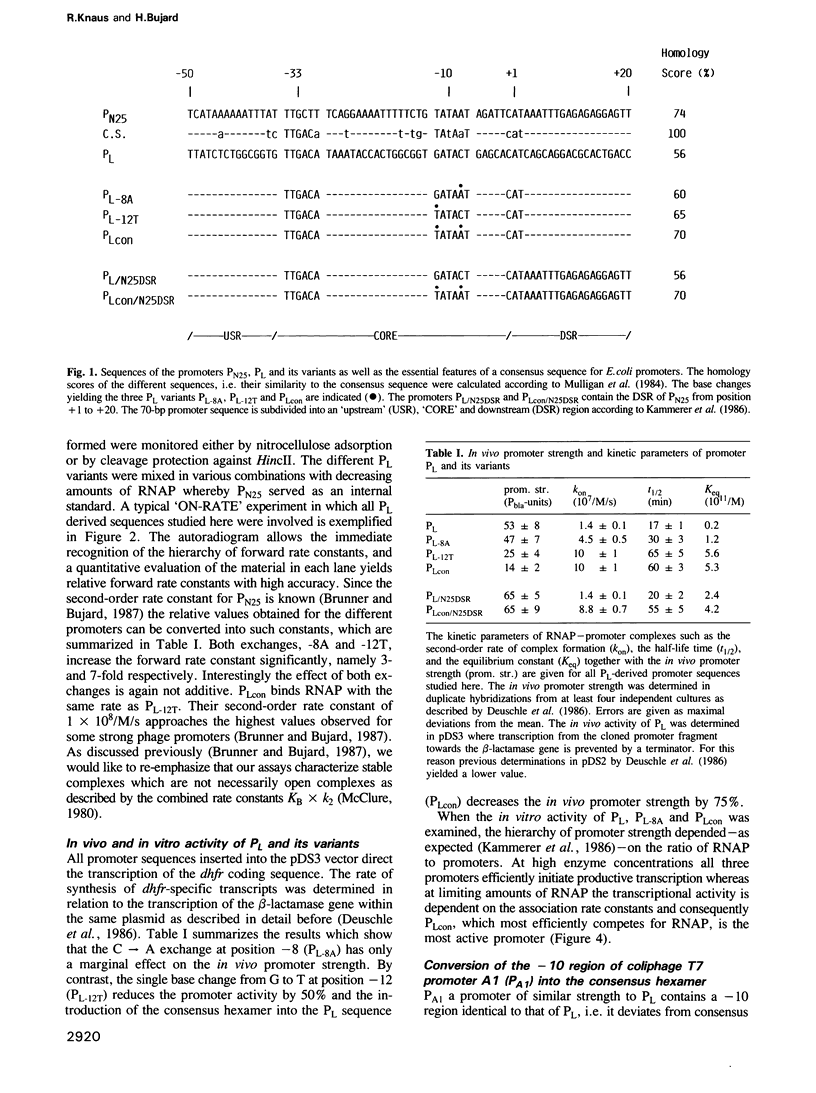
Abstract
Promoter PL of coliphage lambda is highly active in vivo although it is recognized 15-30 times less efficiently by RNA polymerase when compared with promoters of similar strength. Moreover, it differs significantly from the consensus sequence for Escherichia coli promoters. Sequence variants of PL which are more homologous to consensus promoters bind RNA polymerase with increased efficiency. They are nevertheless significantly reduced in their in vivo strength. High activity can be restored by a downstream sequence of a typical consensus-like promoter. Evidently, such elements are required for the efficient release of a stably bound RNA polymerase into a transcriptional elongation complex. We propose that the functional programme encoded in a promoter sequence can be optimized in alternative ways.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunner M., Bujard H. Promoter recognition and promoter strength in the Escherichia coli system. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3139–3144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc H., McClure W. R. Kinetics of open complex formation between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and the lac UV5 promoter. Evidence for a sequential mechanism involving three steps. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2712–2723. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Stefano J. E., Gralla J. D. 5' nucleotide heterogeneity and altered initiation of transcription at mutant lac promoters. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 5;157(4):619–633. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90502-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Kammerer W., Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters of Escherichia coli: a hierarchy of in vivo strength indicates alternate structures. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2987–2994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W., Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. Functional dissection of Escherichia coli promoters: information in the transcribed region is involved in late steps of the overall process. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2995–3000. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Rate-limiting steps in RNA chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5634–5638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe J. H., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Temperature dependence of the rate constants of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lambda PR promoter interaction. Assignment of the kinetic steps corresponding to protein conformational change and DNA opening. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):441–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90293-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E., Gralla J. Lac UV5 transcription in vitro. Rate limitation subsequent to formation of an RNA polymerase-DNA complex. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1063–1067. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straney D. C., Crothers D. M. A stressed intermediate in the formation of stably initiated RNA chains at the Escherichia coli lac UV5 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Bouvier S., Susskind M. M. Sequence determinants of promoter activity. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





