF, Grainge MJ, Mallen C, Zhang W, Doherty M. Rising burden of gout in the UK but continuing suboptimal management: a nationwide population study. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:661–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Mikuls TR, Farrar JT, Bilker WB, Fernandes S, Schumacher HR Jr, Saag KG. Gout epidemiology: results from the UK General Practice Research Database, 1990‐1999. Ann Rheum Dis 2005;64:267–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Winnard D, Wright C, Jackson G, Gow P, Kerr A, McLachlan A, et al. Gout, diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the Aotearoa New Zealand adult population: co‐prevalence and implications for clinical practice. N Z Med J 2013;126:53–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Neogi T. Gout. N Engl J Med 2011;364:443–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Johnson SR, Goek ON, Singh‐Grewal D, Vlad SC, Feldman BM, Felton DT, et al. Classification criteria in rheumatic diseases: a review of methodologic properties. Arthritis Rheum 2007;57:1119–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Wallace SL, Robinson H, Masi AT, Decker JL, McCarty DJ, Yu TF. Preliminary criteria for the classification of the acute arthritis of primary gout. Arthritis Rheum 1977;20:895–900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Janssens HJ, Fransen J, van de Lisdonk EH, van Riel PL, van Weel C, Janssen M. A diagnostic rule for acute gouty arthritis in primary care without joint fluid analysis. Arch Intern Med 2010;170:1120–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Pelaez‐Ballestas I, Hernandez Cuevas C, Burgos‐Vargas R, Hernandez Roque L, Teran L, Espinoza J, et al. Diagnosis of chronic gout: evaluating the American College of Rheumatology proposal, European League Against Rheumatism recommendations, and clinical judgment. J Rheumatol 2010;37:1743–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Kellgren JH, Jeffrey MR, Ball J. The epidemiology of chronic rheumatism. Vol. I Oxford: Blackwell Scientific; 1963. p. 326–7. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Decker JL. Report from the subcommittee on diagnostic criteria for gout. In: Bennett PH, Wood PH, editors. Proceedings from the Third International Symposium; 1966 June 5‐10; New York, New York. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation; 1968:385–7.
- 15. Taylor WJ, Fransen J, Dalbeth N, Neogi T, Schumacher HR, Brown M, et al. Performance of classification criteria for gout in early and established disease. Ann Rheum Dis 2014. E‐pub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Malik A, Schumacher HR, Dinnella JE, Clayburne GM. Clinical diagnostic criteria for gout: comparison with the gold standard of synovial fluid crystal analysis. J Clin Rheumatol 2009;15:22–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Harrold LR, Mazor KM, Negron A, Ogarek J, Firneno C, Yood RA. Primary care providers’ knowledge, beliefs and treatment practices for gout: results of a physician questionnaire. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013;52:1623–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Pal B, Foxall M, Dysart T, Carey F, Whittaker M. How is gout managed in primary care? A review of current practice and proposed guidelines. Clin Rheumatol 2000;19:21–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Dalbeth N, Fransen J, Jansen TL, Neogi T, Schumacher HR, Taylor WJ. New classification criteria for gout: a framework for progress. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013;52:1748–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Prowse RL, Dalbeth N, Kavanaugh A, Adebajo AO, Gaffo AL, Terkeltaub R, et al. A Delphi exercise to identify characteristic features of gout—opinions from patients and physicians, the first stage in developing new classification criteria [published erratum appears in J Rheumatol 2013;40:1634]. J Rheumatol 2013;40:498–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Taylor W, Fransen J, Jansen TL, Dalbeth N, Schumacher HR, Brown M, et al. Study for Updated Gout Classification Criteria (SUGAR): identification of features to classify gout. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2015. E‐pub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Berendsen D, Jansen TL, Taylor W, Neogi T, Fransen J, Pascual E, et al. A critical appraisal of the competence of crystal identification by rheumatologists [abstract]. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72 Suppl 3:A981–2. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Ogdie A, Taylor WJ, Weatherall M, Fransen J, Jansen TL, Neogi T, et al. Imaging modalities for the classification of gout: systematic literature review and meta‐analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 2014. E‐pub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO III, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:2569–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO III, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1580–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A, et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 2013;65:2737–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A, et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:1747–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Neogi T, Aletaha D, Silman AJ, Naden RL, Felson DT, Aggarwal R, et al. The 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: phase 2 methodological report. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:2582–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Johnson SR, Naden RP, Fransen J, van den Hoogen F, Pope JE, Baron M, et al. Multicriteria decision analysis methods with 1000Minds for developing systemic sclerosis classification criteria. J Clin Epidemiol 2014;67:706–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Hansen P, Ombler F. A new method for scoring additive multi‐attribute value models using pairwise rankings of alternatives. J Multi‐Crit Decis Anal 2008;15:87–107. [Google Scholar]
- 31. Filippucci E, Di Geso L, Grassi W. Tips and tricks to recognize microcrystalline arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012;51 Suppl 7:vii18–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Naredo E, Uson J, Jimenez‐Palop M, Martinez A, Vicente E, Brito E, et al. Ultrasound‐detected musculoskeletal urate crystal deposition: which joints and what findings should be assessed for diagnosing gout? Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1522–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Glazebrook KN, Guimaraes LS, Murthy NS, Black DF, Bongartz T, Manek NJ, et al. Identification of intraarticular and periarticular uric acid crystals with dual‐energy CT: initial evaluation. Radiology 2011;261:516–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Mallinson PI, Coupal T, Reisinger C, Chou H, Munk PL, Nicolaou S, et al. Artifacts in dual‐energy CT gout protocol: a review of 50 suspected cases with an artifact identification guide. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2014;203:W103–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Aggarwal R, Ringold S, Khanna D, Neogi T, Johnson SR, Miller A, et al. Distinctions between diagnostic and classification criteria? Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2015;67:891–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting Information


