Abstract
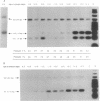
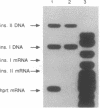
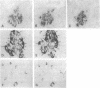
In the mouse, insulin is produced from two similar but nonallelic genes that encode proinsulins I and II. We have investigated expression of these two genes during mouse embryonic development, using a PCR to detect the two gene transcripts and immunocytochemistry to visualize the two corresponding proteins. At appearance of the dorsal pancreatic anlage at day 9.5 of gestation, both mRNAs could be detected in the embryos, and both proteins were present together in the same cells of the developing pancreas. At days 9.5 and 10.5, when the ventral anlage appears, there were fewer proinsulin II mRNAs than proinsulin I mRNAs. At day 12.5 this ratio was reversed. Proinsulin II mRNA, but not proinsulin I mRNA, could be detected at day 8.5 in the prepancreatic embryo. Proinsulin II mRNA, but not proinsulin I mRNA, was also found in the heads of embryos at day 9.5 and at all later stages studied. These results indicate that the two proinsulin genes are regulated independently, at least in part. They also suggest that insulin might play a role as a growth factor in the developing mouse brain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch N. P., Christie D. L., Renwick A. G. Proinsulin-like material in mouse foetal brain cell cultures. FEBS Lett. 1984 Mar 26;168(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume N., Petersen J. S., Andersen L. C., Kofod H., Dyrberg T., Michelsen B. K., Serup P., Madsen O. D. Immature transformed rat islet beta-cells differentially express C-peptides derived from the genes coding for insulin I and II as well as a transfected human insulin gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):299–307. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd G. C., Pansky B., Cordell B. Detection of insulin synthesis in mammalian anterior pituitary cells by immunohistochemistry and demonstration of insulin-related transcripts by in situ RNA-DNA hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 May;34(5):673–678. doi: 10.1177/34.5.2422249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe D. T., Tsai M. J. Mutagenesis of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region defines sequences important for expression in HIT cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1784–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deltour L., Leduque P., Paldi A., Ripoche M. A., Dubois P., Jami J. Polyclonal origin of pancreatic islets in aggregation mouse chimaeras. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):1115–1121. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Carnaghi L. R. Selective expression and developmental regulation of the ancestral rat insulin II gene in fetal liver. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1363–1369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Carnaghi L. R. The two nonallelic rat insulin mRNAs and pre-mRNAs are regulated coordinately in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3845–3849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Carnaghi L. Rat insulin II gene expression by extraplacental membranes. A non-pancreatic source for fetal insulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9462–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittes G. K., Rutter W. J. Onset of cell-specific gene expression in the developing mouse pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim N. Z., Permutt M. A. Identical transcription initiation sites for proinsulin messenger ribonucleic acid in three insulin-expressing tissues. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1710–1715. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera P. L., Huarte J., Sanvito F., Meda P., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. Embryogenesis of the murine endocrine pancreas; early expression of pancreatic polypeptide gene. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1257–1265. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyner S., Smith R. M., Schultz G. A. Temporally regulated expression of insulin and insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in early mammalian development. Bioessays. 1989 Dec;11(6):171–176. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J., Edlund T. Individual protein-binding domains of the insulin gene enhancer positively activate beta-cell-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):823–827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koranyi L., Permutt M. A., Chirgwin J. M., Giddings S. J. Proinsulin I and II gene expression in inbred mouse strains. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1895–1902. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduque P., Paulin C., Chayvialle J. A., Dubois P. M. Immunocytological evidence of motilin- and secretin-containing cells in the human fetal gastro-entero-pancreatic system. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;218(3):519–527. doi: 10.1007/BF00210111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde S., Nielsen J. H., Hansen B., Welinder B. S. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic analyses of insulin biosynthesis in isolated rat and mouse islets. J Chromatogr. 1989 Jan 13;462:243–254. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)91351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muglia L., Locker J. Extrapancreatic insulin gene expression in the fetal rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3635–3639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau K., Muglia L., Locker J. Insulin-gene expression in extrafetal membranes of rats. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38(1):39–43. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano J., Bevins C. L., Young S. W., de Pablo F. Insulin gene expression in chicken ontogeny: pancreatic, extrapancreatic, and prepancreatic. Dev Biol. 1989 Apr;132(2):410–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., de Pablo F., Moore C. A., Roth J. Two nonallelic insulin genes in Xenopus laevis are expressed differentially during neurulation in prepancreatic embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7679–7683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaventi R., Antica M., Pavelić K. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) in early mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1990 Mar;108(3):491–495. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Methods for the assessment of peptide precursors. Studies insulin biosynthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:326–345. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. M., Schaefer I. M., Villa-Komaroff L., Chirgwin J. M. Characterization of the two nonallelic genes encoding mouse preproinsulin. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(4):305–312. doi: 10.1007/BF02100639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Poon D., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific expression of the rat insulin II gene is controlled by positive and negative cellular transcriptional elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3253–3259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widness J. A., Goldman A. S., Susa J. B., Oh W., Schwartz R. Impermeability of the rat placenta to insulin during organogenesis. Teratology. 1983 Dec;28(3):327–332. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420280304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Sabata V., Frerichs H., Stubbe P. Evidence for the impermeability of the human placenta for insulin. Horm Metab Res. 1969 Nov;1(6):274–275. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd Periventricular hypothalamic cells in the rat brain contain insulin mRNA. Neuropeptides. 1986 Aug-Sep;8(2):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(86)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]