Abstract
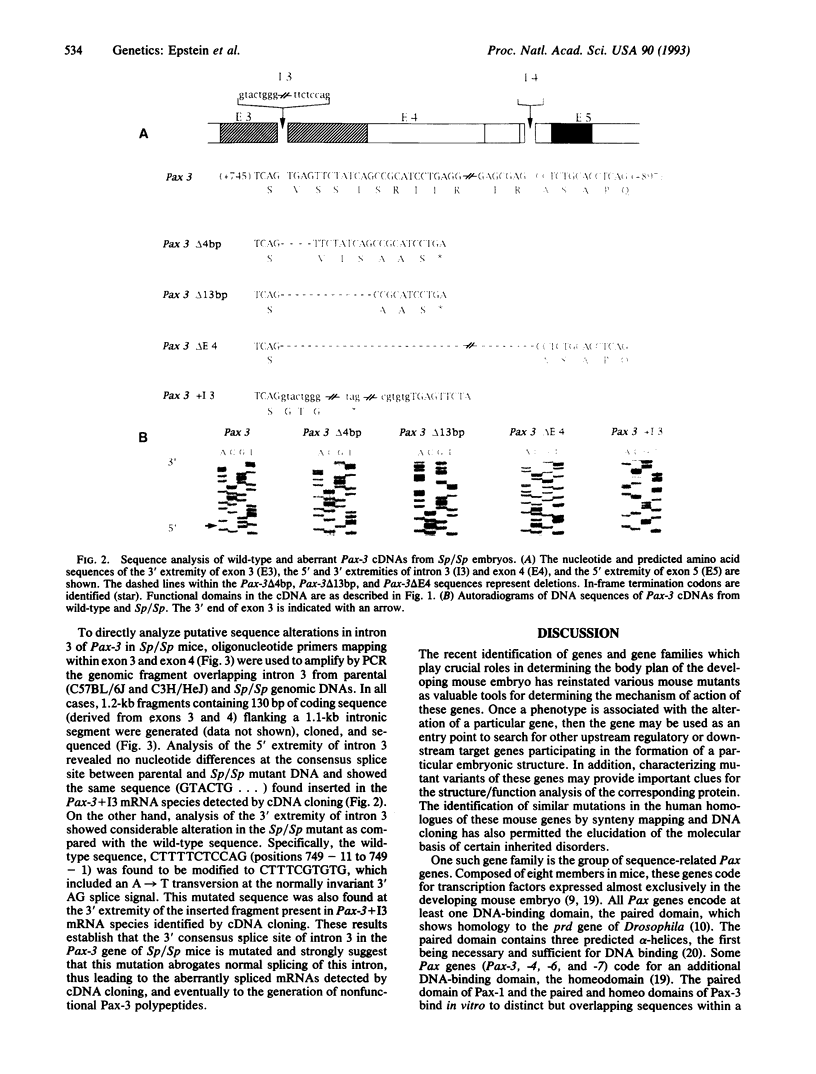
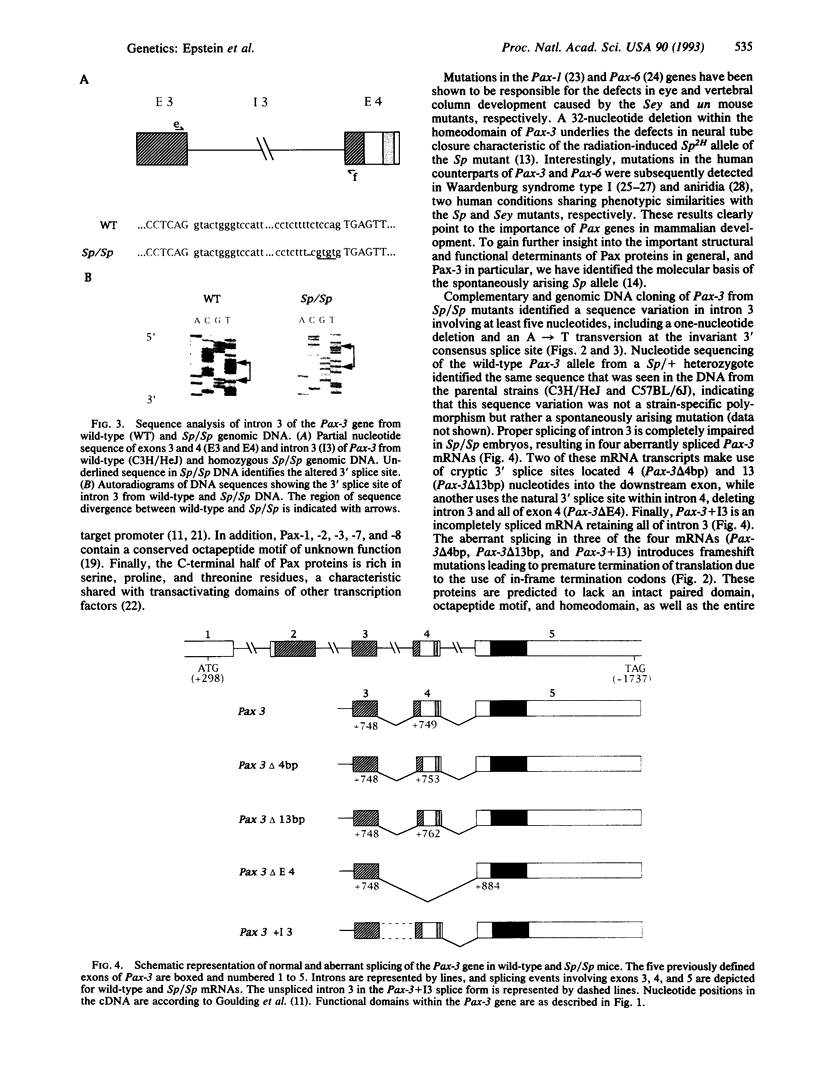
The splotch (Sp) mouse mutant displays defects in neural tube closure in the form of exencephaly and spina bifida. Recently, mutations in the Pax-3 gene have been described in the radiation-induced Spr and Sp2H alleles. This led us to examine the integrity of the Pax-3 gene and its cellular mRNA transcript in the original, spontaneously arising Sp allele. A complex mutation in the Pax-3 gene including an A-->T transversion at the invariant 3' AG splice acceptor of intron 3 was identified in the Sp/Sp mutant. This genomic mutation abrogates the normal splicing of intron 3, resulting in the generation of four aberrantly spliced mRNA transcripts. Two of these Pax-3 transcripts make use of cryptic 3' splice sites within the downstream exon, generating small deletions which disrupt the reading frame of the transcripts. A third aberrant splicing event results in the deletion of exon 4, while a fourth retains intron 3. These aberrantly spliced mRNA transcripts are not expected to result in functional Pax-3 proteins and are thus responsible for the phenotype observed in the Sp mouse mutant.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh G. F., Anagnou N. P., Shearin J., Forget B. G., Kaufman R. E. Beta-thalassemia resulting from a single nucleotide substitution in an acceptor splice site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):777–790. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. T., Hoth C. F., Amos J. A., da-Silva E. O., Milunsky A. An exonic mutation in the HuP2 paired domain gene causes Waardenburg's syndrome. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):637–638. doi: 10.1038/355637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balling R., Deutsch U., Gruss P. undulated, a mutation affecting the development of the mouse skeleton, has a point mutation in the paired box of Pax 1. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):531–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Burri M., Baumgartner S., Frigerio G., Noll M. Conservation of a large protein domain in the segmentation gene paired and in functionally related genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1033–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90818-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burri M., Tromvoukis Y., Bopp D., Frigerio G., Noll M. Conservation of the paired domain in metazoans and its structure in three isolated human genes. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Fritsch R., Fickenscher H., Deutsch U., Goulding M., Gruss P. The molecular basis of the undulated/Pax-1 mutation. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):873–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90434-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copp A. J., Brook F. A., Estibeiro J. P., Shum A. S., Cockroft D. L. The embryonic development of mammalian neural tube defects. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(5):363–403. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90037-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKIE M. M. NEW SPLOTCH ALLELES IN THE MOUSE. J Hered. 1964 May-Jun;55:97–101. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. J., Vekemans M., Gros P. Splotch (Sp2H), a mutation affecting development of the mouse neural tube, shows a deletion within the paired homeodomain of Pax-3. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz T. Defective ensheathment of motoric nerves in the Splotch mutant mouse. Acta Anat (Basel) 1990;138(3):246–253. doi: 10.1159/000146947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz T. Persistent truncus arteriosus in the Splotch mutant mouse. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1989;180(5):457–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00305120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding M. D., Chalepakis G., Deutsch U., Erselius J. R., Gruss P. Pax-3, a novel murine DNA binding protein expressed during early neurogenesis. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1135–1147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Walther C. Pax in development. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):719–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90281-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillermit H., Fanen P., Ferec C. A 3' splice site consensus sequence mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene. Hum Genet. 1990 Sep;85(4):450–453. doi: 10.1007/BF02428306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Favor J., Hogan B. L., Ton C. C., Saunders G. F., Hanson I. M., Prosser J., Jordan T., Hastie N. D., van Heyningen V. Mouse small eye results from mutations in a paired-like homeobox-containing gene. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):522–525. doi: 10.1038/354522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan T., Hanson I., Zaletayev D., Hodgson S., Prosser J., Seawright A., Hastie N., van Heyningen V. The human PAX6 gene is mutated in two patients with aniridia. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):328–332. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Murine developmental control genes. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):374–379. doi: 10.1126/science.1974085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson G., Gutman G. A. Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):203–221. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancino F., Vekemans M., Trasler D. G., Gros P. Segregation analysis reveals tight genetic linkage between the spontaneously arising neural tube defect gene splotch (Sp) and Pax-3 in an intraspecific mouse backcross. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;61(2):143–145. doi: 10.1159/000133393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Drumm M., Saulino A., Collins F. S. Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1154–1154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moase C. E., Trasler D. G. Splotch locus mouse mutants: models for neural tube defects and Waardenburg syndrome type I in humans. J Med Genet. 1992 Mar;29(3):145–151. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.3.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell R., Friedman T. B., Moeljopawiro S., Hartono, Soewito, Asher J. H., Jr A frameshift mutation in the HuP2 paired domain of the probable human homolog of murine Pax-3 is responsible for Waardenburg syndrome type 1 in an Indonesian family. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):243–247. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. Role of the 3' splice site consensus sequence in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):732–734. doi: 10.1038/317732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Porro E. B., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Scanning from an independently specified branch point defines the 3' splice site of mammalian introns. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):243–247. doi: 10.1038/342243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Read A. P., Newton V. E., Harris R., Balling R., Gruss P., Strachan T. Waardenburg's syndrome patients have mutations in the human homologue of the Pax-3 paired box gene. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):635–636. doi: 10.1038/355635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Harris E., Desplan C. The paired box encodes a second DNA-binding domain in the paired homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):594–604. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther C., Guenet J. L., Simon D., Deutsch U., Jostes B., Goulding M. D., Plachov D., Balling R., Gruss P. Pax: a murine multigene family of paired box-containing genes. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]