Abstract
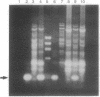
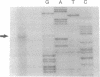
Deoxycytidine kinase (NTP:deoxycytidine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.74) is an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorylation of deoxyribonucleosides and a number of nucleoside analogs that are important in antiviral and cancer chemotherapy. Deficiency of this enzyme activity is associated with resistance to these agents, whereas increased enzyme activity is associated with increased activation of such compounds to cytotoxic nucleoside triphosphate derivatives. To characterize the regulation of expression of this gene, we have isolated genomic clones encompassing its entire coding and 5' flanking regions and delineated all the exon/intron boundaries. The gene extends over more than 34 kilobases on chromosome 4 and the coding region is composed of 7 exons ranging in size from 90 to 1544 base pairs (bp). The 5' flanking region is highly G+C-rich and contains four regions that are potential Sp1 binding sites. A 697-bp fragment encompassing 386 bp of 5' upstream region, the 250-bp first exon, and 61 bp of the first intron was demonstrated to promote chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity in a T-lymphoblast cell line and to have > 6-fold greater activity in a Jurkat T-lymphoblast than in a Raji B-lymphoblast cell line. Our data suggest that these 5' sequences may contain elements that are important for the tissue-specific differences in deoxycytidine kinase expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronow B. J., Silbiger R. N., Dusing M. R., Stock J. L., Yager K. L., Potter S. S., Hutton J. J., Wiginton D. A. Functional analysis of the human adenosine deaminase gene thymic regulatory region and its ability to generate position-independent transgene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4170–4185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronow B., Lattier D., Silbiger R., Dusing M., Hutton J., Jones G., Stock J., McNeish J., Potter S., Witte D. Evidence for a complex regulatory array in the first intron of the human adenosine deaminase gene. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1384–1400. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Kaye J., Seegmiller J. E. Lymphospecific toxicity in adenosine deaminase deficiency and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency: possible role of nucleoside kinase(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5677–5681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. J., Shimada T., Moulton A. D., Cline A., Humphries R. K., Maizel J., Nienhuis A. W. The functional human dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3933–3943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chottiner E. G., Shewach D. S., Datta N. S., Ashcraft E., Gribbin D., Ginsburg D., Fox I. H., Mitchell B. S. Cloning and expression of human deoxycytidine kinase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1531–1535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Lee J. W., Dosch H. M., Gelfand E. W. The expression of deoxyguanosine toxicity in T lymphocytes at different stages of maturation. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1578–1582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M. S., Yang B., Sorscher D. Regulation of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase gene expression in mice and men. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(3):237–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrow A. L., Rickles R. J., Pecorino L. T., Strickland S. Transcription factor Sp1 is important for retinoic acid-induced expression of the tissue plasminogen activator gene during F9 teratocarcinoma cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5883–5893. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Huang E. S. Transfer and expression of plasmids containing human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene 1 promoter-enhancer sequences in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1988 Feb;10(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Feldman P. A., Colberg-Poley A. M., Buckery R. M., Neubauer R. H. A sensitive method for the detection of beta-galactosidase in transfected mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):739-40, 742-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D. A relational database of transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1749–1756. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Blake M., Azizkhan J., Nevins J. R. Role of E2F transcription factor in E1A-mediated trans activation of cellular genes. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3547–3552. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3547-3552.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Onwuta U. S., Lee Y. I., Li R., Botchan M. R., Robbins P. D. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates Sp1-mediated transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2455–2463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A., Tuttle J. V., Koszalka G. W., Chen I. S., Beacham L. M., 3rd, Rideout J. L., Elion G. B. Deoxycytidine kinase from calf thymus. Substrate and inhibitor specificity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4055–4061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufe D. W., Spriggs D. R. Biochemical and cellular pharmacology of cytosine arabinoside. Semin Oncol. 1985 Jun;12(2 Suppl 3):34–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K., Landau N. R., Smale S. T. LyF-1, a transcriptional regulator that interacts with a novel class of promoters for lymphocyte-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5229–5243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Transcriptional regulation. A closer look at E2F. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):375–376. doi: 10.1038/358375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne W. R. Nucleoside kinases in T and B lymphoblasts distinguished by autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson B. E., Nasheuer H. P., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene: sequences controlling expression in cycling and serum-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2081–2095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piro L. D. 2-Chlorodeoxyadenosine treatment of lymphoid malignancies. Blood. 1992 Feb 15;79(4):843–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurman H. J., van Laarhoven J. P., Broekhuizen R., Spierenburg G. T., Brekelmans P., Figdor C. G., de Bruyn C. H., Kater L. Lymphocyte maturation in the human thymus. Relevance of purine nucleotide metabolism for intrathymic T cell function. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Dec;18(6):539–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick A. G., Blake M. C., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Functional analysis of GC element binding and transcription in the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9291–9304. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Weintraub H. Activation and repression of myogenesis in somatic cell hybrids: evidence for trans-negative regulation of MyoD in primary fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90285-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerio D., Duyvesteyn M. G., Dekker B. M., Weeda G., Berkvens T. M., van der Voorn L., van Ormondt H., van der Eb A. J. Adenosine deaminase: characterization and expression of a gene with a remarkable promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):437–443. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiginton D. A., Kaplan D. J., States J. C., Akeson A. L., Perme C. M., Bilyk I. J., Vaughn A. J., Lattier D. L., Hutton J. J. Complete sequence and structure of the gene for human adenosine deaminase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8234–8244. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]