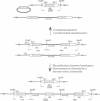
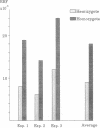
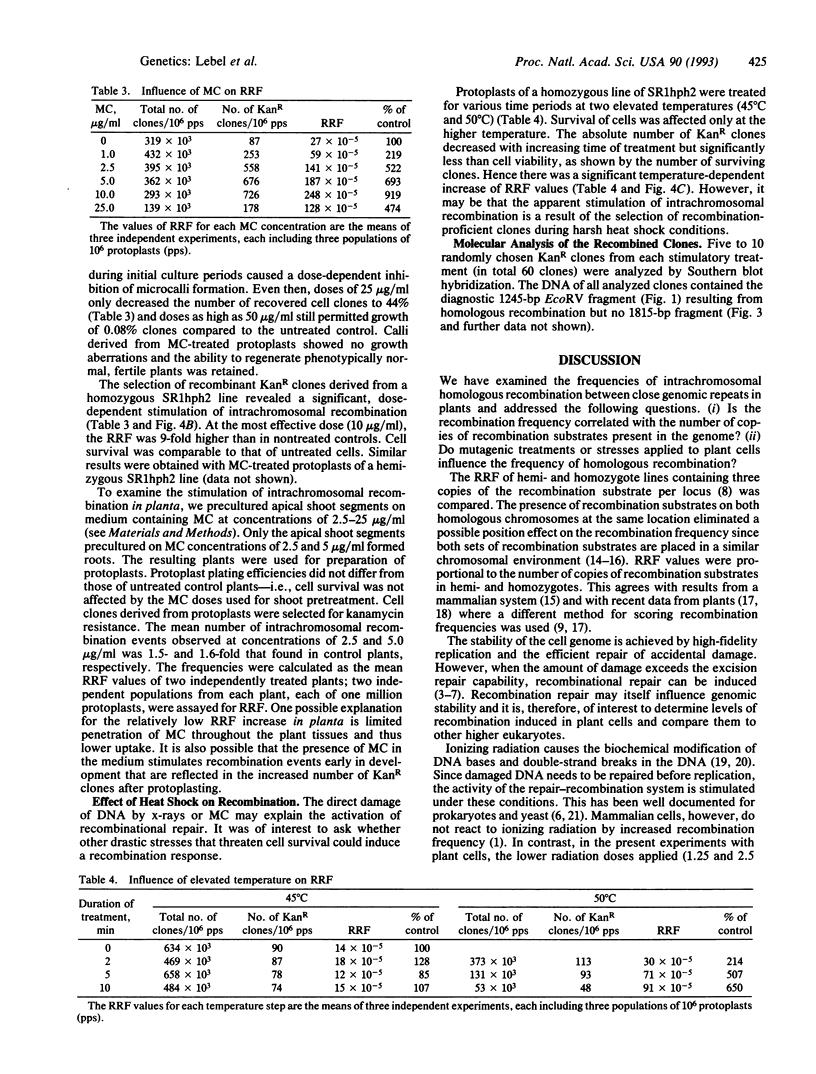
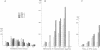Abstract
Levels of induced homologous recombination between chromosomal repeats in plant somatic cells were examined. Transgenic plants of Nicotiana tabacum hemi- or homozygous for pairs of deletion derivatives of the neomycin phosphotransferase (nptII) marker gene integrated at a single genomic locus were produced. Homologous recombination within the overlapping parts of the nptII gene restored the function and the resulting kanamycin resistance was used for scoring recombination frequency. The recombination events were confirmed by the appearance of a characteristic 1245-base-pair EcoRV fragment detected in all kanamycin-resistant clones tested. The rate of spontaneous recombination was found to be related to the copy number of recombination substrates and was 9 x 10(-5) and 19 x 10(-5) for hemi- and homozygote strains, respectively. Ionizing radiation, mitomycin C, and heat shock markedly increased the frequency of intrachromosomal recombination. Low doses of x-rays (1.25 Gy) enhanced the relative recombination frequency to approximately twice the spontaneous value. The presence of mitomycin C increased the frequency of recombination 9-fold and exposure to an elevated temperature (50 degrees C) increased it 6.5-fold. The x-ray and heat shock treatments reduced cell viability to 53% and 8%, respectively. Mitomycin C treatment had no effect on cell survival.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya N. P., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Ability of structurally related polycyclic aromatic carcinogens to induce homologous recombination between duplicated chromosomal sequences in mouse L cells. Mutat Res. 1989 Apr;211(2):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya N. P., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Effect of nucleotide excision repair in human cells on intrachromosomal homologous recombination induced by UV and 1-nitrosopyrene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3945–3951. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckardt F., Haynes R. H. Kinetics of mutation induction by ultraviolet light in excision-deficient yeast. Genetics. 1977 Feb;85(2):225–247. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal S., Pisan B., Hohn T., Grimsley N., Hohn B. Genomic homologous recombination in planta. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1571–1578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07677.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLIDAY R. THE INDUCTION OF MITOTIC RECOMBINATION BY MITOMYCIN C IN USTILAGO AND SACCHAROMYCES. Genetics. 1964 Sep;50:323–335. doi: 10.1093/genetics/50.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. Chemical changes induced in DNA by ionizing radiation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:115–154. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IIJIMA T., HAGIWARA A. Mutagenic action of mitomycin C on Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Feb 6;185:395–396. doi: 10.1038/185395b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz B. A., Haynes R. H. Phenomenology and genetic control of mitotic recombination in yeast. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:57–89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupiec M., Petes T. D. Allelic and ectopic recombination between Ty elements in yeast. Genetics. 1988 Jul;119(3):549–559. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsou A., Liskay R. M. Effect of the molecular nature of mutation on the efficiency of intrachromosomal gene conversion in mouse cells. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):759–769. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichten M., Haber J. E. Position effects in ectopic and allelic mitotic recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 Oct;123(2):261–268. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliga P., Sz-Breznovits A., Márton L. Streptomycin-resistant plants from callus culture of haploid tobacco. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 4;244(131):29–30. doi: 10.1038/newbio244029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchel R. E., Morrison D. P. Inducible error-prone repair in yeast. Suppression by heat shock. Mutat Res. 1986 Jan-Feb;159(1-2):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(86)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszkowski J., Shillito R. D., Saul M., Mandák V., Hohn T., Hohn B., Potrykus I. Direct gene transfer to plants. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2717–2722. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterhans A., Schlüpmann H., Basse C., Paszkowski J. Intrachromosomal recombination in plants. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3437–3445. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D., Hill C. W. Recombination between repeated genes in microorganisms. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:147–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW M. W., COHEN M. M. CHROMOSOME EXCHANGES IN HUMAN LEUKOCYTES INDUCED BY MITOMYCIN C. Genetics. 1965 Feb;51:181–190. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI D. T. EFFECTS OF MITOMYCIN C ON CROSSING OVER IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1965 Apr;51:635–640. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.4.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Rubnitz J. Recombination events after transient infection and stable integration of DNA into mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):659–666. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovar J., Lichtenstein C. Somatic and Meiotic Chromosomal Recombination between Inverted Duplications in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Plant Cell. 1992 Mar;4(3):319–332. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimura T., Maher V. M., Godwin A. R., Liskay R. M., McCormick J. J. Frequency of intrachromosomal homologous recombination induced by UV radiation in normally repairing and excision repair-deficient human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1566–1570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Téoule R. Radiation-induced DNA damage and its repair. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1987 Apr;51(4):573–589. doi: 10.1080/09553008414552111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. Y., Maher V. M., Liskay R. M., McCormick J. J. Carcinogens can induce homologous recombination between duplicated chromosomal sequences in mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):196–202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]