Significance
For horizontally transmitted, facultative symbionts, cycles of infection and escape from the host are crucial for the persistence over host generations. The hydrothermal vent tubeworm Riftia pachyptila is entirely nourished by its thiotrophic endosymbiotic bacteria, which are acquired horizontally in settled larvae; however, release back into the environment has not been demonstrated. We show experimentally that viable symbionts are released upon host death. Moreover, observations of turnover of tubeworm clumps after a volcanic eruption provide evidence for rapid colonization, growth, and death. The observed connectivity of host-associated and free-living symbiont populations helps to explain the stability of this mutualism over ecological and evolutionary timescales.
Keywords: symbiosis, mutualism stability, symbiont seeding, tubeworms, Vestimentifera
Abstract
Theory predicts that horizontal acquisition of symbionts by plants and animals must be coupled to release and limited dispersal of symbionts for intergenerational persistence of mutualisms. For deep-sea hydrothermal vent tubeworms (Vestimentifera, Siboglinidae), it has been demonstrated that a few symbiotic bacteria infect aposymbiotic host larvae and grow in a newly formed organ, the trophosome. However, whether viable symbionts can be released to augment environmental populations has been doubtful, because (i) the adult worms lack obvious openings and (ii) the vast majority of symbionts has been regarded as terminally differentiated. Here we show experimentally that symbionts rapidly escape their hosts upon death and recruit to surfaces where they proliferate. Estimating symbiont release from our experiments taken together with well-known tubeworm density ranges, we suggest a few million to 1.5 billion symbionts seeding the environment upon death of a tubeworm clump. In situ observations show that such clumps have rapid turnover, suggesting that release of large numbers of symbionts may ensure effective dispersal to new sites followed by active larval colonization. Moreover, release of symbionts might enable adaptations that evolve within host individuals to spread within host populations and possibly to new environments.
The evolution of cooperation between species (mutualism) represents a challenge for evolutionary theory (1–5). The host provides benefits to the symbiont by supporting its partner’s offspring at the expenses of its own offspring (6, 7). To assure beneficial coexistence after establishment of an association, partner sanctions and/or partner fidelity feedback may act as postinfection mechanisms (1, 8–12). During vertical transmission, hosts transmit symbionts directly to offspring during reproduction (1, 5, 7, 13). During horizontal transmission, partners must reassociate anew each host generation (13). Limited dispersal following release of the cooperating symbiont back into the environment might keep the offspring of both partners in close proximity (14–18) and thereby enhance the probability that the offspring of both partners can reassociate (7, 14, 16, 18–20). Therefore, the processes of symbiont release back into the environment are key factors in understanding interspecies cooperation in ecological and evolutionary timescales.
In facultative horizontally transmitted pathogens, escape from the infected host and long survival in the environment are crucial to reinfect susceptible hosts, especially in cases when host density is low (21, 22). Although some pathogens are capable of growing outside the host, others follow a sit-and-wait strategy in the absence of proliferation in the environment (21). Several studies have shown that host-associated and free-living beneficial symbiont populations apparently can rejoin. The majority of horizontally transmitted bioluminescent Vibrio fischeri housed in the light organ of the bobtail squid are expelled into the environment daily and remain viable for at least 1 d (23, 24). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reproduce when associated with the plant host and repopulate the soil to infect new vascular plants (25). Likewise, a dense population of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia reenters the soil upon root nodule senescence in legume hosts and remains there for years (25–27). Genetically identical symbiont lineages to those being released were shown to reinfect the next host generation in the squid and legume symbiosis (28, 29).
Transmission is also horizontal in the mutualism between the sessile tubeworm Riftia pachyptila and its thiotrophic gammaproteobacterial endosymbiont Candidatus Endoriftia persephone (short Endoriftia) from deep-sea hydrothermal vents (30). Endoriftia exhibits an identical 16S rRNA sequence to the co-occurring hydrothermal vent vestimentiferan symbionts of Tevnia jerichonana and nearly identical 16S rRNA sequences to the symbionts of Oasisia alvinae and Ridgeia piscesae (31–33). A high level of genetic homogeneity in the internal transcribed spacer (ITS), with one dominant 16S rRNA phylotype and ITS subtypes, is present in intracellular Endoriftia (34). While associated, Riftia provides all substrates necessary for chemosynthesis to the symbiont (35), which ultimately allows the symbiont to grow to more than a billion symbiont cells⋅g−1 trophosome (36, 37). In return, the symbiont provides benefits through release of fixed organic carbon to the host, thus entirely nourishing the gutless host (38, 39). The intracellular symbionts are located in specialized host cells, the bacteriocytes, deep within the host body with no openings toward the exterior (40–42). The bacteria divide within unipotent bacteriocyte stem cells mostly as rods, convert into small and large cocci in the proliferating bacteriocytes, and are digested before host bacteriocyte apoptosis (43). Whereas in some mutualisms, release of symbionts may happen during the host’s life, such as in the V. fischeri–squid (23, 24) and rhizobia–legume (25–27) partnerships, in Riftia there is no support for such a release (44), and it has been suggested that the vast majority of symbionts are terminally differentiated during the host’s life (43).
Because vestimentiferan hosts lack any obvious organs that could mediate symbiont release (44), we hypothesized that symbionts escape from decaying host tissue. Here we combine high-pressure experiments and ecological observations in one of the best-studied microbial mutualisms (44) to provide evidence for a very different mode of symbiont release into the environment upon host death. We propose that this symbiont escape mechanism facilitates the intergenerational persistence of this cooperation thriving at temporally and spatially highly dynamic deep-sea hydrothermal vents (45).
Results and Discussion
Symbiont Fate upon Host Death.
To test the potential of symbiont escape from decaying host tissue, custom-designed symbiont recruitment plates (SRPs) were developed. SRPs were equipped with a sterile porous capsule (100- to 120-µm pore size) for the trophosome tissue and five sterile glass coverslips for symbiont recruitment (Fig. S1). Live worms were dissected and 0.4 g wet weight trophosome was placed in the capsules and incubated in sterile filtered seawater in high-pressure flowthrough vessels at simulated cold deep-sea or simulated hydrothermal vent conditions. For simulated deep-sea conditions, samples were incubated at 250 bar and 4 °C with 171.6 ± 0.5 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen and without sulfide addition in seawater and without flow for up to 10 d. To simulate hydrothermal vent conditions, incubations at 22.4 ± 0.6 °C, 280 ± 48 µmol⋅L−1 ∑H2S [i.e., sum of all forms of dissolved sulfide; short sulfide (46)] and 107 ± 29 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen with continuous water flow were performed to approximate habitat conditions for thriving Riftia (46–48) and previous maintenance conditions (49). As a control, trophosome tissue was fixed in 100% ethanol or frozen in liquid nitrogen prior to incubations to test for dead symbionts or dead bacteriocytes (containing dead symbionts) being rinsed out of the capsules passively. Water samples and coverslips from SRPs in high-pressure vessels were analyzed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using simultaneously a mixture of symbiont-, host-, and bacteria-specific oligonucleotide probes and epifluorescence microscopy to localize symbionts and other microbes in the water and on surfaces (Table S1).
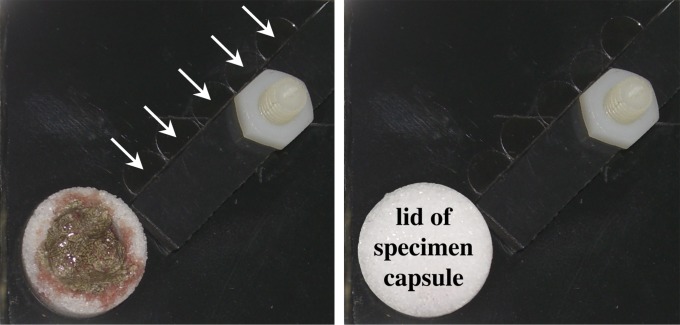
Fig. S1.
Symbiont recruitment plates (SRPs). SRPs with freshly dissected 0.4 g trophosome of Riftia pachyptila in a microporous specimen capsule equipped with five glass coverslips (5-mm-diameter). Coverslips are held in place with a bar, which is screwed to the plate. The microporous specimen capsule is closed with a microporous lid after being filled with trophosome (Right). Coverslips are highlighted with white arrows.
Table S1.
Oligonucleotide probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization and Endoriftia-specific primers for 16S rRNA PCR
| Probe/Primer | Sequence, 5′-3′ | Specificity | Formamide, % | Ref. |
| Probe | ||||
| EUB338 I | GCT GCC TCC CGT AGG AGT | Most bacteria (EUB I+II+III) | 35 | (70) |
| EUB338 II | GCA GCC ACC CGT AGG TGT | Most bacteria (EUB I+II+III) | 35 | (71) |
| EUB338 III | GCT GCC ACC CGT AGG TGT | Most bacteria (EUB I+II+III) | 35 | (71) |
| RifTO445 | TCC TCA GGC TTT TCT TCC | Rif/Tev/Oas symbiont | 35 | (30) |
| NON-338 EUB | ACT CCT ACG GGA GGC AGC | Negative control | 10 | (72) |
| RP1752 | CGA CCT CTA AGC CGT CAA | Riftia host | 40 | (73) |
| Primer | ||||
| RifTO44 forward | GGC CTA GAT TGA CGC TGC GGT A | Rif/Tev/Oas symbiont | (34) | |
| RifTO445 reverse | TCC TCA GGC TTT TCT TCC | Rif/Tev/Oas symbiont | (30) |
Probes were labeled at the 5′ end either with Cy3, FITC, or Atto 488 to highlight simultaneously host and symbiont areas and to analyze other bacteria on the tissue sections, filters, and coverslips. A NON-338 EUB probe was used as negative control. All simultaneous hybridizations of host probe, symbiont-specific probe, and general bacterial probe mix were carried out at 35% (vol/vol) formamide stringency (given as % formamide in the hybridization buffer) and counterstained with the general DNA stain DAPI. The Endoriftia oligonucleotide probe RifTO445 (30) is specific for the 16S rRNA of the R. pachyptila, T. jerichonana, and Oasisia alvinae symbionts, as all three vestimentiferans share an identical (Tevnia) or nearly identical (Oasisia) 16S rRNA symbiont phylotype (Rif/Tev/Oas) (31–33). Symbiont-specific 16S rRNA gene-targeted primers (RifTO44 and RifTO445) were used for PCR (30, 34).
FISH analyses revealed that Endoriftia quickly left the dead host tissue and recruited to surfaces under deep-sea and vent conditions. Colonization of Endoriftia on replicate coverslips was highly variable but not significantly different between treatments after half a day of incubation time. Endoriftia was not detected with FISH and specific 16S rRNA gene-targeted PCR in incubation water sampled before the experiments, but was detected after incubations with FISH (Fig. S2). Symbionts killed within the trophosome before the experiments were not detected in the water or on the coverslips in any control incubations. This indicates that under our experimental conditions only live Endoriftia can leave the dead host tissue and colonize surfaces. Host cells (or partial host cells containing ribosomes or host nuclei in the size range of symbionts) were neither detected by FISH and DAPI staining in the water nor on coverslips outside of the trophosome capsules in any treatment. This suggests that bacteriocytes housing symbionts or host nuclei were not passively flushed into the water during the experiments. Instead, it may indicate an active escape process similar to rhizobia escaping the infection threat upon dissolution of the senescent nodule (50). Rhizobia and V. fischeri, although host-associated, do not express flagella, but produce flagella while free-living (29, 51). Also, metagenomic data suggest that Endoriftia may have the capability for flagellar movement, but do not produce flagella as endosymbionts (52).
Fig. S2.
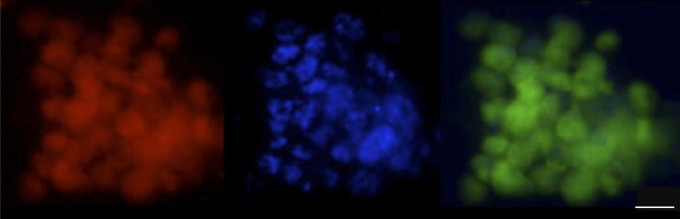
Symbionts released into the water of high-pressure vessels and filtered. Endoriftia symbionts detected in the water column of the high-pressure vessel after 8 d of incubation under simulated deep-sea conditions without flow. Red, EUB338 probe mix; blue, DAPI as a general nucleic acid stain for symbiont nuclei; green, symbiont-specific probe RifTO445. (Scale bar, 5 µm.)
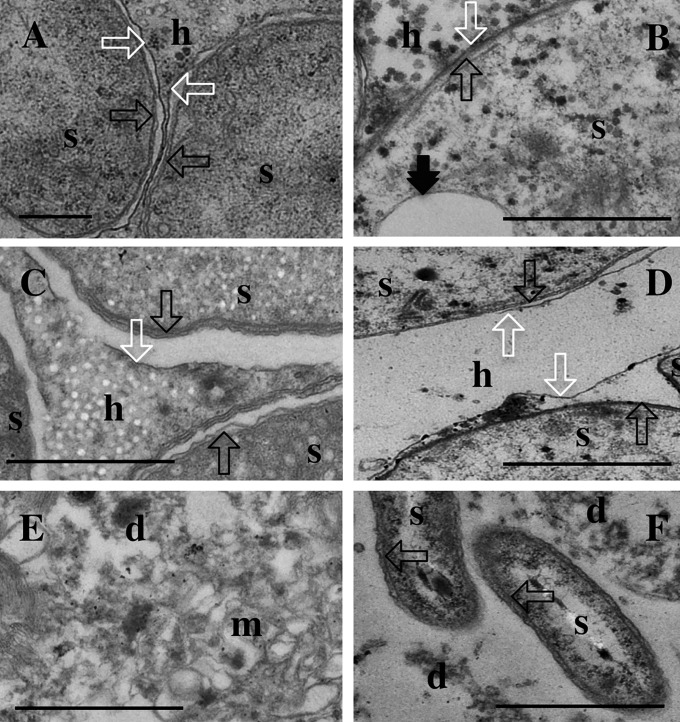
Further, the degradation process in the trophosome was followed by evaluating the integrity of the host and symbiont membranes to determine the time frame of symbiont disintegration. Using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), we analyzed in detail 30 sections of three freshly collected trophosome samples each (Fig. 1 A and B) and all trophosomes incubated in triplicate for different time periods under the described conditions. Under deep-sea conditions, most of the symbiont and bacteriocyte membranes remained intact for 10 d (Fig. 1C) with a similar symbiont ultrastructure compared with the fresh fixed samples. Under vent conditions, TEM revealed symbiont outer and inner membranes as well as sulfur vesicle membranes intact after 1 d, similar to the fresh trophosome, whereas bacteriocyte tissue was distorted and visible as debris with host cell membranes partly disintegrated (Fig. 1D). However, even after 6 d of vent incubation a few morphologically intact symbionts were detected but, in most symbionts, membranes were distorted (Fig. 1 E and F). The 6-d incubations under vent conditions showed a high degree of autolysis, initiated through endogenous enzymes upon host death leading to cytoplasm breakdown and membrane destruction and resulting in amorphous debris when analyzed with TEM. Temporal differences in degradation between deep-sea and vent conditions are likely due to temperature, known to be retarded at low temperatures but accelerated at temperatures up to 30 °C (53, 54).
Fig. 1.
Ultrastructure of the decay of incubated trophosome over time under simulated flowthrough vent conditions and simulated deep-sea conditions without flow. Thirty micrographs of the center and median regions of the trophosome lobules of each trophosome were analyzed (Table S2). The micrographs are representative of each time point and treatment. h, host tissue; d, cellular debris; m, membranes of unknown origin; s, indication of symbiont presence in the trophosome; black arrow, double symbiont membranes; black double arrow, sulfur vesicle membrane; white arrow, host symbiosome membrane. (A and B) Fresh trophosome. (C) Ten-day deep-sea incubation without flow. (D) One-day flowthrough vent incubation. (E and F) Six-day flowthrough vent incubation. (Scale bars, 500 nm.)
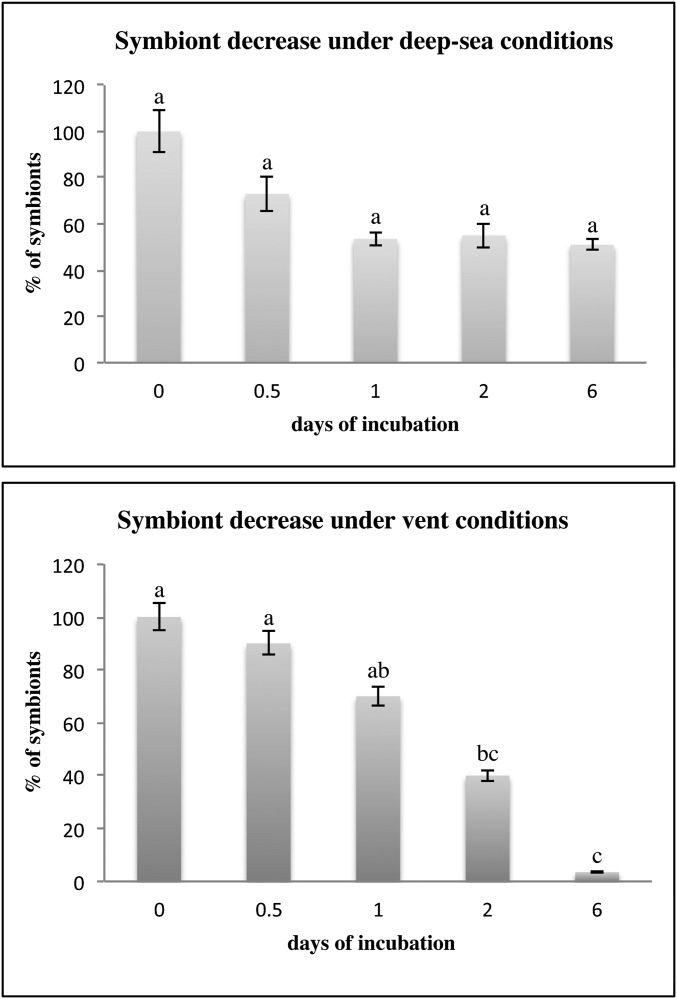
Symbiont relative density (100% in fresh trophosome) decreased faster in the decaying trophosome under vent conditions with only 3% symbiont presence compared with deep-sea conditions with 51% symbiont presence after 6 d (Fig. S3 and Table S2). Symbiont recruitment to surfaces confirmed these results of a decelerated symbiont escape under deep-sea incubation conditions compared with vent conditions. In the deep-sea treatment the oxygen concentration was reduced from 86.2 ± 0.8% (0.5 d) to 10.0 ± 0.2% (from 6 d on) due to closed chambers. Whereas under the simulated deep-sea treatment the peak release occurred after 6 d, under vent conditions most symbionts were released in the half-day incubations (Table 1). These results indicate that the time window for symbiont escape may be relatively short under vent conditions but much longer under deep-sea conditions.
Fig. S3.
Symbiont decrease in number in the trophosome during simulated deep-sea incubations without flow and simulated flowthrough vent incubations of up to 6 d. All incubated and freshly fixed trophosome pieces were visually analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (fresh three specimens; 0.5 day cold two specimens and warm three specimens; 1 d cold two specimens and warm three specimens; 2 d cold and warm one specimen, each; 6 d cold one specimen and warm two specimens; Table S2). In detail, symbionts in a total of 30 transmission electron micrographs for each trophosome were counted, accounting for an area of 7,260 µm2 for each treatment and time point. Symbiont density is displayed as percent compared with fresh trophosome. Only samples from the cruise in 2011 are displayed. Letters give statistical differences of symbiont decrease in numbers in trophosome under simulated deep-sea conditions without flow and simulated flowthrough vent conditions over time of incubation. Percentage of symbionts is given in mean and SD of symbiont counts over 30 micrographs.
Table S2.
Symbiont decrease in number in the trophosome during simulated stagnant deep-sea and simulated flowthrough vent incubations of up to 6 d
| Incubation, d (replicate number) | Symbiont counts | Symbiont percentage, % |
| 0 (1) | 15.1 ± 4.5 | |
| 0 (2) | 30.0 ± 10.8 | |
| 0 (3) | 25.9 ± 11.5 | |
| Average 0 | 23.7 ± 11.3 | 100.0 ± 47.7 |
| Deep-sea | ||
| 0.5 (1) | 18.8 ± 10.9 | |
| 0.5 (2) | 15.7 ± 3.9 | |
| Average 0.5 | 17.3 ± 8.3 | 73.0 ± 35.0 |
| 1 (1) | 11.2 ± 1.4 | |
| 1 (2) | 14.2 ± 4.9 | |
| Average 1 | 12.7 ± 3.9 | 53.6 ± 16.5 |
| 2 (1) | 13.0 ± 5.4 | 54.9 ± 22.8 |
| 6 (1) | 12.0 ± 2.2 | 50.6 ± 9.3 |
| Vent | ||
| 0.5 (1) | 20.6 ± 11.2 | |
| 0.5 (2) | 22.3 ± 5.8 | |
| 0.5 (3) | 21.9 ± 9.2 | |
| Average 0.5 | 21.6 ± 8.9 | 91.1 ± 37.6 |
| 1 (1) | 14.7 ± 5.6 | |
| 1 (2) | 17.2 ± 6.8 | |
| 1 (3) | 17.5 ± 7.4 | |
| Average 1 | 16.5 ± 6.7 | 69.6 ± 28.3 |
| 2 (1) | 9.4 ± 4.7 | 39.7 ± 19.8 |
| 6 (1) | 0.7 ± 0.7 | |
| 6 (2) | 0.8 ± 1.1 | |
| Average 6 | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 3.8 |
The central and median lobule zones of all incubated and freshly fixed trophosome pieces were analyzed by counting the symbionts in 30 micrographs (7,260 µm2) of each trophosome for each treatment and time point. Symbiont numbers are given as average and SD of symbiont counts over 30 micrographs. Replicates are represented as trophosome pieces from different specimens in different incubation chambers. The average of the counts on freshly fixed trophosome pieces represents 100% symbiont presence under initial conditions.
Table 1.
Symbionts colonizing coverslips in high-pressure vessels under simulated, deep-sea, and flowthrough vent conditions
| Incubation, d | Replicates | Symbionts, mm−2 | FDC, % | Rods, % | Length, µm | Width, µm | Cocci, % | Diameter, µm |
| Deep-sea | ||||||||
| 0.5 | 3 (3,3,4) | 16.3 ± 15.7 | 1.3 ± 2.0 | 0.0 | N/A | N/A | 100.0 | 4.2 ± 0.7 |
| 1 | 3 (3,3,5) | 47.1 ± 60.0 | 3.3 ± 3.9 | 0.5 ± 1.2 | 2.3 ± 1.3 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 99.5 ± 1.2 | 3.7 ± 0.5 |
| 2 | 3 (3,2,5) | 30.4 ± 30.0 | 2.0 ± 3.5 | 2.8 ± 5.3 | 1.8 ± 0.9 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 97.2 ± 5.3 | 4.3 ± 0.6 |
| 6 | 2 (3,5) | 377.9 ± 507.5 | 20.0 ± 28.3 | 0.0 | N/A | N/A | 100.0 | 3.3 ± 1.2 |
| 8 | 1 (5) | 9.8 ± 7.1 | 4.0 ± 6.9 | 0.0 | N/A | N/A | 100.0 | 4.2 ± 0.5 |
| 10 | 1 (5) | 25.9 ± 29.0 | 1.6 ± 1.3 | 0.5 ± 1.1 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 99.5 ± 1.1 | 4.3 ± 0.6 |
| Vent | ||||||||
| 0.5 | 3 (3,3,3) | 80.0 ± 133.8 | 7.4 ± 12.9 | 0.1 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 99.9 ± 0.4 | 3.1 ± 1.4 |
| 1 | 3 (3,3,3) | 51.1 ± 84.1 | 5.8 ± 8.2 | 0.0 | N/A | N/A | 100.0 | 2.5 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | 1 (3) | 26.1 ± 42.9 | 4.3 ± 7.5 | 0.0 | N/A | N/A | 100.0 | 4.0 ± 0.2 |
| 6 | 2 (3,3) | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | N/A | N/A | 100.0 | 2.4 ± 0.1 |
Trophosome pieces were incubated under simulated deep-sea conditions at 4 °C and 171.6 ± 0.5 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen without flow or under simulated flowthrough vent conditions at 22.4 ± 0.6 °C, 280 ± 48 µmol⋅L−1 ∑H2S and 107 ± 29 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen. Density of symbionts released and settled on coverslips (FISH-positive cells stained with symbiont-specific probe, EUB338 probe mix, and DAPI were counted on 1.125 mm2 of glass coverslips), frequency of dividing cells, relative density of rods (length and width), and cocci (diameter) are given as mean and SD. To analyze the morphological variability, a total of 100 rods and cocci (when present) was counted for each coverslip and length and width for rods and diameter for cocci were measured. Incubations were conducted in triplicate (three different specimens incubated in different high-pressure incubation vessels) for each treatment for 0.5, 1, and 2 d. The longer 6-d incubations under vent and deep-sea conditions were done in duplicate. In addition, simulated deep-sea incubations were also run for 8 and 10 d once. Replicates are given: The numbers refer to trophosome samples of different specimens, and the numbers in parentheses refer to the number of coverslips analyzed in total. N/A, data not available.
Symbiont Morphological Variability and Proliferation Activity.
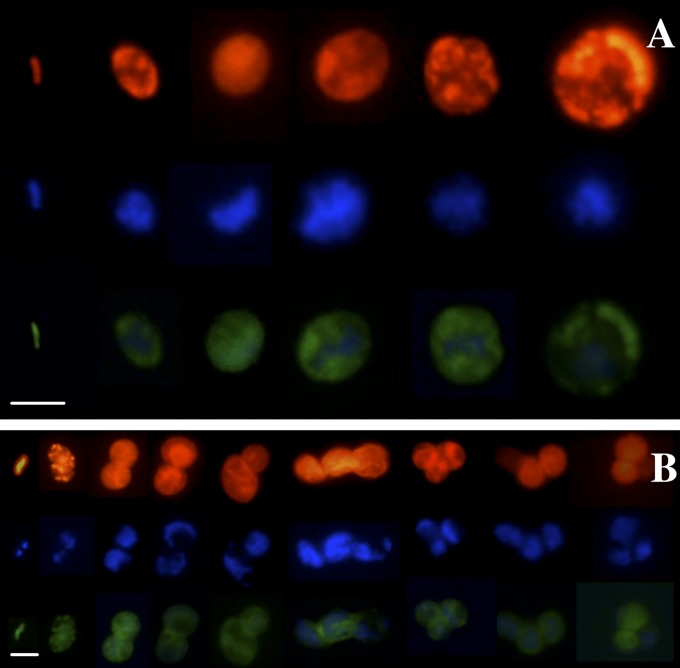
Because symbionts are differentiated into rods and cocci in the trophosome (42), we tested whether any of these morphotypes is preferentially released using FISH by simultaneously applying the symbiont-specific probe and the bacteria-specific probe mix. Symbionts recruited onto coverslips were composed of up to 3.3% rods (1.0–2.4 µm length, 0.5–0.9 µm width) and 96.7–100.0% cocci (0.5–13.6 µm diameter) (Fig. 2A), indicating a morphological variability similar to the endosymbiotic population (2.1% rods, 97.9% cocci) (42). No significant differences in relative densities of morphotypes were detected in the different treatments and after different incubation times (Table 1). Some bacterial contaminations on the coverslips could be detected in some experiments, but did not statistically influence the colonization of symbionts. In contrast, the specific 16S rRNA phylotype of Endoriftia detected on glass slides deployed after 1 y in deep-sea vents in Riftia aggregations as well as on bare basalt under ambient deep-sea conditions was all rod-shaped (34). Nevertheless, the ITS of free-living Endoriftia might be variable, as it is within the host (34).
Fig. 2.
Symbiont settlement on coverslips. (A) Symbiont population settlement on SRP glass coverslips: rod-shaped symbionts, small cocci, and large cocci of Endoriftia detected by FISH. (B) Symbiont settlement on SRP glass coverslips and division of settled symbiont morphotypes and formation of small colonies of the settled symbiont as detected by FISH along with symbiont DNA stained with the general nucleic acid stain DAPI. Characteristic samples are shown. Red, EUB338 probe mix targeting most bacteria; green, symbiont-specific probe RifTO445; blue, DAPI. (Scale bars, 5 µm.)
To analyze the viability and proliferation activity of released symbionts, we estimated the frequency of dividing cells (FDC) using DAPI and FISH staining simultaneously. An FDC of 4.9 ± 0.8% was detected on coverslips, whereas division could not be unambiguously determined in the symbiont populations detected in the water samples from the SRPs (Fig. S2). This further supports that escape and colonization are active processes of viable symbionts.
In contrast to restricted proliferation of rods and small cocci in the trophosome (43), all morphotypes of the released symbionts apparently divided after release and settling on surfaces (Fig. 2B), and the majority of proliferating symbionts were large cocci. These findings suggest that tubeworms control proliferation of Endoriftia during its symbiotic life, whereas Endoriftia released from host control initiates proliferation, similar to rhizobia in indeterminate root nodules of legumes (55, 56), which dedifferentiate upon entering the soil (57). No statistically significant differences in FDC between vent and deep-sea conditions or an increase of FDC over time were found (Table 1). This pattern may be explained by a balance between proliferation and death in the recruited population that thus retained constant density over the experimental time frame. Similar behavior was found in rhizobia entering a viable but inactive stage upon release from legumes into the soil (25).
Estimates of Symbiont Escape and Colonization.
Our experiments on trophosome tissue are indicative of processes that may happen when hydrothermal flux wanes. Due to the lack of substrate for chemosynthesis, the thiotrophic symbiont ceases to nourish the host, and ultimately the starving host dies. Endoriftia also must escape through the skin to leave the dead host. This migration process through the skin, albeit in opposite direction, has been observed during transmission (30). At the East Pacific Rise (EPR) 9°50′N region, tubeworm clumps were reported ranging from a few individuals only to large clumps with 2,000 individuals⋅m−2 (58, 59). A medium-sized worm of 20 g wet weight with a 3-g trophosome (60, 61) houses about 1.11 × 1010 symbionts (36, 37). Under cold deep-sea conditions about 7 × 105 symbionts would escape from such a dead worm within half a day. Because Endoriftia must also escape through the skin to leave the dead host, further loss may be involved; however, this factor is currently difficult to quantify, so the estimates provided represent an upper bound. Taking the variability of tubeworm density in such patches into account, a remarkable seeding event of Endoriftia into the environmental population must occur when a tubeworm clump dies within a short time upon cessation of vent flux. Roughly between 7 million (7 × 106 estimated for 10 worms) and 1.5 billion symbionts (1.4 × 109 estimated for 2,000 worms) may enter the environment upon such an event. In situ experiments have shown that crabs rapidly feed on dead trophosome pieces (62). Although this fast scavenging behavior reduces the number of symbionts, it may at the same time facilitate escape of the remaining symbionts due to the crabs opening the body and/or sloppy feeding.
Monitoring of Tubeworm Clump Longevity at the EPR.
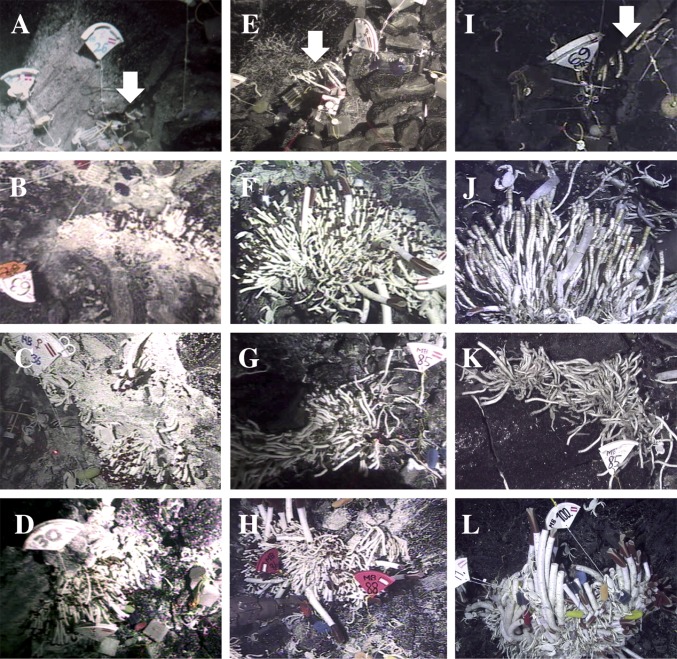
Riftia is one of the fastest-growing invertebrates known (63); however, it may not live very long. We monitored several discrete tubeworm clumps from the sites Tica, P-Vent, and Sketchy at the EPR 9°50′N region in the area that was covered with new lava during the eruption in late 2005/early 2006 (64) between approximately 11 mo and 4 y posteruption (Table S3). The assessment of viability was done by in situ observations, videos, and collections. Clumps composed of more than 95% empty tubes were classified as dead. Initially, all patches were dominated by T. jerichonana [but also housing Endoriftia (31)] (Fig. 3 A–E). Although all patches at Sketchy were, with at most 2 y, relatively short-lived (Fig. 3I), some patches at P-Vent and Tica were colonized longer than 1 y (Fig. 3 F–H) but less than 4 y (Fig. 3 J and K) or more than 4 y (Fig. 3L), respectively. Initially, Tevnia dominated these vents, but within 2 y posteruption Riftia replaced the pioneer Tevnia, confirming an earlier study of the previous eruption in 1992 (58). This indicates that over a relatively short time, a tremendous amount of Endoriftia may escape dead tubeworms and increase the density of the free-living population.
Table S3.
Monitoring tubeworm clumps at the East Pacific Rise after the volcanic eruption in late 2005/early 2006 at four different sites
| Site | Markers | Deployment | Alvin dive | Max. T | Fig. 3 | Recovery | Alvin dive | Max. T | Fig. 3 | Viability |
| Sketchy | 24, 25, 26 | 1 Nov 2006 | 4260 | 12.9 | A | 29 Dec 2006 | 4291 | 3.3 | B | alive |
| Sketchy | 68, 69, 70 | 29 Dec 2006 | 4291 | 2.3 | 27 Nov 2007 | 4372 | 2.7 | C | dead | |
| P-Vent | 27, 28, 29 | 2 Nov 2006 | 4261 | 26.7 | 16 Dec 2006 | 4288 | 28.0 | alive | ||
| P-Vent | 62, 63, 64 | 16 Dec 2006 | 4288 | 28.0 | D | 17 Nov 2007 | 4366 | 13.0 | alive | |
| P-Vent | 80, 81, 82 | 17 Nov 2007 | 4366 | 17.9 | E | 17 Dec 2009 | 4575 | 6.2 | F | dead |
| Tica 1 | 36 | 14 Nov 2006 | 4273 | N/A | G | 13 Dec 2006 | 4285 | 27.0 | alive | |
| Tica 1 | 59 | 13 Dec 2006 | 4285 | 27.0 | 22 Nov 2007 | 4369 | 4.6 | alive | ||
| Tica 1 | 85 | 22 Nov 2007 | 4369 | 4.3 | H | 23 Dec 2009 | 4580 | 2.0 | I | dead |
| Tica 2 | 30, 31, 32 | 5 Nov 2006 | 4264 | 25.0 | J | 13 Dec 2006 | 4285 | 15.9 | alive | |
| Tica 2 | 33, 34, 35 | 13 Dec 2006 | 4285 | 15.9 | 26 Nov 2007 | 4371 | 14.8 | alive | ||
| Tica 2 | 86, 87, 88 | 26 Nov 2007 | 4371 | 16.1 | K | 17 Dec 2009 | 4575 | 19.0 | alive | |
| Tica 2 | 99, 100, 101 | 17 Dec 2009 | 4575 | 8.0 | L | alive |
Colonization devices were deployed in selected patches with markers for a different succession study. Deployments and recoveries of devices with Alvin dive numbers and maximal temperatures (in °C) measured are listed, as well as corresponding figures and assessment of viability of most tubeworms in a specific clump. N/A, data not available; T, temperature.
Fig. 3.
Temporal colonization of vent patches over 4 y after a volcanic eruption in 2005/2006. Patches of T. jerichonana at Sketchy (A), P-Vent (B), Tica location 1 (C), and Tica location 2 (D) 11 mo posteruption. Same patches with live tubeworms (mostly Tevnia, but also Riftia) at Sketchy 1 y posteruption (E) and at P-Vent (F), Tica location 1 (G), and Tica location 2 (H) 2 y posteruption. Same patches with mostly dead tubeworms, assessed by their empty tubes, at Sketchy (I), P-Vent (J), and Tica location 1 (K) 4 y posteruption. Patch of live Riftia and Tevnia at Tica location 2 (L) 4 y posteruption. Note one live Riftia among empty tubes in J, Lower Left. Note that the two laser points in E and G mark 10 cm; figures show a slice of a bucket lid for size comparison. Arrows highlight tubeworms at Sketchy in A, E, and I.
Host–Symbiont Life-History Traits.
Adult tubeworms are sessile, but dispersal is through aposymbiotic larvae in the pelagial (65) and facilitates recruitment to already-existing and newly opened vents. Likewise, the free-living symbiont must colonize such new vents. Hence, both partners must reach new vent sites separately, yet although larvae are motile, for symbionts this must be a passive process. The potentially pulsed release of symbionts from dying tubeworm clumps may ensure reliable colonization of nearby new vent fields. However, how new sites that arise often hundreds of kilometers away are colonized remains an open question but possibly involves a more directed dispersal process, either by currents or by carriage on motile animals that actively seek out new vent sites. In contrast to the highly disturbed vent environment, which requires dispersal of tubeworm larvae and symbionts to new sites, the dispersal of hatched juvenile squids as well as daily expelled V. fischeri (23, 24, 66) in the relatively stable subtidal sands may indeed be rather limited and in accordance with the benign nature of the habitat in which they thrive.
Conclusions
Our unique finding of Endoriftia escaping dead tubeworms and seeding the environment through a temporally and spatially highly dynamic process in this fluctuating and disturbed vent ecosystem confirms the connectivity from the host-associated population to the environmental population. Considering the maximal number of 20 symbionts, which was previously found to infect each host larva (30), and our estimates of 7 × 105 symbionts leaving a medium-sized worm upon host death may indicate the fitness benefits for Endoriftia to engage in a temporary association with tubeworms. The hosts provide nutrients for carbon fixation and growth to the symbiont in a competition-free habitat (67). The release of symbionts is in accordance with theoretical predictions and suggests a mechanism for adaptation that arises in individual tubeworms to spread among host populations. However, whether the symbionts infecting new hosts are indeed those that have been released from other dead tubeworms remains to be shown. Now that this principal mode of host-associated and free-living symbiont connectivity is known, we can start to decipher the stability of this mutualism in situ in the framework of population genetics and metapopulation ecology.
Materials and Methods
Monitoring Discrete Tubeworm Clumps in Situ.
During four cruises with the research vessel (R/V) Atlantis and the human-occupied vehicle (HOV) Alvin in October/November 2006, November/December 2006, November 2007, and December 2009, colonization devices were deployed in one patch at the sites Sketchy and P-vent each and in two patches at Tica (Table S3). The colonization of the foundation species Riftia and Tevnia and their health were monitored with live observations, videos, and collections of samples. Clumps were classified as dead when more than 95% of tubes were empty. In addition, upon recovery of the devices and samples, the viability of small tubeworms was checked using a dissection microscope. Temperature, a proxy for vent flow (48), was measured in situ with the low-temperature probe of Alvin.
Collections of Vestimentiferans and High-Pressure Incubations.
Vestimentiferan tubeworms were collected by the R/V L’Atalante with the deep-submergence vehicle (DSV) Nautile in May 2010 and by the R/V Atlantis and remotely-operated vehicle (ROV) Jason in November 2011 at the hydrothermal vent sites Tica and north of P-Vent at the East Pacific Rise. Tubeworms were dissected and incubated aboard the ship. To follow the symbiont escape process, we used custom-designed symbiont recruitment plates equipped with glass coverslips in high-pressure vessels to simulate deep-sea conditions of bottom water with 175 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen (65) and about 2–3 °C at the basalt surfaces in the axial summit trough of the EPR (68). Pressure vessels for the simulated deep-sea treatments were filled with 0.2 µm sterile-filtered seawater and kept at 4 °C without flow and 171.6 ± 0.5 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen at the beginning (short deep-sea conditions; SI Materials and Methods). To approximate vent habitat conditions for thriving Riftia (46–48) and previous maintenance conditions (49), simulated vent conditions (short vent conditions) were performed with continuous flow at 22.4 ± 0.6 °C, 280 ± 48 µmol⋅L−1 ∑H2S [i.e., sum of all forms of dissolved sulfide; short sulfide (46)] and 107 ± 29 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen for up to 6 d. Approximately 0.4 g wet weight freshly dissected trophosome was filled but not squeezed into microporous specimen capsules (pore size: 120–200 µm) and incubated in triplicate (three specimens in one vessel each) for each treatment of deep-sea and vent conditions for 0.5, 1, and 2 d, each. The longer 6-d incubations under vent and deep-sea conditions were done in duplicate. In addition, deep-sea incubations were also run for 8 and 10 d once. As controls, trophosome pieces were fixed in 100% ethanol or frozen in liquid nitrogen to kill symbionts before incubation under deep-sea conditions for 0.5 and 1 d once (SI Materials and Methods). During experiments, the sulfide concentration (47), salinity, oxygen, and temperature were monitored continuously.
Specimen Fixation and Preparation.
At the end of each experiment, the entire water (28 mL) of the pressure vessels for SRP incubations was filtered (Millipore; GTTP 0.22 µm). Incubated trophosome, glass coverslips, and filters were fixed for fluorescence in situ hybridization in 100% ethanol or 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde, and trophosome was embedded in LR White resin [London Resin (30)]. One-micrometer semithin sections were cut using a Leica EM UC7 microtome. For transmission electron microscopy, incubated trophosome was fixed in 5% (wt/vol) glutaraldehyde, 4% (vol/vol) formaldehyde, embedded in low-viscosity resin (Agar Scientific), and cut into 70-nm ultrathin sections (SI Materials and Methods).
Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization and Transmission Electron Microscopy.
FISH was performed as previously described (30). As a positive control, glass coverslips and filter pieces were hybridized simultaneously with the probe RifTO445 (short symbiont-specific probe) (30) and the general bacterial probe mixes EUB338 I, II, and III (Table S1). The nonsense probe NON-388 EUB was used with the same fluorescence label as the probes on a separate coverslip or on a filter piece of the same treatment as a negative control. DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) was used as a general DNA counterstain. Simultaneous hybridizations of host probe, symbiont-specific probe, and general bacterial probe mix were carried out at 35% (vol/vol) formamide concentration.
All filters and glass coverslips were analyzed with the Riftia host probe RP1752 (Table S1) with a Zeiss Axio Imager epifluorescence microscope. Additionally, filtered water sampled before the experiments was checked by FISH and 16S rRNA gene PCR (SI Materials and Methods) using the symbiont-specific probe RifTO445 and the primers RifTO44 and RifTO445, respectively (30, 34). For TEM investigations, 30 randomly selected pictures were taken from the central and median lobule zones (43) of each trophosome with a Zeiss EM 902 transmission electron microscope. The average of symbiont counts for each replicate and each treatment, as well as the percentages compared with the freshly fixed trophosome under initial conditions taken as 100%, is listed in Table S2 (Fig. S3).
Counting and Statistical Analyses.
Whole-glass coverslips and filters were investigated for symbiont density and proliferation (estimated by the frequency of dividing cells). All symbiont cells stained simultaneously by the symbiont-specific probe, the EUB338 probe mix, and DAPI were counted on 1.125 mm2 of three glass coverslips each and on 0.156 mm2 of one filter, containing all the water from the incubation vessel. Bacteria other than the symbiont (positive with EUB338 probe mix, negative with symbiont-specific probe) were also counted. To test whether the bacteria had an influence on the recruitment behavior of Endoriftia, we used the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test (P < 0.01). To test for differences between treatments and time in density of FDC of symbionts on coverslips and in the water and of symbiont decay in numbers in fresh and incubated trophosome (Fig. S3 and Table S2), we used the Kruskal–Wallis test (P < 0.01) for several independent samples to compare the means of more than one dataset. To compare each of the treatments, time of incubation, and symbiont decay in number, we used the multiple comparison post hoc Tamhane test for unequal variances (P < 0.01) in SPSS 22.0 (IBM).
Symbiont Release/Recruitment Model.
To estimate how many symbionts may escape after host death and may colonize surfaces in nature, we took the mean density of symbionts we found after half a day under deep-sea conditions on a coverslip and extrapolated this density to the entire inner surface of the incubation vessel (5772.7 mm2) and related the 0.4 g incubated trophosome to the mean symbiont density (3.7 × 109 g−1 trophosome) (36) to the mean trophosome weight (15.3 ± 4.9% of total host’s wet weight) (60) in a tubeworm with 20 g wet weight (35). To estimate the impact of symbiont release after the waning of vent flux, we extrapolated the minimal release from one worm to the ranges of tubeworm clumps (11 individuals in a small clump covering 0.02 m2 basalt to 2,000 individuals⋅m−2 in a large clump) (58, 59) reported from this vent region.
SI Materials and Methods
Monitoring Discrete Tubeworm Clumps in Situ.
During four cruises with the research vessel (R/V) Atlantis and the human-occupied vehicle (HOV) Alvin in October/November 2006, November/December 2006, November 2007, and December 2009, colonization devices (for a different succession study) were deployed in one patch at the sites Sketchy (9°50.06′N, 104°17.44′W, 2,506 m) and P-vent (9°50.27′N, 104°17.47′W, 2,508 m) each and in two patches at the vent site Tica ∼11 m apart (9°50.41′N, 104°17.5′W, 2,512 m) (Table S3). The colonization of the foundation species Riftia and Tevnia and their health were monitored with live observations, videos, and collection of colonization devices and tubeworms. Especially for small tubeworms not visible in the videos, we checked viability using this approach. We used markers to ensure that we were monitoring the same clumps over time.
Collections of Vestimentiferans and High-Pressure Incubations.
Vestimentiferan tubeworms were collected by the R/V L’Atalante with the DSV Nautile in May 2010 and by the R/V Atlantis and remotely-operated vehicle (ROV) Jason in October 2011 at the hydrothermal vent sites Tica and north of P-Vent at the East Pacific Rise. Tubeworms were collected at the end of each dive, transported to the surface aboard the ship within 1.5 h, and dissected and prepared for the incubations within 15 min. To follow the symbiont escape process, we used Plexiglas [poly(methyl methacrylate)] custom-designed symbiont recruitment plates (SRPs) (3.5 cm × 3.5 cm) equipped with glass coverslips (5-mm-diameter, 19.635 mm2 total coverslip area) in high-pressure vessels (3.5 cm inside diameter × 3.5 cm inside height) with 0.2 µm sterile-filtered seawater at 4 °C without flow (short deep-sea conditions). To avoid contamination by repeated oxygen measurements, we used a parallel set of chambers to measure the oxygen concentration at the beginning (171.6 ± 0.5 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen) and end of each experiment (0.5 d: 147.1 ± 1.4; 1 d: 121.1 ± 0.8; 2 d: 90.0 ± 0.6; 6 d: 17.1 ± 0.3 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen). Simulated vent condition (short vent conditions) were run at a continuous flow at 22.4 ± 0.6 °C, 280 ± 48 µmol⋅L−1 ∑H2S [i.e., the sum of all forms of dissolved sulfide; short sulfide (46)] and 106 ± 29 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen to approximate habitat conditions for thriving Riftia (46–48) and previous maintenance conditions (49). Approximately 0.4 g wet weight freshly dissected trophosome was filled but not squeezed into microporous specimen capsules (inside diameter: 8 mm; inside height: 9 mm; pore size: 120–200 µm) and incubated in triplicate (three different specimens incubated in different high-pressure incubation vessels) for each treatment of deep-sea and vent conditions for 0.5, 1, and 2 d each. The longer 6-d incubations under simulated vent and deep-sea conditions were done in duplicate. In addition, deep-sea incubations were also run for 8 and 10 d once. As controls, trophosome pieces were fixed in 100% ethanol or frozen in liquid nitrogen to kill symbionts before incubation under deep-sea conditions (4 °C, 171.6 ± 0.5 µmol⋅L−1 initial oxygen concentration and 135 µmol⋅L−1 oxygen after 1 d of incubation) for 0.5 and 1 d once.
Specimen Fixation and Preparation.
At the end of each experiment, the entire water (28 mL) of the pressure vessels for SRP incubations was filtered (Millipore; Isopore membrane polycarbonate filter, 25-mm-diameter, GTTP 0.22 µm). Incubated trophosome, glass coverslips, and filters were fixed for FISH in 100% ethanol or in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde, 0.01 M PBS (pH 7.4) containing 10% (wt/vol) sucrose at 4 °C for 12 h, washed in 0.01 M PBS three times, and dehydrated in ethanol, and trophosome was embedded in LR White resin (London Resin) and cut into 1-µm semithin sections using a Leica EM UC7 Ultramicrotome. For transmission electron microscopy (TEM), incubated trophosome was fixed in 5% (wt/vol) glutaraldehyde, 4% (vol/vol) formaldehyde in 0.08 M sodium phosphate buffer, embedded in low-viscosity resin medium-grade (Agar Scientific), and cut into 70-nm ultrathin sections using a Leica EM UC7 Ultramicrotome.
Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization and Transmission Electron Microscopy.
FISH was performed as previously described (30). Glass coverslips were hybridized upright from both sides in a silicone grid holder pad (Ted Pella), and filter pieces were placed on a slide for hybridization. Glass coverslips and filter pieces were hybridized simultaneously with the probe RifTO445 (short symbiont-specific probe), specific for the 16S rRNA phylotype of the endosymbiont of Riftia, Tevnia jerichonana, and Oasisia alvinae, called Rif/Tev/Oas symbiont (30), labeled with either FITC or Cy3 and the general bacterial probe mix EUB338 I, II, III labeled with either Cy3 or FITC. Simultaneously, hybridizations of host probe, symbiont-specific probe, and general bacterial probe mix were carried out at 35% (vol/vol) formamide concentration (Table S1). Additionally, filtered water sampled before the experiments was checked by FISH and 16S rRNA gene PCR using the symbiont-specific probe RifTO445 and the primers RifTO44 and RifTO445, respectively (30, 34). PCR reactions were carried out by an initial 3-min denaturation at 95 °C, 35 cycles of 30-s denaturation at 95 °C, 30-s annealing at 50 °C, 45-s extension at 72 °C, and a final extension for 10 min at 72 °C in a 50-µL reaction with 0.2 mM dNTPs, 0.02 U/µL Taq polymerase, 0.5 µM primers, 2 mM MgCl2 (Fermentas), 0.01 mg/mL BSA (Invitrogen) with an annealing temperature of 50 °C and extension time of 45 s.
Currently, the RifTO445 probe fully matches 11 sequences in the SILVA high-quality ribosomal RNA database (69), with most of the sequences originating from the trophosome of tubeworms or free-living samples from tubeworm habitats. It should be noted that other probe bacteria pose as target site including a few uncultured gammaproteobacteria and some uncultured Neisseriaceae/Uruburella betaproteobacteria from nonvent environments, which will most likely not interfere with our experiments, as the seawater used for the incubations was filtered with a 0.2-µm filter prior to incubations. For TEM investigations, ultrathin sections were stained with 0.5% uranyl acetate or 2.5% (wt/vol) gadolinium and 3% (wt/vol) lead citrate. To analyze the symbiont decay in the incubated trophosome, three different trophosome samples from three specimens per treatment were analyzed using 30 randomly selected pictures taken from the central and median lobule zones (43) of each trophosome with a Zeiss EM 902 transmission electron microscope.
Counting and Statistical Analyses.
Whole-glass coverslips and filters were investigated for symbiont density and proliferation (estimated by FDC). Bacteria other than the symbiont (positive with EUB338 probe mix, negative with symbiont-specific probe) were also counted. Fixation medium and bacterial contaminations had no influence on the density of symbionts on coverslips over time, analyzed by the Kruskal–Wallis test for several independent samples (P < 0.01). To compare each of the treatments, time of incubations, and the symbiont decay in number, we used the multiple comparison post hoc Tamhane test for unequal variances (P < 0.01) after applying the Kruskal–Wallis (P < 0.01) test for several independent samples.
Acknowledgments
We thank the captains and crews of the R/V Atlantis and R/V L’Atalante, the crews of the submersibles Alvin and Nautile and the ROV Jason, and the chief scientists F. Lallier, J. Ledwell, L. Mullineaux, S. Nooner, and A. Thurnherr for their support throughout several cruises, and the Core Facility of Cell Imaging and Ultrastructure at the University of Vienna for technical advice. We gratefully acknowledge C. Hauert, E. G. Ruby, and the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on the manuscript. This work was funded by European Marie Curie Network Symbiomics 264774 Seventh Framework Program (FP7)-PEOPLE-2010-International Training Network (ITN) (granted to M.B. and M.W.) and Austrian Science Fund P20282-B17 (to M.B.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1501160112/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Sachs JL, Mueller UG, Wilcox TP, Bull JJ. The evolution of cooperation. Q Rev Biol. 2004;79(2):135–160. doi: 10.1086/383541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.West SA, Griffin AS, Gardner A. Evolutionary explanations for cooperation. Curr Biol. 2007;17(16):R661–R672. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gardner A, Foster KR. The evolution and ecology of cooperation—History and concepts. In: Korb J, Heinze J, editors. Ecology of Social Evolution. Springer; Berlin: 2008. pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Douglas AE. The Symbiotic Habit. Princeton Univ Press; Princeton, NJ: 2010. Vol 51, pp 197–198. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Leimar O, Hammerstein P. Cooperation for direct fitness benefits. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010;365(1553):2619–2626. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Trivers RL. The evolution of reciprocal altruism. Q Rev Biol. 1971;46(1):35–57. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Frank SA. Genetics of mutualism: The evolution of altruism between species. J Theor Biol. 1994;170(4):393–400. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1994.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bull JJ, Rice WR. Distinguishing mechanisms for the evolution of co-operation. J Theor Biol. 1991;149(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Noë R, Hammerstein P. Biological markets: Supply and demand determine the effect of partner choice in cooperation, mutualism and mating. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 1994;35(1):1–11. [Google Scholar]
- 10.West SA, Kiers ET, Denison RF. Sanctions and mutualism stability: When should less beneficial mutualists be tolerated? J Evol Biol. 2002;15:830–837. [Google Scholar]
- 11.West SA, Kiers ET, Simms EL, Denison RF. Sanctions and mutualism stability: Why do rhizobia fix nitrogen? Proc Biol Sci. 2002;269(1492):685–694. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2001.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Archetti M, et al. Economic game theory for mutualism and cooperation. Ecol Lett. 2011;14(12):1300–1312. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bright M, Bulgheresi S. A complex journey: Transmission of microbial symbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8(3):218–230. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Doebeli M, Knowlton N. The evolution of interspecific mutualisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95(15):8676–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.15.8676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nowak MA, May RM. Evolutionary games and spatial chaos. Nature. 1992;359:826–829. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yamamura N, Higashi M, Behera N, Yuichiro Wakano J. Evolution of mutualism through spatial effects. J Theor Biol. 2004;226(4):421–428. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2003.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hamilton WD. Altruism and related phenomena, mainly in social insects. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 1972;3:193–232. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wilkinson DM, Sherratt TN. Horizontally acquired mutualisms, an unsolved problem in ecology? Oikos. 2001;92(2):377–384. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Herre EA, Knowlton N, Mueller UG, Rehner SA. The evolution of mutualisms: Exploring the paths between conflict and cooperation. Trends Ecol Evol. 1999;14(2):49–53. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5347(98)01529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Genkai-Kato M, Yamamura N. Evolution of mutualistic symbiosis without vertical transmission. Theor Popul Biol. 1999;55(3):309–323. doi: 10.1006/tpbi.1998.1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sundberg L-R, Kunttu HM, Valtonen ET. Starvation can diversify the population structure and virulence strategies of an environmentally transmitting fish pathogen. BMC Microbiol. 2014;14(1):67. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Anttila J, Ruokolainen L, Kaitala V, Laakso J. Loss of competition in the outside host environment generates outbreaks of environmental opportunist pathogens. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e71621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee K-H, Ruby EG. Effect of the squid host on the abundance and distribution of symbiotic Vibrio fischeri in nature. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994;60(5):1565–1571. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.5.1565-1571.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lee K, Ruby EG. Symbiotic role of the viable but nonculturable state of Vibrio fischeri in Hawaiian coastal seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995;61(1):278–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.1.278-283.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Denison RF, Kiers ET. Life histories of symbiotic rhizobia and mycorrhizal fungi. Curr Biol. 2011;21(18):R775–R785. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Denison RF, Kiers ET. Lifestyle alternatives for rhizobia: Mutualism, parasitism, and forgoing symbiosis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004;237(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Oke V, Long SR. Bacteroid formation in the Rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999;2(6):641–646. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(99)00035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vincent JM. A Manual for the Practical Study of Root-Nodule Bacteria. Blackwell Scientific; Oxford: 1970. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ruby EG, Asato LM. Growth and flagellation of Vibrio fischeri during initiation of the sepiolid squid light organ symbiosis. Arch Microbiol. 1993;159(2):160–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00250277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nussbaumer AD, Fisher CR, Bright M. Horizontal endosymbiont transmission in hydrothermal vent tubeworms. Nature. 2006;441(7091):345–348. doi: 10.1038/nature04793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Feldman RA, Black MB, Cary CS, Lutz RA, Vrijenhoek RC. Molecular phylogenetics of bacterial endosymbionts and their vestimentiferan hosts. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol. 1997;6(3):268–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vrijenhoek RC. Genetics and evolution of deep-sea chemosynthetic bacteria and their invertebrate hosts. Top Geobiol. 2010;33:15–49. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gardebrecht A, et al. Physiological homogeneity among the endosymbionts of Riftia pachyptila and Tevnia jerichonana revealed by proteogenomics. ISME J. 2012;6(4):766–776. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Harmer TL, et al. Free-living tube worm endosymbionts found at deep-sea vents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008;74(12):3895–3898. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02470-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Childress JJ, Girguis PR. The metabolic demands of endosymbiotic chemoautotrophic metabolism on host physiological capacities. J Exp Biol. 2011;214(Pt 2):312–325. doi: 10.1242/jeb.049023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cavanaugh CM, Gardiner SL, Jones ML, Jannasch HW, Waterbury JB. Prokaryotic cells in the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila Jones: Possible chemoautotrophic symbionts. Science. 1981;213(4505):340–342. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4505.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Powell MA, Somero GN. Adaptations to sulfide by hydrothermal vent animals: Sites and mechanisms of detoxification and metabolism. Biol Bull. 1986;171(1):274–290. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Felbeck H, Jarchow J. Carbon release from purified chemoautotrophic bacterial symbionts of the hydrothermal vent tubeworm Riftia pachyptila. Physiol Zool. 1998;71(3):294–302. doi: 10.1086/515931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bright M, Keckeis H, Fisher CR. An autoradiographic examination of carbon fixation, transfer and utilization in the Riftia pachyptila symbiosis. Mar Biol. 2000;136(4):621–632. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bosch C, Grassé PP. Cycle partiel des bactéries chimiautotrophes symbiotiques et leur rapports avec les bactériocytes chez Riftia pachyptila Jones (Pogonophore Vestimentifère). I. Le trophosome et les bactériocytes. Sci de la Vie. 1984;299:371–376. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bosch C, Grassé PP. Cycle partiel des bactéries chimiautotrophes symbiotiques et leur rapports avec les bactériocytes chez Riftia pachyptila Jones (Pogonophore Vestimentifère). II. L’evolution des bactéries symbiotiques et des bactériocytes. Sci de la Vie. 1984;299:413–419. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bright M, Sorgo A. Ultrastructural reinvestigation of the trophosome in adults of Riftia pachyptila (Annelida, Siboglinidae) Invertebr Biol. 2003;122(4):347–368. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pflugfelder B, Cary SC, Bright M. Dynamics of cell proliferation and apoptosis reflect different life strategies in hydrothermal vent and cold seep vestimentiferan tubeworms. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;337(1):149–165. doi: 10.1007/s00441-009-0811-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bright M, Lallier FH. The biology of vestimentiferan tubeworms. Oceanog Mar Biol. 2010;48:213–266. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Etter RJ, Mullineaux L. 2001. Deep-sea communities. Marine Ecology, eds Bertness MD, Gaines S, Hay M (Sinauer, Sunderland, MA), pp 367–393.
- 46.Le Bris N, Govenar B, Le Gall C, Fisher CR. Variability of physico-chemical conditions in 9°50′N EPR diffuse flow vent habitats. Mar Chem. 2006;98(2-4):167–182. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Le Bris N, Sarradin PM, Caprais JC. Contrasted sulphide chemistries in the environment of 13°N EPR vent fauna. Deep Sea Res Part I Oceanogr Res Pap. 2003;50(6):737–747. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Le Bris N, Rodier P, Sarradin P-M, Le Gall C. Is temperature a good proxy for sulfide in hydrothermal vent habitats? Cah Biol Mar. 2006;47(4):465–470. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Girguis PR, Childress JJ. Metabolite uptake, stoichiometry and chemoautotrophic function of the hydrothermal vent tubeworm Riftia pachyptila: Responses to environmental variations in substrate concentrations and temperature. J Exp Biol. 2006;209(Pt 18):3516–3528. doi: 10.1242/jeb.02404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Vance CP, Johnson LEB, Halvorsen AM, Heichel GH, Barnes DK. Histological and ultrastructural observations of Medicago sativa root nodule senescence after foliage removal. Can J Bot. 1980;58(3):295–309. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tambalo DD, et al. Regulation of flagellar, motility and chemotaxis genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum by the VisN/R-Rem cascade. Microbiology. 2010;156(Pt 6):1673–1685. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.035386-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Robidart JC, et al. Metabolic versatility of the Riftia pachyptila endosymbiont revealed through metagenomics. Environ Microbiol. 2008;10(3):727–737. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Toner PG, Carr KE, Ferguson A, Mackay C. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic studies of human intestinal mucosa. Gut. 1970;11(6):471–481. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.6.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.D’Arceuil H, de Crespigny A. The effects of brain tissue decomposition on diffusion tensor imaging and tractography. Neuroimage. 2007;36(1):64–68. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mergaert P, et al. Eukaryotic control on bacterial cell cycle and differentiation in the Rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(13):5230–5235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600912103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Maunoury N, et al. Differentiation of symbiotic cells and endosymbionts in Medicago truncatula nodulation are coupled to two transcriptome-switches. PLoS One. 2010;5(3):e9519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Denison RF. Legume sanctions and the evolution of symbiotic cooperation by rhizobia. Am Nat. 2000;156(6):567–576. doi: 10.1086/316994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Shank TM, et al. Temporal and spatial patterns of biological community development at nascent deep-sea hydrothermal vents (9°50′N, East Pacific Rise) Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr. 1998;45(1-3):465–515. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Govenar B, et al. Epifaunal community structure associated with Riftia pachyptila aggregations in chemically different hydrothermal vent habitats. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2005;305:67–77. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fisher CR, et al. Microhabitat variation in the hydrothermal vent mussel, Bathymodiolus thermophilus, at the Rose Garden on the Galapagos Rift. Deep-Sea Res. 1988;35(10/11):1769–1791. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Goffredi SK, Girguis PR, Childress JJ, Desaulniers NT. Physiological functioning of carbonic anhydrase in the hydrothermal vent tubeworm Riftia pachyptila. Biol Bull. 1999;196(3):257–264. doi: 10.2307/1542950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Micheli F, et al. Predation structures communities at deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Ecol Monogr. 2002;72(3):365–382. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lutz RA, et al. Rapid growth at deep-sea vents. Nature. 1994;371(6499):663–664. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Soule SA, Fornari DJ, Perfit MR, Rubin KH. New insights into mid-ocean ridge volcanic processes from the 2005–2006 eruption of the East Pacific Rise, 9°46′N–9°56′N. Geology. 2007;35(12):1079–1082. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Marsh AG, Mullineaux LS, Young CM, Manahan DT. Larval dispersal potential of the tubeworm Riftia pachyptila at deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Nature. 2001;411(6833):77–80. doi: 10.1038/35075063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.McFall-Ngai MJ, Ruby EG. Symbiont recognition and subsequent morphogenesis as early events in an animal-bacterial mutualism. Science. 1991;254(5037):1491–1494. doi: 10.1126/science.1962208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Di Meo CA, et al. Genetic variation among endosymbionts of widely distributed vestimentiferan tubeworms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66(2):651–658. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.2.651-658.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gollner S, Govenar B, Fisher CR, Bright M. Size matters at deep-sea hydrothermal vents: Different diversity and habitat fidelity patterns of meio- and macrofauna. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2015;520:57–66. doi: 10.3354/meps11078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Quast C, et al. 2013. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D590–D596.
- 70.Amann RI, Krumholz L, Stahl DA. Fluorescent-oligonucleotide probing of whole cells for determinative, phylogenetic, and environmental studies in microbiology. J Bacteriol. 1990;172(2):762–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.762-770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Daims H, Brühl A, Amann R, Schleifer K-H, Wagner M. The domain-specific probe EUB338 is insufficient for the detection of all Bacteria: Development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1999;22(3):434–444. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(99)80053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Wagner M, Schleifer K-H. Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of Proteobacteria: Problems and solutions. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1992;15(4):593–600. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pradillon F, Schmidt A, Peplies J, Dubilier N. Species identification of marine invertebrate early stages by whole-larvae in situ hybridisation of 18S ribosomal RNA. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2007;333:103–116. [Google Scholar]