Abstract
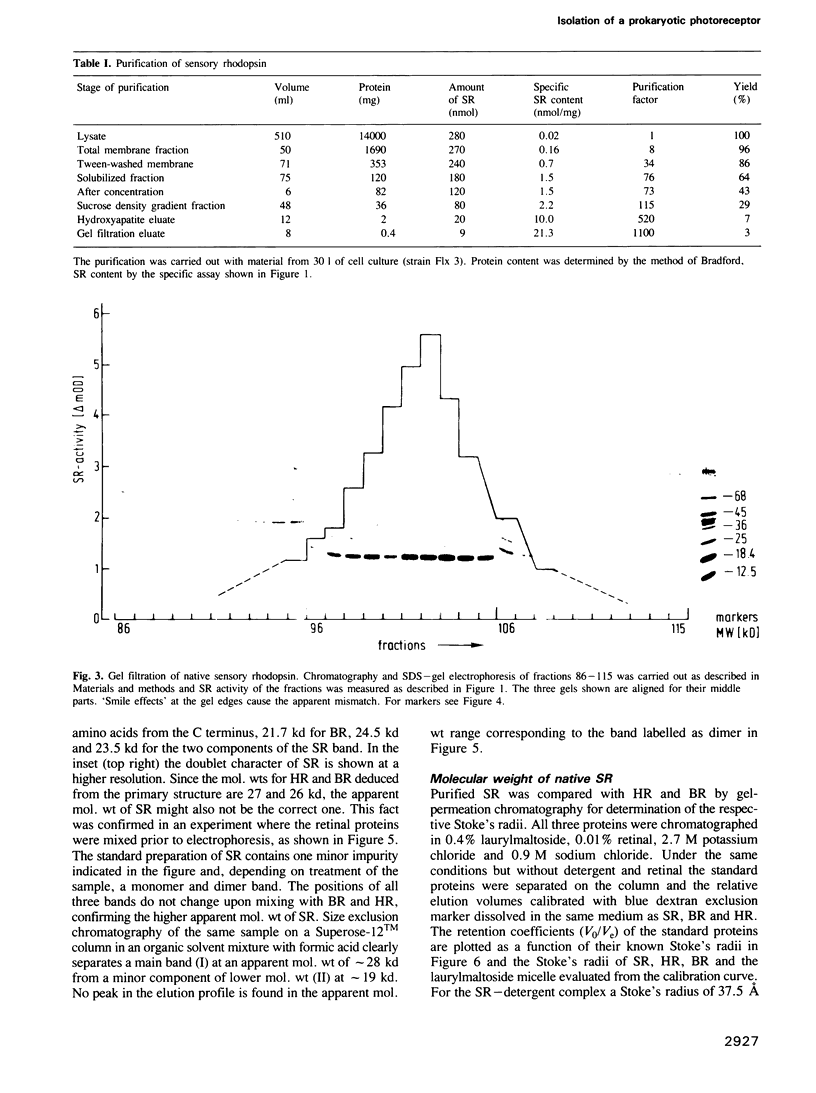
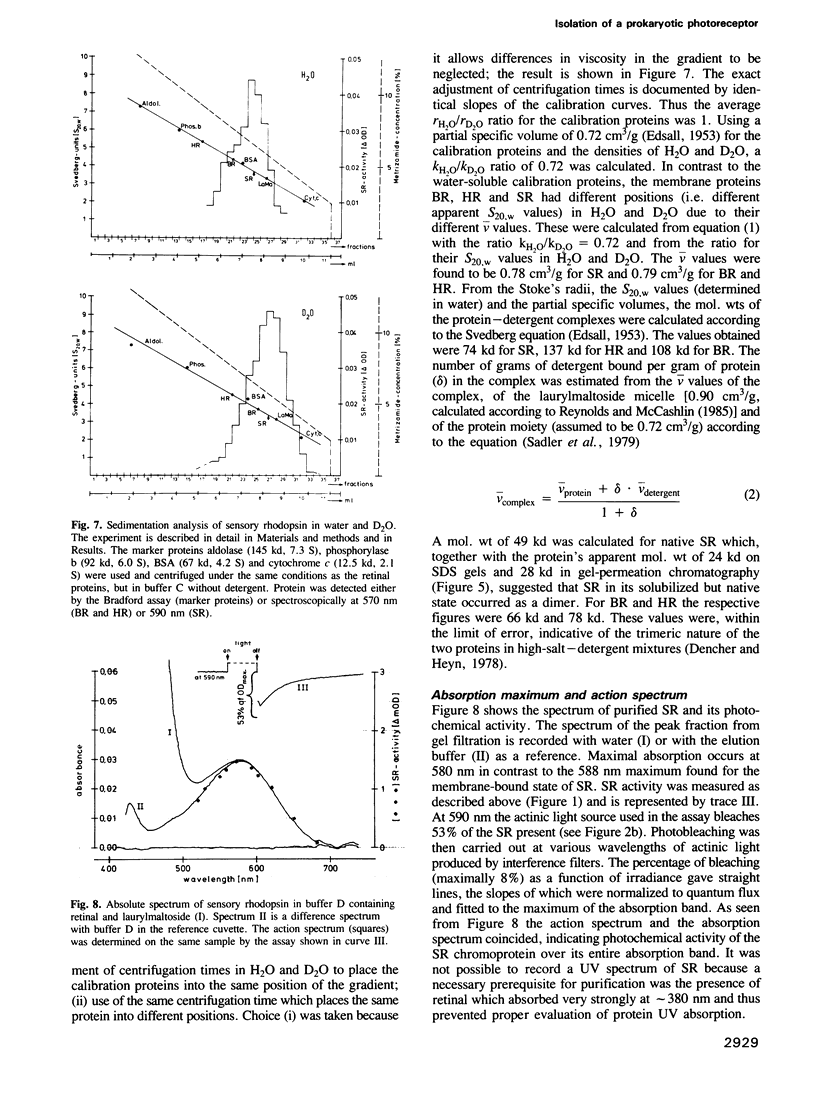
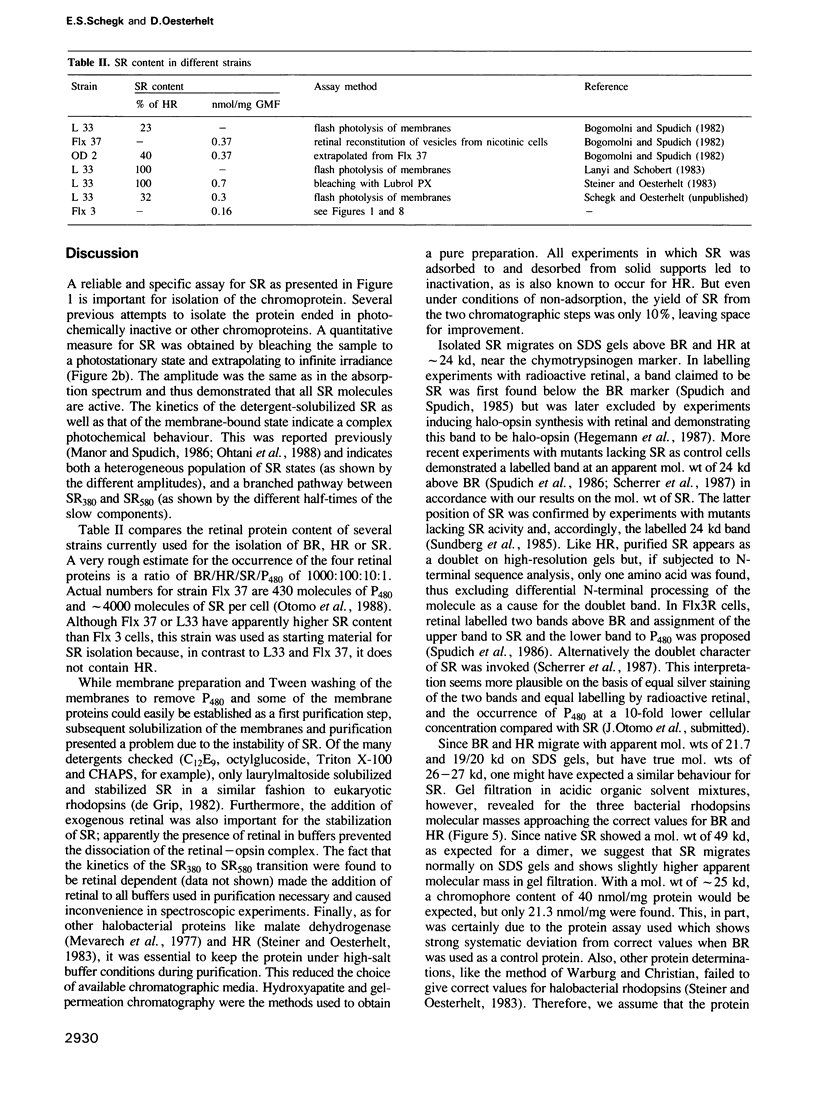
The photoreceptor sensory rhodopsin was isolated from halobacterial cell membranes solubilized in laurylmaltoside. In the presence of retinal, detergent and salt the native protein was obtained in pure form by sucrose density gradient centrifugation, hydroxyapatite chromatography and gel filtration. The apparent mol. wt of the molecule was 24 kd if analysed by SDS gel electrophoresis, and 49 kd by sedimentation and size-exclusion chromatographic analysis. The chromoprotein had an absorption maximum at 580 nm which was 8 nm blueshifted compared to the membrane-bound state. The molecule was photochemically active and the action spectrum for formation of SR380, the long-lived intermediate, coincided with the absorption spectrum.
Keywords: archaebacteria, halobacteria, photoreceptor, sensory rhodopsin, isolation, molecular weight
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Identification of a third rhodopsin-like pigment in phototactic Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6250–6254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childress C. C., Sacktor B. Regulation of glycogen metabolism in insect flight muscle. Purification and properties of phosphorylases in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun 10;245(11):2927–2936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Grip W. J. Thermal stability of rhodopsin and opsin in some novel detergents. Methods Enzymol. 1982;81:256–265. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)81040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Heyn M. P. Formation and properties of bacteriorhodopsin monomers in the non-ionic detergents octyl-beta-D-glucoside and Triton X-100. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 15;96(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R., Sickinger H. D., Oesterhelt D. Anaerobic growth of halobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3821–3825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbacher C. A., Spudich J. L., Dewey T. G. Circular dichroism of halorhodopsin: comparison with bacteriorhodopsin and sensory rhodopsin I. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2540–2546. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazemoto N., Kamo N., Terayama Y., Kobatake Y., Tsuda M. Photochemistry of two rhodopsinlike pigments in bacteriorhodopsin-free mutant of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1983 Oct;44(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84277-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann P., Blanck A., Vogelsang-Wenke H., Lottspeich F., Oesterhelt D. The halo-opsin gene. I. Identification and isolation. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):259–264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04748.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann P., Steiner M., Oesterhelt D. Isolation and characterization of the retinal-binding component of halorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1177–1183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand E., Dencher N. Two photosystems controlling behavioural responses of Halobacterium halobium. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):46–48. doi: 10.1038/257046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwan W., Oesterhelt D. Signal formation in the halobacterial photophobic response mediated by a fourth retinal protein (P480). J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90654-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Olsen R. W., Changeux J. P. Studies on the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus. Effect of detergents on some hydrodynamic properties of the receptor protein in solution. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 15;24(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Eisenberg H., Neumann E. Malate dehydrogenase isolated from extremely halophilic bacteria of the Dead Sea. 1. Purification and molecular characterization. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 23;16(17):3781–3785. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Krippahl G. Phototrophic growth of halobacteria and its use for isolation of photosynthetically-deficient mutants. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Jul-Aug;134B(1):137–150. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(83)80101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani H., Kobayashi T., Tsuda M. Branching photocycle of sensory rhodopsin in halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):493–496. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83128-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., McCaslin D. R. Determination of protein molecular weight in complexes with detergent without knowledge of binding. Methods Enzymol. 1985;117:41–53. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)17005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. E., Rearick J. I., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Purification to homogeneity of a beta-galactoside alpha2 leads to 3 sialyltransferase and partial purification of an alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha2 leads to 6 sialyltransferase from porcine submaxillary glands. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4434–4442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer P., McGinnis K., Bogomolni R. A. Biochemical and spectroscopic characterization of the blue-green photoreceptor in Halobacterium halobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):402–406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling W., Schimz A. Photosensory retinal pigments in Halobacterium halobium. Biophys Struct Mech. 1980;6(2):165–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00535752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Genetic and biochemical resolution of the chromophoric polypeptide of halorhodopsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):332–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91835-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Spudich J. L. Biochemical characterization of halorhodopsin in native membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1208–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Sundberg S. A., Manor D., Spudich J. L. Properties of a second sensory receptor protein in Halobacterium halobium phototaxis. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):239–246. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., Bogomolni R. A. Mechanism of colour discrimination by a bacterial sensory rhodopsin. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):509–513. doi: 10.1038/312509a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner M., Oesterhelt D. Isolation and properties of the native chromoprotein halorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1379–1385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg S. A., Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Selection and properties of phototaxis-deficient mutants of Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):282–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.282-287.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. E., Bogomolni R. A., Weber H. J. Purification of photochemically active halorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka H., Kamo N., Takahashi T., Kobatake Y. Photochemical intermediate of third rhodopsin-like pigment in Halobacterium halobium by simultaneous illumination with red and blue light. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):989–994. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanAken T., Foxall-VanAken S., Castleman S., Ferguson-Miller S. Alkyl glycoside detergents: synthesis and applications to the study of membrane proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:27–35. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff E. K., Bogomolni R. A., Scherrer P., Hess B., Stoeckenius W. Color discrimination in halobacteria: spectroscopic characterization of a second sensory receptor covering the blue-green region of the spectrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7272–7276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





