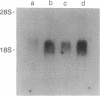
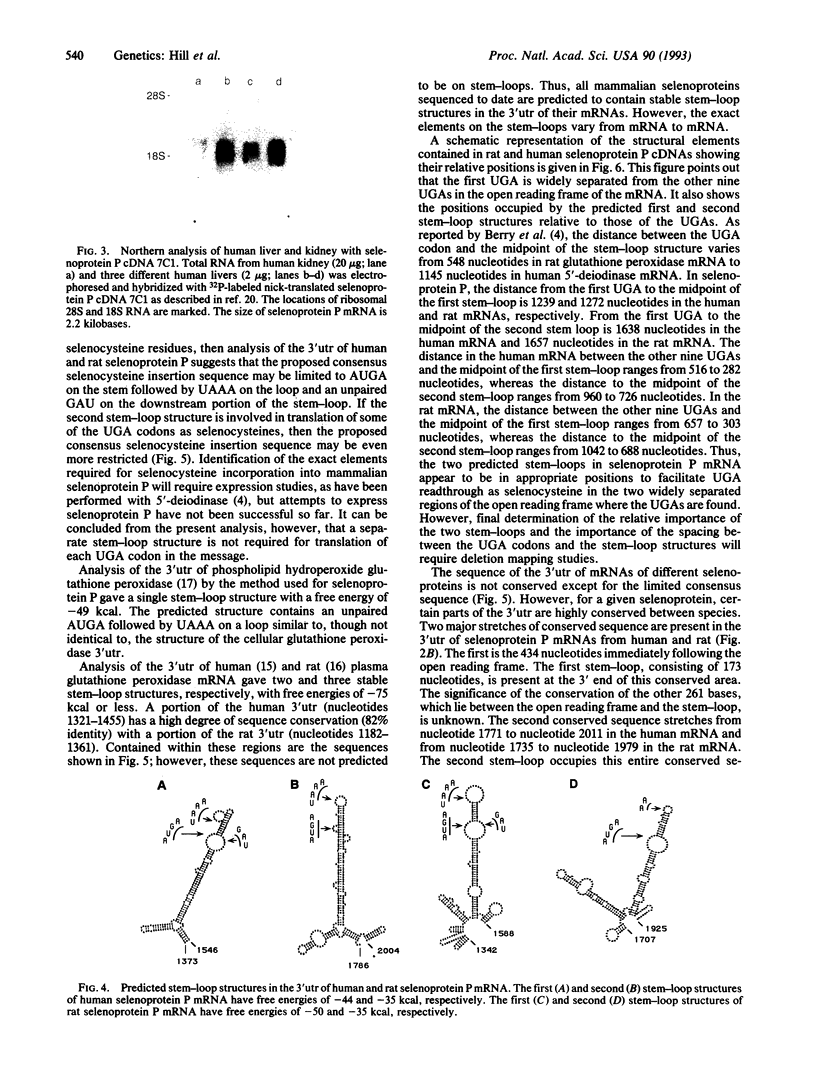
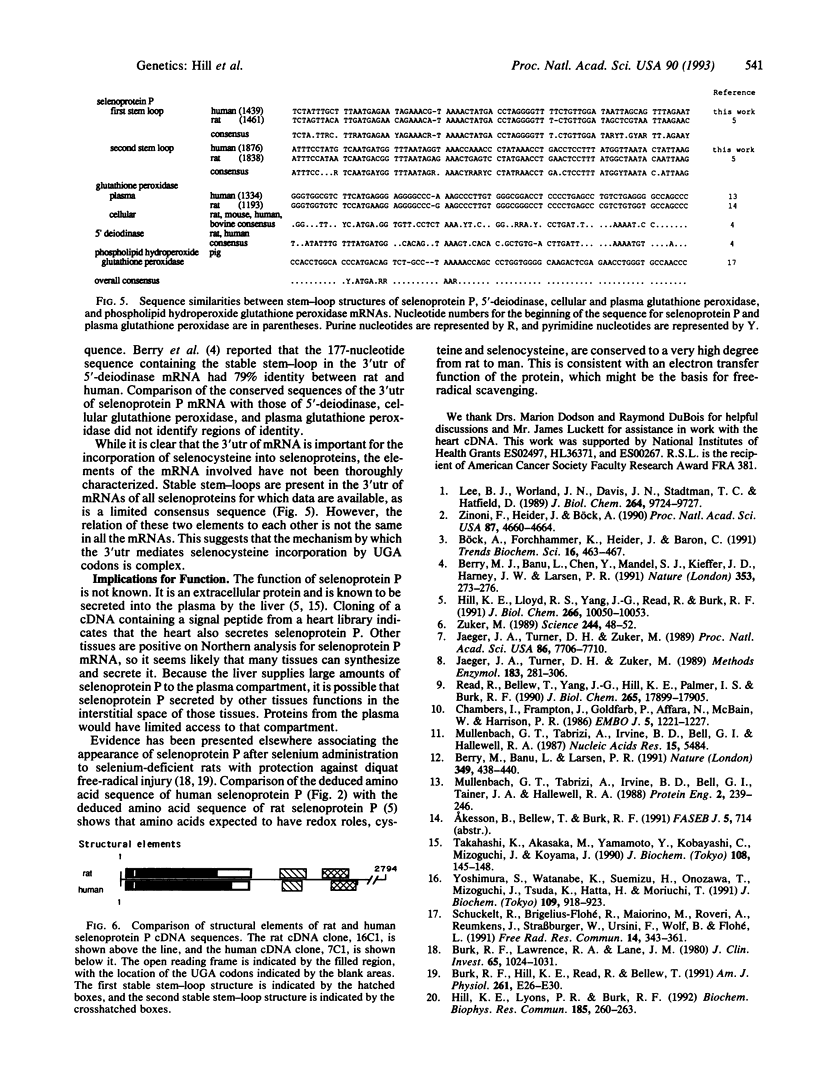
Abstract
Rat liver selenoprotein P contains 10 selenocysteine residues in its primary structure (deduced). It is the only selenoprotein characterized to date that has more than one selenocysteine residue. Selenoprotein P cDNA has been cloned from human liver and heart cDNA libraries and sequenced. The open reading frames are identical and contain a signal peptide, indicating that the protein is secreted by both organs and is therefore not exclusively produced in the liver. Ten selenocysteine residues (deduced) are present. Comparison of the open reading frame of the human cDNA with the rat cDNA reveals a 69% identity of the nucleotide sequence and 72% identity of the deduced amino acid sequence. Two regions in the 3' untranslated portion have high conservation between human and rat. Each of these regions contains a predicted stable stem-loop structure similar to the single stem-loop structures reported in 3' untranslated regions of type I iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase and glutathione peroxidase. The stem-loop structure of type I iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase has been shown to be necessary for incorporation of the selenocysteine residue at the UGA codon. Because only two stem-loop structures are present in the 3' untranslated region of selenoprotein P mRNA, it can be concluded that a separate stem-loop structure is not required for each selenocysteine residue.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Chen Y. Y., Mandel S. J., Kieffer J. D., Harney J. W., Larsen P. R. Recognition of UGA as a selenocysteine codon in type I deiodinase requires sequences in the 3' untranslated region. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):273–276. doi: 10.1038/353273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Larsen P. R. Type I iodothyronine deiodinase is a selenocysteine-containing enzyme. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):438–440. doi: 10.1038/349438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. F., Hill K. E., Read R., Bellew T. Response of rat selenoprotein P to selenium administration and fate of its selenium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):E26–E30. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.1.E26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. F., Lawrence R. A., Lane J. M. Liver necrosis and lipid peroxidation in the rat as the result of paraquat and diquat administration. Effect of selenium deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1024–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI109754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Forchhammer K., Heider J., Baron C. Selenoprotein synthesis: an expansion of the genetic code. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers I., Frampton J., Goldfarb P., Affara N., McBain W., Harrison P. R. The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1221–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill K. E., Lloyd R. S., Yang J. G., Read R., Burk R. F. The cDNA for rat selenoprotein P contains 10 TGA codons in the open reading frame. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10050–10053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill K. E., Lyons P. R., Burk R. F. Differential regulation of rat liver selenoprotein mRNAs in selenium deficiency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):260–263. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80984-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Predicting optimal and suboptimal secondary structure for RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:281–306. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. J., Worland P. J., Davis J. N., Stadtman T. C., Hatfield D. L. Identification of a selenocysteyl-tRNA(Ser) in mammalian cells that recognizes the nonsense codon, UGA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9724–9727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullenbach G. T., Tabrizi A., Irvine B. D., Bell G. I., Hallewell R. A. Sequence of a cDNA coding for human glutathione peroxidase confirms TGA encodes active site selenocysteine. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5484–5484. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullenbach G. T., Tabrizi A., Irvine B. D., Bell G. I., Tainer J. A., Hallewell R. A. Selenocysteine's mechanism of incorporation and evolution revealed in cDNAs of three glutathione peroxidases. Protein Eng. 1988 Sep;2(3):239–246. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R., Bellew T., Yang J. G., Hill K. E., Palmer I. S., Burk R. F. Selenium and amino acid composition of selenoprotein P, the major selenoprotein in rat serum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17899–17905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuckelt R., Brigelius-Flohé R., Maiorino M., Roveri A., Reumkens J., Strassburger W., Ursini F., Wolf B., Flohé L. Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase is a selenoenzyme distinct from the classical glutathione peroxidase as evident from cDNA and amino acid sequencing. Free Radic Res Commun. 1991;14(5-6):343–361. doi: 10.3109/10715769109093424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Akasaka M., Yamamoto Y., Kobayashi C., Mizoguchi J., Koyama J. Primary structure of human plasma glutathione peroxidase deduced from cDNA sequences. J Biochem. 1990 Aug;108(2):145–148. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura S., Watanabe K., Suemizu H., Onozawa T., Mizoguchi J., Tsuda K., Hatta H., Moriuchi T. Tissue specific expression of the plasma glutathione peroxidase gene in rat kidney. J Biochem. 1991 Jun;109(6):918–923. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Heider J., Böck A. Features of the formate dehydrogenase mRNA necessary for decoding of the UGA codon as selenocysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]