Abstract
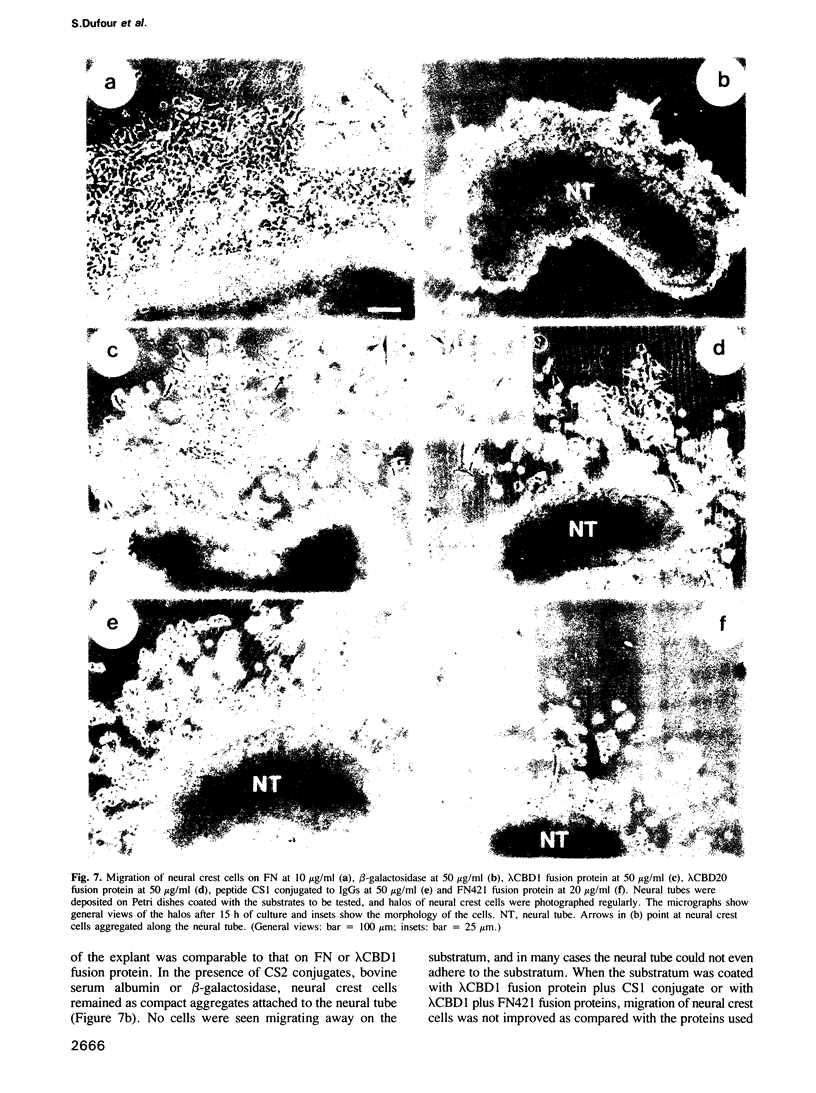
Cellular adhesion to fibronectin (FN) can be mediated by several sequences located in different portions of the molecule. In human FN, these are: (i) the bipartite RGDS domain containing the RGDS cell-binding sequence functioning in synergy for full cellular adhesion with a second site (termed here the synergistic adhesion site) and (ii) the recently characterized CS1 and REDV adhesion sites within the alternatively-spliced type III homology-connecting segment. Using specific adhesive ligands and inhibitory probes, we have examined the role of each of these domains in the adhesion, spreading, and motility of avian neural crest cells in vitro. Both the RGDS domain and the CS1 adhesion site were found to promote attachment of neural crest cells, but only the RGDS domain supported their spreading. However, the RGDS sequence could mediate both attachment and spreading efficiently only when it was associated with the synergistic adhesion site. In migratory assays, it was found that both the RGDS domain and the CS1 site are required in association, each with functional specificity, to permit effective locomotion of neural crest cells. The REDV adhesion site was apparently not recognized by avian neural crest cells, presumably because this sequence is absent from chicken FN. Finally, it was found that recognition of both the RGDS domain and CS1 binding site by neural crest cells involved receptors belonging to the integrin family. From these results, we conclude that neural crest cells can interact with several binding sites of FN molecules, and use them for distinct functions. Our results also suggest the possibility of an instructive role for FN in the control of adhesive and migratory events during embryonic development.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. K., Hasegawa E., Hasegawa T., Yamada K. M. The interaction of fibronectin fragments with fibroblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13256–13260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucaut J. C., Darribère T., Poole T. J., Aoyama H., Yamada K. M., Thiery J. P. Biologically active synthetic peptides as probes of embryonic development: a competitive peptide inhibitor of fibronectin function inhibits gastrulation in amphibian embryos and neural crest cell migration in avian embryos. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1822–1830. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner-Fraser M. An antibody to a receptor for fibronectin and laminin perturbs cranial neural crest development in vivo. Dev Biol. 1986 Oct;117(2):528–536. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. T., Hasegawa E., Hasegawa T., Weinstock C., Yamada K. M. Development of cell surface linkage complexes in cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1103–1114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duband J. L., Rocher S., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M., Thiery J. P. Cell adhesion and migration in the early vertebrate embryo: location and possible role of the putative fibronectin receptor complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):160–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T., Hasegawa E., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M. Characterization of a membrane-associated glycoprotein complex implicated in cell adhesion to fibronectin. J Cell Biochem. 1985;28(4):307–318. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240280409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. Adhesive protein receptors on hematopoietic cells. Immunol Today. 1988 Apr;9(4):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Akiyama S. K., Komoriya A., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of an alternatively spliced site in human plasma fibronectin that mediates cell type-specific adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2637–2647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Akiyama S. K., Komoriya A., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Neurite extension of chicken peripheral nervous system neurons on fibronectin: relative importance of specific adhesion sites in the central cell-binding domain and the alternatively spliced type III connecting segment. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1289–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Komoriya A., Akiyama S. K., Olden K., Yamada K. M. Identification of two distinct regions of the type III connecting segment of human plasma fibronectin that promote cell type-specific adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6886–6892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen K. A., Horwitz A. F., Buck C. A. A monoclonal antibody identifies a glycoprotein complex involved in cell-substratum adhesion. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Mar;157(1):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Umezawa K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Primary structure of human fibronectin: differential splicing may generate at least 10 polypeptides from a single gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1755–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Hagen S. T., Furcht L. T. Human fibronectin contains distinct adhesion- and motility-promoting domains for metastatic melanoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):179–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugnai G., Lewandowska K., Carnemolla B., Zardi L., Culp L. A. Modulation of matrix adhesive responses of human neuroblastoma cells by neighboring sequences in the fibronectins. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):931–943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgreen D. F., Gibbins I. L., Sauter J., Wallenfels B., Wütz R. Ultrastructural and tissue-culture studies on the role of fibronectin, collagen and glycosaminoglycans in the migration of neural crest cells in the fowl embryo. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;221(3):521–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00215700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgreen D. F., Ritterman M., Peters E. A. Morphology and behaviour of neural crest cells of chick embryo in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Nov;203(1):115–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00234333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Hynes R. O. Alternative splicing of chicken fibronectin in embryos and in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4297–4307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Rocher-Dufour S., Kornblihtt A., Thiery J. P., Yamada K. M. Expression of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin in E. coli. Identification of sequences promoting full to minimal adhesive function. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Kang M. S., Yamada K. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cell-binding domain of human fibronectin: separable, synergistic sites mediate adhesive function. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Variants of the cell recognition site of fibronectin that retain attachment-promoting activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5985–5988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickmann M., Fawcett J. W., Keynes R. J. The migration of neural crest cells and the growth of motor axons through the rostral half of the chick somite. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Dec;90:437–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. L., Letourneau P. C., Peterson B. A., Furcht L. T., McCarthy J. B. Selective interaction of peripheral and central nervous system cells with two distinct cell-binding domains of fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1435–1442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovasio R. A., Delouvee A., Yamada K. M., Timpl R., Thiery J. P. Neural crest cell migration: requirements for exogenous fibronectin and high cell density. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):462–473. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Schwarzbauer J. E., Hynes R. O. A single rat fibronectin gene generates three different mRNAs by alternative splicing of a complex exon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboletti G., Roberts D. D., Liotta L. A. Thrombospondin-induced tumor cell migration: haptotaxis and chemotaxis are mediated by different molecular domains. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2409–2415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teillet M. A., Kalcheim C., Le Douarin N. M. Formation of the dorsal root ganglia in the avian embryo: segmental origin and migratory behavior of neural crest progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):329–347. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Duband J. L., Delouvée A. Pathways and mechanisms of avian trunk neural crest cell migration and localization. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):324–343. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Duband J. L., Tucker G. C. Cell migration in the vertebrate embryo: role of cell adhesion and tissue environment in pattern formation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:91–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker G. C., Ciment G., Thiery J. P. Pathways of avian neural crest cell migration in the developing gut. Dev Biol. 1986 Aug;116(2):439–450. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. P., Erickson C. A. Morphology and behavior of quail neural crest cells in artificial three-dimensional extracellular matrices. Dev Biol. 1984 Aug;104(2):390–405. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. Identification of multiple cell adhesion receptors for collagen and fibronectin in human fibrosarcoma cells possessing unique alpha and common beta subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1873–1884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Amino acid sequence specificities of an adhesive recognition signal. J Cell Biochem. 1985;28(2):99–104. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240280203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Dualistic nature of adhesive protein function: fibronectin and its biologically active peptide fragments can autoinhibit fibronectin function. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):29–36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Peptide inhibitors of fibronectin, laminin, and other adhesion molecules: unique and shared features. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jan;130(1):21–28. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]