Abstract
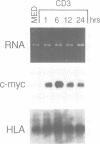
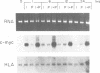
Quiescent normal human T cells express low levels of steady-state c-myc mRNA as a result of low constitutive promoter utilization, a block to transcriptional elongation within the gene, and rapid degradation of c-myc mRNA in the cytoplasm. Following the activation of the T cell receptor (TCR)/CD3 complex, quiescent T cells are induced to express c-myc mRNA. Two intracellular pathways, one involving protein kinase C activation and the other mediated by increased intracellular calcium concentration, are activated by TCR/CD3 receptor stimulation. These two pathways, which can be activated by phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and ionomycin respectively, appear to play complementary roles in the transcriptional induction of c-myc gene expression by the antigen receptor complex. Ionomycin treatment of quiescent cells leads to enhanced c-myc expression primarily as a result of increased transcriptional initiation. In contrast, PMA contributes to c-myc expression, at least in part, by decreasing the block to transcriptional elongation present within the gene. Both the PMA- and ionomycin-mediated induction of c-myc expression can be independently enhanced by stabilization of c-myc mRNA in the cytoplasm. These observations demonstrate that multiple mechanisms co-operate to regulate c-myc gene expression during normal T cell activation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Novel promoter upstream of the human c-myc gene and regulation of c-myc expression in B-cell lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3481–3489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Sequence requirements for premature termination of transcription in the human c-myc gene. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Cory S., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Adams J. M. Sequence of the murine and human cellular myc oncogenes and two modes of myc transcription resulting from chromosome translocation in B lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2375–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., Dani C., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Pouyssegur J., Jeanteur P. c-myc gene is transcribed at high rate in G0-arrested fibroblasts and is post-transcriptionally regulated in response to growth factors. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):443–445. doi: 10.1038/317443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler A. J., Rothstein T. L., Sonenshein G. E. Two-step stimulation of B lymphocytes to enter DNA synthesis: synergy between anti-immunoglobulin antibody and cytochalasin on expression of c-myc and a G1-specific gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1371–1375. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesarman E., Dalla-Favera R., Bentley D., Groudine M. Mutations in the first exon are associated with altered transcription of c-myc in Burkitt lymphoma. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1272–1275. doi: 10.1126/science.3685977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Imagawa M., Imbra R. J., Bockoven J. R., Karin M. Multiple cis- and trans-acting elements mediate the transcriptional response to phorbol esters. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):648–651. doi: 10.1038/329648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Levine R. A., Campisi J. c-myc regulation during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 cells is posttranscriptional and associated with growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Bornkamm G. W. Transcriptional arrest within the first exon is a fast control mechanism in c-myc gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8331–8346. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Piechaczyk M., Henglein B., Blanchard J. M., Traub B., Kofler E., Wiest S., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Aberrant c-myc RNAs of Burkitt's lymphoma cells have longer half-lives. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3717–3725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O. Enforced expression of the c-myc oncogene inhibits cell differentiation by precluding entry into a distinct predifferentiation state in G0/G1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1614–1624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Thompson C. B., Eisenman R. N. c-myc oncogene protein synthesis is independent of the cell cycle in human and avian cells. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):366–369. doi: 10.1038/314366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Ferris D. K., Vinocour M., Holt J. T., Farrar W. L. Specific inhibition of c-myc protein biosynthesis using an antisense synthetic deoxy-oligonucleotide in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2431–2435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayday A. C., Gillies S. D., Saito H., Wood C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of a translocated human c-myc gene by an enhancer in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):334–340. doi: 10.1038/307334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis G. F., Gazdar A. F., Bertness V., Kirsch I. R. Complex translocation disrupts c-myc regulation in a human plasma cell myeloma. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Gillespie M. M., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. T-cell proliferation involving the CD28 pathway is associated with cyclosporine-resistant interleukin 2 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4472–4481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Klein E. Evolution of tumours and the impact of molecular oncology. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):190–195. doi: 10.1038/315190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Gentry L. E., June C. H., Rabinovitch P. S., Purchio A. F. Stimulation of T cells through the CD3/T-cell receptor complex: role of cytoplasmic calcium, protein kinase C translocation, and phosphorylation of pp60c-src in the activation pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):650–656. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Y., Chang S. C., Lee A. S. A calcium ionophore-inducible cellular promoter is highly active and has enhancerlike properties. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lømo J., Holte H., de Lange Davies C., Ruud E., Laukas M., Smeland E. B., Godal T., Blomhoff H. K. Downregulation of c-myc RNA is not a prerequisite for reduced cell proliferation, but is associated with G1 arrest in B-lymphoid cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Sep;172(1):84–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B. Regulation of expression of the c-myc proto-oncogene. Bioessays. 1987 Jan;6(1):28–32. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Schubach W., Eisenman R., Linial M. Expression of c-myc RNA in bursal lymphoma cell lines: identification of c-myc-encoded proteins by hybrid-selected translation. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90415-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts P. H., Watson J. V., Lamond A., Forster A., Stinson M. A., Evan G., Fischer W., Atherton E., Sheppard R., Rabbitts T. H. Metabolism of c-myc gene products: c-myc mRNA and protein expression in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2009–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03885.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Sabath D. E., Hoover R. G., Prystowsky M. B. Recombinant interleukin 2 regulates levels of c-myc mRNA in a cloned murine T lymphocyte. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3361–3368. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resendez E., Jr, Ting J., Kim K. S., Wooden S. K., Lee A. S. Calcium ionophore A23187 as a regulator of gene expression in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2145–2152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeland E. B., Beiske K., Ek B., Watt R., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Blomhoff H. K., Godal T., Ohlsson R. Regulation of c-myc transcription and protein expression during activation of normal human B cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Sep;172(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeland E., Godal T., Ruud E., Beiske K., Funderud S., Clark E. A., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Ohlsson R. The specific induction of myc protooncogene expression in normal human B cells is not a sufficient event for acquisition of competence to proliferate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truneh A., Albert F., Golstein P., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Early steps of lymphocyte activation bypassed by synergy between calcium ionophores and phorbol ester. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):318–320. doi: 10.1038/313318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J. B. Cell surface molecules and early events involved in human T lymphocyte activation. Adv Immunol. 1987;41:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]