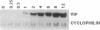Abstract
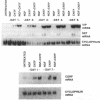
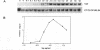
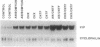
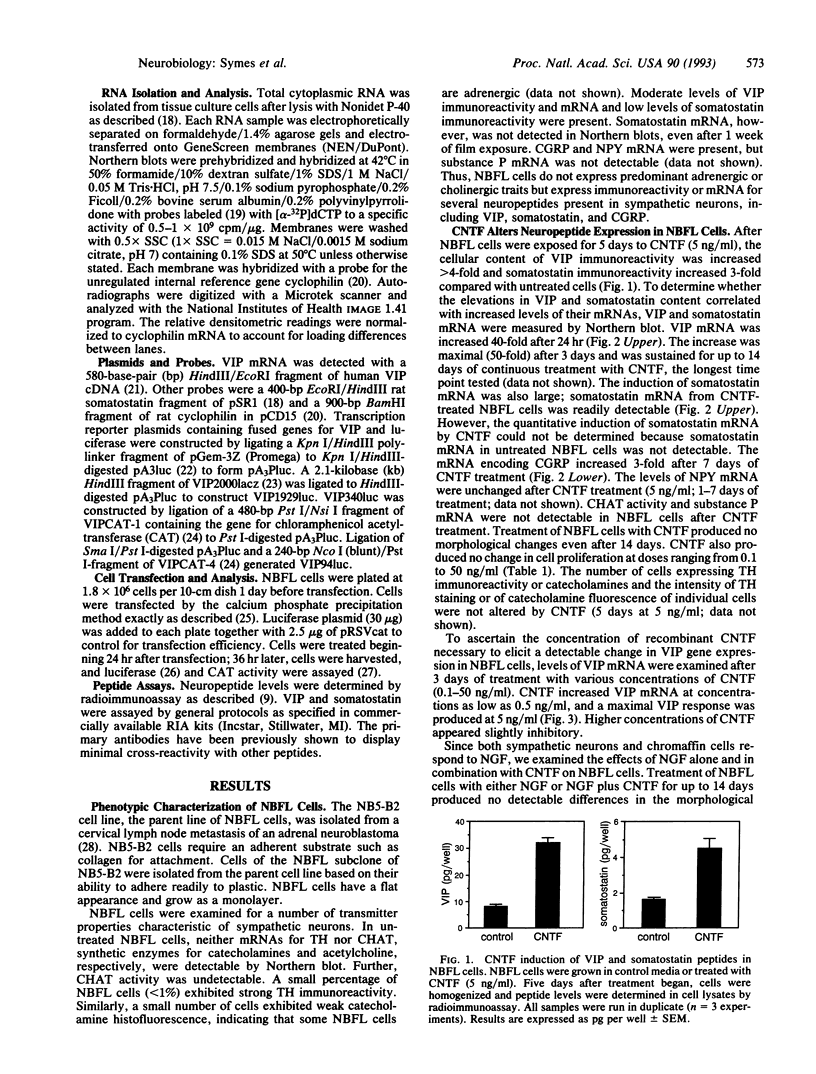
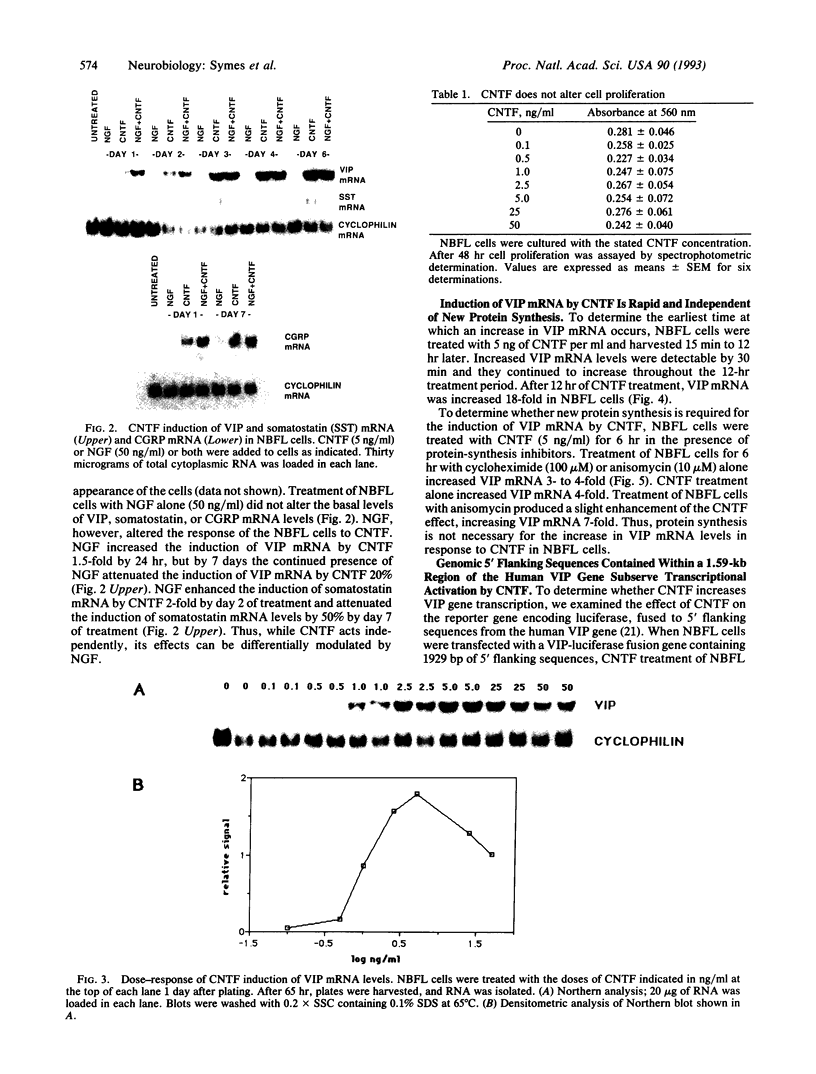
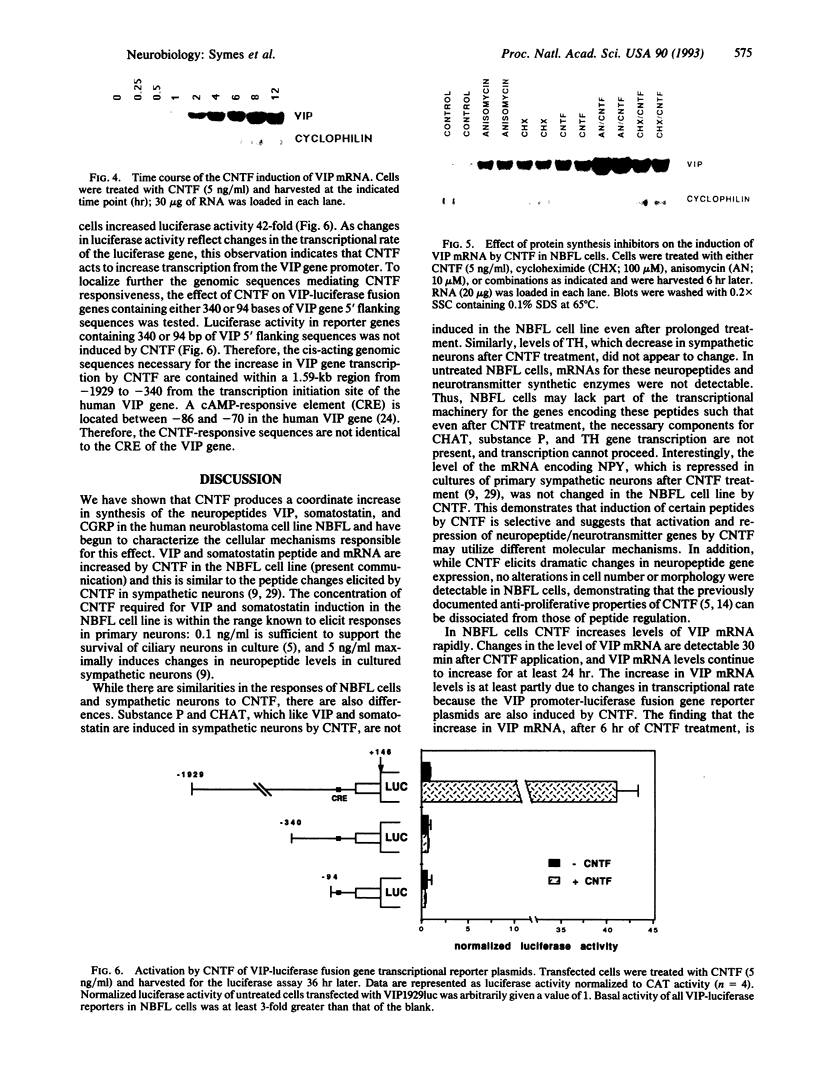
Differentiation factors have been identified that influence the phenotype of sympathetic neurons by altering expression of classical neurotransmitters and neuropeptides. Investigation of the molecular mechanisms through which such factors act would be facilitated by the availability of a neuronal cell line that responds to these factors in a fashion similar to sympathetic neurons. We have identified a human neuroblastoma cell line, NBFL, that responds to the differentiation factor ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) by coordinately inducing multiple neuropeptide genes as do sympathetic neurons. Treatment of NBFL cells with CNTF increases vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), somatostatin, and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) mRNAs but does not change other neurotransmitter properties. The induction of VIP mRNA by CNTF in NBFL cells is dose dependent, rapid, sustained, and independent of new protein synthesis. Genomic 5' flanking sequences located within a 1.59-kilobase region of the human VIP gene and distinct from the previously defined cAMP-responsive element subserve transcriptional activation by CNTF. Further examination of NBFL cells should permit the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms by which CNTF and other differentiation factors coordinately activate neuropeptide gene transcription to influence neuronal differentiation. Similar mechanisms may mediate the effect of CNTF on neuronal survival.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbin G., Manthorpe M., Varon S. Purification of the chick eye ciliary neuronotrophic factor. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1468–1478. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Neuropoietic cytokines in the hematopoietic fold. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger U., Sendtner M., Rohrer H. Proliferation and differentiation of embryonic chick sympathetic neurons: effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor. Neuron. 1989 Mar;2(3):1275–1284. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90312-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. S., Verhave M., Walton K., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-induced transcriptional activation are mediated by the same enhancer element in the human vasoactive intestinal peptide gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3882–3887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., Comeau M. R., Friend D. J., Gimpel S. D., Thut C. J., McGourty J., Brasher K. K., King J. A., Gillis S., Mosley B. The IL-6 signal transducer, gp130: an oncostatin M receptor and affinity converter for the LIF receptor. Science. 1992 Mar 13;255(5050):1434–1437. doi: 10.1126/science.1542794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. M., Lillien L. E., Raff M. C., Rohrer H., Sendtner M. Ciliary neurotrophic factor induces type-2 astrocyte differentiation in culture. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):70–73. doi: 10.1038/335070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Nye S. H., Boulton T. G., Davis S., Taga T., Li Y., Birren S. J., Yasukawa K., Kishimoto T., Anderson D. J. CNTF and LIF act on neuronal cells via shared signaling pathways that involve the IL-6 signal transducing receptor component gp130. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1121–1132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. F., Mismer D., Lile J. D., Armes L. G., Butler E. T., 3rd, Vannice J. L., Collins F. Purification, cloning, and expression of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF). Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1023–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.2587985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Abdollahi A., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 trigger the same immediate early response, including tyrosine phosphorylation, upon induction of myeloid leukemia differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4371–4379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell I. H., Harrison G. S., Wood W. M., Maxwell F. A DNA cassette containing a trimerized SV40 polyadenylation signal which efficiently blocks spurious plasmid-initiated transcription. Biotechniques. 1989 Mar;7(3):276–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Low M. J., Tapia-Arancibia L., Reichlin S., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Cyclic AMP regulates somatostatin mRNA accumulation in primary diencephalic cultures and in transfected fibroblast cells. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):1171–1176. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-01171.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Sah D. W. Different biological activities in conditioned media control the expression of a variety of neuropeptides in cultured sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90102-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W., Prevette D., Yin Q. W., Collins F., MacDonald J. Control of embryonic motoneuron survival in vivo by ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1616–1618. doi: 10.1126/science.2011743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Landis S. C. Characterization of a target-derived neuronal cholinergic differentiation factor. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):899–910. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90350-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Symes A., Malik N., Shoyab M., Fink J. S., Landis S. C. Oncostatin M regulates VIP expression in a human neuroblastoma cell line. Neuroreport. 1992 Oct;3(10):865–868. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199210000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. S., Tyrrell S., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) and depolarization on neuropeptide expression in cultured sympathetic neurons. Dev Biol. 1992 Apr;150(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Fink J. S., Gilman M. Z., Walsh D. A., Goodman R. H., Feramisco J. R. The catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces expression of genes containing cAMP-responsive enhancer elements. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):83–86. doi: 10.1038/336083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose T. M., Bruce A. G. Oncostatin M is a member of a cytokine family that includes leukemia-inhibitory factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8641–8645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saadat S., Sendtner M., Rohrer H. Ciliary neurotrophic factor induces cholinergic differentiation of rat sympathetic neurons in culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1807–1816. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sendtner M., Kreutzberg G. W., Thoenen H. Ciliary neurotrophic factor prevents the degeneration of motor neurons after axotomy. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):440–441. doi: 10.1038/345440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos M., Scarpa S., Ross R. A., Triche T. J. Differentiation of human neuroblastoma recapitulates neural crest development. Study of morphology, neurotransmitter enzymes, and extracellular matrix proteins. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):484–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Fink J. S., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a region in the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide gene responsible for regulation by cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8743–8747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Horovitch S. J., Montminy M. R., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Structure of the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide gene. DNA. 1985 Aug;4(4):293–300. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]