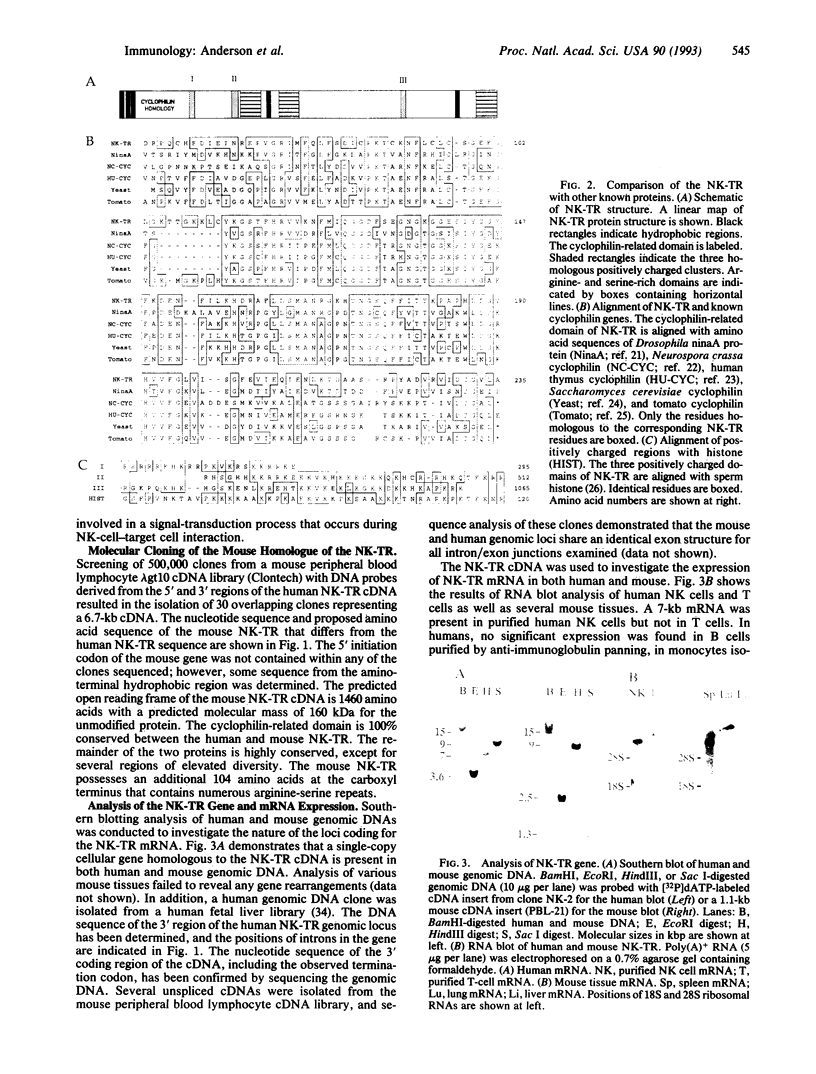
Abstract
Natural killer cells are non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted large granular lymphocytes that can recognize and destroy tumor cells without prior stimulation. A 150-kDa molecule on the surface of human natural killer cells was identified as a component of a putative tumor-recognition complex. We report here the isolation of cDNAs coding for the 150-kDa tumor-recognition molecule from human and mouse cDNA libraries. The amino terminus of the predicted protein contains a large hydrophobic region followed by a domain that is highly homologous to cyclophilin/peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase. The remainder of the protein is extremely hydrophilic and contains three homologous positively charged clusters. There are also three regions that contain extensive arginine- and serine-rich repeats. Comparison of the human and mouse predicted amino acid sequences revealed > 80% homology.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Chou T. B., Mims I., Zachar Z. On/off regulation of gene expression at the level of splicing. Trends Genet. 1988 May;4(5):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bino T., Frey J. L., Ortaldo J. R. Mechanism of target cell recognition by CD3- LGL. I. Development of a monoclonal antibody to a K562-associated target cell antigen. Cell Immunol. 1992 Jun;142(1):28–39. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90266-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst J., van de Griend R. J., van Oostveen J. W., Ang S. L., Melief C. J., Seidman J. G., Bolhuis R. L. A T-cell receptor gamma/CD3 complex found on cloned functional lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):683–688. doi: 10.1038/325683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacalano N. A., Chen B. X., Cleveland W. L., Erlanger B. F. Evidence for a functional receptor for cyclosporin A on the surface of lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4353–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einfeld D. A., Brown J. P., Valentine M. A., Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. Molecular cloning of the human B cell CD20 receptor predicts a hydrophobic protein with multiple transmembrane domains. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):711–717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast L. D., Beatty P., Hansen J. A., Newman W. T cell nature and heterogeneity of recognition structures of human natural killer (NK) cells. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2404–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Wittmann-Liebold B., Lang K., Kiefhaber T., Schmid F. X. Cyclophilin and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase are probably identical proteins. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):476–478. doi: 10.1038/337476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J. L., Bino T., Kantor R. R., Segal D. M., Giardina S. L., Roder J., Anderson S., Ortaldo J. R. Mechanism of target cell recognition by natural killer cells: characterization of a novel triggering molecule restricted to CD3- large granular lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1527–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser C. S., Gunning D. A., Budelier K. A., Brown S. M. Structure and expression of cytosolic cyclophilin/peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase of higher plants and production of active tomato cyclophilin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9519–9523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert C. W., Zaroukian M. H., Esselman W. J. Poly-N-acetyllactosamine structures on murine cell surface T200 glycoprotein participate in natural killer cell binding to YAC-1 targets. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2821–2828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haendler B., Hofer-Warbinek R., Hofer E. Complementary DNA for human T-cell cyclophilin. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):947–950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haendler B., Keller R., Hiestand P. C., Kocher H. P., Wegmann G., Movva N. R. Yeast cyclophilin: isolation and characterization of the protein, cDNA and gene. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding M. W., Handschumacher R. E., Speicher D. W. Isolation and amino acid sequence of cyclophilin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8547–8555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W., Ortaldo J. R. Mechanism of cytotoxicity by natural killer (NK) cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:651–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik D., Sellos D., Belaïche D., Sautiere P. Primary structure of the two variants of a sperm-specific histone H1 from the annelid Platynereis dumerilii. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 15;150(2):359–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Cwirla S., Federspiel N., Phillips J. H. Human natural killer cells isolated from peripheral blood do not rearrange T cell antigen receptor beta chain genes. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):209–214. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Bingham P. M. Arginine/serine-rich domains of the su(wa) and tra RNA processing regulators target proteins to a subnuclear compartment implicated in splicing. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz J., Campen T. J., Schmidt R. E., Royer H. D., Hercend T., Hussey R. E., Reinherz E. L. Analysis of T-cell receptor gene rearrangement and expression in human natural killer clones. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1540–1543. doi: 10.1126/science.2409597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Rosén A., Fenyö E. M., Troy F. A. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer cell system: isolation of target structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1405–1409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Shortridge R. D., Larrivee D. C., Ono T., Ozaki M., Pak W. L. Drosophila ninaA gene encodes an eye-specific cyclophilin (cyclosporine A binding protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5390–5394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90111-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh B. H., Stamnes M. A., Seavello S., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The ninaA gene required for visual transduction in Drosophila encodes a homologue of cyclosporin A-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):67–70. doi: 10.1038/338067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Hayano T., Suzuki M. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase is the cyclosporin A-binding protein cyclophilin. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):473–475. doi: 10.1038/337473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Nicholson D. W., Hartl F. U., Köhler H., Pfanner N., Wachter E., Neupert W. Cyclosporin A-binding protein (cyclophilin) of Neurospora crassa. One gene codes for both the cytosolic and mitochondrial forms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14433–14440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W. Analysis of T cell receptors in highly purified rat and human large granular lymphocytes (LGL): lack of functional 1.3 kb beta-chain mRNA. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2701–2704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






