Abstract
“Personalized medicine” has become a generic term referring to techniques that evaluate either the host or the disease to enhance the likelihood of beneficial patient outcomes from treatment interventions. There is, however, much more to personalization of care than just identifying the biotherapeutic strategy with the highest likelihood of benefit. In its new meaning, “personalized medicine” could overshadow the individually tailored, whole-person care that is at the bedrock of what people need and want when they are ill. Since names and definitional terms set the scope of the discourse, they have the power to define what personalized medicine includes or does not include, thus influencing the scope of the professional purview regarding the delivery of personalized care. Taxonomic accuracy is important in understanding the differences between therapeutic interventions that are distinguishable in their aims, indications, scope, benefits, and risks. In order to restore the due emphasis to the patient and his or her needs, we assert that it is necessary, albeit belated, to deconflate the contemporary term “personalized medicine” by taxonomizing this therapeutic strategy more accurately as “biologically personalized therapeutics” (BPT). The scope of truly personalized medicine and its relationship to biologically personalized therapeutics is described, emphasizing that the best of care must give due recognition and emphasis to both BPT and truly personalized medicine.
Words matter. Concepts matter. Words guide us, constrain us, and help us. Concepts shape our perceptions and our imagination. An emerging concept in medicine has arrived, with its new name, new technologies, and a bright new future. But it should not be allowed to eclipse a concept of medical care that shares its name. “Personalized medicine” in its new meaning could overshadow the individually tailored, whole-person care that is at the bedrock of what people need and want when they are ill.
Without undermining the needs and potential of the new area, we wish to keep the terminology of medicine suited to the needs of patients. The era of “personalized medicine” in its new meaning seems to herald a new epoch in the care of cancer patients. Rather than having medications recommended on the basis of diagnosis and staging, “personalized medicine” suggests that tailored treatments based on assessment of biological parameters of the individual or the underlying disease can improve patient outcomes by identifying those patients most likely to benefit from specific therapies and, simultaneously, diminishing the use of medications for patients who can be predicted not to derive benefit from them (1,2). Consequently, it may reduce costs and the risk of adverse effects from ineffectual treatments, and it may prevent delays in employing alternative therapeutic options with a higher likelihood of benefit. We welcome this development.
“Personalized medicine” has become a generic term referring to techniques that evaluate either the host or the disease to enhance the likelihood of beneficial patient outcomes from treatment interventions (3). Approaches evaluating the individual patient/host include evaluation of germline polymorphisms and pharmacogenomics to better select drugs and avoid toxicity (4,5). Techniques evaluating the disease include strategies to target specific identifiable molecular targets (targeted therapy) (6–8), genomic analysis for positive or negative predictive indicators for specific therapeutic options (9–12), scanning with radiolabeled ligand probes for specific receptors (13), individualized drug selection based on sophisticated in vivo drug testing of individual patient tumor clones, for example, grown in mice avatars (14,15) or through the identification of rare altered molecules in bodily fluids to monitor disease burden and response to treatment (16). Again, we welcome the development but not the name it has chosen to purloin.
In its current incarnation, the term first appeared in the recent medical literature in the late 1990s (17,18). However, truly targeted therapy directed at the estrogen receptor in breast cancer had been introduced decades earlier. “Personalized medicine” is also sometimes called pharmacogenomics (19), theragnostics or theranostics (20), personalized molecular medicine (21), clinical proteomics (21) or individualized targeted therapy (22), stratified medicine (23), and precision medicine (24,25). Despite this burgeoning nomenclature, the term “personalized medicine” has predominated (26) and is incorporated into the title of no fewer than six medical journals (Table 1) and into the titles of dedicated sessions in major cancer conferences. Although “personalized medicine” has been largely developed for cancer care, it is also a developing area of interest in neurology (27–29), psychiatry (29,30), cardiology (31–33), pulmonology (34), rheumatology (35,36), endocrinology (37), and ophthalmology (38).
Table 1.
Medical journals with “personalized medicine” in titles
| Personalized Medicine Universe |
| Current Pharmacogenomics And Personalized Medicine |
| Journal Of Functional Informatics And Personalized Medicine |
| Journal Of Personalized Medicine |
| Personalized Medicine |
| Personalized Medicine In Oncology |
There is, however, much more to personalization of care than just identifying the biotherapeutic strategy with the highest likelihood of benefit. The lived experience of cancer is complex, and this is reflected in the tailored care needs of all persons’ suffering in all its dimensions, biological and beyond (39–44). Skilled cancer care, especially of those with advanced cancer, requires an approach that is cognizant of these diverse, personallyvspecific needs. This underscores the necessity for oncologists to develop an understanding and sensitivity to the broad scope of patient care needs, as is recognized by names of cancer centers that include terms such as “comprehensive cancer care.”
These needs include tumor control and symptom management in general, and a detailed understanding of the specific care needs, concerns, and potential complicating factors in each individual patient’s circumstances. These circumstances vary with patients’ values, cultural backgrounds, social circumstances, and/or psychological well being. The quality of the therapeutic relationship between the patient and/or family and the health care providers requires that professionals are honest, sensitive, respectful, patient, and accessible. The professional team must use these skills to understand and respond to the myriad possible ways in which patients and families cope as they deal with uncertainty and fear, sadness and/or anger, supporting them as they maintain a sense of control, find meaning, handle the emotional distress of others, and navigate their changes in self-perception (physical, family, social, sexual).
The critical importance of these issues is underscored by studies conducted to determine the content of areas for the development of tools to evaluate the needs of patients with advanced cancer (45,46) and the severity and causes of patient distress that Saunders called ‘total pain’ (47). These emphasize the importance of multiple domains, including: medical communication and information giving, psychological and emotional well being, activities of daily living, financial concerns, symptom control, spiritual concerns, and social supports and functioning (48).
This approach to personalization was highlighted by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) in an important statement “Toward Individualized Care for Patients With Advanced Cancer” (49). This special paper outlined the issues in personalizing care, the need for careful patient evaluation and nuanced counseling regarding treatment options, careful follow-up, and the early introduction of integrated palliative and supportive care. In its original use, dating back to the 1940s, the recently recoined term “personalized medicine,” refers to a whole-person approach to care (50). In contrast, the term “individualized medicine” has a more limited history, and in the three years since the ASCO Statement (49) it has received little or no attention. Indeed, in recent literature it is used interchangeably with “personalized medicine” in referring to biologically targeted therapies (22), further edging out the major bedrock concept of whole-person, tailored care.
In addition to the fact that the contemporary use of the term “personalized medicine” is too narrow, at the expense of the critical concept it used to refer to, the field sometimes exudes an overconfidence in its deliverables, which have actually been variable (some outcomes have been dramatic, others minor or inconsequential) (51,52). Furthermore, the term is sometimes used as a marketing strategy for institutions, investigations, and new medical technologies that could falsely appeal to an expectation of whole-person care.
If the term is not respectfully limited to its intent, it will have to account for potential harm insofar as its bioscience emphasis implicitly diminishes the scope of what constitutes personal medical care and the biopsychosocial complexity of personhood. This claim is supported by the observation that considerations of the individual, needs and/or distress assessment, and of all of the complex aspects of providing a comprehensive care plan are glaringly absent in the chapters, journals, reviews, and meetings dedicated to the new concept now denoted by the term “personalized medicine.” Indeed, the literature devoted to personalized medicine is characterized by a striking paucity of attention to the patient communication and decision-making issues associated with the proposal of these approaches. This shortcoming is particularly salient when considering the application of such approaches in the advanced stages of disease when disease-modifying options may be limited, quality of life and symptom burden are substantial, and life expectancy is short.
This bioscience culture of care characterized by the contemporary understanding of “personalized medicine” has not gone unnoticed by patients and patient advocacy groups. It is not that they do not want the benefits of the new technologies and the fruits of the rapid advances in the understanding of disease biology; they do and rightly so. However, they also want to be seen and treated as more than the biology of their diseases (42,44,53–58), and we want this for them too. Along with the new therapeutic approaches, they want a commitment of care that is sensitive to their complex and often changing needs as they confront the ravages of illness and the vicissitudes of treatments undertaken, in trust, with the hope of benefit and in fear of harm. They want physicians who are confident, empathetic, humane, personal, forthright, respectful, and thorough (59). These standards are mandated by credentialing bodies and increasingly addressed in medical school training programs (60–63) and have received strong endorsement in the oncology literature addressing principles of professionalism (51,64,65) and the incorporation of psychosocial issues as a core element of cancer care (66,67).
Finally, names and definitional terms are not just a matter of fussy semantics. They set the scope of the discourse (68) and have the power to define what personalized medicine includes or does not include, thus influencing the scope of the professional purview regarding the delivery of personalized care. Medicine is more than just the administration of therapeutic interventions; it incorporates pharmacological and biological therapeutics as part of a complex interpersonal intervention that constitutes medical care (69–73).
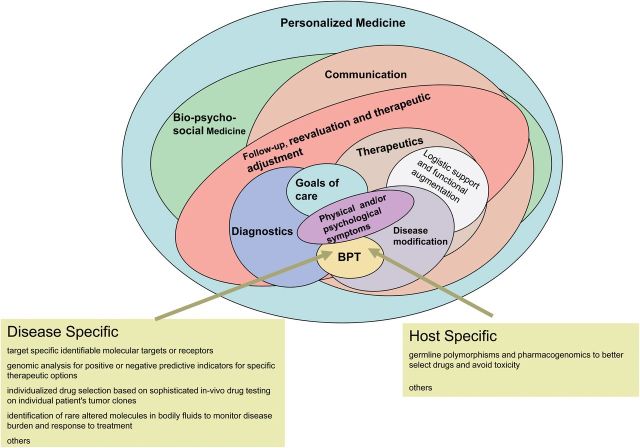
Taxonomic accuracy, understood to be critical for diagnoses, is no less important in understanding the therapeutic interventions that are distinguishable in their aims, indications, scope, benefits, and risks. In order to restore the due emphasis to the patient and their needs, we assert that it is necessary, albeit belated, to deconflate the contemporary term “personalized medicine” by taxonomizing this therapeutic strategy more accurately as “biologically personalized therapeutics” (BPT). BPT should be a part of true personalized medicine (Figure 1), but it is far from being the embodiment of it.
Figure 1.
The relationship between personalized medicine and biologically personalized therapeutics (BPT).
Table 2 sets out areas of the biopsychosocial model of medicine that must be as personalized as the genetically informed biological care. Each person has individual needs for communication, for psychological and emotional well being, social functioning, and spiritual expression and care; in very few cases would the exact same approach work for all people with a similar condition. Moreover, for each domain, there is no substitute for getting to know the person and how he or she works; without this step, an appropriate tailored approach to care is impossible. This is illustrated by considering the relative gravity of these considerations in the care of a 73-year-old woman with metastatic melanoma (Table 3).
Table 2.
The purview of personalized medicine
| Psycho social evaluation | |
| Communication and information giving preferences | |
| Psychological and emotional well being | |
| Financial concerns | |
| Spiritual concerns | |
| Social supports | |
| Goals of care | |
| Fears and concern | |
| Hopes and ambitions | |
| Disease evaluation | |
| Accurate diagnosis | |
| Relevant biological evaluation of host and disease | |
| Symptom evaluation | |
| Functional evaluation | |
| Therapeutic Personalization | |
| Agreed and relevant goals of care | |
| Effective supportive communication | |
| Evaluation of therapeutic options and preferences | |
| Disease and stage appropriate therapeutics | |
| Biologically personalized therapeutics | |
| Symptom management | |
| Supportive care | |
| Psychological | |
| Functional enhancement | |
| Support strategies: social, financial | |
| Spiritual | |
| Longitudinal care | |
| Reevaluation | |
| Therapeutic adjustments | |
Table 3.
A case for consideration: personalizing the care of a 73-year-old woman with metastatic melanoma
| Biologic personalized therapeutics |
| Mrs. M is a 73-year-old woman with metastatic melanoma with multiple pleural masses and genomics revealing an actionable B-RAF V600E mutation indicating that the disease is amenable to treatment with vemurafenib. |
| Other dimensions of personalizing medical care |
| Mrs. M is a 73-year old-widow who lives alone in a third-floor walk-up apartment. She has metastatic melanoma with multiple pleural masses that are complicated by moderate to severe chronic pain and dyspnea on exertion. Controlled release morphine tablets are providing only partial and inadequate relief of her pain, and she is distressed by constipation. She has a daughter who is able to help her on weekends. She is anxious about her future and fearful about the prospects of severe pain or suffocation at the end of life. She is aware that her disease is incurable and that her anticipated life expectancy is limited. She is interested in life-prolonging treatment but only if it has minimal risk of side effects. She is a pensioner with limited financial resources and her insurance has a 25% copayment on medications. |
This return conceptualization of personalized medicine restores due emphasis to biopsychosocial care by including communication and information giving, psychological and emotional well being, enhancing function, addressing financial concerns, symptom control, spiritual concerns, and social supports.
Indeed, the best of care must give due recognition and emphasis to both “biologically personalized therapeutics” (BPT) and truly personalized medicine.
DS (Champtions Oncology) and LS-G (Oncotype Teva) have active commercial interests in companies promoting and selling biologically personalized therapy testing. No other conflicts of interest by other authors.
References
- 1. Weston AD, Hood L. Systems biology, proteomics, and the future of health care: Toward predictive, preventative, and personalized medicine. J Proteome Res. 2004;3(2):179–196., [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ng PC, Venter JC, Murray SS, Levy S. An agenda for personalized medicine. Nature. 2009;461(7265):724–726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Schleidgen S, Klingler C, Bertram T, Rogowski WH, Marckmann G. What is personalized medicine: sharpening a vague term based on a systematic literature review. BMC Med Ethics. 2013;14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Miller CR, McLeod HL. Pharmacogenomics of cancer chemotherapy-induced toxicity. J Support Oncol. 2007;5(1):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Sweeney BP. Pharmacogenomics and anaesthesia: explaining the variability in response to opiates. European J Anaesthesiol. 2007;24(3):209–212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Ross JS, Slodkowska EA, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, Ravdin PM, Hortobagyi GN. The HER-2 receptor and breast cancer: Ten years of targeted anti-HER-2 therapy and personalized medicine. Oncologist. 2009;14(4):320–368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Roberts PJ, Stinchcombe TE, Der CJ, Socinski MA. Personalized medicine in non-small-cell lung cancer: Is KRAS a useful marker in selecting patients for epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy? J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(31):4769–4777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Dietel M, Sers C. Personalized medicine and development of targeted therapies: the upcoming challenge for diagnostic molecular pathology. A review. Virchows Archiv. 2006;448(6):744–755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Paik S, Tang G, Shak S, et al. Gene expression and benefit of chemotherapy in women with node-negative, estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(23):3726–3734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15(4):415–453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Eberhard DA, Johnson BE, Amler LC, et al. Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor and in KRAS are predictive and prognostic indicators in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy alone and in combination with erlotinib. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(25):5900–5909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Khambata-Ford S, Garrett CR, Meropol NJ, et al. Expression of epiregulin and amphiregulin and K-ras mutation status predict disease control in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with cetuximab. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(22):3230–3237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Serpe L, Gallicchio M, Canaparo R, Dosio F. Targeted treatment of folate receptor-positive platinum-resistant ovarian cancer and companion diagnostics, with specific focus on vintafolide and etarfolatide. Pharmacogenomics Pers Med. 2014;7:31–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Malaney P, Nicosia SV, Dave V. One mouse, one patient paradigm: New avatars of personalized cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2013;344(1):1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Ruano G. Quo vadis personalized medicine? Personalized medicine. 2004;1(1):1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Dawson S-J, Tsui DW, Murtaza M, et al. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to monitor metastatic breast cancer. New Engl J Med. 2013;368(13):1199–1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Marshall A. Laying the foundations for personalized medicines. Nature Biotechnol. 1998;16:6–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Langreth R, Waldholz M. New era of personalized medicine: targeting drugs for each unique genetic profile. Oncologist. 1999;4(5):426–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Mancinelli L, Cronin M, Sadee W. Pharmacogenomics: the promise of personalized medicine. AAPS PharmSci. 2000;2(1):E4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Pene F, Courtine E, Cariou A, Mira J-P. Toward theragnostics. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(1):S50-–S58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Liotta LA, Kohn EC, Petricoin EF. Clinical proteomics: personalized molecular medicine. JAMA. 2001;286(18):2211–2214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Weller M, Stupp R, Hegi M, Wick W. Individualized targeted therapy for glioblastoma: fact or fiction? Cancer J. 2012;18(1):40–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Trusheim MR, Berndt ER, Douglas FL. Stratified medicine: strategic and economic implications of combining drugs and clinical biomarkers. Nature Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6(4):287–293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Mirnezami R, Nicholson J, Darzi A. Preparing for precision medicine. New Engl J Med. 2012;366(6):489–491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. National Cancer Institutes. Personalized Medicine. Available at: http://www.cancer.gov/dictionary?cdrid=561717. Accessed August 20, 2014.
- 26. Simmons LA, Dinan MA, Robinson TJ, Snyderman R. Personalized medicine is more than genomic medicine: confusion over terminology impedes progress towards personalized healthcare. Personalized Med. 2012;9(1):85–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Wurtman RJ. Personalized medicine strategies for managing patients with parkinsonism and cognitive deficits. Metabolism. 2013;62 Suppl 1:S27-–S29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Verweij CL, Vosslamber S. Relevance of the type I interferon signature in multiple sclerosis towards a personalized medicine approach for interferon-beta therapy. Discov Med. 2013;15(80):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Costa e Silva JA. Personalized medicine in psychiatry: new technologies and approaches. Metabolism. 2013;62 Suppl 1:S40-–S44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Ozomaro U, Wahlestedt C, Nemeroff CB. Personalized medicine in psychiatry: problems and promises. BMC Med. 2013;11:132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Tantry US, Gurbel PA. The next 10 years in personalized medicine in cardiology. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2013;11(8):933–935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Lenfant C. Prospects of personalized medicine in cardiovascular diseases. Metabolism. 2013;62 Suppl 1:S6-–S10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. de Groote P, Pinet F, Bauters C. New technologies, new therapies: toward personalized medicine in heart failure patients? Eur Heart J. 2013;34(9):636–637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Poon AH, Hamid Q. Asthma endotypes: the right direction towards personalized medicine for asthma. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012;8(7):595–596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Burmester GR, Feist E. [Personalized medicine in rheumatology - hype or hope?]. Z Rheumatol. 2013;72(1):10–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Sawitzke AD. Personalized medicine for osteoarthritis: where are we now? Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013;5(2):67–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Jia W. Personalized medicine of type 2 diabetes. Front Med. 2013;7(1):1–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Souied EH, Leveziel N. Toward personalized medicine for age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;154(3):427–428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Soothill K, Morris SM, Thomas C, Harman JC, Francis B, McIllmurray MB. The universal, situational, and personal needs of cancer patients and their main carers. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2003;7(1):5–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Aranda S, Schofield P, Weih L, et al. Mapping the quality of life and unmet needs of urban women with metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Care. 2005;14(3):211–222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. White K, D’Abrew N, Katris P, O’Connor M, Emery L. Mapping the psychosocial and practical support needs of cancer patients in Western Australia. Eur J Cancer Care. 2012;21(1):107–116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Sanson-Fisher R, Girgis A, Boyes A, Bonevski B, Burton L, Cook P. The unmet supportive care needs of patients with cancer. Cancer. 2000;88(1):226–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Bonevski B, Sanson-Fisher R, Girgis A, Burton L, Cook P, Boyes A. Evaluation of an instrument to assess the needs of patients with cancer. Cancer. 2000;88(1):217–225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Soothill K, Morris SM, Harman J, Francis B, Thomas C, McIllmurray MB. The significant unmet needs of cancer patients: probing psychosocial concerns. Support Care Cancer. 2001;9(8):597–605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Rainbird KJ, Perkins JJ, Sanson-Fisher RW. The Needs Assessment for Advanced Cancer Patients (NA-ACP): A measure of the perceived needs of patients with advanced, incurable cancer. A study of validity, reliability and acceptability. Psychooncology. 2005;14(4):297–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Akizuki N, Yamawaki S, Akechi T, Nakano T, Uchitomi Y. Development of an Impact Thermometer for use in combination with the Distress Thermometer as a brief screening tool for adjustment disorders and/or major depression in cancer patients. J Pain Sympt Manage. 2005;29(1):91–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Saunders C. The philosophy of terminal cancer care. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1987;16(1):151–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Emanuel EJ, Emanuel LL. The promise of a good death. Lancet. 1998;351(Suppl 2):SII21-–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Peppercorn JM, Smith TJ, Helft PR, et al. American society of clinical oncology statement: toward individualized care for patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(6):755–760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Ryle JA. Social medicine: its meaning and its scope. Br Med J. 1943;2(4324):633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Surbone A. Professionalism in global, personalized cancer care: restoring authenticity and integrity. American Society of Clinical Oncology educational book / ASCO American Society of Clinical Oncology Meeting. 2013;33:152–156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Chabner BA, Ellisen LW, Iafrate AJ. Personalized Medicine: Hype or Reality. Oncologist. 2013;18(6):640–643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Puts MT, Papoutsis A, Springall E, Tourangeau AE. A systematic review of unmet needs of newly diagnosed older cancer patients undergoing active cancer treatment. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20(7):1377–1394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Ng R, Verkooijen HM, Ooi LL, Koh WP. Unmet psychosocial needs among cancer patients undergoing ambulatory care in Singapore. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20(5):1049–1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Molassiotis A, Wilson B, Blair S, Howe T, Cavet J. Unmet supportive care needs, psychological well-being and quality of life in patients living with multiple myeloma and their partners. Psychooncology. 2010;20(1):88–97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Pigott C, Pollard A, Thomson K, Aranda S. Unmet needs in cancer patients: development of a supportive needs screening tool (SNST). Support Care Cancer. 2009;17(1):33–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Palmer S, Mitchell A, Thompson K, Sexton M. Unmet needs among adolescent cancer patients: a pilot study. Palliat Support Care. 2007;5(2):127–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Salminen E, Vire J, Poussa T, Knifsund S. Unmet needs in information flow between breast cancer patients, their spouses, and physicians. Support Care Cancer. 2004;12(9):663–668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Bendapud NM, Berry LL, Frey KA, Parish JT, Rayburn WL. Patients’ perspectives on ideal physician behaviors. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81(3):338–344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Weinberger SE, Smith LG, Collier VU, Educ Comm Am Coll P. Redesigning training for internal medicine. Ann Int Medicine. 2006;144(12):927–932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Cruess RL, Cruess SR. Teaching professionalism: general principles. Med Teach. 2006;28(3):205–208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Suchman AL, Williamson PR, Litzelman DK, et al. Toward an informal curriculum that teaches professionalism - Transforming the social environment of a medical school. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19(5):501–504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Arnold L. Assessing professional behavior: Yesterday, today, and tomorrow. Acad Med. 2002;77(6):502–515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Abeloff MD, Reynolds PP. Professionalism and cancer care. Bull AmerColl Surg. 1994;79(5):12–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Pentz RD, Joffe S, Emanuel EJ, Schnipper LE, Haskell CM, Tannock IF. ASCO core values. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(36):5780–5782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Jacobsen PB, Holland JC, Steensma DP. Caring for the whole patient: the science of psychosocial care. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(11):1151–1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Jacobsen PB, Wagner LI. A new quality standard: The integration of psychosocial care into routine cancer care. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(11):1154–1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Good BJ, Good M-JDV. The semantics of medical discourse. In: Mendelsohn E, Elkana Y, editors. Sciences and Cultures: Anthropological and Historical Studies of the Sciences. 5 ed: Springer; 1981:177–212. [Google Scholar]
- 69. Cassell EJ. The nature of suffering and the goals of medicine. N Engl J Med. 1982;306(11):639–645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Cassell E. The nature of suffering and the goals of medicine: Oxford University Press; US; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 71. Pellegrino ED. Professionalism, profession and the virtues of the good physician. Mt Sinai J Med. 2002;69(6):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Pellegrino ED. The human person, the physician, and the physician’s ethics. Linacre Q. 1995;62(1):74–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Pellegrino ED. The personal ethics of the physician: curing medicine from within. Mt Sinai J Med. 1991;58(5):452–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]