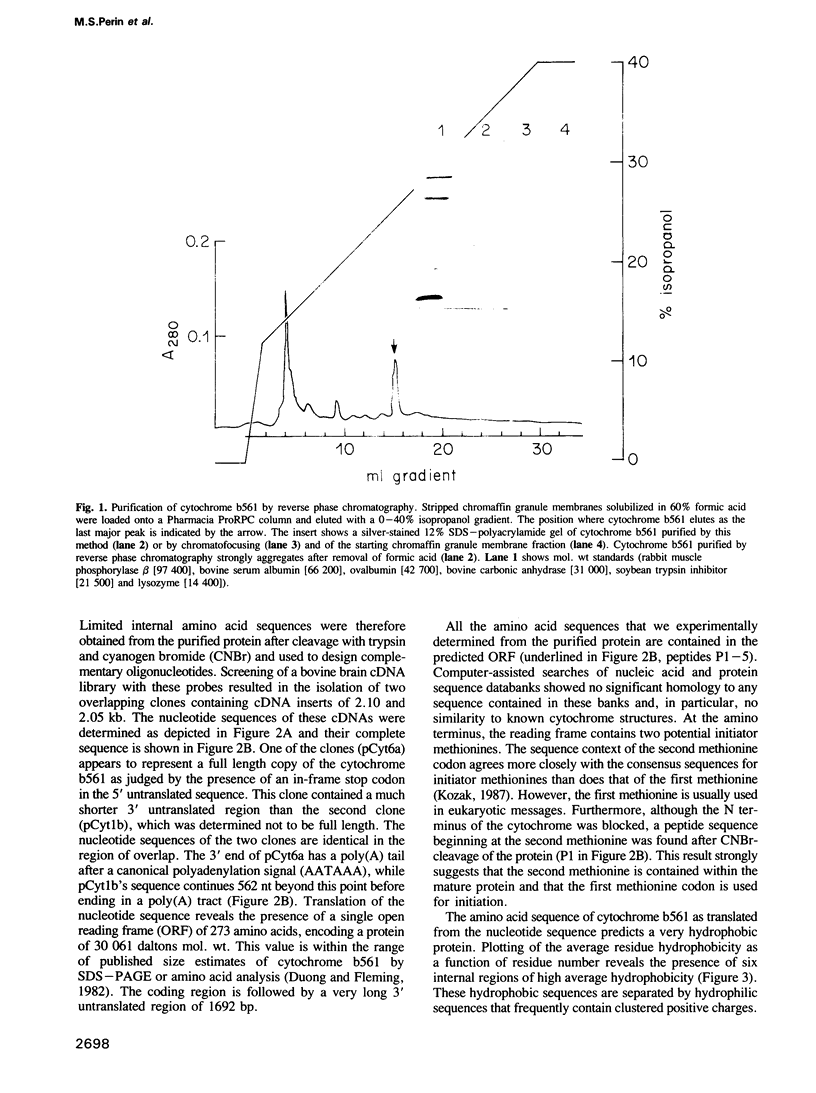
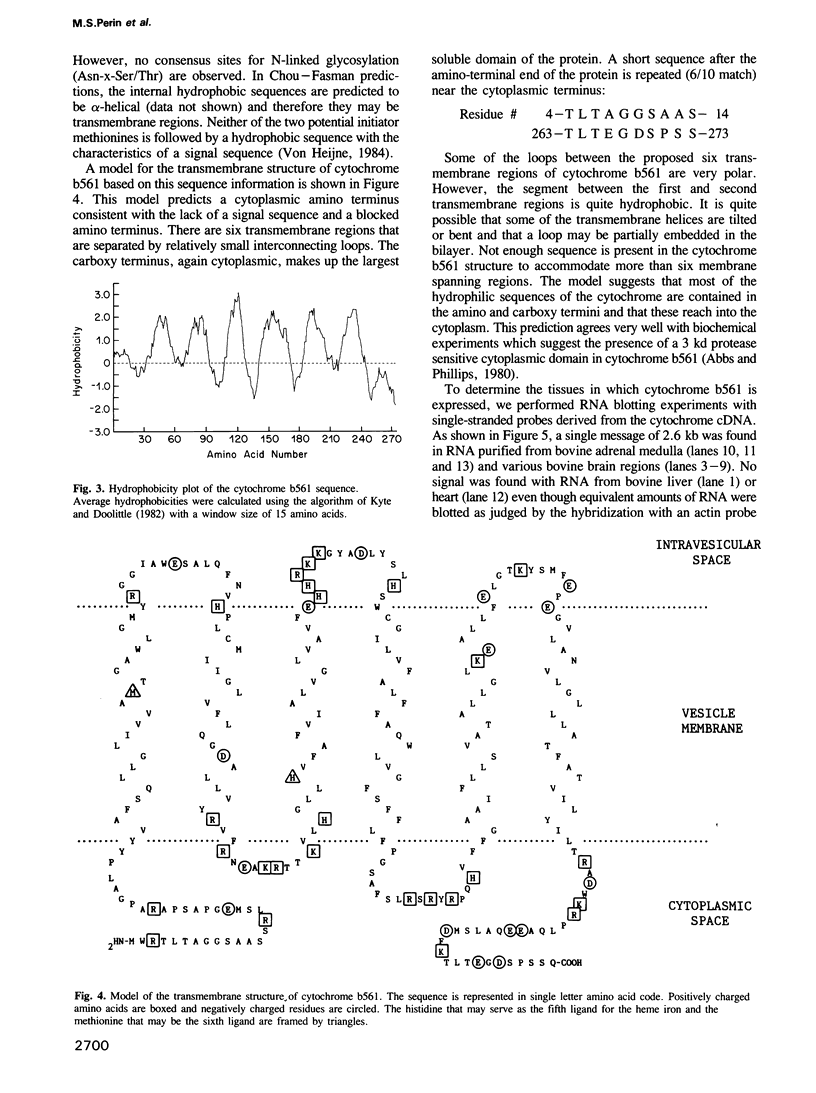
Abstract
Cytochrome b561 is a transmembrane electron transport protein that is specific to a subset of secretory vesicles containing catecholamines and amidated peptides. This protein is thought to supply reducing equivalents to the intravesicular enzymes dopamine-beta-hydroxylase and alpha-peptide amidase. We have purified cytochrome b561 from bovine adrenal chromaffin granules by reverse phase chromatography and have determined internal amino acid sequences from peptides. Complementary oligonucleotides were used to isolate two cDNA clones from a bovine brain library. The structure predicted by the sequences of these cDNAs suggests a highly hydrophobic protein of 273 amino acids which spans the membrane six times with little extramembranous sequence. Cytochrome b561 is not homologous to any other cytochrome and thus represents a new class of electron carriers. RNA blotting experiments indicate that cytochrome b561 is expressed in the adrenal medulla and all brain regions of the cow, but not in visceral organs. This result agrees well with the putative function of this unique cytochrome and with the notion that this protein is localized to large dense-core synaptic vesicles.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbs M. T., Phillips J. H. Organisation of the proteins of the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):200–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps D. K., Pryde J. G., Phillips J. H. Cytochrome b561 is identical with chromomembrin B, a major polypeptide of chromaffin granule membranes. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2279–2287. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90143-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury A. F., Finnie M. D., Smyth D. G. Mechanism of C-terminal amide formation by pituitary enzymes. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):686–688. doi: 10.1038/298686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duong L. T., Fleming P. J. Isolation and properties of cytochrome b561 from bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8561–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatmark T., Terland O. Cytochrome b 561 of the bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. A high potential b-type cytochrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 7;253(2):487–491. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Croop J., Housman D. Mammalian multidrug resistance gene: complete cDNA sequence indicates strong homology to bacterial transport proteins. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtnagl H., Winkler H., Lochs H. Immunological studies on a membrane protein (chromomembrin B) of catecholamine-storing vesicles. J Neurochem. 1973 Apr;20(4):977–985. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent U. M., Fleming P. J. Purified cytochrome b561 catalyzes transmembrane electron transfer for dopamine beta-hydroxylase and peptidyl glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase activities in reconstituted systems. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8174–8178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopito R. R., Lodish H. F. Primary structure and transmembrane orientation of the murine anion exchange protein. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):234–238. doi: 10.1038/316234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Alu-Alu recombination deletes splice acceptor sites and produces secreted low density lipoprotein receptor in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3354–3361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leube R. E., Kaiser P., Seiter A., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W., Rehm H., Knaus P., Prior P., Betz H., Reinke H. Synaptophysin: molecular organization and mRNA expression as determined from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3261–3268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews F. S. The structure, function and evolution of cytochromes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;45(1):1–56. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy A. S., Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. Purification and characterization of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase from bovine neurointermediate pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1815–1822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Njus D., Knoth J., Cook C., Kelly P. M. Electron transfer across the chromaffin granule membrane. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):27–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M. Monoclonal antibodies to chromaffin cells can distinguish proteins specific to or specifically excluded from chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1987 Jul;22(1):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. T., Levine M., Njus D. Electron transfer across posterior pituitary neurosecretory vesicle membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. A simple method for the isolation of adrenal chromaffin granules on a large scale. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):480–482. doi: 10.1042/bj1030480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava M., Duong L. T., Fleming P. J. Cytochrome b561 catalyzes transmembrane electron transfer. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8072–8075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Lottspeich F., Greengard P., Mehl E., Jahn R. A synaptic vesicle protein with a novel cytoplasmic domain and four transmembrane regions. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1142–1144. doi: 10.1126/science.3120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. 42 bp element from LDL receptor gene confers end-product repression by sterols when inserted into viral TK promoter. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1061–1069. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90713-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Slaughter C. A., Leznicki I., Barjon P., Reynolds G. A. Human 67-kDa calelectrin contains a duplication of four repeats found in 35-kDa lipocortins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Walker J. H., Obrocki J. Calelectrin self-aggregates and promotes membrane aggregation in the presence of calcium. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1167–1170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terland O., Silsand T., Flatmark T. Cytochrome b-561 as the single heme protein of the bovine adrenal chromaffin granule membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 8;359(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Cass A. E., Radda G. K. Electron transfer across the chromaffin granule membrane. Use of EPR to demonstrate reduction of intravesicular ascorbate radical by the extravesicular mitochondrial NADH:ascorbate radical oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9746–9752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Cass A. E., Radda G. K. Functional coupling between enzymes of the chromaffin granule membrane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9739–9745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Cass A. E., Radda G. K. Isolation of a membrane protein by chromatofocusing: cytochrome b-561 of the adrenal chromaffin granule. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Sep;9(4):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Fried V. A. Early steps initiating a degradation pathway in Escherichia coli. Characterization of the first intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6357–6364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Analysis of the distribution of charged residues in the N-terminal region of signal sequences: implications for protein export in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2315–2318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]